Many thanks to SWLing Post contributor Jerome van der Linden, who writes:
For some time, I have subscribed to a service that alerts me via email when our weather bureau wants to inform people about the likelihood of aurora activity that might lead to the ability to observe the southern hemisphere auroras, such this example:
SUBJ: ASWFC AURORA OUTLOOK
ISSUED AT 0627 UT ON 31 May 2025
FROM THE AUSTRALIAN SPACE WEATHER FORECASTING CENTRE
A halo CME is expected to impact Earth on 01-Jun at 2100UT +/- 8 hours. This impact is expected to produce auroral activity on 01-02 Jun, with a chance of continued activity on 03-Jun. Warnings and/or alerts will follow if significant geomagnetic activity occurs.
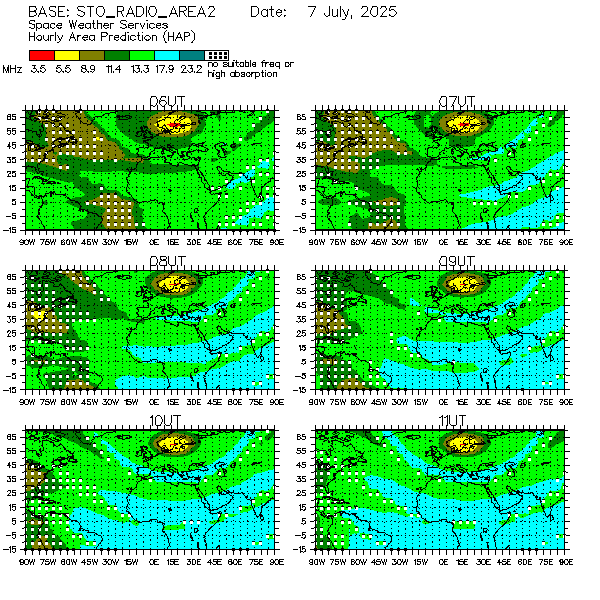
Quite recently, I discovered that the Bureau of Meteorology (“the BOM”) in Australia has, as part of its www.bom.gov.au website, an Australian Space Weather Forecasting Centre: https://www.sws.bom.gov.au/. It has a number of interesting headings (with links) that may be of interest to others in the SW hobby, such as “Solar”;”HF Systems”, and “Products and Services”. With the respect to the last, it would appear that a number of organisations subscribe to services provided by the BOM, including Australian airlines. In addition it seems even Stockholm Radio subscribes to some of the services, and an example of hour by hour HF frequency area prediction is shown in these graphs:
There’s far too much for me to review on this website, so I suggest interested SWLers may care to have a look for themselves, as there’s a lot of information there, which is updated regularly.