RF filters are used (as the name implies) to filter/remove the frequencies you are not interested in and/or let frequencies you want pass . They come in lots of types. For example a band-pass filter lets the signals in a frequency range to pass through it and rejects/attenuates other frequencies. The opposite of band-pass filter is a band-reject or band-stop filter (also called a notch filter) which rejects/attenuates signals in a specific range and lets other frequencies get through the filter. Lots of different filters are used in SDRs and traditional radios. For example AM low-pass filters (only let frequencies lower than 1.7MHZ or so pass) or band-pass filters for various ham radio bands.
RF filters are used (as the name implies) to filter/remove the frequencies you are not interested in and/or let frequencies you want pass . They come in lots of types. For example a band-pass filter lets the signals in a frequency range to pass through it and rejects/attenuates other frequencies. The opposite of band-pass filter is a band-reject or band-stop filter (also called a notch filter) which rejects/attenuates signals in a specific range and lets other frequencies get through the filter. Lots of different filters are used in SDRs and traditional radios. For example AM low-pass filters (only let frequencies lower than 1.7MHZ or so pass) or band-pass filters for various ham radio bands.
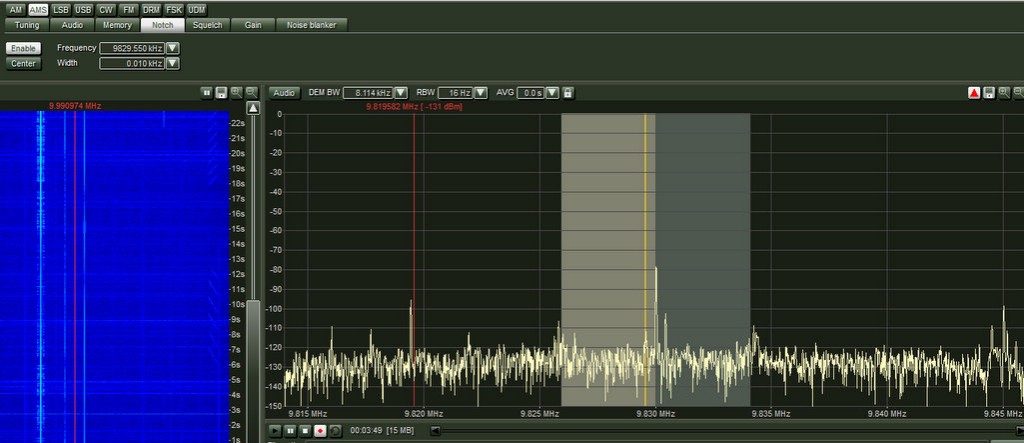
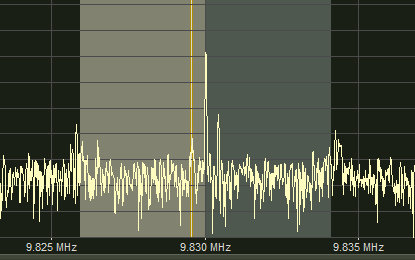
One of the popular use cases for a notch filter is in the FM broadcast range (88-108 MHZ in most parts of the world)
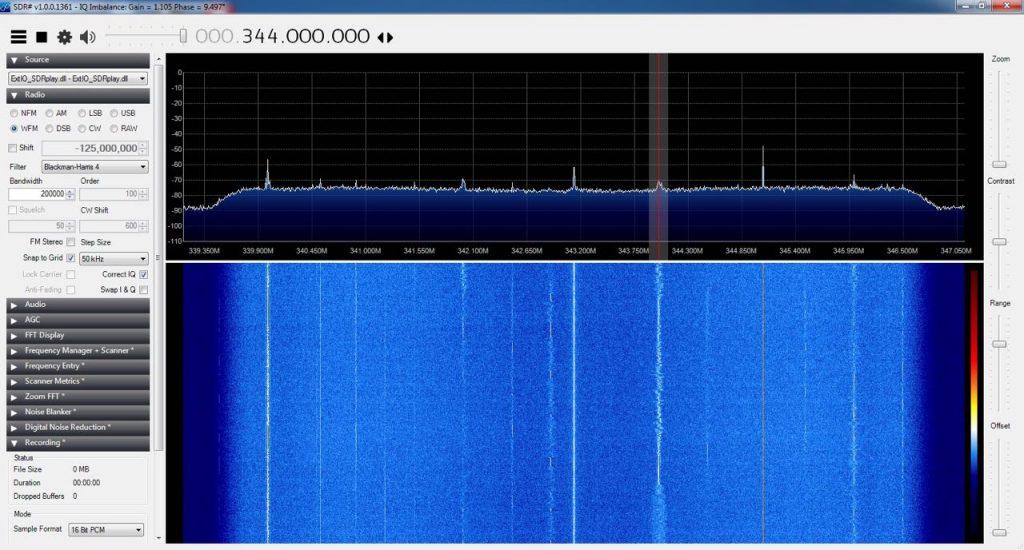
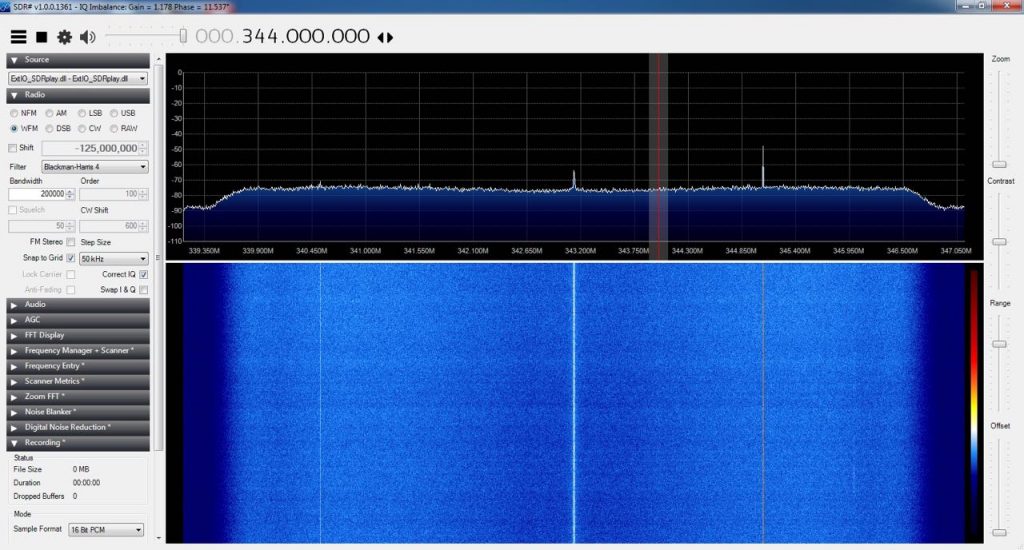
When you live near a powerful transmitter, it can affect the operation of your receiver in other near frequencies (or overload your receiver’s front-end), but I didn’t want the notch filter for this reason. I’ve got a SDRPlay RSP1 (among many other SDRs) which due to its architecture, has some images of FM band in the UHF range (for example in 330-350 MHZ). In fact they’re the images of the product of LO harmonics and FM frequencies.
You can temporarily move/shift the frequency by changing the LO frequency which does not remove them, but moves them around.
Another method to remove these images is using a band-stop filter.
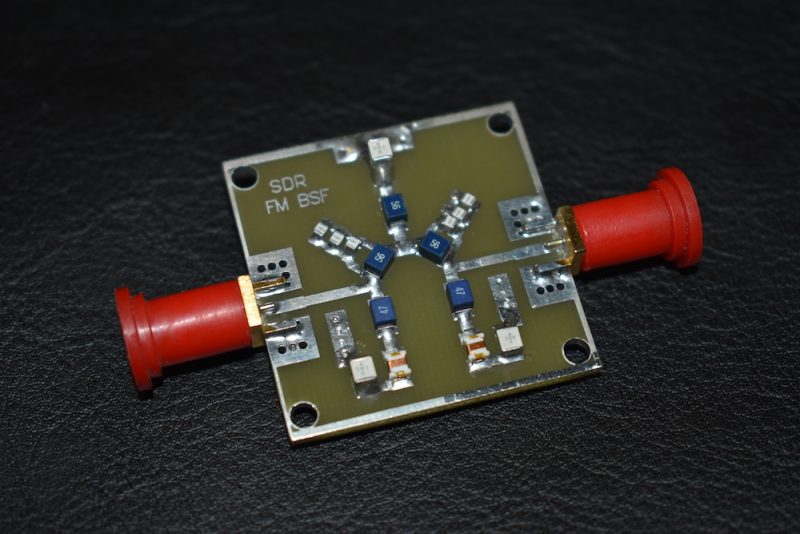
This is the filter I’m using (Thanks to my friend Amirhosein Hasanpur who designed and built it):
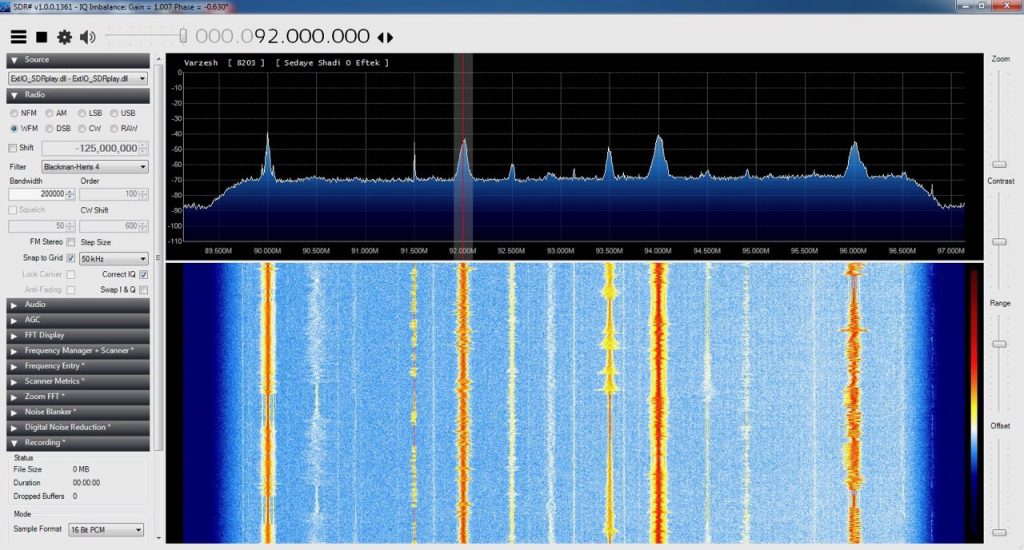
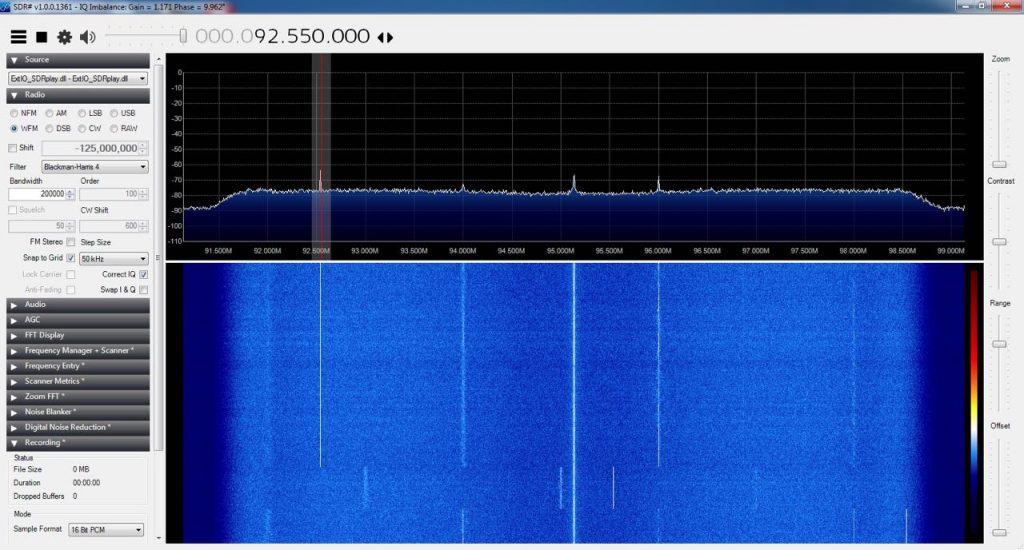
Here you can see the effect of using a FM notch filter on my SDRPlay RSP1:
FM, without filter:
FM, with filter:
UHF (images) without filter:
UHF (images) with filter:
Here’s a link to a Zip file containing the PCB (in Protel), schematics (pdf) and S Parameters (pdf):
https://www.dropbox.com/s/l98kylrofohgqxf/SWLing.zip?dl=0
Note: Like any other SDR test/review, the results depend on lots of different parameters (various gain values, LNA, antenna, software, etc). These pictures are captured with the same conditions just to show the effectiveness of this filter and your milage will definitely vary, but expect a similar outcome. If you live close to a powerful transmitter or use LNAs, you will receive some signals, even when using the filter.
Final note: this issue is solved in the newer version of SDRPlay (RSP2) : it has software-selectable notch filters for FM and MW broadcast frequencies.
Mehdi Asgari, the author of this post, is a regular contributor to the SWLing Post. Mehdi lives in Tehran and is an active member of the EP2C amateur radio club.