Many thanks to SWLing Post contributor, Troy Riede, who shares the following news from Spaceweather.com:
Spaceweather.com
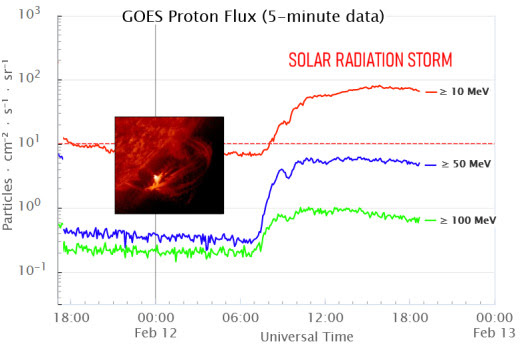
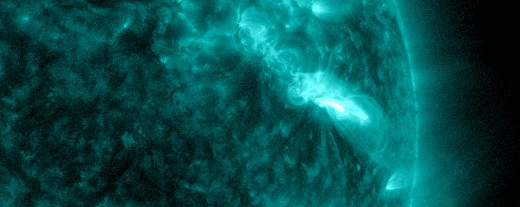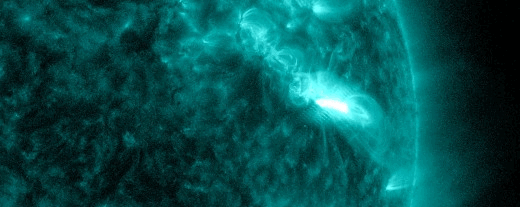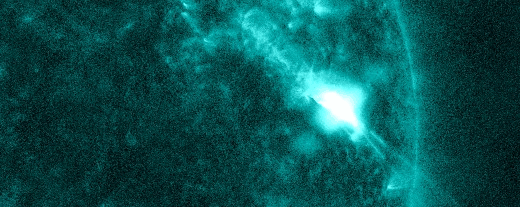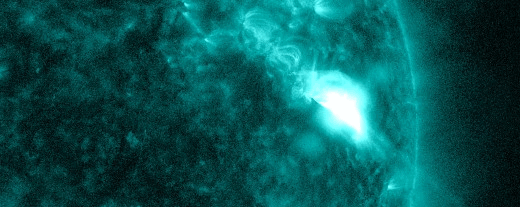
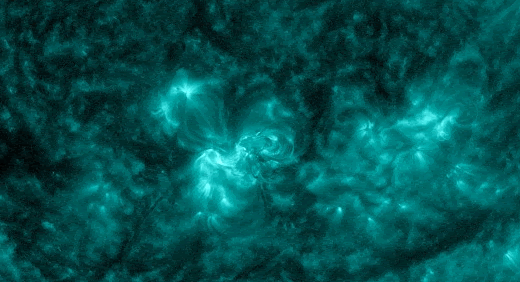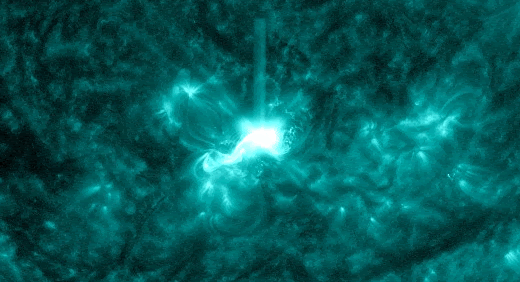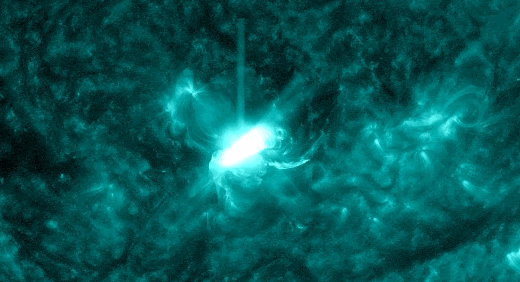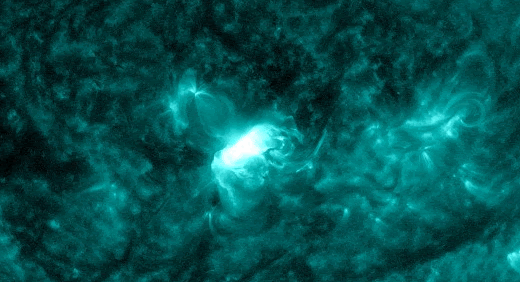
SOLAR RADIATION STORM–NOW: For the second time in less than a week, energetic solar protons are raining down on Earth’s upper atmosphere. Forecasters call this a “solar radiation storm.” Today’s storm (near category S2) is rich in “hard protons” wiith energies greater than 50 MeV. It is causing a shortwave radio blackout inside the Arctic Circle and speckling the cameras of some Earth-orbiting satellites.
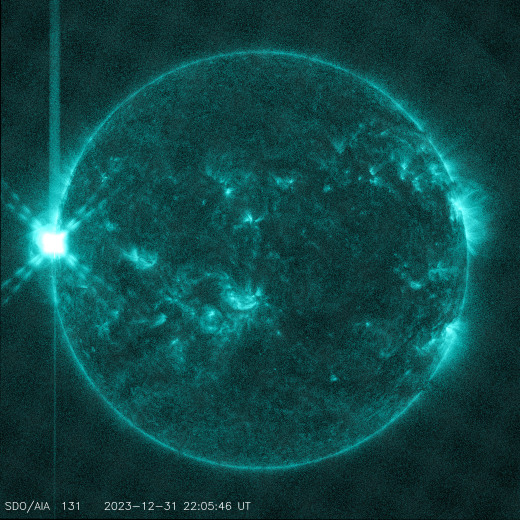
The plot above shows storm data recorded by NOAA’s GOES-18 satellite in Earth orbit. Sensors on the satellite are counting energetic protons as they pass by en route to Earth. Triggered by an explosion near the sun’s southwestern limb (inset), this storm could last for another 24 hours.
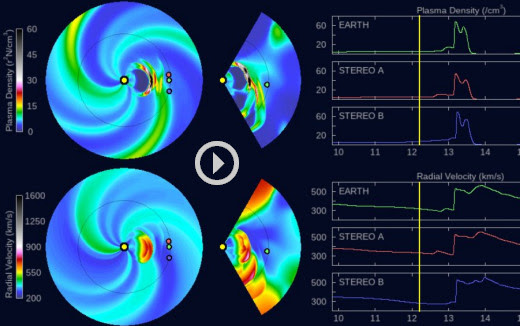
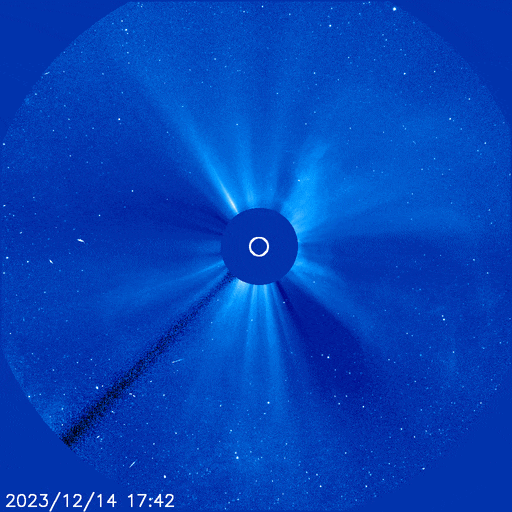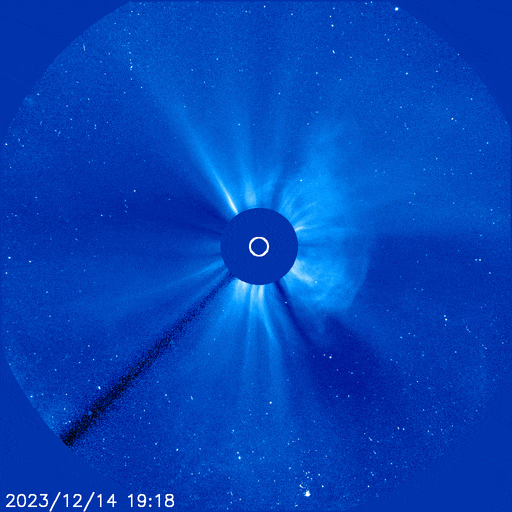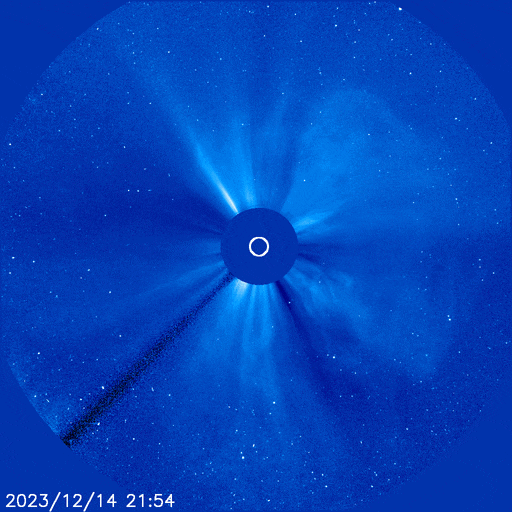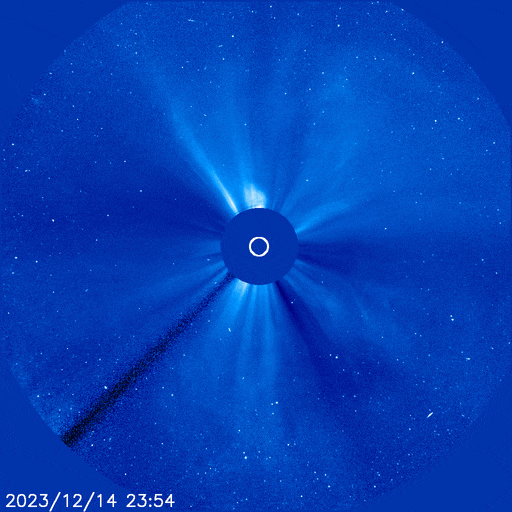
IS A ‘CANNIBAL CME’ COMING? Since Feb. 7th, the sun has hurled multiple CMEs into space. A handful of them might hit Earth this week. A new NOAA forecast model shows at least three solar storm clouds approaching for strikes on Feb. 13th:
Click to play the animated forecast model
The closely-spaced arrival of these three CMEs could spark G1 (Minor) to G2-class (Moderate) geomagnetic storms with high-latitude auroras in northern Europe, Canada, and northern-tier US states from Maine to Washington.
There’s a chance the CMEs will pile up to form a Cannibal CME. This happens when one fast-moving CME sweeps up slower-moving CMEs in front of it. Cannibal CMEs typically contain strong shocks and enhanced magnetic fields that do a good job sparking geomagnetic storms. If such a pile-up occurs, the combined strike could cause a G3 (Strong) geomagnetic storm with auroras at mid-latitudes.