(This is an article from the August 2023 edition of The Spectrum Monitor, used with the kind permission of Ken Reitz, editor — Robert Gulley, K4PKM)
 Perseid meteor streak. (Courtesy: European Southern Observatory, via Wikimedia creative commons)
Perseid meteor streak. (Courtesy: European Southern Observatory, via Wikimedia creative commons)
Incoming! An Introduction to Meteor Scatter Propagation
By Robert Gulley K4PKM
One of my all-time favorite quotes from Shakespeare comes from Hamlet: “There are more things in heaven and earth, Horatio, than are dreamt of in your philosophy.” When I first heard about bouncing a signal off the moon and back to earth I thought “how can that be?”
Then I heard some German folks had bounced a signal off Venus and received it back. “How can that possibly happen?” Indeed, there are more things in heaven and earth than are dreamt of in my philosophy! Enter Meteor Scatter.
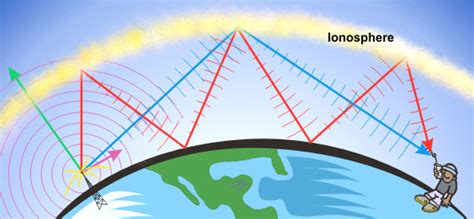
Meteor Scatter is a propagation phenomenon where signals sent up into the atmosphere are reflected back down to earth by the ionization trails left by meteors as they cross our skies. As the meteors move through the atmosphere, they heat up vapor particles which can then reflect VHF and UHF signals in irregular patterns. These trails typically only last for a few milliseconds up to a few seconds, but with modern digital software, that’s enough time for a lot of information to be passed along. This occurs in the “E” layer of the atmosphere.
Likely you have heard of E-skip propagation, where VHF (and occasionally UHF) signals can travel much further than the typical line-of-sight propagation. Meteor scatter works similarly to allow much greater DX distances, typically up to 1000 or so miles, and occasionally even greater distances. Similar to other propagation modes, meteor scatter can occur as forward or backward scatter.
What’s even more exciting, it does not take a super-station to hear or make these contacts! An
antenna and radio capable of receiving 6-meter signals will work just fine with the right software. Radios that can receive 6 meters can have their audio sent to WSJT-X software using the MSK144 mode to listen in, and amateur radio operators can transmit using typical radio output power to either a 6-meter vertical or horizontal dipole. While a directed antenna will produce the best results, the variable nature of the reflected signals makes almost any antenna capable of 6-meter reception/transmission useable.
Unlike line-of-sight propagation which typically works best with matching polarization, there is no one pattern to meteor scatter. Elevation, meteor trail direction, location of stations, forward vs. backward scatter, all are variables that make working meteor scatter more fun and more frustrating!
As an aside, working distances of 1200 miles or so is considered DX on 6 meters, and definitely on 2 meters and above. DX is relative to the band and mode being used, not strictly working other countries. Where I live, 1200 miles is excellent, but won’t take me to Europe or over into the Pacific. However, the DX is just as exciting knowing I am pushing the limits of a given mode and frequency combination.
A Little History
In 1929 a Japanese scientist, Hantaro Nagaoka, first suggested observable propagation from meteors in a paper entitled: Possibility of the Radio Transmission being disturbed by Meteoric Showers. By the 1940s, meteor scatter was further established by Stanley Hey, a British physicist and radio astronomer. His work during WWII with radar led directly to discoveries of both meteor scatter and radio waves coming from the sun and other galaxies. I highly recommend reading about him!
Having close ties to military research, it was not long before the military started using meteor scatter as a means of long-range communication by the 1950s. Canadians developed a meteor scatter program called JANET. A NATO document from December 6, 1961, requests information on communications via “meteor trails.” NATO’s Supreme Headquarters Allied Powers Europe
developed a program of meteor scatter communications called COMET (COmmunication by MEteor Trails), with stations in the Netherlands, France, Italy, West Germany, the United Kingdom, and Norway. With the introduction of satellites, meteor scatter communications took a backseat, as satellite communications were assumed to be more reliable.
However, due to vulnerabilities of satellite communications being intercepted, meteor scatter has once again become a source of communication for the military as well as other governmental agencies. (This history, as well as much additional information on meteor scatter communications can be found by searching: Meteor Burst Communications: An Additional Means Of Long-Haul Communications by Major John P. Jernovics Sr., USMC.
Amateur Radio and SWL Use
Amateur radio operators have for years been using various modes to take advantage of the expanded reach meteor scatter can provide, including SSB, Morse code, and digital mode software such as WSJT-X. Before our current digital mode software, CW was in common use, where data would be sent and recorded in bursts up to 800 words per minute. Specially modified tape recorders would then play back the messages at much slower speeds to allow copying the code at normal speeds. With the advent of personal computers, this made the sending/copying process much easier.
Fortunately, today we have readily and freely available software to allow communication in real time. The wildly popular WSJT-X software by Joe Taylor has meteor scatter software built in. Using the MSK144 protocol, signals are coordinated between both sending and receiving stations to allow for the most efficient transfer of information. While listening to meteor scatter transmissions has always been possible for shortwave listeners, today’s digital software makes it incredibly easy to receive these signals and log some very interesting stations and locations. Many SDR radios are capable of 6-meter reception, as well as the 2-meter and 70-cm bands. SDRs also have the benefit of digital filtering, allowing the signals to be pulled out more
cleanly.
On the transmitting side, if you are familiar with FT8 and FT4 then switching to MSK144 will not be much of a learning curve. If you are new to WSJT-X or similar software, I would advise spending some time getting comfortable with FT8 and/or FT4 before diving into meteor scatter
work. While one does not have to know these modes to use meteor scatter, I believe it helps.
For the sake of brevity, I will assume a basic familiarity with digital modes, and concentrate on how meteor scatter works within WSJT-X.
Unlike FT8 and other standard digital modes, meteor scatter MSK144 has standard frequencies which, while not absolute, are very widely acknowledged among users. When choosing a band, the default frequencies brought up by the software should be used, unless you know for certain a station is transmitting (or listening for you) on a non-standard frequency. I recommend starting with 6 meters, as it is by far the most active. If you have 2 meter/70cm all-mode capability, wait until you are comfortable with the back-and-forth flow of contacts before moving on from 6 meters.
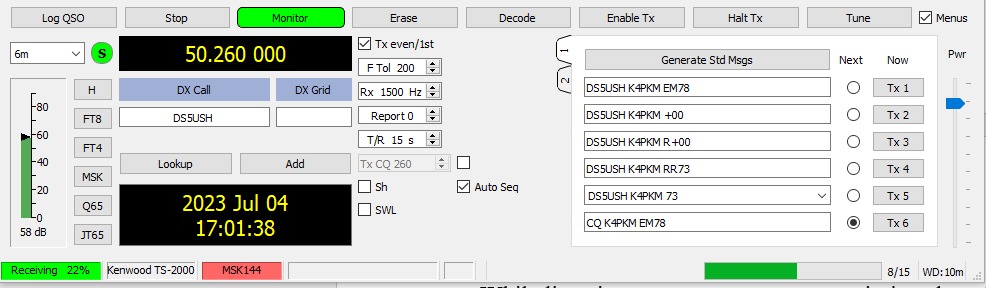
Notice the default settings on the WSJT-X screen for meteor scatter in the screen capture. F Tol (frequency tolerance) is set to 200, RX (Receive) is set to 1500 Hz, and Report is set to 0. I would also suggest having your radio’s pre-amp turned on for this mode. You can adjust the Fast Graph shown below) brightness through sliders on the panel or use the auto level feature.
One place where this meteor scatter protocol differs from standard FT8 or similar modes is the mutually agreed upon standard practice of stations transmitting (pointing) to the east transmit on even cycles (each cycle is 15 seconds long: 00, 15, 30, 45, 00), so they would transmit on 00 and 30 second marks, while stations transmitting (pointing) west transmit on the odd cycles (15, 45).
You will notice there is a check box for TX even/1st – stations transmitting toward the east coast would have this box checked, whereas stations trying to work to the west would leave the box unchecked. Clear as mud, right?! Perhaps an acronym will help you remember the proper sequence. PETE = Point East Transmit Even.
This is of primary importance when calling CQ. When answering a CQ call (sometimes referred to as search and pounce mode), the software will handle transmitting on the proper cycle. This is the style of operating I use most, but I do occasionally call CQ in an effort to find out if anyone can hear me. This is when I need to make sure I am following the standard protocol.
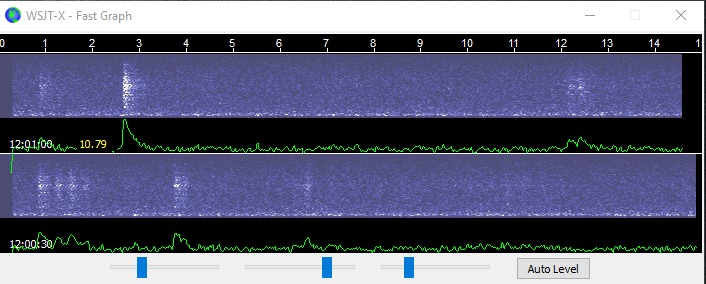
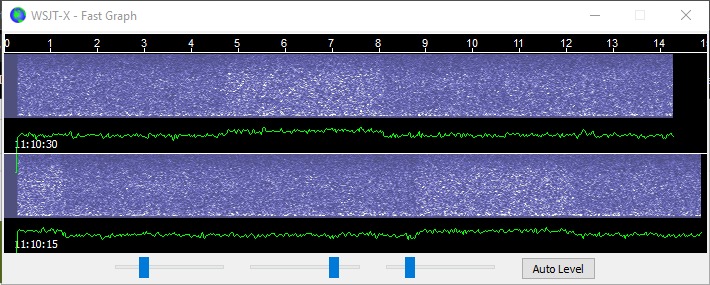
Top: The Fast Graph display shows a base level reception which can be adjusted for
brightness and contrast similar to an SDR waterfall. Bottom: Typical reception graph
with signals making vertical markings and sounds similar to static crashes.
The hardest part of working meteor scatter is waiting for a signal to show up calling CQ, or having one answer you if you are trying to initiate contact with CQ. This can take time. Remember, you are depending on wispy trails of ionization to reflect your signal to someone else on the planet, either to answer their call or reach someone with your call. Be patient! It is not uncommon for a station to call 5, 10, even 15 times before someone responds. And the waiting is not over . . . .
To complete a contact after hearing CQ, you may have to respond to that CQ call over a number of cycles before the meteor trail gods bring all those meteors into alignment so that your response reaches the person on the other end. It is not uncommon for contacts to range over 10 minutes or more. Fortunately, it is usually much less. However, this is not like a DXpedition where once you are called back the rest of the contact is over in 30 seconds.
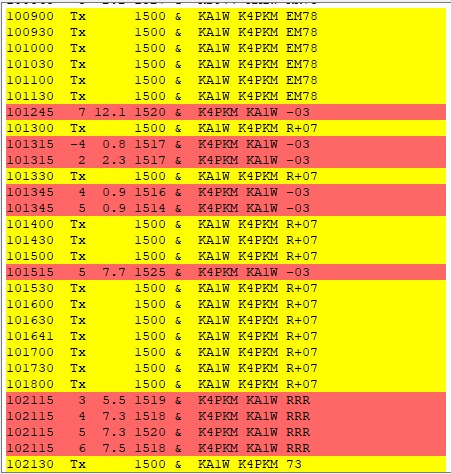
Left: While not always typical, contacts can take 10 minutes or more to complete on days when meteor activity is low; typically contacts last over several minutes or more.
In the screen capture showing a typical contact, notice I initiated my response call at 10:09:00 (as I was pointing east), and the contact continues over 36 cycles (I counted for you!) and spans 12 minutes. Now before you tune out and say “Whoa, no way, man! That’s crazy!” I have two very valid points to make. 1) If you are chasing a rare DX station as I often do, it is nothing for me to try for 20 minutes or more to break the pileup and make the contact. I have actually spent 3 hours or more attempting to work a really rare DX station. Compared to that, 5, 10, or even 15 minutes is not a long time. 2) Stop and think about how totally cool it is to be using meteors to be making a contact with someone!! That’s definitely worth some real bragging
rights to your ham buddies who have never done this, and just the cool factor alone keeps me coming back to see how far I can make a meteor scatter contact!
If you are like me, radio is still magical, and meteor scatter is all the more so – we are interacting with particles that have travelled thousands and thousands of miles to get here! That’s awe inspiring!
While perhaps not quite as amazing as bouncing your signal off the moon to contact someone halfway around the world, it is still really exciting to think you can send massive amounts of data in a short burst before a meteor trail fizzles out in a matter of seconds or less. MSK144 transmits a complete data package, including redundant data features, every 70 milliseconds!!
This is why you may see a half dozen or more repeats of a signal in the same cycle as each data package is received and decoded. The redundant nature of the transmission helps to deal with the chaotic randomness of the meteors. If even one data package gets through, then the receiving station can answer accordingly.
You might be wondering, “How can I react fast enough to respond to packets sent in 70 millisecond intervals?” You do not have to. Remember we are dealing with 15 second cycles,
so once a CQ comes through and you double click on it to respond (just as with FT8 etc.), the software does the rest, assuming Auto Sequence is checked. The software then follows the
same pattern as when making auto-sequenced FT8 or FT4 contacts. If you are calling CQ, the auto sequence is even easier once someone responds, again, just like FT8.
You can see why I said it is best to get familiar with FT8/FT4 before trying meteor scatter. You will be a lot more relaxed making these amazing contacts with some real digital mode experience to fall back on.
Strategies for Working/Catching Contacts
The best time for hearing or working other stations is during the early morning hours, typically between a little before dawn until several hours after daylight. By the time the sun comes up in your area the signals will mostly fade away as the atmosphere heats up and signals are absorbed.
Don’t expect every day to produce lots of signals, conditions vary a great deal. As I discuss further down, there are times of high meteor activity, but most days have varying opportunities, much like normal contacts and propagation vagaries. If the atmosphere is disturbed by geomagnetic storms, solar flares, CMEs and the like, then listening conditions will be adversely affected with this mode just as with other modes. However, don’t just assume conditions will be poor based on the typical propagation reports (good advice for any mode!). Because we are dealing with extremely short data bursts, signals may come through even when conditions
seem difficult for other modes.
The main thing is to not get frustrated with trying to hear or work meteor scatter contacts. It is a very special mode, and with some experience and understanding of how the mode works, you will hear and/or make a good number of contacts over time.
Unlike FT8 or other digital modes, I turn the volume up on the radio to a reasonable level to hear the meteor signals. With FT8, FT4, JT65 or similar modes, I keep the volume off unless I am wanting to try to identify something causing interference, such as a different mode being used or something local. Meteor scatter (MSK144) signals sound like static bursts rather than the familiar tones of FT8. By having the volume turned up I am able to quickly tell when there are signals present. This allows me to do other things while monitoring the band, useful when
there are slow signal days. As a matter of fact, I am listening to the band and switching screens as needed while writing this article – actual multitasking!
Contacts are made in much the same way as other digital modes, but with a couple of notable exceptions. As shown in the screen capture with contacts happening over 9 minutes, there is often a lot of repetition. Even when signals seem strong coming into your station on the receive cycle, it does not mean the other station is going to hear your response on the next transmit
cycle.
Here’s an example of a typical contact. I hear A8XYZ sending CQ. I respond to his call on my next transmit cycle. I then hear him calling CQ again on his next transmit cycle. This may go on for several cycles or more, but since he is a new grid for me, I persist.
Finally, he responds to my call with a signal report as part of the auto sequence feature of the software, once he has heard me calling him. His computer then sends me his signal report over multiple cycles as needed until my computer sends him a RRR or RR73 depending on my settings. Since he does not receive my RR73 the first time I send it, his computer continues to send a signal report. When he finally does receive my RR73, he sends his 73 to indicate the completed contact. He likely does this for only one or two cycles because otherwise we would end up in a continuous loop of 73s back and forth.
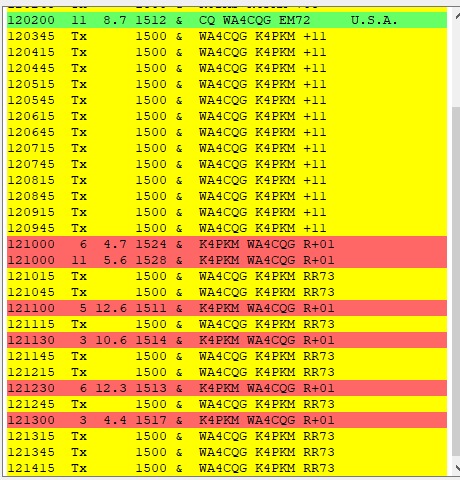
Here’s a case where the contact was not completed, and so it is up to you and the other station as to whether the contact is confirmed.
Sometimes the whole contact is over in a couple of minutes, sometimes longer. Then there are the times as indicated in the screen capture with WA4CQG, I never received a 73 from him after repeatedly sending my RR73. Since he continued to send a signal report, he does not know that I have acknowledged his signal report, and thus is not a full, standard contact.
To Confirm or not to Confirm, that is the Question!
Now, here’s the tricky part in terms of the contact with WA4CQG; technically we made a valid contact and can log it as such, even though we never got past his signal report. Since he was calling CQ, and I answered his CQ with a signal report (which he obviously received based on his then sending a signal report), that is all that is needed for a valid contact. Many people will not log it as such because they do not feel it was a full contact, but some will. Since I was sending RR73 to his signal report, my computer automatically logged the contact to my logging software, and I will upload it to LOTW and eQSL. Now it will be up to WA4CQG as to whether or not he logs the contact on his end to determine if we have a completed and confirmed QSL in our respective logs. (And yes, this is happening in real time as I write this article!)
I use this contact as an example to make an important point: just because you know it is a valid contact does not mean the other station sees it as such, and thus diplomacy is the order of the day if you choose to pursue the issue with the other station (I won’t in this case, it’s not a rare contact I need in my log). The choice to confirm the contact, and it is definitely a choice and not an obligation, rests solely in the other station’s hands.
[Additional Note: He did end up confirming the contact!]
Good operating etiquette requires that if you contact the other station requesting confirmation, you do so knowing full well it is purely the other station’s prerogative to confirm or not. I typically say something like “I show us making a contact on [date] and [time] with a signal report of [xx]. Since you apparently did not receive my 73, the call is yours as to whether or not you confirm the contact, and I will respect your decision either way. If I can provide more info, please let me know. Thank you!!” Good manners and friendly attitudes are far more important than a log entry!
Awards: If you like chasing awards, one of the more fun ones, and relatively easy to achieve over time, is the ARRL’s VUCC award for working 100 or more maidenhead grid squares. You can combine 6-meter E-skip, trans-equatorial contacts, and meteor scatter VHF contacts, as well as other VHF propagation/mode contacts for this award (but not contacts made using a repeater). If you happen to use the excellent program JTAlert, you can set alerts to indicate new
grid squares, allowing you to more quickly achieve the 100 needed grids for the award (assuming the other stations will confirm on Logbook of the World or through QSL cards).
Web Resource for Tracking/Scheduling/Posting: A great resource on the internet is Chris Cox N0UK’s site, pingjockey.net. From there you will want to go to the Ping Jockey Central page and put in your details under “User Details” where you can then read and send messages with other meteor scatter users. There is good camaraderie there, as well as the opportunity to see who’s active, and possibly set up a scheduled contact with another station. [Or, if you are just monitoring the meteor scatter frequencies, you can let folks know you have heard them, which is a big help to them.]
Additionally, while you are not allowed to short-circuit the contact process, it is common to let another station know you are receiving them and trying to call them back. This helps the other station at least know they are being heard, and they can continue to call in hopes of a contact. It also allows you or the other station to decide when to stop trying for the contact, so that neither are wasting time calling someone who has moved on.
Meteor Showers
I have saved the best for last! If you are reading this August issue as it comes out in 2023, the annual Perseids meteor shower is already underway, and is expected to peak on August 13 with up to 84 meteors per hour – that’s prime meteor scatter communication time! (As a bonus, for the purposes of viewing the Perseids, the moon will be a waning crescent, meaning a darker sky on the August 12-13).
The last several weeks of July and most of the month of August, the atmosphere will be primed for some great meteor scatter contacts. Give it a try while the “gettin’s good” as they say. And while meteors are in the sky literally every day, special times like the Perseids offer the chance to rack up a large number of contacts in a relatively short time, and that will make the experience all the more rewarding! While the Perseids are the largest meteor show, there are a number of meteor showers throughout the year. You may want to research other meteor showers and mark your calendar accordingly.
Wrap-up
Meteor scatter signals are a lot of fun to receive and to fill your logs with some very interesting contacts, whether as a shortwave listener or an amateur radio operator. With modern software the process is about as easy as one can get, and our radio forefathers would be quite jealous of our capabilities.
Something I did when starting out was to leave my radio on overnight to see what stations were being heard, and this gave me an idea of when signals were the most active. Keep in mind the various time regions and when they might start getting active or ending.
For me, in the Midwest portion of the United States, as morning comes and the sun gets stronger, I turn toward the western part of the country to try to work stations which are just approaching dawn. This allows for a longer contact period, and thus more opportunities to hear more distant stations. I believe my longest contact has been 949 miles. I can’t wait to reach over 1000!
Meteor scatter is a mode that rewards patience. Admittedly, it takes some getting used to in terms of repetition and the duration of contacts, but it is well worth the effort. Even if you only work the mode during known meteor shower opportunities, there will be many interesting contacts possible. And who knows? You may just find the mode as addicting as I have!
Robert Gulley, K4PKM, is the author of this post and a regular contributor to the SWLing Post.