 Many thanks to SWLing Post contributor, Rob Gray, who shares the following tips:
Many thanks to SWLing Post contributor, Rob Gray, who shares the following tips:
Extracting Audio Stream Information from Reciva
Here is a proposed procedure for extracting audio streams from Reciva, while the website still exists.
[Please note that in these examples, the Brave web browser is being used in a Windows environment. The procedure is nearly identical for Chrome. Other web browsers and operating systems may vary slightly.]
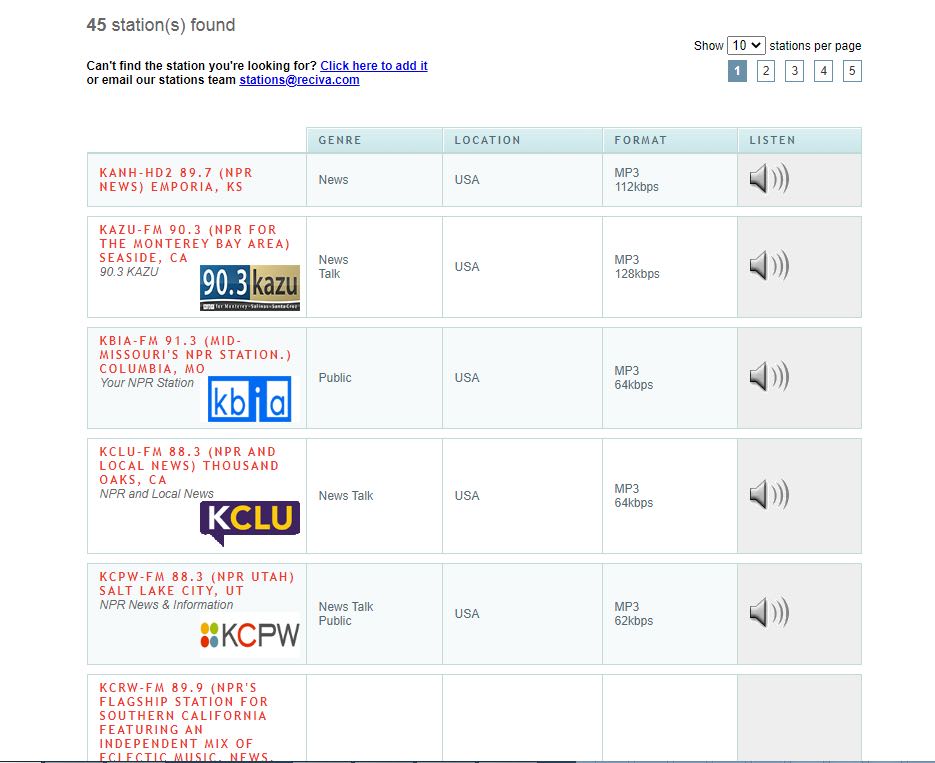
Image 1 (Click to enlarge)
After logging in and searching for your desired station(s) (as shown in Image 1 above using NPR as an example search), click the speaker icon of the station of interest (see Image 2 below).
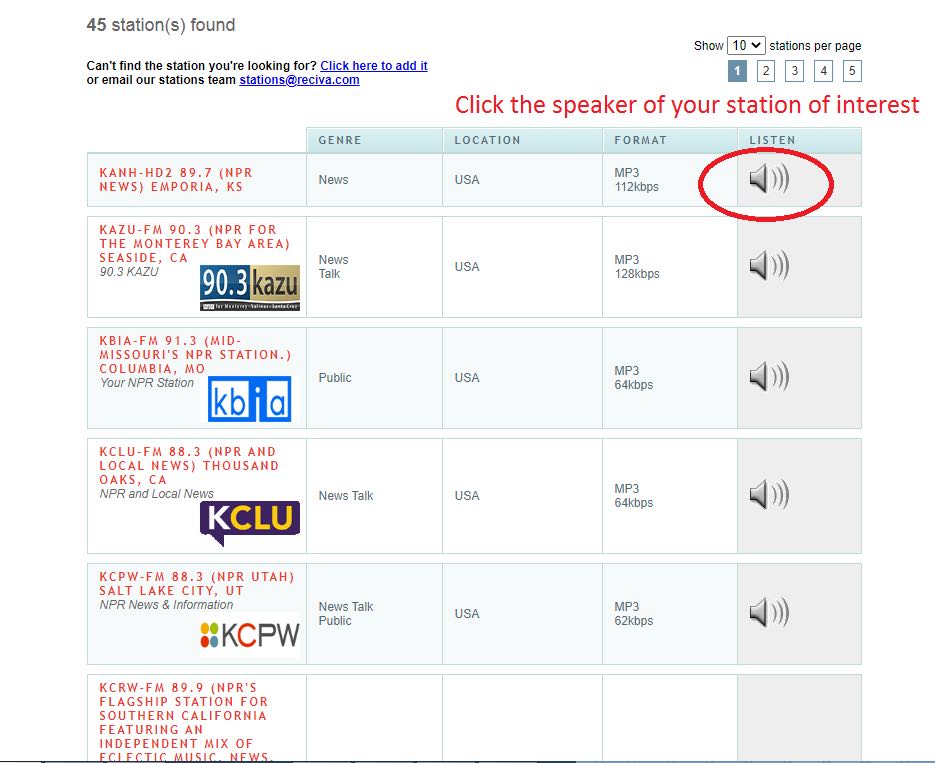
That brings up another browser window (center-right window in Image 3 below). Pressing “F12” brings up another window of DevTools (Developer Tools).
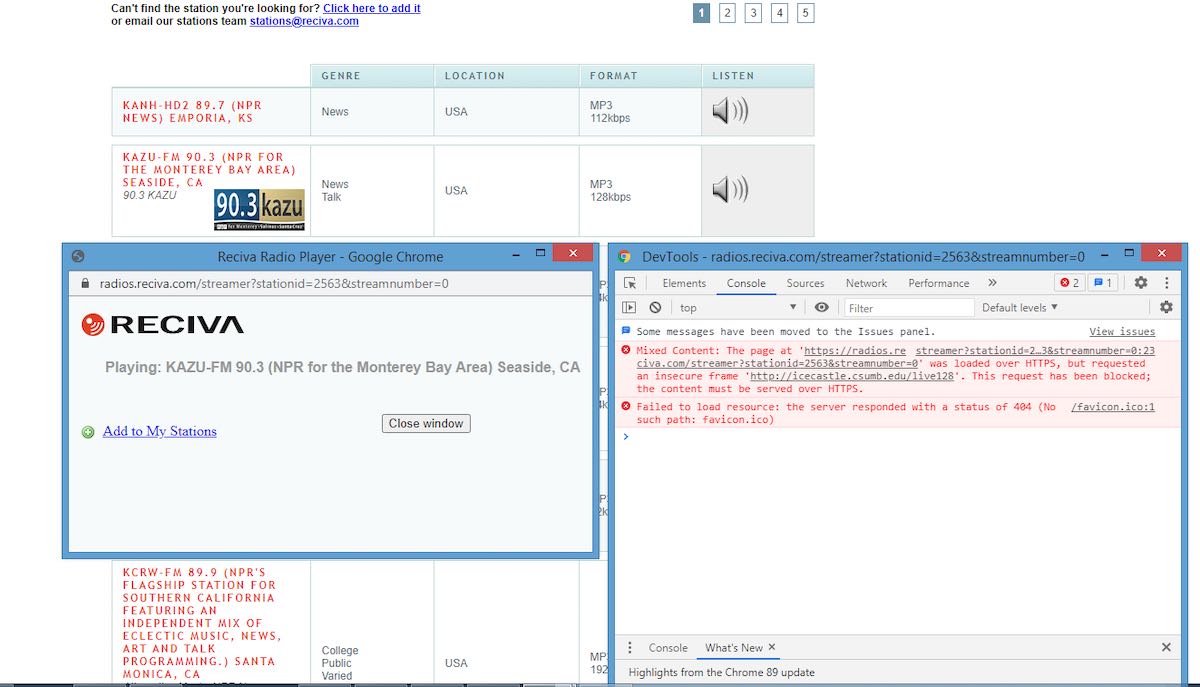
Under “DevTools”, select “Console” (you may find it under the >>) as shown in the image above. The URL is shown in the “Console” window (image 04), and should be http://xxxxxx, and not the secure https://xxxxxx.
Extracting Audio Stream Information from station websites
Digging out streams from station websites can be a little trickier. Using an example of the webpage for the NPR station KCLU, once loaded, press “F12” to bring up the developer tools as shown on the right-hand side of Image 4 below.
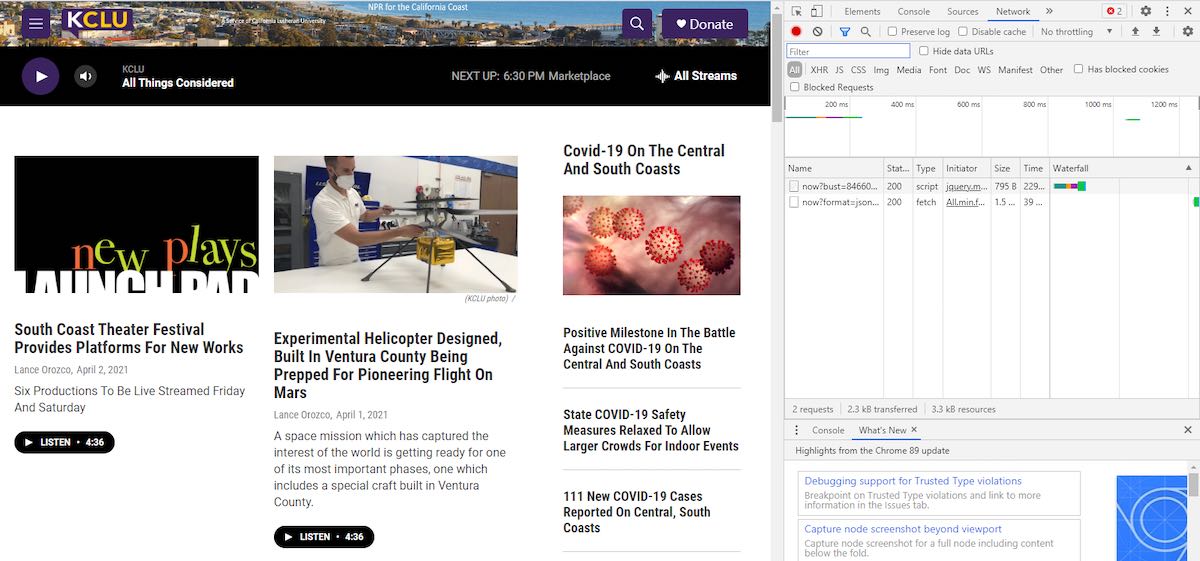
Then Press “F5” to reload the page, and the Play button to start the audio stream.
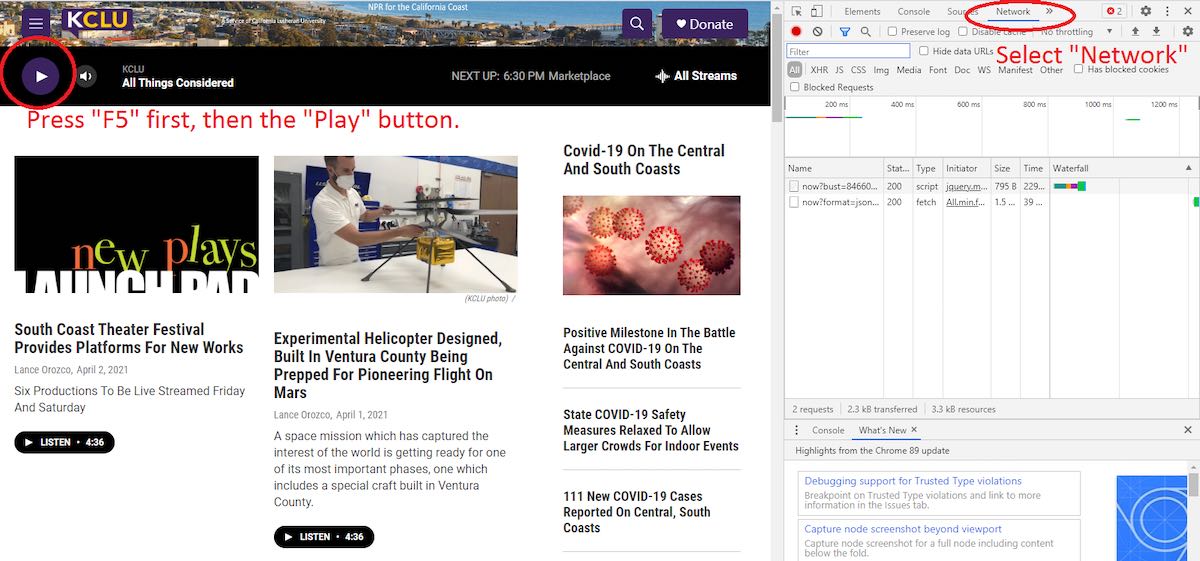
In the Developer Tools window, select “Network”, as shown in the Image 5 above.
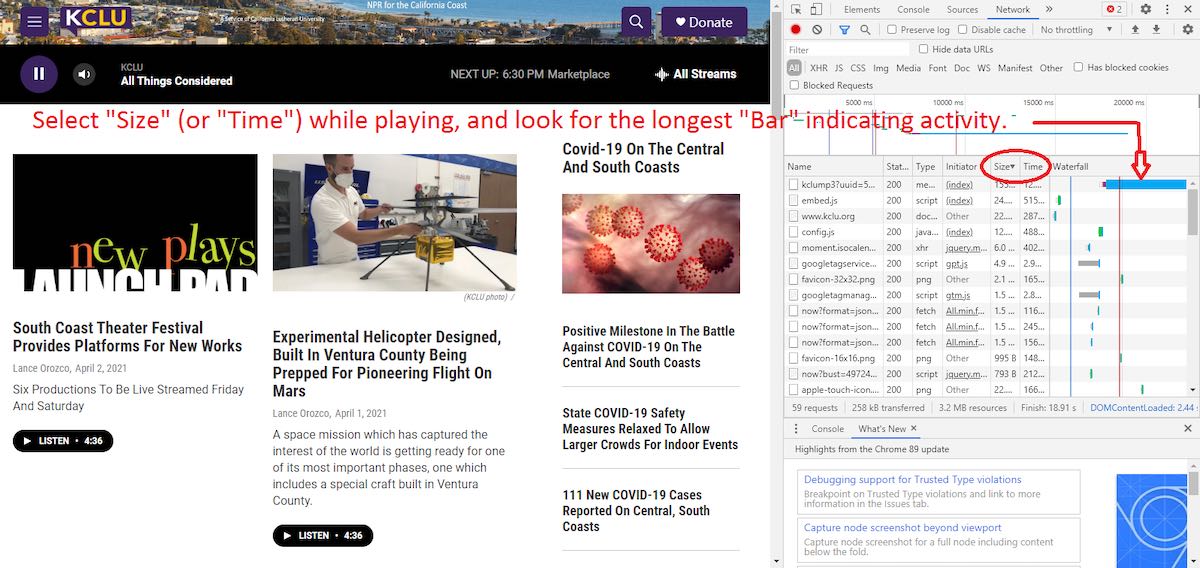
While the stream is playing, look for the longest bar, which indicates activity. Sorting the files in this window by size or time (if descending order, be at the top of the list, if descending order at the bottom of the list) can make searching for the “bar” easier, or just look for it in the list as shown in the Image 6 above. Look for the file associated with the “bar” under “Name”, right-click on that file, Copy, and left-click “Copy link address” as shown in the Image 7 below.
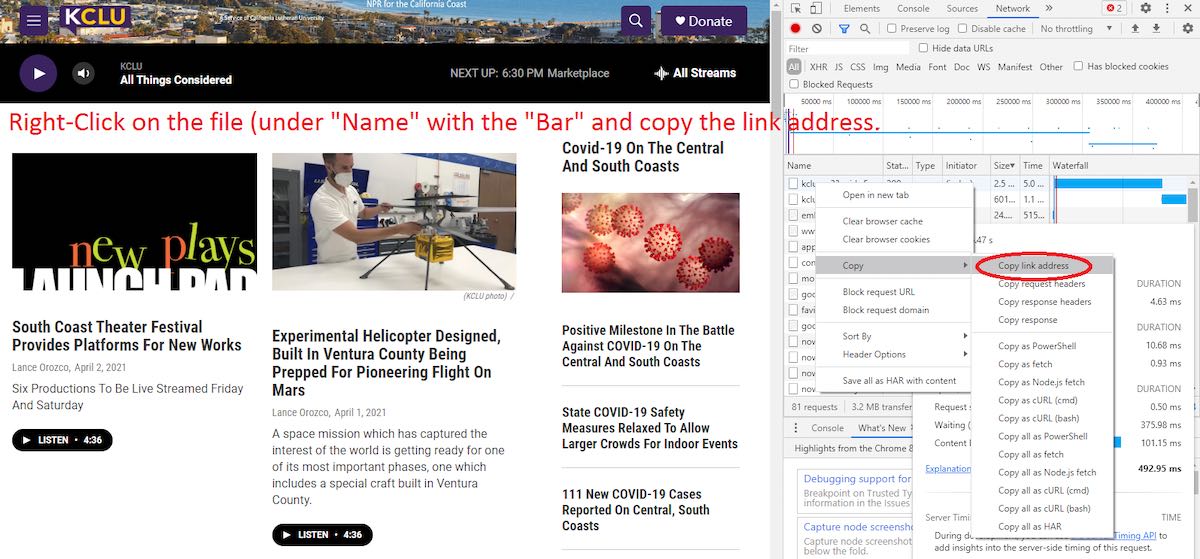
That is usually your stream, or something close to it. In this example, this is the link address copied:
https://kclustream.callutheran.edu:8090/kclump3?uuid=5blcmxjpp
That’s a little messy, and you can experiment with shortening it. In this case, the link can be shortened to: https://kclustream.callutheran.edu:8090/kclump3 [removing the question mark and all characters following it] and the stream still plays in a web browser on the computer–while I’ve not tested it, it would probably play in your internet radio. You’ll just have to experiment.
However, in this case (and most certainly not all), shortening the link to https://kclustream.callutheran.edu:8090/ brings up another page with all sorts of data, and clicking the M3U file on that page downloads a file. Opening that file with Notepad reveals this link ( https://kclustream.callutheran.edu:8090/kcluaac ), which also plays the stream, and in my guess, is probably the real stream URL.
Different web pages will reveal different ‘formats’ of URLs–one simply has to experiment to get something to work. The procedure is essentially the same with other pages, though there is often variation so a certain amount of experimentation is sometimes needed to tease out the stream URLs. There isn’t really any one set of instructions that will work for everything (that I’ve found anyway!).
The examples shown used Google Chrome, and the Brave browser works exactly the same. The operating system used was Windows. Firefox seems similar (F12) and other browsers probably also work similar, though the appearance might be a bit different.
A few things that might add clarification with ‘odd’ streams:
In the developer tools window under Name, sometimes those items (files) are labelled as just a semicolon, or are labelled something like ‘stream.’
Sometimes the stream URL is httpS://…., with those, try dropping the “s” and the http://…. often works.
I often tried any proposed streams out on my desktop computer first, however there were some that wouldn’t play on the desktop that did on the Reciva radio, and vise-versa. But generally, if it didn’t work on the computer, it didn’t work on the internet radio.
Sometimes the URLs point to a link with a .pls extension. In a browser, those links tend to initiate a download (at least on my setup, and was the case with the M3U file in the KCLU example). You can download the file, then open with a text editor (Notepad for example) and read the link there.
For some, the URL won’t work. For those, I would get them to work by adding a semicolon (;) to the end of what you think might be the link. I’ve had a few work with that trick!
While digging out steams is tedious–especially if you have a lot of them–there’s a potentially very rewarding payoff! When you create the .pls files (as described in other Reciva postings in this blog), you can easily copy those to many other devices (Android phone/tablet, iPod/iPhone, other computers, Kodi, etc.) and use them there. I’ve only started on this project, but I used an old (very old) iPod touch, entered the stream URL into Safari, placed the iPod in a docking station (a dime/dozen at second-hand stores) and basically created an internet radio facsimile. As the iPod is too old for the App Store, entering the URL’s and bookmarking them should provide convenience. The .pls files work well in my Android devices with VLC player, and even with Kodi (on a Raspberry Pi). They also work on my TV by placing the files in the “Video” section, read from external media (can probably use the boot SD card for memory storage as well, the files are very small).
Thank you for sharing this, Rob!
I recall our friend, Tracy Wood, discussing in some detail how to find radio streams a few years ago at the Winter SWL Fest. He was on a mission to find rare local and regional South American stations that aren’t easily available outside the area.
I have used the approach you mentioned above and it is effective.
Readers: if you have other tips, please feel free to share them in the comments section.
Of course, we should note again that the Reciva website will be taken down at the end of April 2021. We suspect some or all Reciva radios may eventually fail in the absence of receiving a token over the Internet. While we haven’t received a confirmation, my industry sources seem to think this is a real possibility. Let’s hope not.
 Many thanks to SWLing Post contributor, Chris, who writes:
Many thanks to SWLing Post contributor, Chris, who writes:











