The new budget would expand Leaning English content, but reduce, “low-impact, long-form English language radio created for shortwave.”
The Broadcasting Board Of Governors is requesting a reduced budget from congress for FY 2015 and re-focusing efforts on services to Asia and Africa.
Of course, this will be at the expense of Azerbaijani, Georgian, Persian, and Uzbek language programming and a complete cut of programs to Serbia, Albania, Bosnia-Herzegovina, and Macedonia. Programming to Cuba will be reduced as well.
The FY 2015 Budget Request also outlines the closure of VOA’s bureaus in Jerusalem and Houston.
For a quick summary, read the VOA News article below.
After the article, I’ve clipped quotes where the BBG specifically mentions shortwave radio in the 2015 budget, so continue reading.
(Source: VOA News)
The Broadcasting Board of Governors, the U.S. government entity that oversees the Voice of America, has released details of a 2015 budget request that will cut Balkan language services but add spending aimed at Asia and Africa.
The BBG is asking Congress for $721 million, a reduction from a $731 million budget in the current fiscal year. Agency officials say their goal is to reach a new generation of audiences through media that global listeners and viewers increasingly use.
The 2015 budget request includes youth-oriented video and digital initiatives for Cambodia, Vietnam, and Burma – also known as Myanmar.
In China, the BBG plans to increase the use of social media and programs to fight Internet censorship.
The BBG is also planning to set up a new satellite television channel and expand FM radio in the Sahel region of north-central Africa. A new Lingala language service is planned for the Democratic Republic of Congo.
VOA’s English Learning programs would also be expanded.
But the 2015 budget would eliminate the VOA language services for Albania, Bosnia-Herzegovina, Macedonia, and Serbia. The Azerbaijani, Georgian, Persian, and Uzbek services would see reductions and broadcasting to Cuba would also see a very significant cut.
The proposal also calls for the closure of VOA news bureaus in Jerusalem and Houston.
Dave Allison, acting president of the union representing many VOA employees, said with the cuts in services VOA is “retreating” from its historic mission that began in 1942. He said Balkan broadcasters had tears in their eyes when they were told their shows face elimination.
[View this article on the VOA News.]
Shortwave radio in the 2015 budget?
If you take a look inside the FY 2015 Budget Request (click here to download it as a PDF) you will see how they perceive shortwave radio in the media mix moving forward. I particularly find the mention in their summary insightful.
Here are a few highlights:
From page 9 of the FY 2015 Budget Request:
“The FY 2015 Budget Request reflects a host of distribution changes. In the mix of technology and distribution platforms, the BBG sees clearly the global adoption of digital media. Actively underway is the migration from legacy distribution platforms such as shortwave and medium wave (AM) to the media platforms audiences are using today, including satellite TV and audio, FM radio, mobile phone technologies, and social and other digital media. In many of our markets, use of the Internet overall and as a source of news already exceeds radio, and in some cases by a wide margin. The BBG is adapting to this fundamental shift by taking, where appropriate, a digital-first approach and combining digital and traditional media into one integrated strategy.
That said, the BBG remains platform-agnostic, meaning we will use the media on which our audiences prefer to receive information, engage with media and connect with one another.
Shortwave radio will still play a role in selected countries such as Nigeria, Burma, and Afghanistan, among others.”
No money has been budgeted for shortwave radio capital improvements in 2015:
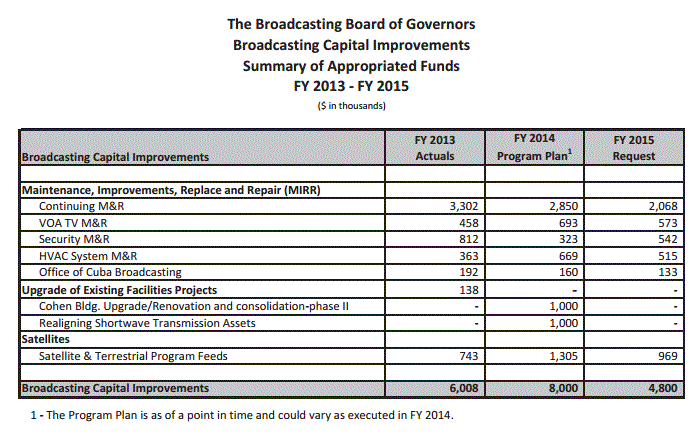
On page 45, the BBG mentions regions where they believe shortwave radio is still an important information medium:
“Audiences accessing VOA using mobile devices and social media grew exponentially in the past year; and VOA has a global network of FM affiliate partners as well as wholly owned FMs. Meanwhile, VOA’s long-standing role as a shortwave broadcaster remains at the forefront in markets where
shortwave is still viable, including the Sahel, where Islamist extremists have carried out terrorist attacks in the past year, and in information-deprived societies such as North Korea and Tibet.”
Then on page 64:
“Capitalizing on current research on audience media habits, TSI will continue taking steps in FY 2014 to move away from less effective legacy distribution systems, such as shortwave and medium wave transmission, toward use of more modern technologies, where appropriate, to reach larger and younger audiences. Where shortwave remains important, TSI is building a more cost-effective transmission infrastructure to support continuing broadcast requirements. In addition, where available, transmitting stations will receive their broadcast content through lower cost digital services, instead of the more expensive satellite distribution. TSI also is using satellite radio in China, including in Tibet, – for just a fraction of the cost of shortwave or medium wave transmissions to that country – as a means of leveraging the widespread use of satellite receive dishes in remote locations or where local cable and Internet access is restricted.”
Burmese broadcasts mentioned on page 74:
“RFA’s Burmese Service is preparing for comprehensive radio and TV coverage of the 2015 national elections, Burma’s first opportunity for truly free and fair elections. At the same time, RFA is reporting on the numerous domestic problems which could derail the move to democratization, especially the need for constitutional reform prior to the elections. RFA
provides a platform for civil, civic dialogue where the people of Burma can express opinions on their problems and possible solutions. RFA will also address religious and ethnic divides,
and more programming will be targeted toward Burma’s rural population, providing basic education in areas such as health, agriculture and basic human rights. Shortwave radio, which still dominates in rural areas where most of the population lives, is the best medium to present such programs.”
Afia Darfur‘s programming on page 78:
“Afia Darfur is broadcast into Darfur via shortwave each evening at 9:00 p.m. local time and targets all people in Darfur and eastern Chad, and it is heard in Khartoum. The 30-minute program is rebroadcast two additional times, once in the evening (10:00 p.m. local time) and again the following morning (6:00 a.m. local time).”
Cost savings through shortwave broadcasts from Kuwait (page 82):
“BCI funds will be used to reconfigure the shortwave broadcast infrastructure at the Kuwait transmitting station to enhance coverage of Iran and achieve cost savings for shortwave
broadcasts. Because of the very low cost of electrical power in Kuwait, the IBB Kuwait Transmitting Station is the least expensive station to operation in the IBB global network. This project will allow the Agency to shift scheduled transmissions from other stations in the IBB network to Kuwait, especially those transmissions from high cost leased facilities wherever possible.”
But, perhaps this clip from the 2015 budget summary provides the best insight:
“In order to serve audiences in less developed areas of the world, the BBG must continue to broadcast via traditional technologies such as shortwave and maintain capability on these platforms by replacing antiquated equipment. But to stay relevant in competitive news markets and serve both current and future audiences, the BBG must also invest in new cutting-edge technology. In areas where the BBG has ceased to broadcast, or where ownership and usage of shortwave radio has declined significantly, the BBG has closed transmission stations, repurposed equipment, and invested these savings in digital media technology and new high-priority programming.”







