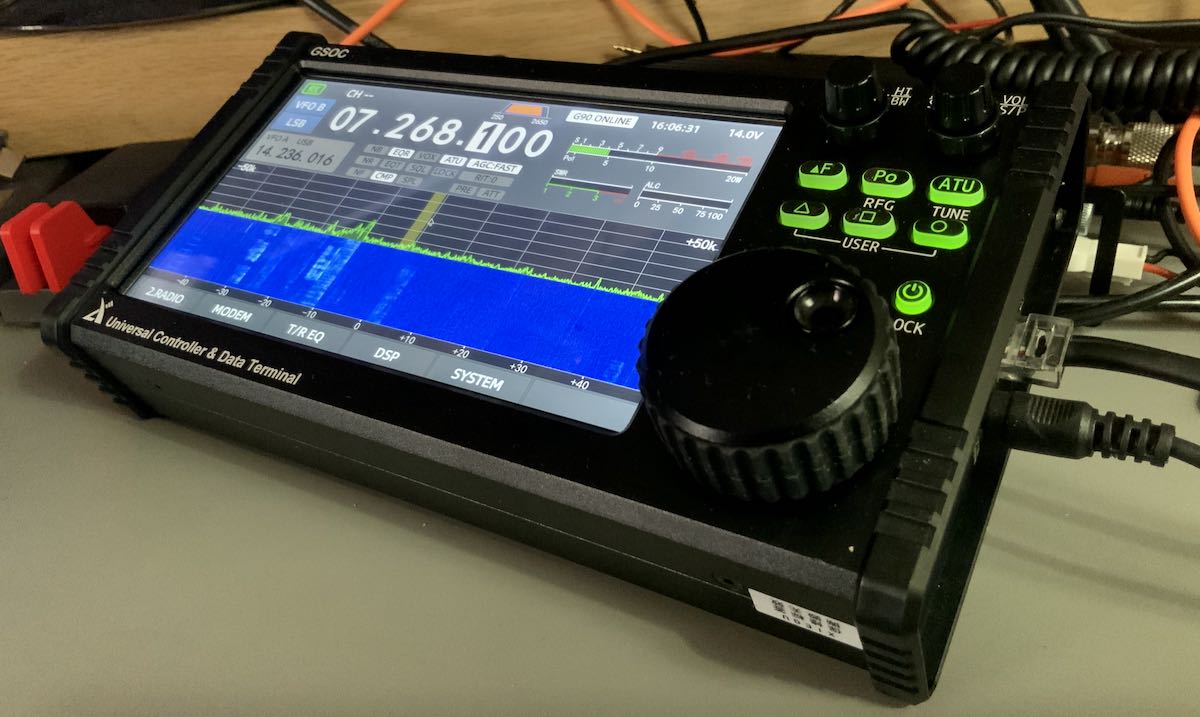
 For those of you who have been asking about the new Xiegu GSOC controller, I just updated my unit with the latest firmware (version 1.1).
For those of you who have been asking about the new Xiegu GSOC controller, I just updated my unit with the latest firmware (version 1.1).
Firmware notes show that it addresses the following items:
Xiegu GSOC FW V1.1
1. Solved the CW sidetone delay problem
2. Solved the problem of unstable system and occasional crash
3. Added RTTY modem
4. Added CW decoder
5. Added SWR scanner
6. Added FFT/Waterfall level adjustment
7. Added FFT line/fill color mixer
The list above was copied directly from the version notes.
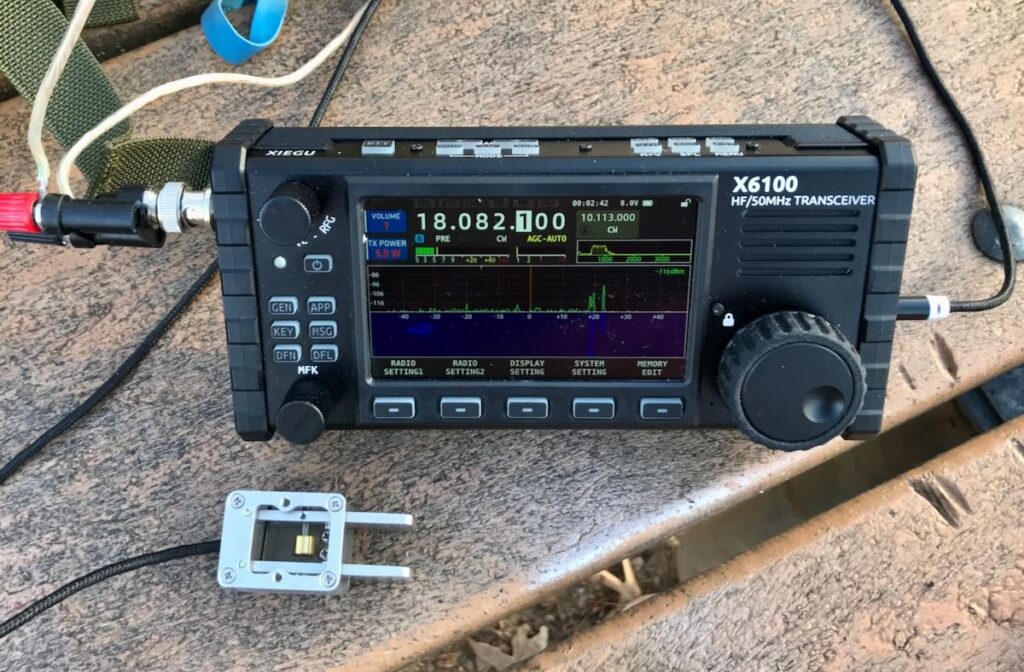
I’m currently evaluating the GSOC/G90 pair which were kindly sent to me on loan by Radioddity. I upgraded the GSOC firmware to v1.1 this weekend.
What follows are some of my evaluation notes an observations after performing the upgrade.
Updating firmware

Updating the GSOC firmware is a pretty straight-forward process.
First you must download the GSOC firmware package (about 330 MB!) which includes a disk image and application to flash the image to a MicroSD card.
Yes, you’ll need a dedicated MicroSD card to upgrade the GSOC firmware–meaning, you can’t simply use a MicroSD card with data on it you’d like to keep because the process of flashing the ISO file also includes a full format with multiple partitions.
You’ll also need an SD Card reader/writer if your Windows PC doesn’t include one.
The included firmware application/tool makes it quite easy to flash a disk image on the MicroSD card.
After the MicroSD card has been prepared, simply turn off the GSOC, insert the MicroSD card on the left side of the GSOC, turn it back on and the GSOC will automatically boot from the MicroSD card and install the new OS/firmware.
Once the upgrade has completed, the GSOC will turn itself off and you must remove the MicroSD card.
If you want to restore the MicroSD card to one partition, you’ll need to perform another format and shrink the volumes.
CW sidetone latency (still issues)
After performing the upgrade, I hopped on the air and tried to make a few CW contacts since I noted in the version notes that the CW sidetone latency had been addressed. So far, my evaluation has pretty much been on hold because I’m unable to use CW mode with any sense of sending accuracy.
Unfortunately, I’m still finding that there’s still a bit of sidetone latency or keyer timing interfering with my ability to correctly send words and letters.
To my ear, it sounds like there’s much less latency in the sidetone audio now (compared with v1.0 which was a little insane) but I still struggle sending characters that end in a string of dits or dashes. For example, when I try to send a “D” the radio will often produce a “B” by adding one extra dit. Or if I try to send a “W” it might produce a “J”. I know something is a little bit off because I botched up two CW contacts with POTA stations yesterday as I tried to send my own callsign correctly. And “73” was even problematic.
I’m guessing that there may still be a bit of audio lag between the G90 body (where the CW key is plugged in) and the GSOC (where the sidetone audio comes out). At the end of the day, the keying information must be sent to the GSOC from the G90 transceiver body and I assume the processor on the G90 is causing a bit of audio latency. Hopefully, Xiegu can sort this out. It’s a serious issue for anyone who wants to operate CW with the GSOC.
If you own the GSOC and operate CW, I’d love your comments and feedback.
Other updates
I tried using the CW decoder yesterday via the “Modem” menu and had limited success decoding a CW rag chew.
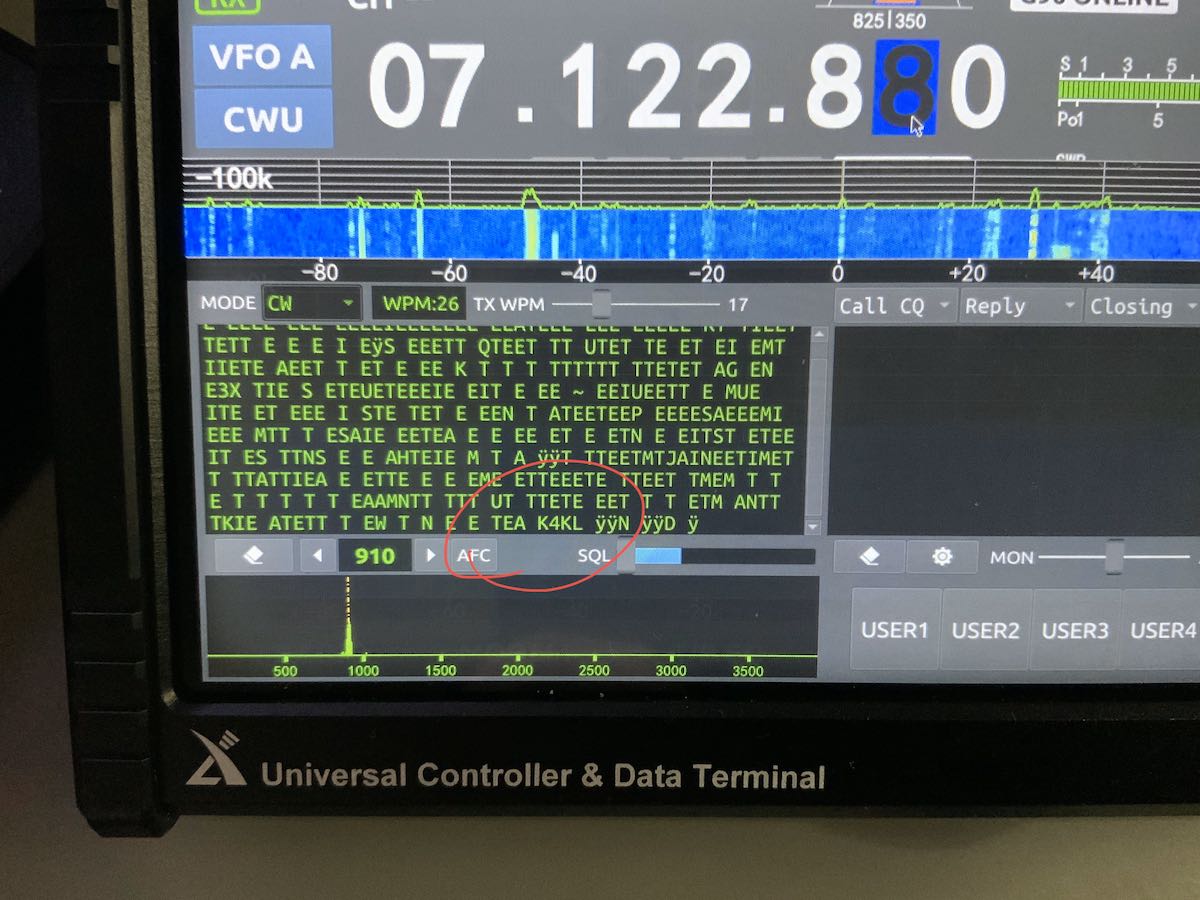
My markup in red: You can see at the very end of this conversation, it decoded the call sign, but interpreted “TU” as “TEA”
The decoder seemed to adjust the WPM rate automatically at one point, but as you can see in the image above, almost every dit was interpreted as an “E” and every dash a “T”. I must assume I don’t have it configured properly, but I don’t have an operator’s manual for reference and instruction. I’ve also tried RTTY decoding, but haven’t been successful so far–I’m pretty sure this is also because I haven’t configured it properly.
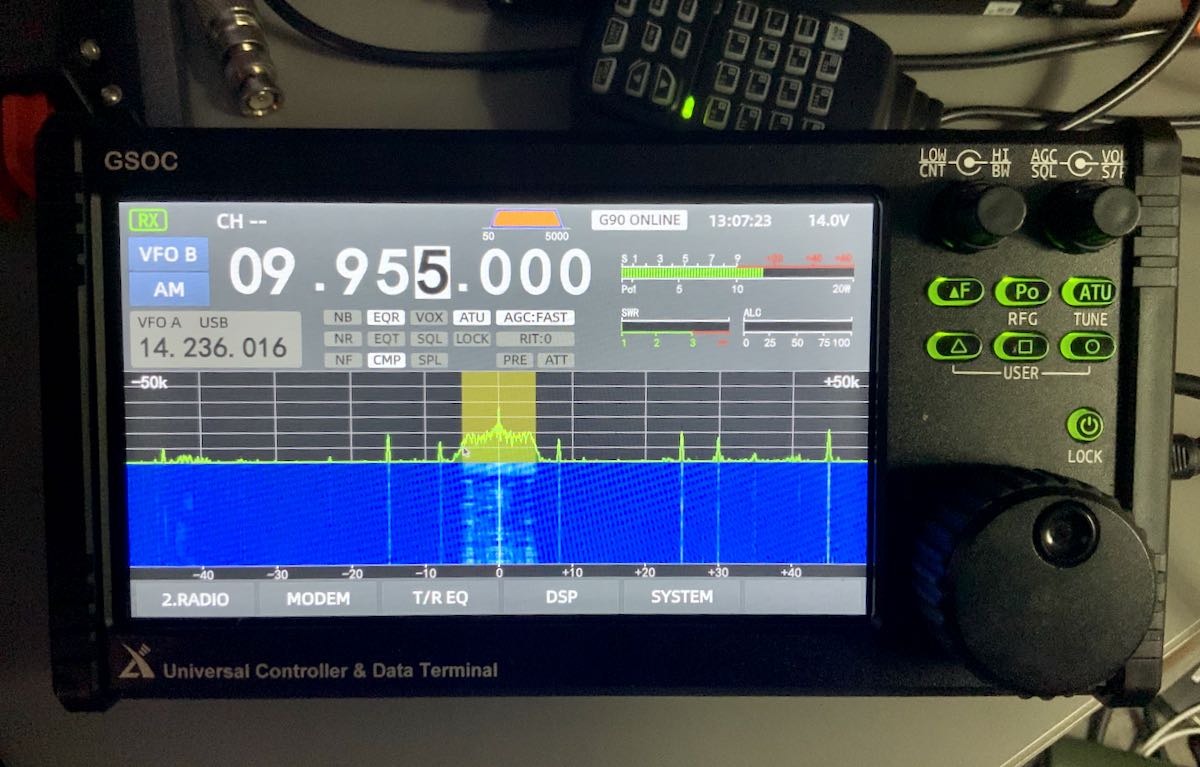
SWR Scanner
I tested the new SWR scanner and it seems to work quite well, plotting SWR across a given frequency range. I did note, however, that it doesn’t seem to confine itself to the ham bands at all. It does inject a signal as it scans (I read 1.5 to 2 watts on my CN-801 meter).
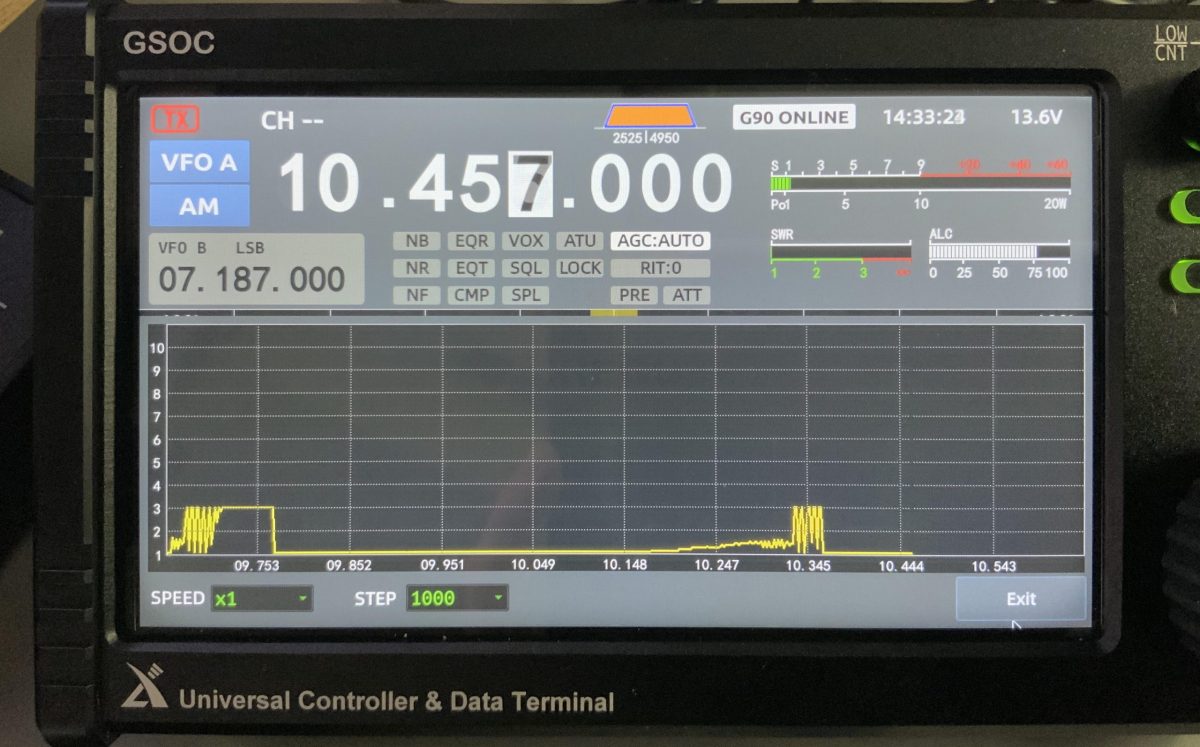
I discovered out-of-band scanning when I took the photo above while trying to do a scan of the 30 meter band. It started around 9.6 MHz–well into the 31M broadcast band where it shouldn’t be transmitting. Xiegu needs to limit transmitted signal to the ham bands.
Memory Keying
I had hoped Voice Memory Keying would be added along with TX/RX recording. I do believe this will eventually be included in a future update. It appears via the “Modem” menu that CW Memory Keying has been added, but I can’t sort out how to make it work (again, a operation manual would be quite handy).
Audio recording
I had hoped transmit and received audio recording would be added in this firmware update; I understand this will eventually be added.
Combined current drain
 As I mentioned in a previous GSOC update, the GSOC controller and G90 transceiver both need a 12V power source–indeed, each has a dedicated power port. The GSOC does not derive power from the G90.
As I mentioned in a previous GSOC update, the GSOC controller and G90 transceiver both need a 12V power source–indeed, each has a dedicated power port. The GSOC does not derive power from the G90.
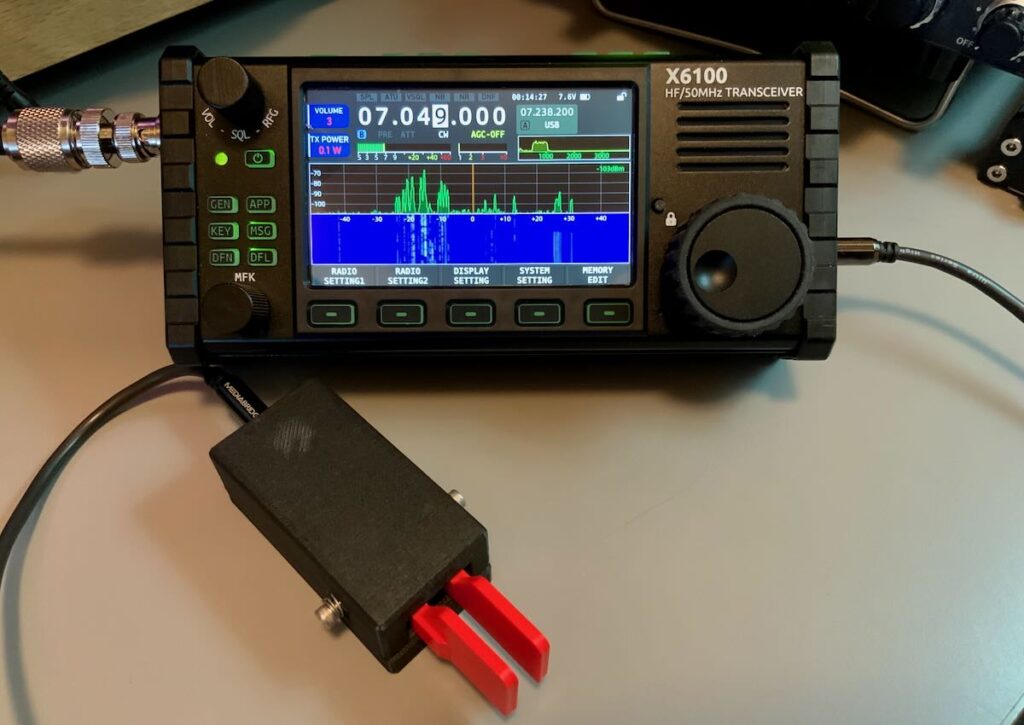
I was originally told that the G90 and GSOC both pull about .60 amps in receive which would total 1.2 amps combined. My Hardened Power Systems QRP Ranger battery pack displays voltage and current; it’s not a lab-grade measurement device, but it’s pretty accurate. When I operate the GSOC and G90 at a moderate volume levels in receive, it appears to draw 0.95 to 0.97 amps–basically, 1 amp.
At home on a power supply, this is inconsequential, but in the field you’d need to keep this in mind when choosing a battery. It’s on par with a number of 100 watt transceivers.
Spectrum display images
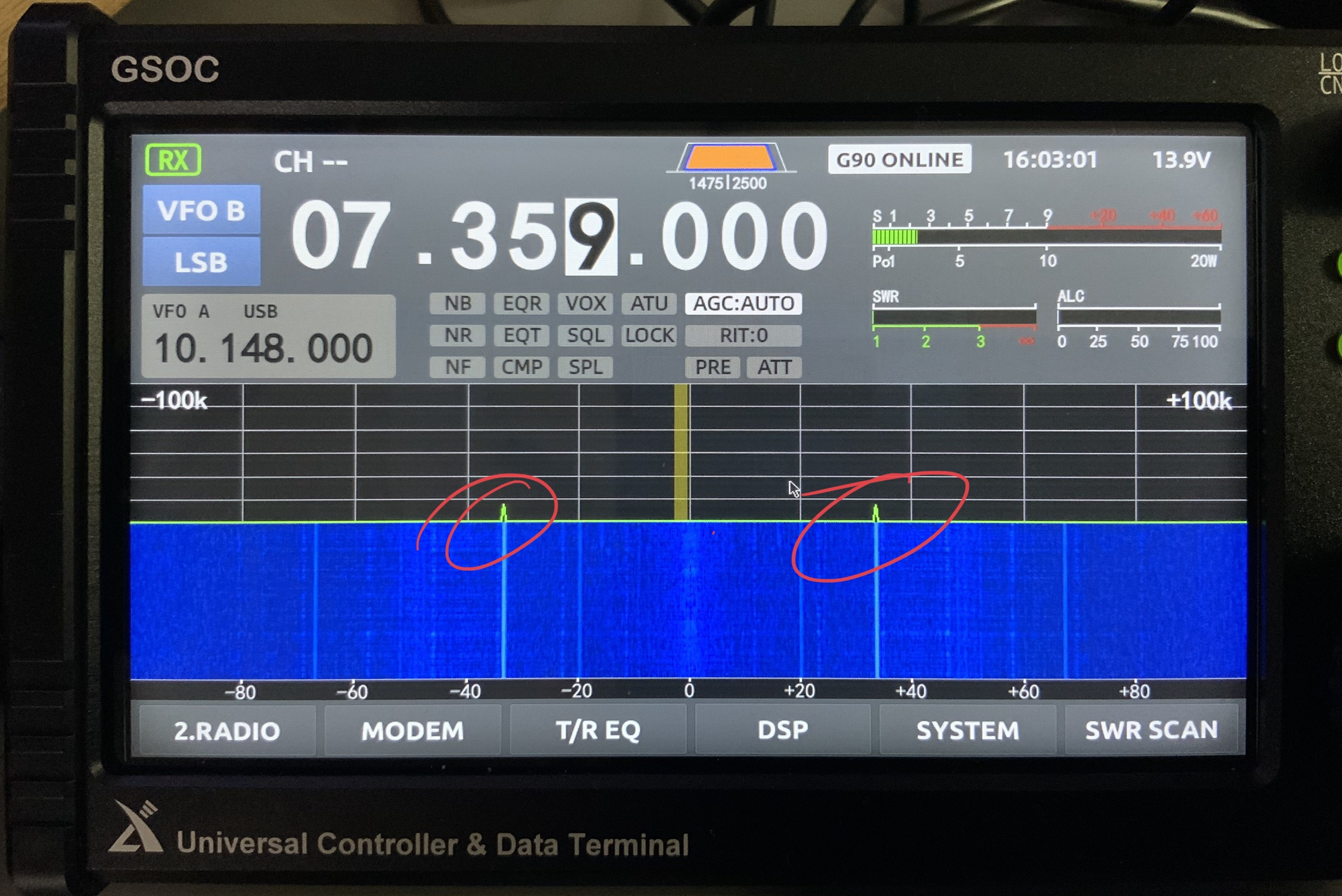
I’m still finding images on the GSOC display that are not present in the received audio. I mentioned this in my initial overview and it doesn’t seem the firmware update addressed this.
I can only assume the spectrum imaging might be due to the I/Q input being too “hot” coming from the G90 via the shielded audio patchcord. Perhaps there’s a function to manually lower the I/Q gain, but I haven’t found that yet.
Spectrum images are most noticeable on the 31 meter band, but found them on the 20 meter ham band as well.
Here are two screen shots that show how images appear when a nearby signal overwhelms the GSOC:
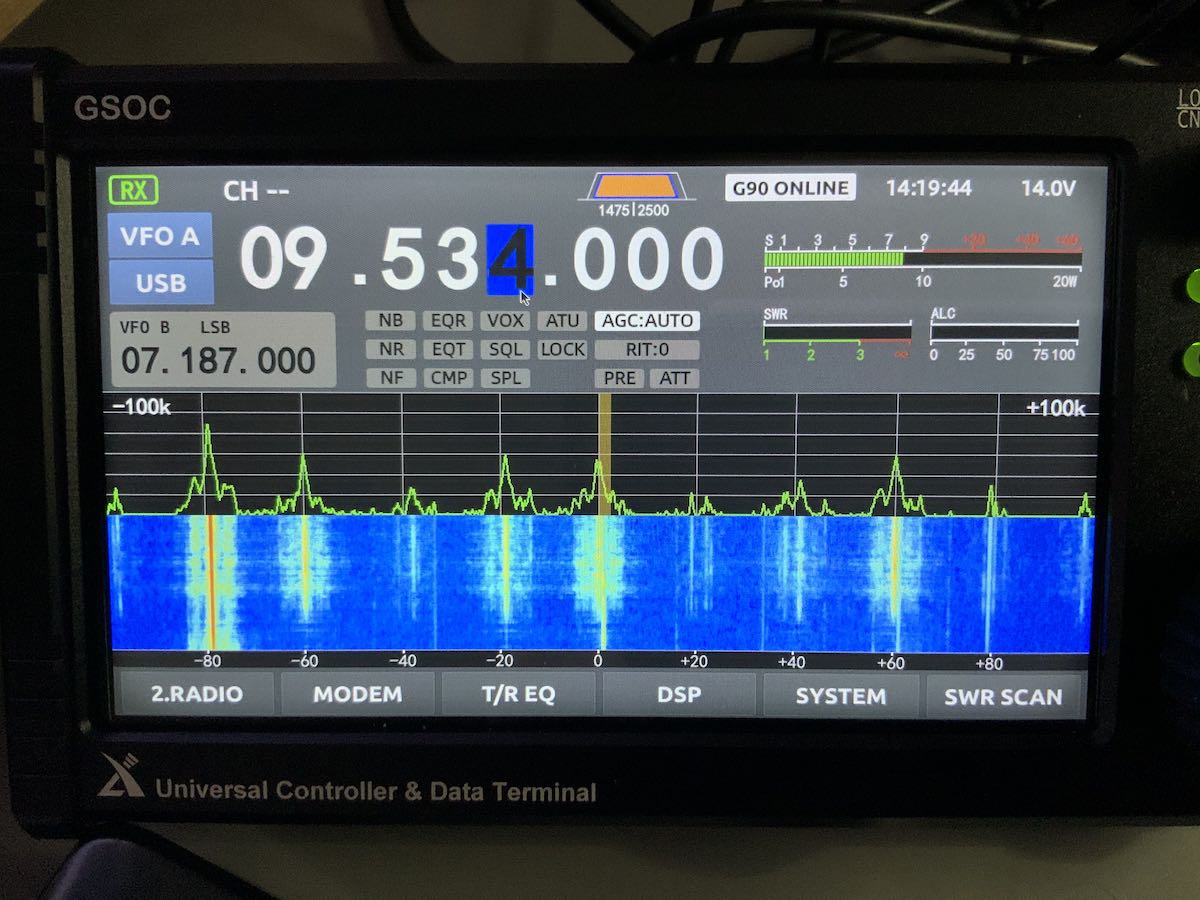
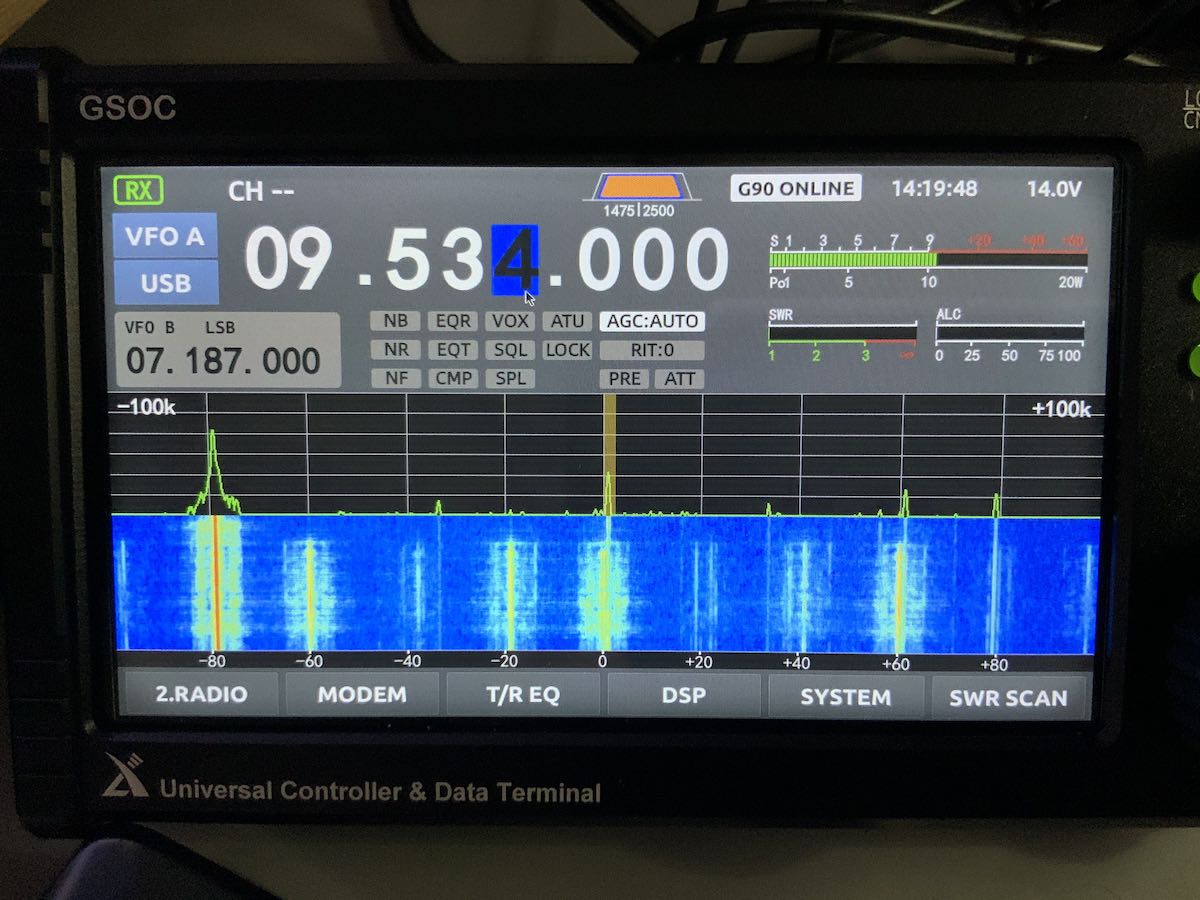 Images are not present all of the time, only when a strong signal intrudes.
Images are not present all of the time, only when a strong signal intrudes.
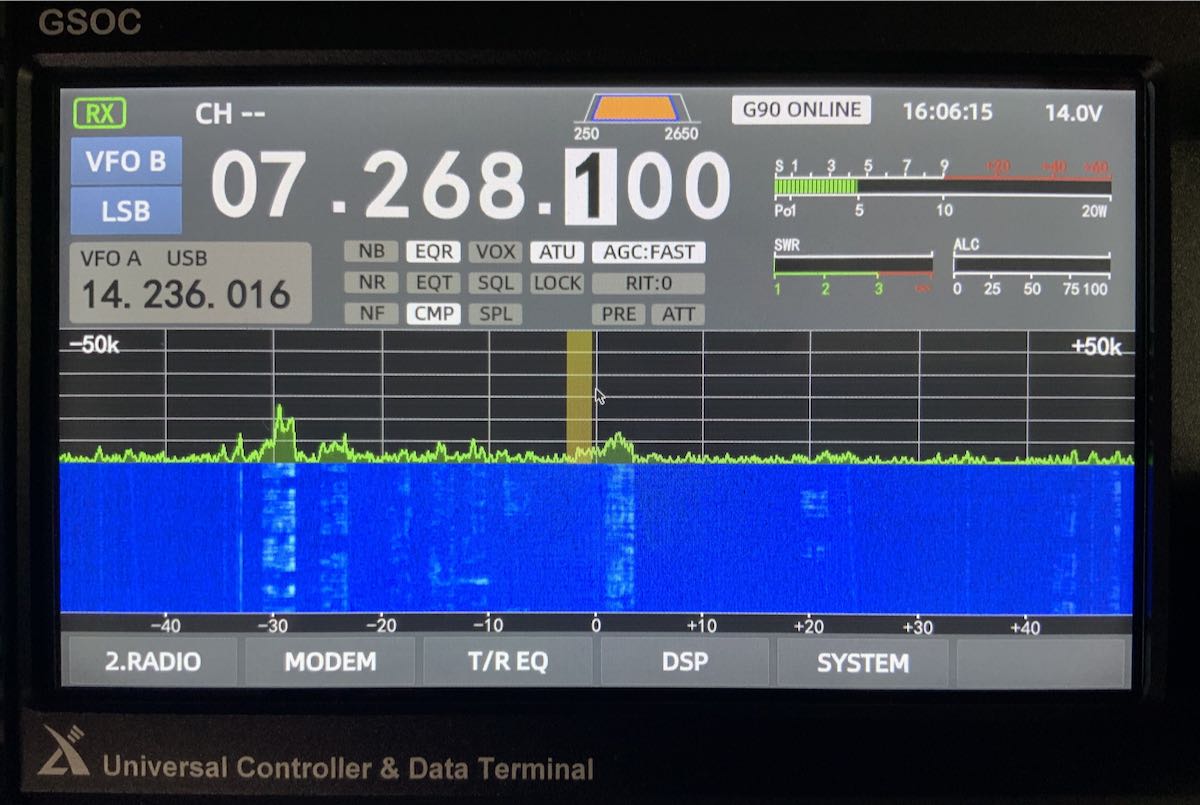
Ever-present noise and spurs in portions of spectrum
Perhaps this is related to the issue above, but there are some spurs on the spectrum display that seem to be present whether the G90/GSOC is hooked up to an antenna or dummy load.
Here’s a photo of the GSOC hooked up to an antenna:
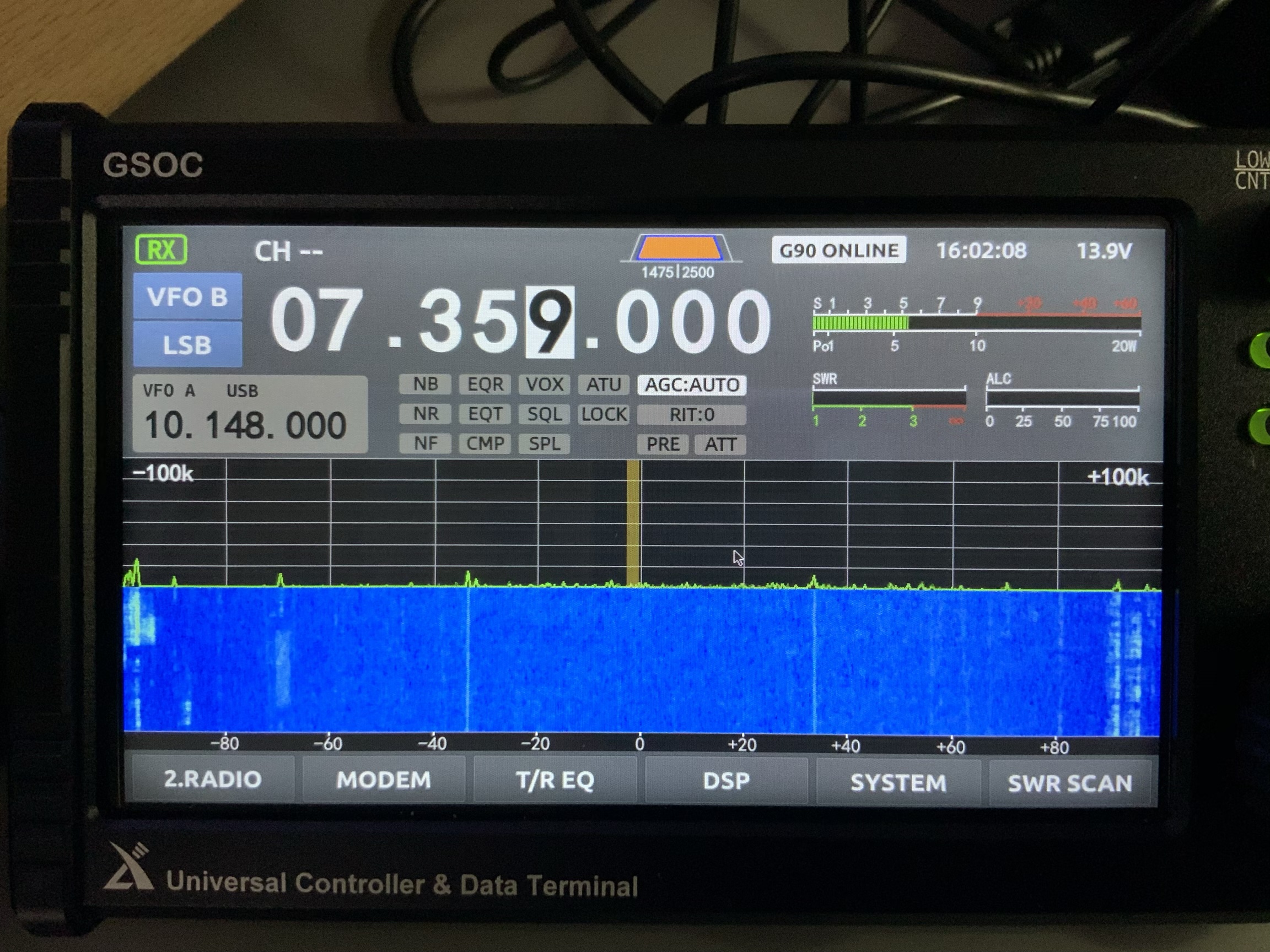 And to a dummy load:
And to a dummy load:
I’ve highlighted the spurs in red and as you can see, the intensity is stronger without an antenna thus I’m guessing this is internally-generated. The spurs do not move on the display as you change frequency.
Other notes
Again, I feel like the GSOC firmware isn’t mature and I can’t yet recommend purchasing it. I feel like Xiegu have rushed this unit to market.
I know that, over time, more features will be added and Xiegu certainly has a track record of following up.
When I evaluate a product, I keep a list of notes that I send to the manufacturer and to keep for my own reference. In Alpha and/or Beta testing, I’d share this info only with the manufacturer. Since the GSOC is a product that’s in production and widely available, however, I thought I’d share them here publicly:
- GSOC volume control scale is 0 to 28. The difference between 0 (muted) to 1 seems to be the biggest increment. Volume 1 is actually a low to moderate volume level (i.e. a bit high).
- Boot up time for the GSOC is 30 seconds
- A keyboard and mouse or capacitive stylus are almost required for accurate operation. Many of the touch screen buttons are quite small and difficult to accurately engage with fingertip. The pointer seems to fall slightly below where fingertip makes contact on the screen.
- Notch Filter seems to have no effect even after the v1.1 upgrade. There is no Auto Notch feature either.
- I can’t seem to engage split operation even though there are A/B switchable VFOs and a “Split” button above the spectrum display. Using a keyboard and mouse doesn’t engage it either.
- There are a number of announced features that I haven’t discovered including some WiFi and Bluetooth wireless functionality.
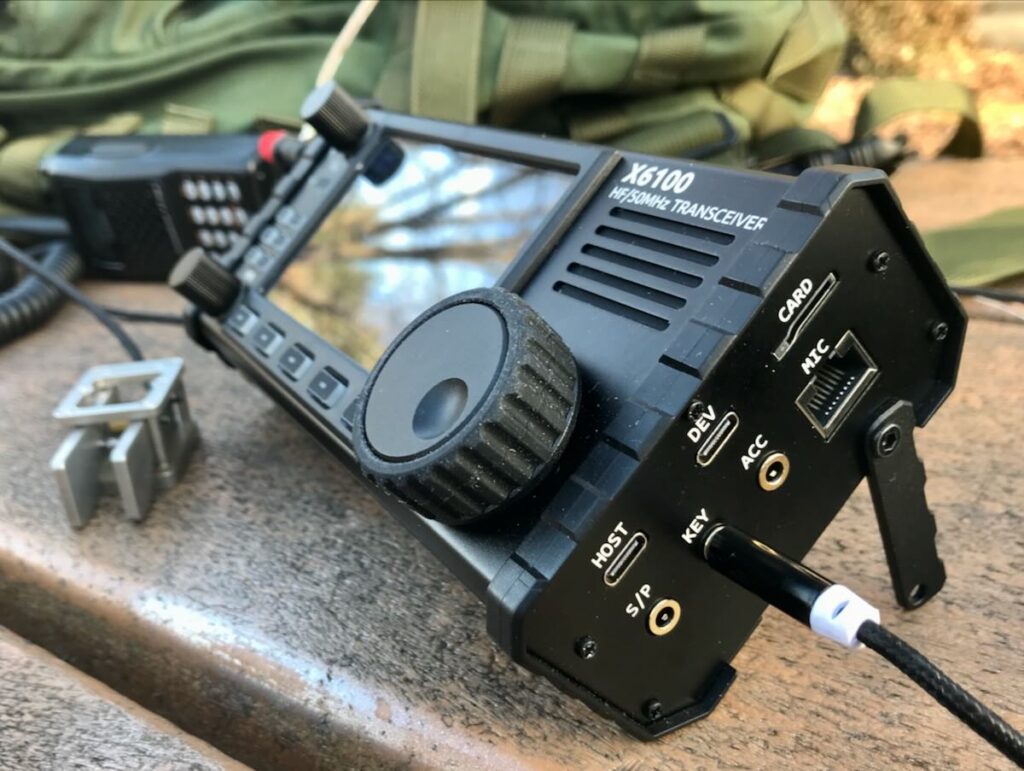
- For field use, you must pack quite a bit of kit: the transceiver, the controller, CW key cable, microphone, serial cable, I/Q cable, G90 Power cable, and GSOC power cable. It would also be advisable to take a wireless keyboard and mouse especially if you plan to use any advanced functions like CW memory keying.
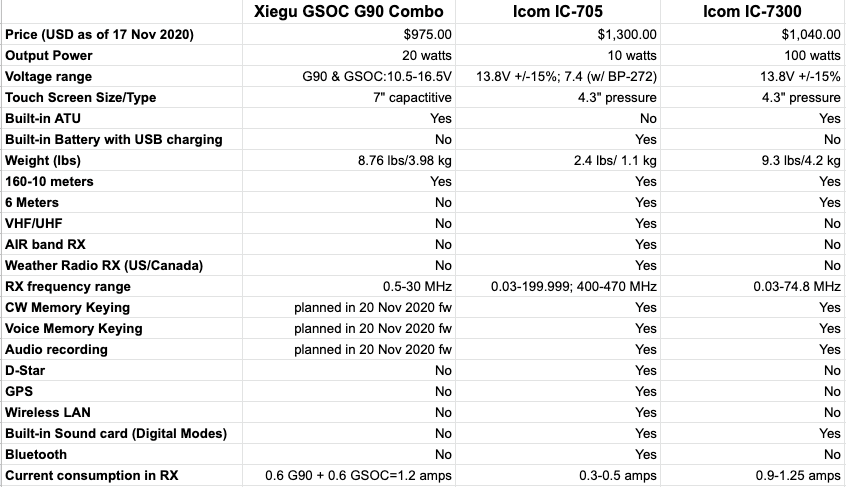
- It doesn’t appear that you have CAT control of the GSOC which complicates digital operation. I believe many of us hoped the GSOC would make digital mode operation easier with the G90, but it hasn’t. Indeed, I assumed the GSOC would have an internal sound card for digi modes much like the Icom IC-7300 and IC-705. Use of VOX control is still the best way to control transmit. I hope this can be upgraded else this would be a missed opportunity.
- Since the v1.1 upgrade, the GSOC hasn’t crashed (it did frequently with the v1.0 firmware).
- Not a pro or con, but I wish the AF Gain/Squelch was AF Gain/RF Gain like most HF transceivers. I’ve accidently engaged squelch twice which essentially muted audio. Pressing and holding the PO (Power Output) button opens the RG Gain control function).
The GSOC Universal Controller is an interesting accessory for the G90 and I’ve read comments from users that love the interface and added functionality.
If I’m being honest, I feel like I’m Beta testing the GSOC. I’ve yet to find a GSOC operation manual–this makes it very difficult to know if one has correctly configured the controller and engaged features/functions correctly. A quick start guide is included with the product, but it really only helps with connections and starting up the GSOC the first time. If you’re a GSOC early adopter, just be aware of this. Again, I’m pretty confident Xiegu will make refinements and include promised features in future firmware updates. I understand their software engineer closely monitors the GSOC discussion group as well. If you’re considering the purchase of a GSOC, I’d encourage you to join the GSOC group.
Questions? Comments?
As I said, I can’t recommend purchasing the GSOC controller yet. So much can change with firmware updates, however, I would encourage you to bookmark the tag GSOC to follow our updates here on the SWLing Post. I will update the GSOC controller each time a new firmware version is issued and until Radioddity asks for the loaner units to be returned. Again, many thanks to Radioddity for making this GSOC and G90 evaluation possible.
Feel free to comment with any questions you might have and I’ll do my best to answer them!