(Source: Wired via David Korchin)
SOME RETIREES TAKE up fly fishing. Others pick up golf. But when Roland—or “F5ZV,” as he’s known on ham radio—left his job in Belfort, France a decade ago, he devoted his newfound leisure to a far more peculiar hobby: hunting radiosondes.
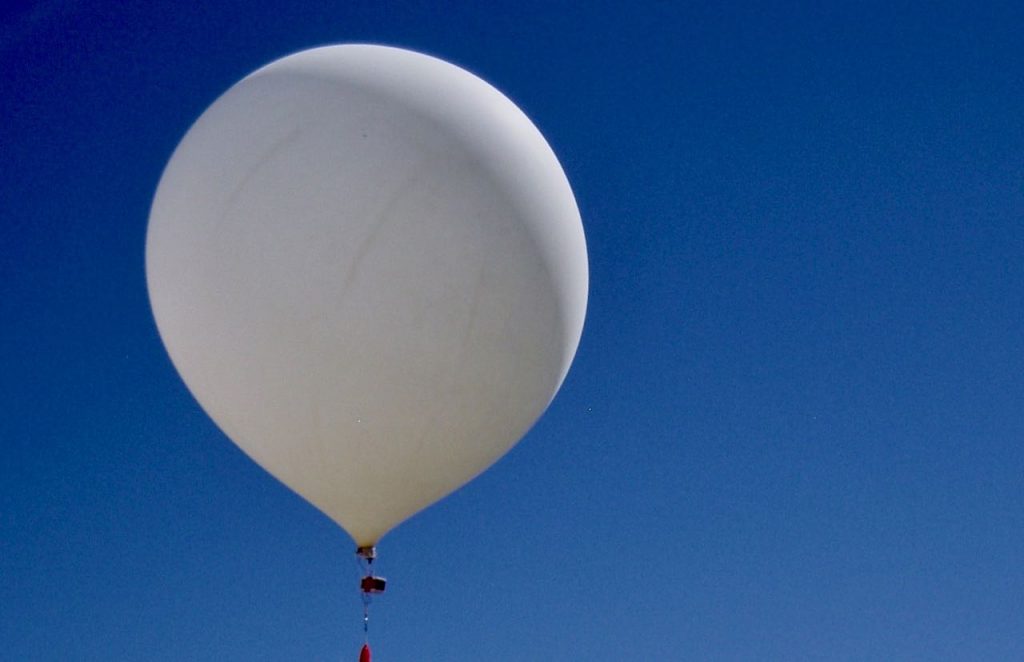
The white plastic boxes contain instruments to measure things like wind, temperature and humidity; meteorologists send them skywards on balloons, and they transmit data back over radio waves. But somewhere around 100,000 feet, the balloons burst, and the radiosondes parachute back to earth.
Roland began using a radio receiver and antenna to track them to the rooftops, parking lots, and random cow pastures where they land. “He was completely obsessed with radiosondes,” says Swiss photographer Vincent Levrat, who documents the chase in his quirky series Catch Me If You Can. “He would wake up at night just to hunt.”
By Roland’s own estimation, there are hundreds of other radiosonde hunters across Europe who monitor launch schedules for weather station balloons. They begin each hunt by using software called Balloon Track to predict the general area where a radiosonde might land; Balloon Track calculates the trajectory based on wind speed and burst altitude.[…]