Many thanks to SWLing Post contributor, Charlie Liberto (W4MEC) for the following guest post:
Vintage receiver frequency counter…sort of
by Charlie Liberto (W4MEC)
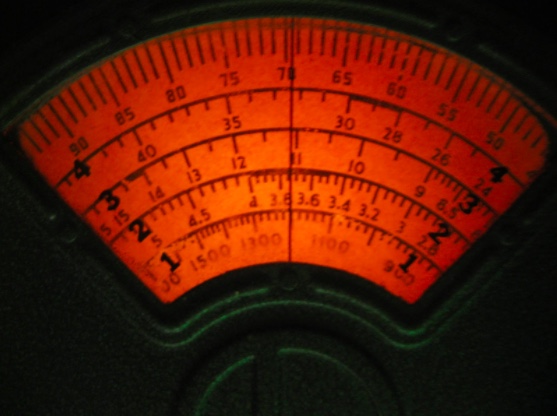
You probably know what a log book is, and maybe a logarithm, but do you know what a ‘Logging Scale’ was meant for? If you are a modern SWL’er, and have a receiver built in the last 40 years or so, you probably don’t have that mysterious 0 to 100 range on your dial, as shown at the top of the picture of the Hallicrafters S20-R main dial, and you may not have a dial at all, peering without question at a digital display of your received frequency.
The Logging Scale on older and vintage receivers had two functions: to let you find a station you might be looking for, when you knew the frequency it would be on, and to determine the frequency of a station, but you had to have known references. How to do that on those old scales that may have had 50 kHz or even 500 kHz hash marks between whole Megahertz numbers, or in that era, KC or MC numbers? The process is fairly straight forward, but did require you to know the operating frequency of at least 2 stations on the band of interest, and the closer they were to the mystery frequency, the better.
Let’s say you are looking for WLMN that is supposed to begin its operation day on 6025 kHz. and your receiver has a mark every 250 kHz between 5 and 7 MHz, that’s pretty iffy as to setting the dial. Now, you know that station WABC is on 5500 kHz, and station GXYZ is on 6525 kHz, so, tuning in WABC you note what number the pointer on the dial is over on the logging scale, maybe it is 40. Then you tune to GXYZ and you find it on 70 on the logging scale. The known difference in frequency between WABC at 5500 kHz and GXYZ at 6525 is 1025 kHz, and the logging scale number difference is 40 to 70 or 30 divisions. Take the 1025 kHz separating your two known stations, divided by the 30 logging scale divisions and you get 34.167 kHz per division. Some more math, the station you are looking for, WLMN is on 6025 kHz, which is 525 kHz away from WABC at 5500 kHz., divide 525 kHz by the logging scale frequency versus division number of 34.167 kHz which equals approximately 16. Take that 16, add it to WABC logging scale number of 40, and you should expect to hear WLMN on logging scale 56 on the dial.
Of course you can flip this process around. If you heard WLMN, but did not know it’s frequency, the same procedure worked backwards to interpolate the logging scale 56 into kHz, added to the WABC frequency/log number, or subtracted from GXYZ numbers, and you would figure out WLMN was on 6025 kHz.
What did this process do? It ‘calibrated’ your receiver dial to known checkpoints by using known frequencies of stations, such that you had a better idea of where you were frequency wise, but it did have it’s limitations. Older receiver dials usually had the lower frequencies divisions of a band close together, and as you tuned to higher frequencies on the same band, hash marks for frequencies got farther apart, while the logging scale stayed linear. This was because builders used the simpler straight line capacitance variable capacitor for tuning, instead of the straightline wavelength or straight line frequency style which would have made the dial more linear. If you used two stations on the low end to set a logging scale reference, chances are it will be quite a bit off in the frequency versus logging scale number on the high end of the dial. So, if you could find two stations that bracketed the one you were examining, that would assure the most accuracy.
After all that, you are probably saying thank God and a lot of engineers for a digital readout.
Thank you, Charlie, for an excellent tutorial and example of using dial logging. I’ve had a number of vintage radios over the years with logging scales and it took some digging to discover how they worked. While digital radios make the process as easy as pie, vintage radios are worth the extra effort!