Radio Waves: Stories Making Waves in the World of Radio
Welcome to the SWLing Post’s Radio Waves, a collection of links to interesting stories making waves in the world of radio. Enjoy!
Since September 2020, ABC Radio has been quietly trialing DRM technology in Victoria
The public-service Australian Broadcasting Corp. and its transmission contractor BAI Communications Transmission Network hosted a public demonstration of Digital Radio Mondiale broadcasts on June 29, 2022. ABC highlighted the use of DRM on both AM and FM in Wagaratta, Victoria.
According to the DRM Consortium, the demonstration was the culmination of almost two years of COVID-impacted work to assess the performance of DRM services in Australia’s VHF and medium-wave bands.
Previously, the Australian Amateur Radio Experimenters Group reported that AREG member Steve Adler (VK5SFA) had been monitoring “a very un-publicized Digital Radio Mondiale (DRM) trial” on 747 kHz from Wangaratta in August 2021.
The Australian Communications and Media Authority provided ABC with a license variation to conduct the DRM 30 trials from September 1, 2020, to August 31, 2022.
At the public demonstration, senior representatives from the public, commercial and community radio sectors, along with regulators and other interested parties, were able to hear and see the capabilities of DRM broadcasting on AM from Dockers Plains and on FM from Mount Baranduda. They were also able to review the transmission equipment at Wagaratta.[Continue reading…]
Also check out the DRM Consortium’s article on this same topic.
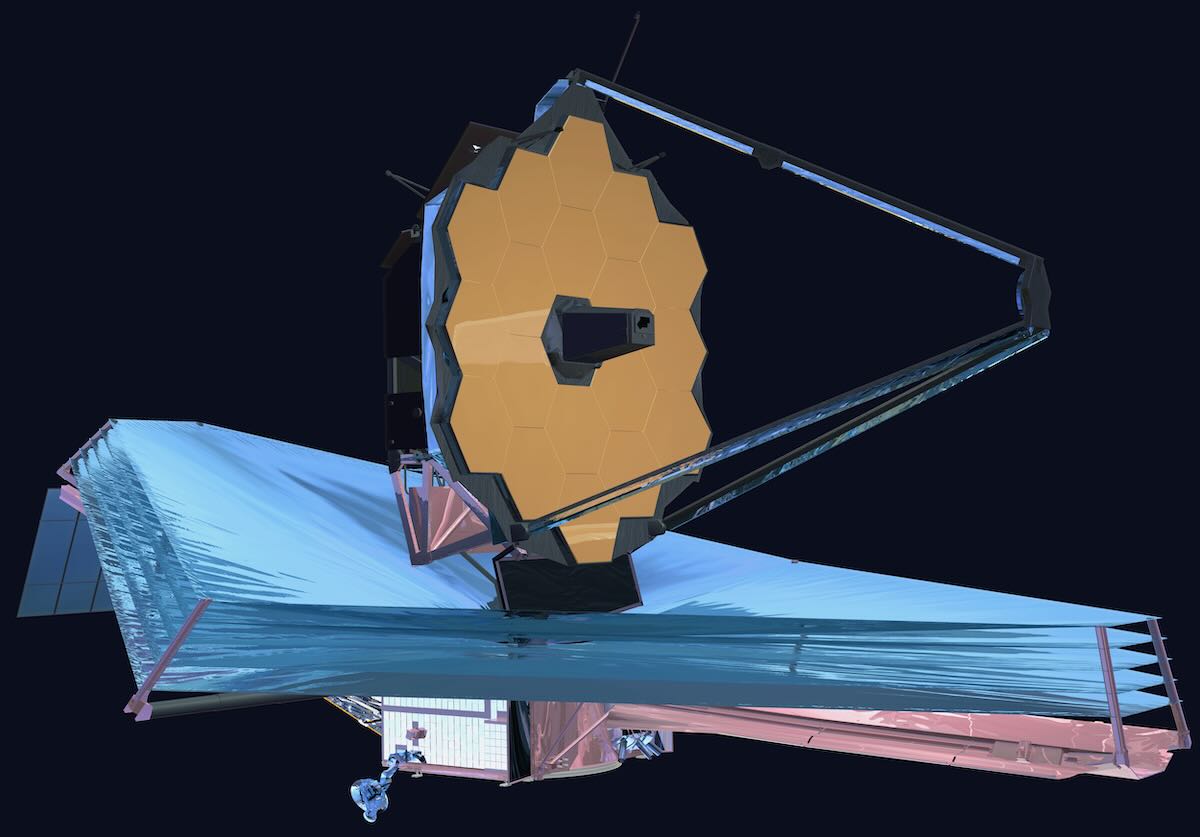
The James Webb Space Telescope probably needs no introduction, since it is perhaps the most important and well-known mission of the last years. It was launched on Christmas day from Kourou, French Guiana, into a direct transfer orbit to the Sun-Earth L2 Lagrange point. JWST uses S-band at 2270.5 MHz to transmit telemetry. The science data will be transmitted in K-band at 25.9 GHz, with a rate of up to 28 Mbps.
After launch, the first groundstation to pick the S-band signal from JWST was the 10 m antenna from the Italian Space Agency in Malindi, Kenya. This groundstation commanded the telemetry rate to increase from 1 kbps to 4 kbps. After this, the spacecraft’s footprint continued moving to the east, and it was tracked for a few hours by the DSN in Canberra. One of the things that Canberra did was to increase the telemetry rate to 40 kbps, which apparently is the maximum to be used in the mission.
As JWST moved away from Earth, its footprint started moving west. After Canberra, the spacecraft was tracked by Madrid. Edgar Kaiser DF2MZ, Iban Cardona EB3FRN and other amateur observers in Europe received the S-band telemetry signal. When Iban started receiving the signal, it was again using 4 kbps, but some time after, Madrid switched it to 40 kbps.
At 00:50 UTC on December 26, the spacecraft made its first correction burn, which lasted an impressive 65 minutes. Edgar caught this manoeuvre in the Doppler track.
Later on, between 7:30 and 11:30 UTC, I have been receiving the signal with one of the 6.1 metre dishes at Allen Telescope Array. The telemetry rate was 40 kbps and the spacecraft was presumably in lock with Goldstone, though it didn’t appear in DSN now. I will publish the recording in Zenodo as usual, but since the files are rather large I will probably reduce the sample rate, so publishing the files will take some time.
In the rest of this post I give a description of the telemetry of JWST and do a first look at the telemetry data. [Continue reading…]
The average person’s perception of a ham radio operator, assuming they even know what that means, is more than likely some graybeard huddled over the knobs of a war-surplus transmitter in the wee small hours of the morning. It’s a mental image that, admittedly, isn’t entirely off the mark in some cases. But it’s also a gross over-simplification, and a generalization that isn’t doing the hobby any favors when it comes to bringing in new blood.
In reality, a modern ham’s toolkit includes a wide array of technologies that are about as far away from your grandfather’s kit-built rig as could be — and there’s exciting new protocols and tools on the horizon. To ensure a bright future for amateur radio, these technologies need to be nurtured the word needs to be spread about what they can do. Along the way, we’ll also need to push back against stereotypes that can hinder younger operators from signing on.
On the forefront of these efforts is Amateur Radio Digital Communications (ARDC), a private foundation dedicated to supporting amateur radio and digital communication by providing grants to scholarships, educational programs, and promising open source technical projects. For this week’s Hack Chat, ARDC Executive Director Rosy Schechter (KJ7RYV) and Staff Lead John Hays (K7VE) dropped by to talk about the future of radio and digital communications. [Continue reading…]
Radio World reports the Electromagnetic Interference generated by Electric Vehicles is causing some EV automakers to drop AM (medium wave) radio
The article says:
Some EV automakers are dropping AM altogether due to audio quality concerns, but that’s just one piece of the puzzle as radio continues to fight for space on the dash.
“As carmakers increase electric vehicle offerings throughout their lineups, the availability of AM radio to consumers is declining,” said Pooja Nair, communications systems engineer with Xperi Corp., in a Radio World guest commentary. “This is because the effects of electromagnetic interference are more pronounced in EVs than in vehicles with internal-combustion engines.”
In other words, electromagnetic frequencies generated by EV motors occupy the same wavelength as AM radio signals. The competing signals clash, effectively cancelling each other out. As EV motors grow more powerful, AM static tends to increase.
Read the full story at
https://www.radioworld.com/news-and-business/headlines/why-are-some-automakers-ditching-am-radio
Do you enjoy the SWLing Post?
Please consider supporting us via Patreon or our Coffee Fund!
Your support makes articles like this one possible. Thank you!
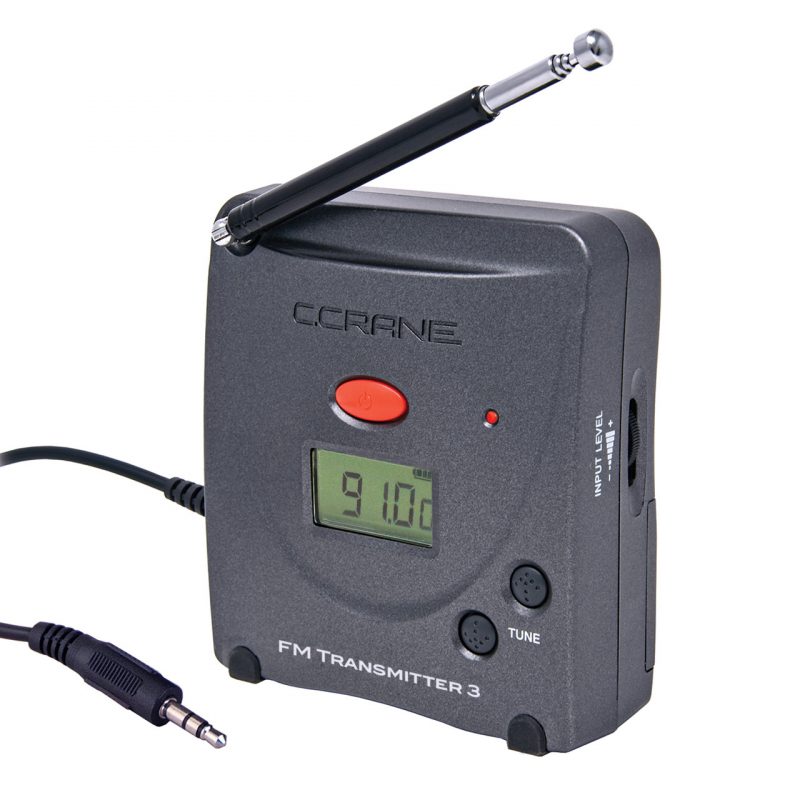
 Many thanks to SWLing Post contributor, Ron, who shares information about the latest C.Crane FM transmitter:
Many thanks to SWLing Post contributor, Ron, who shares information about the latest C.Crane FM transmitter: