Many thanks to SWLing Post contributor Dan Greenall, who writes:
Many thanks to SWLing Post contributor Dan Greenall, who writes:
Hi Thomas
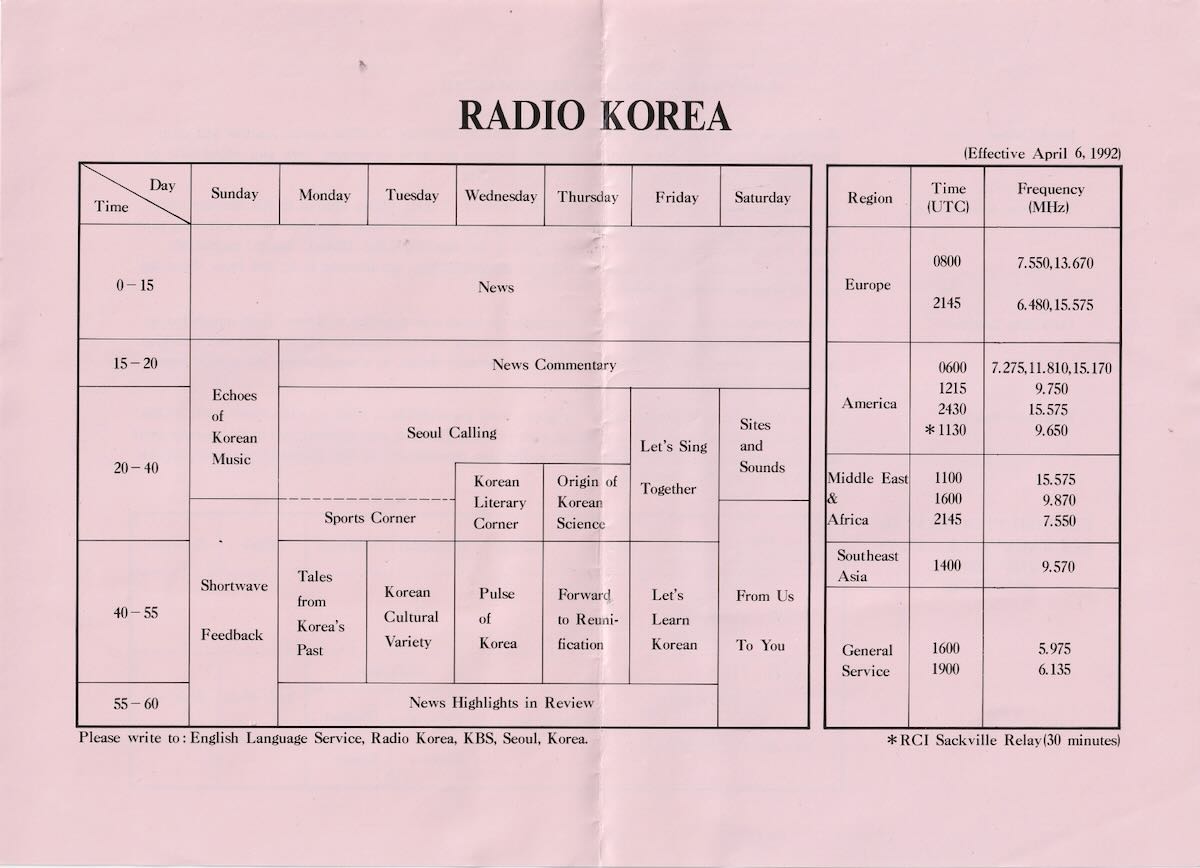
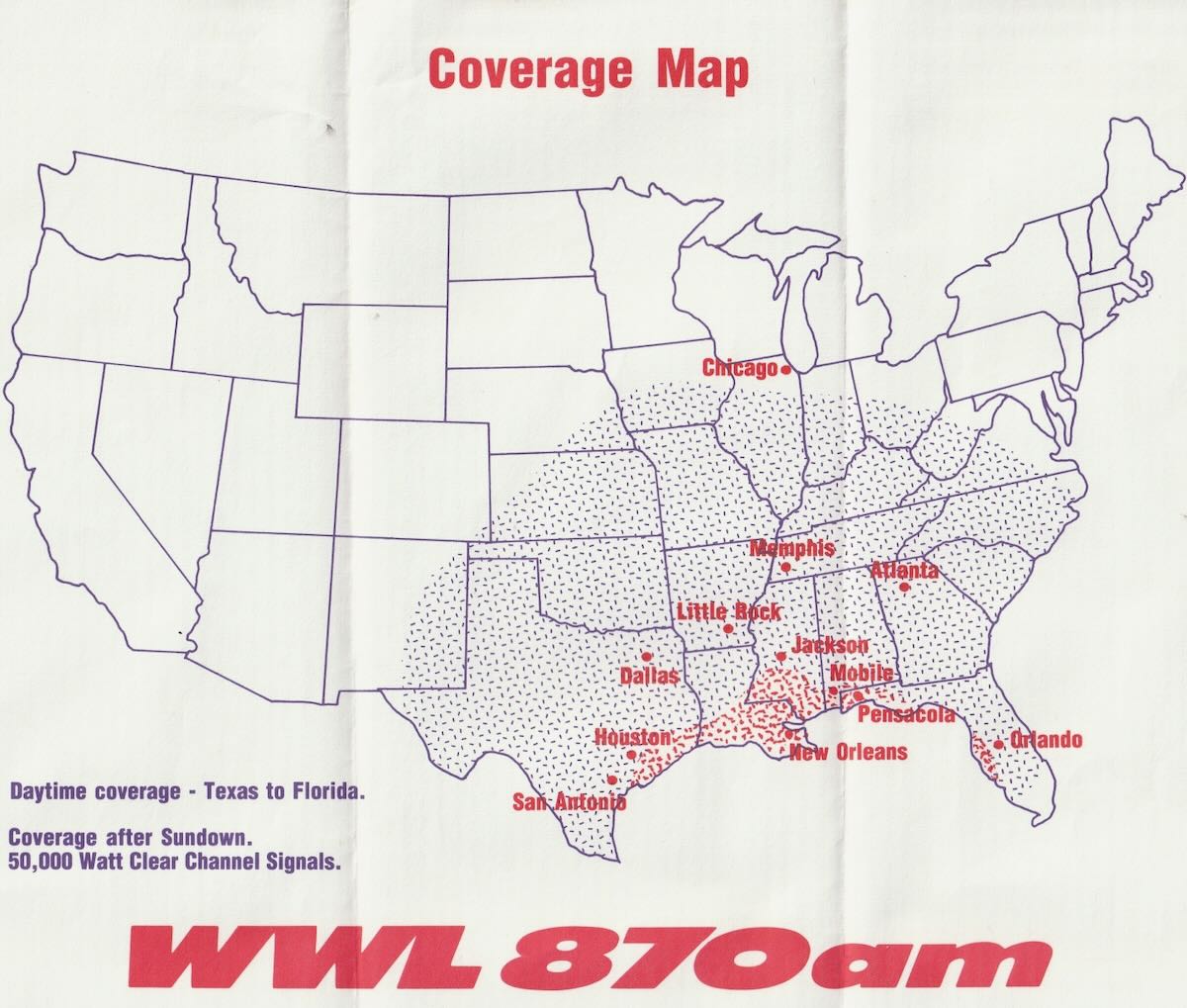
Before the days of the internet and e-mail, handwritten or typed reception reports mailed out to broadcast stations would often net the lucky DXer other goodies, including station brochures, program schedules, frequency guides, station stickers, blank reception report forms, pennants, booklets, and other items in addition to that coveted QSL verification.
The QSLs were stored carefully away in albums or shoe boxes, while much of the other paper ephemera eventually (over the years) made its way into a recycle bin. Recently, while cleaning out some storage boxes in the basement, I came across a number of envelopes containing some of the aforementioned items from the early to mid-1990s. To preserve these newly discovered pieces of radio history, I have scanned much of the material and included it here.
Here’s a sampling:
There are 39 JPEG and 7 PDF files to view: https://archive.org/details/radio-finland-program-guide-1992-3-page-2
73
Dan Greenall VE3HLC, Ontario, Canada
Thank you so much for archiving and sharing these, Dan! Pure radio nostalgia.