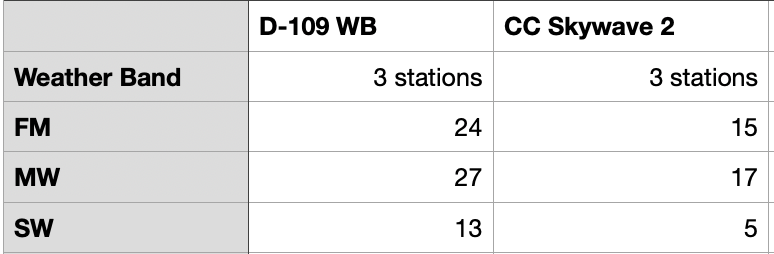
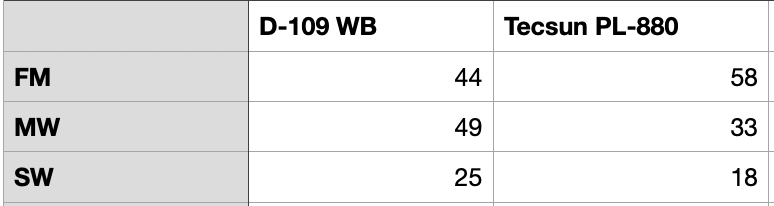
By Jock Elliott, KB2GOM
Size matters . . . especially when it comes to antennas. In general, the more aluminum or wire you can get up in the air (presuming, of course, that it is properly designed), the more signal you are going to pull in. A radio friend has a 560-foot loop erected on his property, and its performance is, well, impressive.
I’ve had my share of high-performance antennas over the years, and I enjoyed them.
Lately, however, I have yearned for simplicity. So when I encountered the phrase “Ultralight DXing” a couple of years ago, it had a kind of magic allure to it.
At first, I was intrigued: “What the heck is that?” I wondered. After poking around on the internet, I discovered that at the heart of ultralight DXing was the notion of having a whole lot of fun trying to hear distant radio stations (usually on the medium wave band) with tiny, shirt-pocket-sized radios.
Gary DeBock got the whole ultralight DXing thing rolling in 2007. He already had deep experience in DXing, having worked 144 countries as a ham radio operator with a 1-2 watt transmitter he had built. That was his apprenticeship in radio propagation. Then in 2007, he wondered if it would be possible, using his skill and knowledge of propagation, to hear Japanese and Korean broadcasters from his home in Washington State using – wait for it – a cheap pocket radio: a Sony Walkman SRS 59. At 1 am on an autumn night, he put propagation and operating skill to work and heard a couple of medium-wave stations from Japan and one from Korea.
In November 2007, he posted his results on the internet and got a lot pushback, the upshot of which was: “How could you possibly do this?”
To which he replied (in essence), “Try it and see for yourself.”
Some people did try for themselves, some with notable success. For example, one DXer from Canada logged 300 stations in 30 days. The idea caught fire, and ultralight DXing was born, concentrating on medium wave stations because there are lots of them to DX. (Ultralight DXers have their own forum, which can be found here: https://ultralightdx.groups.io/g/main )
In the intervening years, ultralight DXers have experimented with exotic antennas and achieved some astonishing results, but for me, the soul of ultralight DXing is simplicity: a tiny radio, a pair of headphones, and a comfortable place to sit.
In 2021, DeBock published an “Ultralight Radio Shootout,” and when I encountered it online, I saved it (I’m a bit of a pack rat with interesting files). Earlier this year, I was rummaging through my computer when I rediscovered the Shootout and found that DeBock thought very highly of the XHDATA D-808.
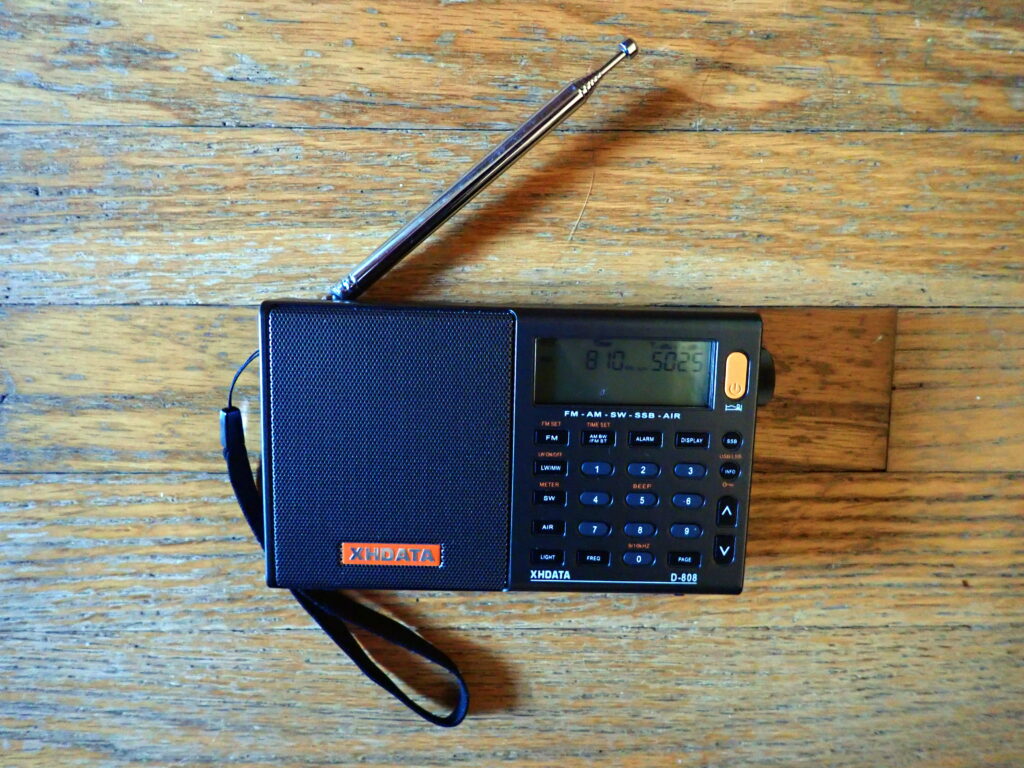
Now, here’s the weird part: strictly speaking, the XHDATA D-808 is not an ultralight radio. A radio must be no bigger than 20 cubic inches to be considered an “official” ultralight radio. The D-808 is actually around 27 cubic inches.
Curious, I contacted the XHDATA folks, asking if they would like to send me one for review, which they did, without charge.
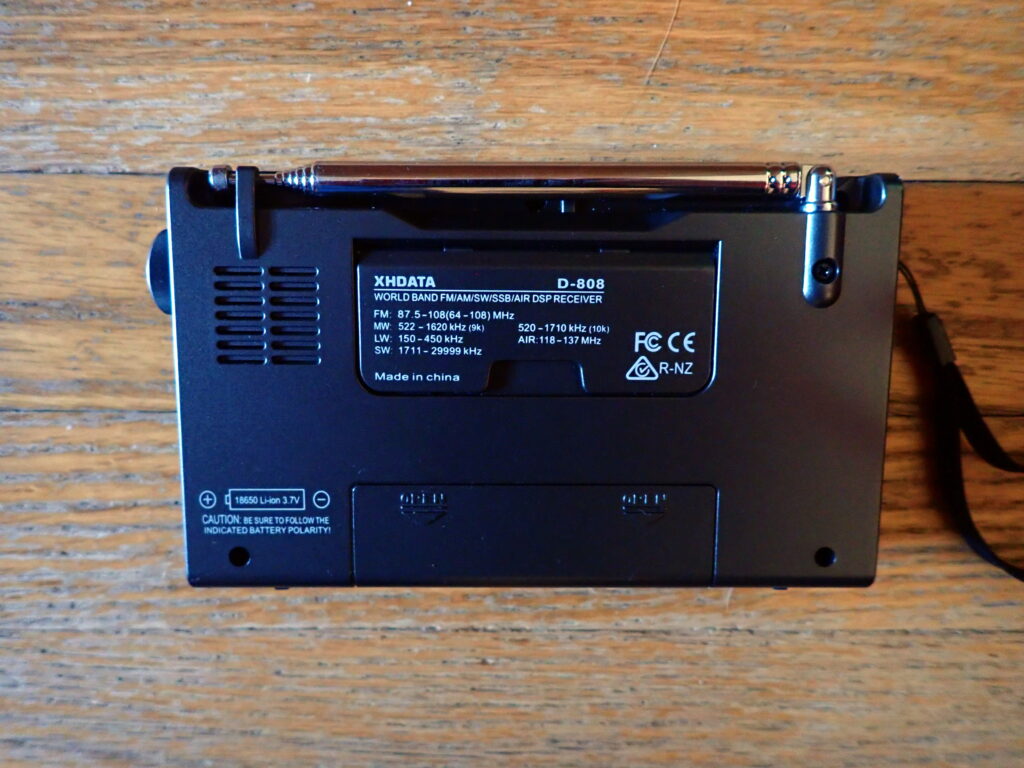

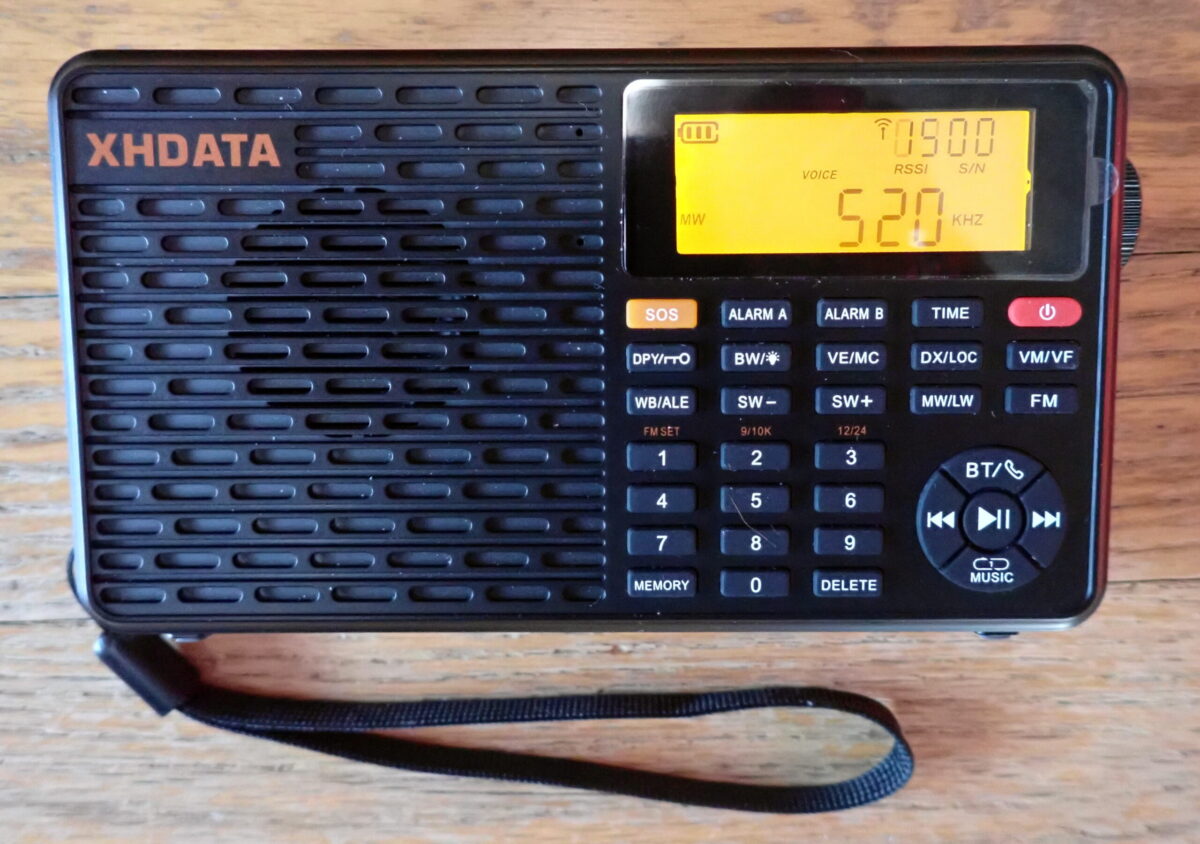
The D-808 measures just under 6 inches wide, 3.5 inches high, and 1.25 inches deep and weighs about a half a pound. It receives: FM: 87.5 – 108 (64-108) MHz, LW: 150 – 450 kHz, MW: 522 – 1620 kHz (9k Step) 520 – 1710 kHz (10k step), SW: 1711 – 29999 kHz (including single sideband), and AIR: 118 – 137 MHz. It is powered by an 18650 battery that can be recharged by a USB cable.
Others have written extensively about the D-808, but my overall verdict is that it is indeed, a neat little radio for listening in general. Because it has a larger internal ferrite rod “loopstick” antenna, it can do a better job of pulling in faint medium wave stations than some of the “official” ultralights with smaller internal antennas. In addition, the D-808 has a longer telescoping antenna that makes it easier to hear faint shortwave stations.
On the face of the D-808 are 24 buttons that control various functions, and they pretty much “work as advertised.” There is, however, one small issue that some users may find confusing. Just below the orange power button is a circular button marked SSB. Push it, and it engages single-sideband mode and can be used on medium wave as well as shortwave signals. Below that button, in tiny orange letters is an indication: USB/LSB. It refers to the INFO button below, NOT to the SSB button above. If you press the SSB button, hoping to switch between upper sideband and lower sideband, it will not work, and you will think the radio is broken (I spent several minutes searching the manual, trying find out what was wrong). When SSB is engaged, press the button marked INFO between to switch between sidebands, got it?
Playing around with the D-808 on a rainy Saturday morning, I found that it is a “hot” receiver – for its size – on medium wave, shortwave, and FM. Using the UP and DOWN buttons to search for stations, and I found that it would, indeed, find interesting stuff to hear that I could not hear so readily on “official” ultralight radios with smaller antennas. It’s a small, fun radio that virtually begs me to find a comfy chair, clap on the headphones, and tune around to see what’s out there.

Having said that, if this were a trip to Santa’s lap, there are a couple of things I would change about the D-808. The first is the soft muting that occurs between tuning steps, which is accompanied by a mechanical “clunk, clunk, clunk” at each step in both the main and fine tuning knobs. It’s like driving down a highway with expansion cracks or tar strips every 20 feet . . . it’s annoying. My personal preference is for smooth, continuous tuning, and, even when a radio has jumps between tuning steps, it is possible to deliver a smooth, “clunkless” tuning experience such as in the CCrane EP-PRO or the Tecsun PL-880. You can, however, get around the clunking by directly entering the frequency you want using the keypad (be sure to press the FREQ button first) or by using the UP and DOWN seek buttons to search for stations . . . the radio simply quiets itself until it find the next signal. Second, while the D-808 seems to just sip power from the 18650 battery, I prefer portable radios that are powered by AA batteries, since they are so readily available in so many places. In the grand scheme of things, that is a relatively minor consideration.
Bottom line: the D-808 packs a whole lot of fun and pleasing performance into a package that can be slipped into a jacket pocket. Even more important, it delivers the simplicity of an ultralight: a radio I can grab, kick back in an easy chair, slide on the headphones, and tune around for a bit of radio fun, and I can heartily recommend it.
Check out the XHDATA D-808 at XHDATA.
Check out the D-808 at Amazon.com (affiliate link).