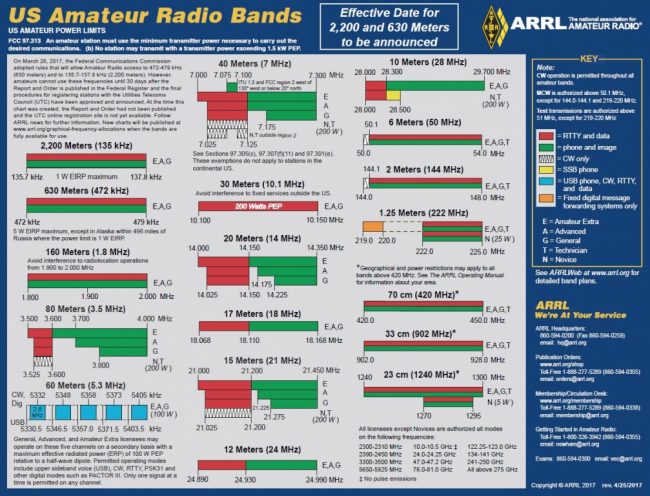
Many thanks to SWLing Post contributor, Steve, who notes that the ARRL has updated their downloadable Frequency Band Charts.
I find it interesting that the ARRL also noted the following on their download page:
NOTE: The new 630-meter and 2200-meter bands are not yet available for Amateur Radio use. The effective date of the recent FCC Report & Order granting these allocations has not yet been determined, and until the start date has been set, it is not legal under an Amateur Radio license to transmit on either band. The FCC will publish a notice in The Federal Register “announcing such approval and the relevant effective date.” ARRL will announce the UTC notification procedures and the effective date to use these new bands as soon as these are known.
I’ve received feedback from SWLing Post readers noting a licensed amateur radio operator in Tennessee who had already set up an active beacon on the 630 meter band. He eventually pulled the plug. No doubt, this was why the ARRL posted a special note.
Downloading and printing the charts
Download and print PDF documents using Adobe Reader.
- Frequency Bands Chart [PDF] (grayscale)
- Frequency Bands Chart [PDF] (black/white)
- Frequency Bands Chart [PDF] (color)
- Frequency Bands Chart [Order Now] (11X17 gloss; color + WAS map)