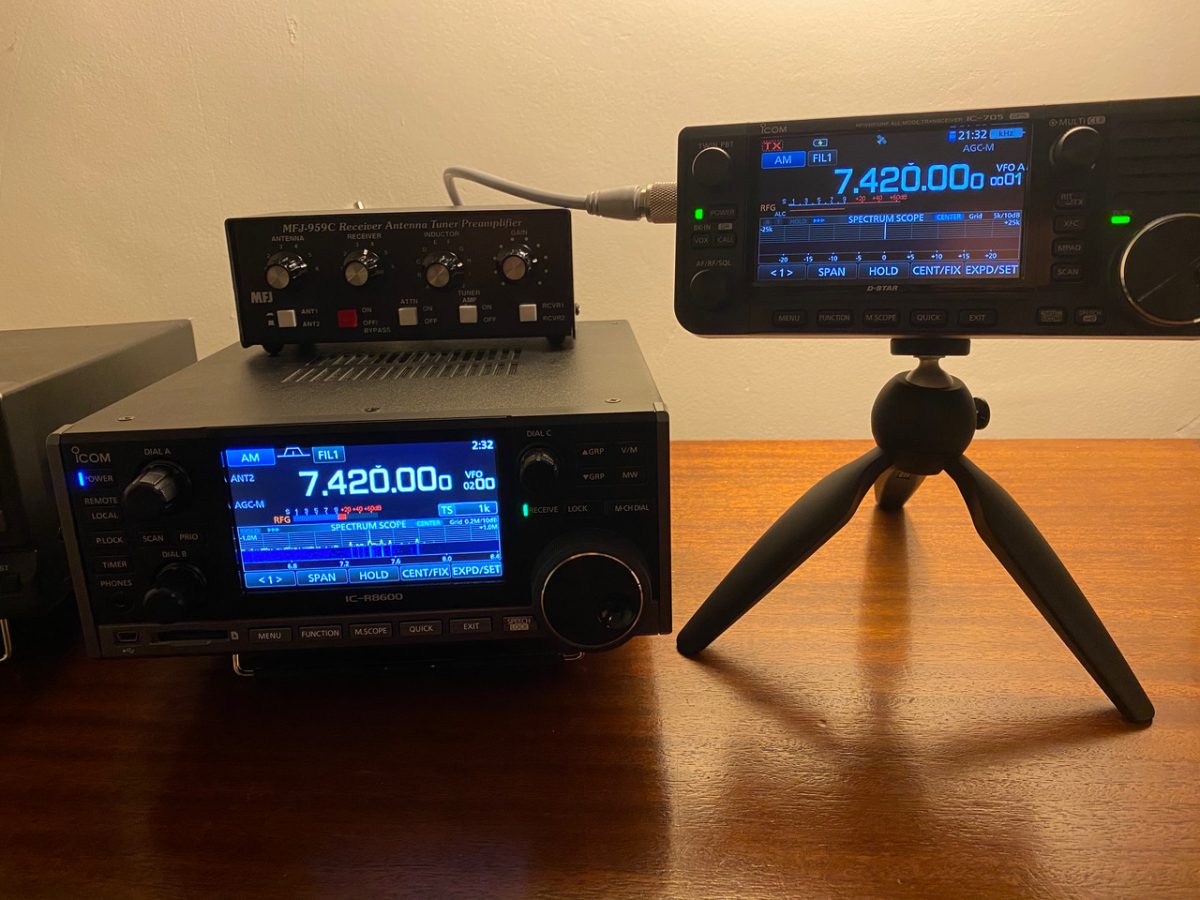
Many thanks to SWLing Post contributor, Giuseppe Fisoni, who reached out a few weeks ago noting that he was very impressed with the Icom IC-705‘s receiver performance even compared with his Icom IC-R8600 wideband receiver.
I asked Giuseppe if he would perhaps write up a short informal report to share here on the SWLing Post. He just sent me the following notes:
Hi Thomas,
[…]Consider this more of a qualitative comparison – just S meter readings with a few brief notes.
My overall impression is that the IC-705 is a fantastic SW receiver, as you’ve already made clear on all your posts. In most cases, it holds up well against the IC-R8600, and even performs better in some cases. I have some notes below, which you are welcome to share with your readers if you’d like. For a while I also had two IC-705s in my hands, so I even got to test “replicas” with the 705 (there was no major difference but it was still fun to do).
A few things about my comparisons:
1. All tests were done using a 50’ long wire antenna (house to tree) with an un-un.
2. The IC-R8600 was operated using an ICOM AC adaptor (creating a disadvantage), while the IC-705 was run on battery. However, I tried to only compare stations where the noise floors were comparable and the 8600 didn’t have any RFI.
3. I tried my best to normalize the RF gains on each radio, but this became somewhat difficult. I’m not sure if they are on the same scale (i.e. does 80% RF gain mean the same thing on both radios?). Also, I very quickly noticed that turning up the RF gain on the 8600 only increased the S meter reading and apparent noise floor on the waterfall spectrum, but it did not actually make the audible signal or noise audibly stronger. This was especially true from 50% and up on the RF gain. In contrast, the RF gain on the 705 operated as you’d expect – the more you turned it up, the higher the gain on the signal (and noise), evenly across 0-100%.
Test #1
2021.02.08
0211 UTC
3,330 kHz CHU
IC-705: weak signal but audible, S6
IC-R8600: no signal!
Winner: clearly 705. Shocked the 8600 couldn’t pick up CHU!
Test #2
2021.02.08
0219 UTC
3,215 kHz WWCR Nashville
IC-705: S9+20
IC-R8600: S9+20 to S9+40.
Winner: Tie – although the 8600 had a stronger signal on the S meter, it didn’t really sound any better than the S9+20 on the 705.
Test #3
2021.02.18
1958 UTC
9,690 kHz Radio Espana Exterior
IC-705: S9 to S9+10
IC-R8600: S9+20
Winner: Another tie – the stronger signal didn’t make much of a difference. The 8600 only sounded slightly better because of its speaker, not the receiver, so I’m calling it a tie.
Test #4
2021.02.18
2001 UTC
10,000 kHZ WWV
IC-705: S3, very weak
IC-R8600: S7 to S9 but high atmospheric noise
Winner: 8600
Test #5
2021.02.18
2006 UTC
11,820 kHz Radio Riyadh
IC-705: S1, barely detectable
IC-R8600: S5 to S7, intelligibility unstable
Winner: 8600
Test #6
2021.02.18
2012 UTC
15,000 kHz WWV
IC-705: S3 to S5
IC-R8600: S9, slightly clearer and crisper tones
Winner: 8600, but not by much
Test #7
2021.02.18
2015 UTC
15,580 kHz VOA Selebi-Phikwe, Botswana
IC-705: S1 to S3, in and out with fading
IC-R8600: S9, much more stable signal
Winner: 8600
Test #8
2021.02.19
00016 UTC
7,780 kHz WRMI Slovakia International
IC-705: S9 solid, stable signal
IC-R8600: S9, same
Winner: Tie
Test #8
2021.02.18
0022 UTC
6,604 kHz USB Gander VOLMET
IC-705: S5 to S7
IC-R8600: S9
Winner: Tie, no real difference
Test #9
2021.04.09
2335 UTC
11,940 kHz Radio Exterior Espana
IC-705: S5 to S9 solid signal with some fading
IC-R8600: S9
Winner: Tie – no obvious difference
Test #10
2344 UTC
9,420 kHz Helliniki Radiophonia, Greece
IC-705: S9 +20. Excellent signal
IC-R8600: S9+ 20-30. Excellent signal
Winner: Again, a tie. But the wonderful Greek music reminds you again how much better the speaker is on the 8600.
Overall
Here’s the important thing: even though in most cases the IC-R8600 pulled in a much higher S meter reading, it often didn’t matter unless the difference between the two radios was a lot. In cases where it mattered, I could have turned up the RF gain or preamp on the 705 to match the signal on the 8600 (unless it was really weak on the 705), but I was trying to avoid that for the sake of having some baseline for comparison. How comparable are RF gain levels across ICOM radios?
IC-705 pros/cons take aways for me:
-
- High level of portability and ability to operate on battery
- Has desktop-like features and controls
- Ability to use tripod or custom stand offers custom ergonomics (I found it easier to look at and interact with than the 8600, which has a lower angle of display)
- All-in-one package: SWR + HF/VHF/UHF transceiver
- Built-in audio speaker leaves a lot to be desired, definitely not desktop receiver audio quality
- No stereo headphone jack
My verdict
I am quite impressed with the IC-705! I am looking to downsize my radios and these comparisons have convinced me that the 705 can really check a lot of boxes for what I am looking for in a radio. I think it really offers a lot in a small footprint, which I find very impressive. So, since I have no use in monitoring anything above UHF, I will be looking to sell the IC-R8600, even though it is also a very great radio.
All the best,
Giuseppe
Fascinating report, Giuseppe! Thank you so much for taking the time to perform these comparisons and sharing them with us.
Like you, I believe the IC-705 could replace a number of my other radios. I originally purchased it for my review and planned to sell it after, but quickly realized there’s no way I’m selling it. In fact, it could convince me to sell other radios it effectively makes redundant.
For SWLs who have limited space for a listening post in their home and who like to take their radio to the field, the IC-705 is a no-brainer. It’s an investment at $1,300 US, but I believe it’s a quality rig and certainly an outstanding, feature-packed unit.
I’ve found that the IC-705’s performance on HF and Mediumwave is truly DX-grade. I imagine its FM performance is as well.
It’s funny that you mention the IC-705 front-facing speaker as a con, because I often tout it as a pro. Thing is, I’m most often comparing the IC-705 with other field-portable QRP transceivers. Compared with them, the IC-705 speaker is amazing. But compared to the IC-R8600 or, say, a Drake R8B or SW8? Yeah, I agree with you 100%–it’s just not in the same league with those tabletop receivers. Of course, you can port out the audio to a better speaker if needed. (Indeed, the IC-705 even has built-in Bluetooth!)
Thanks again for sharing your notes with us, Giuseppe!
 Many thanks to SWLing Post contributor, William, who asks:
Many thanks to SWLing Post contributor, William, who asks: