Many thanks to SWLing Post contributor, Richard Langley, who shares this excellent article by our friend Jonathan Marks in Medium:

Jonathan Marks, Director of Programmes, Radio Netherlands, Hilversum, June 1995 (Source: Medium.com)
Every country claims to have invented radio. In the Netherlands Institute for Sound and Vision in Hilversum they have so far focused on the radio pioneer Hanso Idzerda. He set up a business to make and sell his radios. And he realised that no-one would buy his radios if there was nothing to listen to. I think the evidence shows that he was one of the first, if not the first person to make regular broadcasts following a pre-announced schedule. But I would like to suggest he started off a chain of Dutch “firsts”, many of which are now in danger of being forgotten.
First, Idzerda started international broadcasting. From a rooftop antenna in the Hague, his low power mediumwave signal could be heard in the Southern part of the UK. And he capitalised on that by broadcasting an hour of concert music between 4 and 5 on a Sunday afternoon, responding to listeners correspondence. And he managed to get the programme paid for by the Daily Mail newspaper in London. So, the first international broadcasts were commercial. They were also the world’s first broadcasts using what today we would call narrow band frequency modulation. It wasn’t until 1933 that American engineer Edwin Armstrong, discovered this technique was capable of transmitting much better audio fidelity if you used much higher frequencies and more sensitive receivers.
In 1920’s, no-one understood radio propagation
But in 1919 no-one really understood how radio waves worked and the influence the sun has on the way they propagate. I’m guessing that Idzerda would have had most of his UK listeners in mid-winter when it was starting to get dark.
By 1925, various things were happening in parallel. Physicists like Edward Appelton were showing that there was a layer in the earth’s atmosphere which they later called the ionosphere. It acted like a mirror to radio waves. And the path of the signal followed was dependent on frequency.
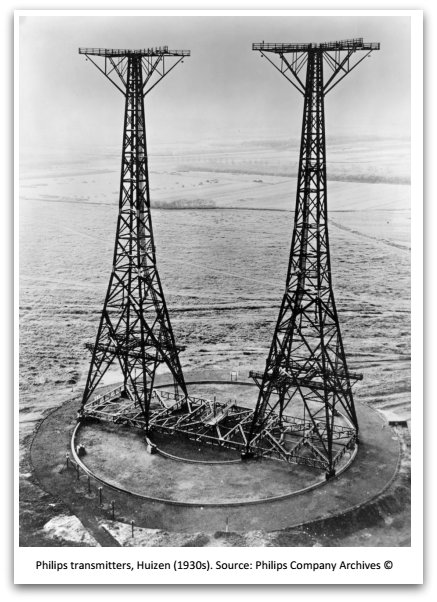
So while Radio Kootwijk was using a high-power long-wave transmitter to try and send Morse code messages to the Dutch colony of the East Indies, now Indonesia, engineers at Philips in Eindhoven realised that shorter wavelengths were best suited to long distance communication using much less power than the 400kW being used in Kootwijk. They ran experiments in 1925 which were received in Malabar Indonesia. A certain Dr de Groot is listed is some accounts as a radio enthusiast. It’s just that he happened to be the head of the Dutch telegraph station in Sitoebondo, East Java and had been busy since 1916 trying to establish a reliable, direct connection between The Netherlands and its colonies. The Dutch were making use of long-distance phone cables owned by the British who were listening in to all the communications.[…]
Click here to continue reading the full article in Medium.