Many thanks to SWLing Post contributor and noted political cartoonist, Carlos Latuff, who shares the latest entry in his Radiofax scrapbook.
Carlos notes:
Today’s Kyodo News English Edition, received via radiofax in Porto Alegre.

Many thanks to SWLing Post contributor and noted political cartoonist, Carlos Latuff, who shares the latest entry in his Radiofax scrapbook.
Carlos notes:
Today’s Kyodo News English Edition, received via radiofax in Porto Alegre.
Many thanks to SWLing Post contributor and noted political cartoonist, Carlos Latuff, who shares the latest entry in his Radiofax scrapbook.
Carlos notes:
Today’s Kyodo News Morning Edition, radiofax received in Porto Alegre.
Many thanks to SWLing Post contributor Carlos Latuff, who writes:
Since the pandemic, I’ve been receiving news in Brazil from the Japanese agency Kyodo News, transmitted by radiofax. From now on, I’ll print the radiofax and paste them into this scrapbook, illustrating one or more news items.

 I love it, Carlos! You’ll fill that book quickly with the number of decodes you log each year!
I love it, Carlos! You’ll fill that book quickly with the number of decodes you log each year!
by Dan Greenall
Shades of the 1970’s. Commercial AM radio (in English) the way it used to be. Heavy on nostalgic music from the 1960’s to the 1990’s, plenty of good old style jingles, and of course, the LM chime every hour.
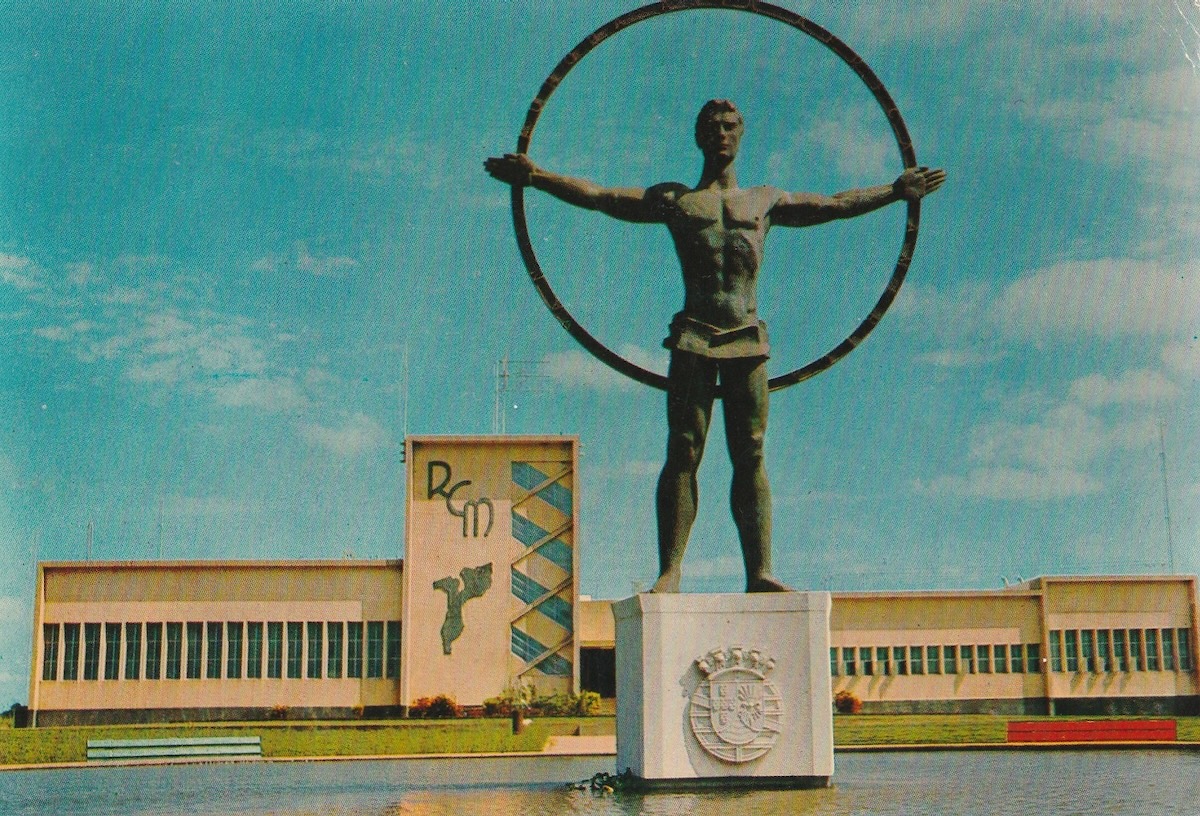
 Decades ago, the “LM” used to stand for Lourenco Marques Radio as the station was based in this city in Mozambique. Today, it is Lifetime Memories Radio, and broadcasts to Maputo and the surrounding area, where it can be heard on 87.8 FM. The station also broadcasts on 702 kHz medium wave from a transmitter near Johannesburg, South Africa, and can be heard worldwide via Kiwi SDR or online stream here https://lmradio.co.za/
Decades ago, the “LM” used to stand for Lourenco Marques Radio as the station was based in this city in Mozambique. Today, it is Lifetime Memories Radio, and broadcasts to Maputo and the surrounding area, where it can be heard on 87.8 FM. The station also broadcasts on 702 kHz medium wave from a transmitter near Johannesburg, South Africa, and can be heard worldwide via Kiwi SDR or online stream here https://lmradio.co.za/
In addition to the live stream, be sure to read about the rich history of the station that began in 1936. The station was shut down in 1975 when Mozambique gained independence, but has re-emerged in the 21st century. A visit to the LM Radio museum is well worth the trip. https://lmradio.co.mz/history/

 In 1973, I was able to hear Radio Clube de Mocambique on 4855 kHz shortwave from here in Canada. If you listen closely, you can hear the LM chime.
In 1973, I was able to hear Radio Clube de Mocambique on 4855 kHz shortwave from here in Canada. If you listen closely, you can hear the LM chime.
Give them a listen, but first, check out these sample recordings made between November 27 and December 8, 2025, through a Kiwi SDR located near Johannesburg:
2025-11-27:
2025-11-28:
2025-11-28:
2025-11-29:
2025-12-04:
2025-12-08:
 Many thanks to SWLing Post contributor Ken, who shares the following announcement:
Many thanks to SWLing Post contributor Ken, who shares the following announcement:
Broadcasting across the globe on shortwave radio, All Tribes Radio champions world peace through an eclectic blend of culturally diverse music, spoken word, and vintage treasures from the golden age of radio.
We offer a welcoming platform for independent artists who license their work through Creative Commons, while also sharing open-source, public-domain, Copyleft, and other copyright-free content.
Founded in 2008, All Tribes Radio (ATR) streamed Creative Commons music 24 hours a day, seven days a week, to an average of 6,000 listeners per month in more than 120 countries across every continent. With studios in Nosara, Costa Rica, ATR’s signal reached the world via an internet server in Tampa, Florida.
In 2011, streaming gave way to podcasting, resulting in the production of 68 one-hour episodes for iTunes, completed in 2012.
ATR entered a new chapter in 2020 with its first shortwave broadcasts: a weekly one-hour program showcasing Creative Commons music in English, Spanish, German, French, and Italian. These were transmitted from WRMI in Okeechobee, Florida, and Channel 292 in Rohrbach, Germany. Unfortunately, the disruptions of Covid-19 brought those broadcasts to an end the following year.
Happily, as of November 30, 2025, ATR has returned to shortwave —now transmitting exclusively from Channel 292 with 10 kW of power and a 315º beam aimed toward northern and western Europe. One-hour broadcasts can be heard each Sunday from 1400–1500 UTC on 9670 kHz. Reception reports are warmly welcomed, and e-QSL verification is available.
Click here to read more about All Tribes Radio on Ken’s Substack.
Many thanks to SWLing Post contributor David Iurescia for sharing the following news and holiday tradition from NDR Hörfunk.
Each Christmas Eve, NDR airs its beloved “Gruß an Bord” (Greetings on Board) program–a broadcast of messages from families in Germany to loved ones serving at sea. It’s a tradition stretching back to 1953, connecting crews on merchant ships, research vessels, and naval ships with home during the holidays.
To ensure these greetings reach listeners far beyond FM and online streams, NDR has leased shortwave frequencies once again this year. Here’s the 2024 recording recorded by Richard Langley on the Shortwave Radio Audio Archive.
Between 18:00 and 21:00 UTC (19:00–22:00 CET), the program will be transmitted on the following frequencies:
Shortwave Frequencies (December 24, 18:00–21:00 UTC):
• Europe: 6080 kHz
• Atlantic – Northwest: 15770 kHz
• Atlantic – South: 13830 kHz
• Atlantic – Northeast: 6030 kHz
• Indian Ocean: 9635 kHz
• Atlantic / Indian Ocean / South Africa: 11650 kHz
If you’ve never heard Greetings on Board, I highly recommend giving it a listen.
You can read the full article here: https://www.yacht.de/en/special/people/greetings-on-board-ndr-broadcasts-christmas-messages/
Let us know if you plan to tune in and when you do, any notes about the broadcast.
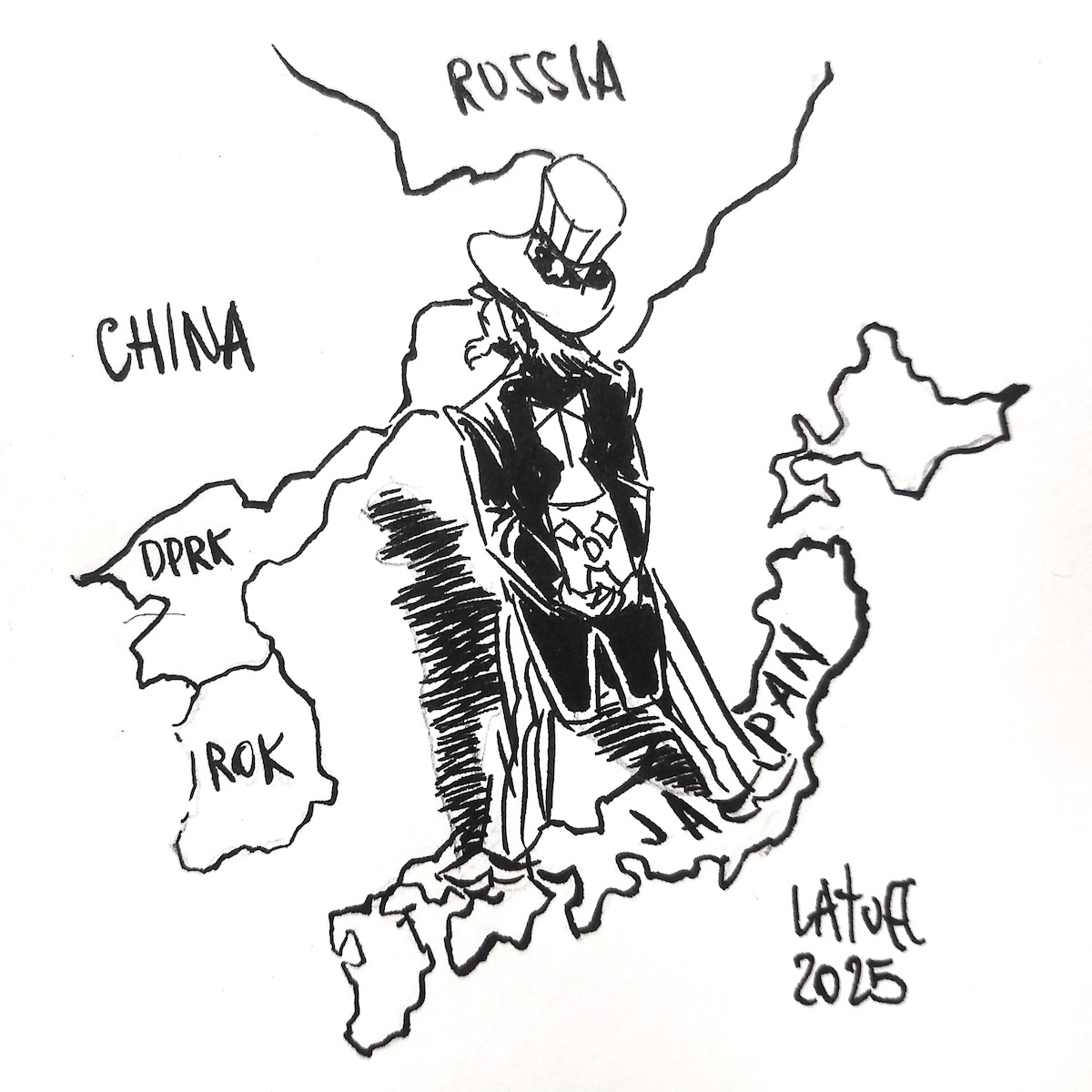
Many thanks to SWLing Post contributor and noted political cartoonist, Carlos Latuff, who shares the following illustrated radio listening report of recent CGTN, NHK, and Radio Taiwan International broadcasts.
China, Japan, Taiwan: War of Words on the Shortwave (CGTN, NHK, Radio Taiwan International)