 Many thanks to a number of SWLing Post readers who share the following announcement–also previously noted by Robert–from the University of Alaska Fairbanks (followed by an announcement from the ARRL):
Many thanks to a number of SWLing Post readers who share the following announcement–also previously noted by Robert–from the University of Alaska Fairbanks (followed by an announcement from the ARRL):
An experiment to bounce a radio signal off an asteroid on Dec. 27 will serve as a test for probing a larger asteroid that in 2029 will pass closer to Earth than the many geostationary satellites that orbit our planet.
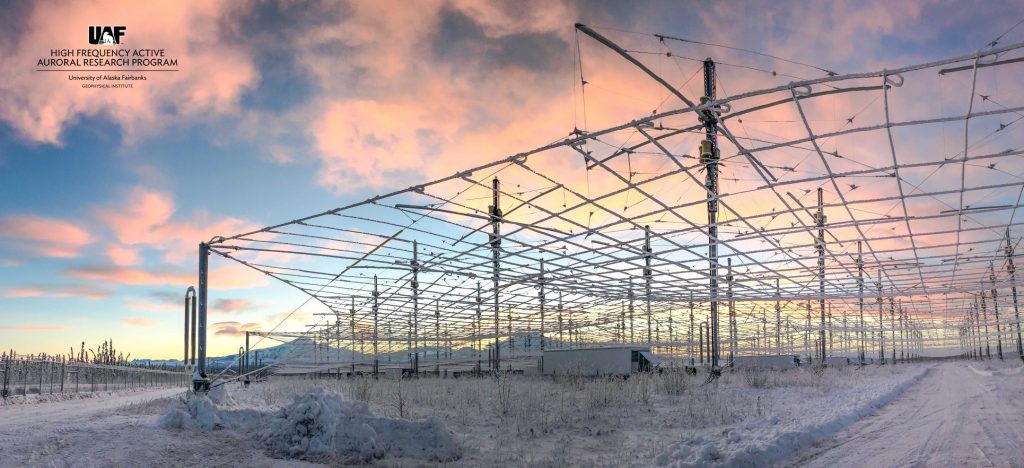
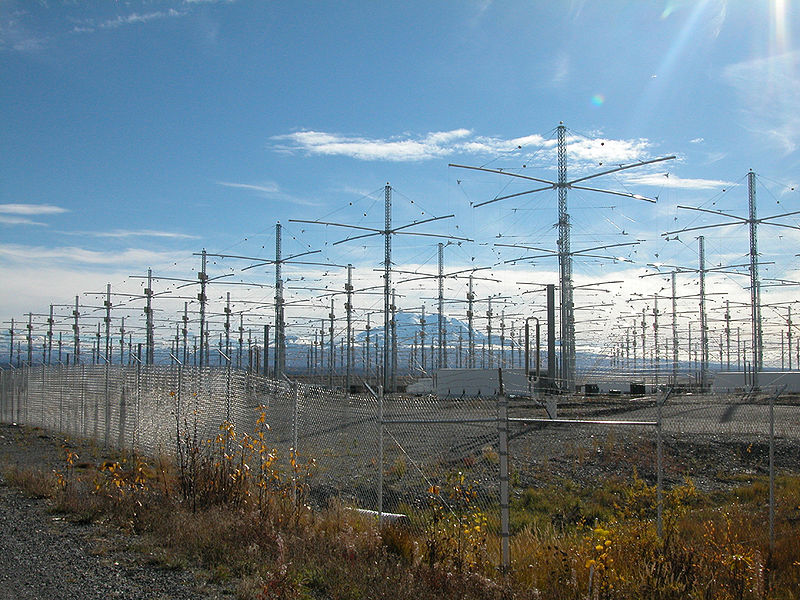
The High-frequency Active Auroral Research Program research site in Gakona will transmit radio signals to asteroid 2010 XC15, which could be about 500 feet across. The University of New Mexico Long Wavelength Array near Socorro, New Mexico, and the Owens Valley Radio Observatory Long Wavelength Array near Bishop, California, will receive the signal.
This will be the first use of HAARP to probe an asteroid.
“What’s new and what we are trying to do is probe asteroid interiors with long wavelength radars and radio telescopes from the ground,” said Mark Haynes, lead investigator on the project and a radar systems engineer at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California. “Longer wavelengths can penetrate the interior of an object much better than the radio wavelengths used for communication.”
Knowing more about an asteroid’s interior, especially of an asteroid large enough to cause major damage on Earth, is important for determining how to defend against it.
“If you know the distribution of mass, you can make an impactor more effective, because you’ll know where to hit the asteroid a little better,” Haynes said.
Many programs exist to quickly detect asteroids, determine their orbit and shape and image their surface, either with optical telescopes or the planetary radar of the Deep Space Network, NASA’s network of large and highly sensitive radio antennas in California, Spain and Australia.
Those radar-imaging programs use signals of short wavelengths, which bounce off the surface and provide high-quality external images but don’t penetrate an object.
HAARP will transmit a continually chirping signal to asteroid 2010 XC15 at slightly above and below 9.6 megahertz (9.6 million times per second). The chirp will repeat at two-second intervals. Distance will be a challenge, Haynes said, because the asteroid will be twice as far from Earth as the moon is. [Continue reading…]
The ARRL provides the following specific information about how SWLs and Hams can participate:
The High-frequency Active Auroral Research Program (HAARP) will be conducting a research campaign/experiment on December 27, 2022, with transmissions between 1100 – 2300 UTC (0200 – 1400 AKST).
[…]Actual transmit times are highly variable based on real-time ionospheric conditions and all information is subject to change. Currently, the Asteroid Bounce (2010 XC15) experiment will take place Dec. 27, 2022, from 1100 UTC to 2300 UTC; 9.6 MHz, LFM (linear FM), 0.5 Hz WRF (waveform repetition frequency), 30 kHz bandwidth. Reports recording echo are encouraged; demodulated recordings in .wav or .mp3 are recommended.
For real-time ionospheric conditions in Gakona, please consult ionograms from the HAARP Diagnostic Suite at https://haarp.gi.alaska.edu/diagnostic-suite.
Amateur radio and radio astronomy enthusiasts are invited to listen to the transmissions/echoes and submit reception reports to the HAARP facility at [email protected] and request a QSL card by mailing a report to:
HAARP
P.O. Box 271
Gakona AK 99586
USA
Click here to read this announcement on the ARRL News website.
 Many thanks to SWLing Post contributor, Bill (WD9EQD), who writes:
Many thanks to SWLing Post contributor, Bill (WD9EQD), who writes:





