Many thanks to SWLing Post contributor, Tracy Wood, who shares the following article from Alaska Public Media:
For decades, the Coast Guard’s NAVTEX towers have broadcast from Cape Cod to Kodiak Island. The global system broadcasts weather and safety information to boats large and small.
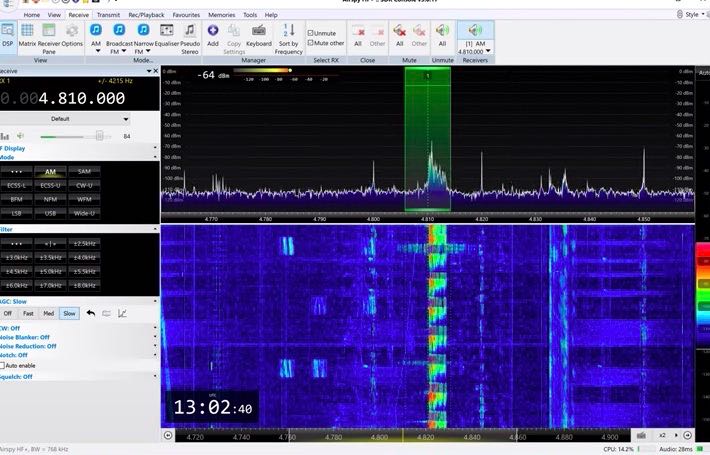
The International Maritime Organization developed the NAVTEX system decades ago as a means to get weather and urgent information to ships on the water. It’s low-tech. Receivers spit out basic telex-type messages onto paper or on a screen.
“The most common thing that you would see is a weather message, but you will also get public safety information messages,” said Derrick Croinex, the Coast Guard chief of spectrum management and telecommunications.
“We need to replace it because the infrastructure is old and it’s failing,” Croinex said.
But before the federal government commits to an expensive upgrade, Croinex said it wants to gauge how vital the service really is.
Right now, the International Maritime Organization is working on upgrading the text-only NAVTEX system to something called NAVDAT. The new system will include images and graphics. And when that system is ready, larger vessels will be required to upgrade to it.
But not if the Coast Guard phases out these radio-based systems completely.
“Our view is, it may be better and more reliable for people to actually switch to satellite,” Croinex said.
But some mariners are urging the Coast Guard to keep the free, low-tech service rather than switch over to subscription-based satellites.[…]
As Tracy also noted, NAVTEX is great because with a simple soundcard, SSB radio and text decoder you can grab the service reliably.
Thanks for sharing, Tracy!