(Source: ARS Technica)
by Rupert Goodwins
It’s a good time to be technical. Maker communities are thriving around the world, tools and materials to create and adapt are cheaper and more powerful now than ever, and open source hardware, software, and information mean that if you can think it, you can learn how to do it and then make it happen.
For one group of technological explorers, this is more than just a golden age of opportunity: it’s providing the means to save one of the oldest traditions in electronic invention and self-education, one that helped shape the modern world: amateur radio. That matters.
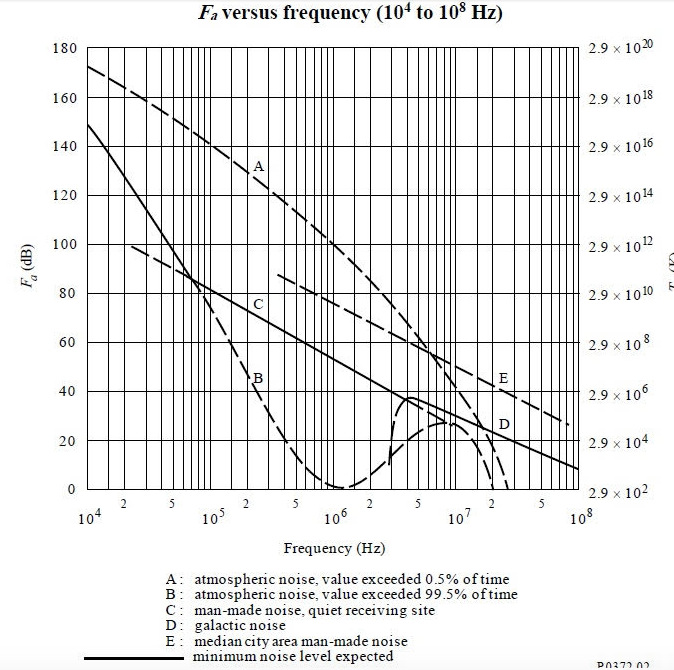
Radio amateurs get a sweet deal, with effectively free access to many gigahertz of the same radio spectrum that companies pay billions for. They’ve earned it. Throughout the history of electronics, they’ve been at the borders of the possible, trying out ideas that commerce or government deem impossible or pointless—and making them work. One example of hundreds: Allied military comms in World War II needed a way to reliably control the radios used by front-line forces, replacing tuning knobs with channel switches. Hams had the answer ready and waiting: quartz crystal oscillators. (That’s part of computing history too—you’re probably using about ten of them right now.).
[…]Then, there’s backup. Take the European HAMNET, for example. That’s a four-thousand-node high speed data network covering a large part of continental Europe and providing full IP connectivity at megabit speeds. It connects to the Internet—ham radio owns 16 million IPV4 addresses, believe it or not—but is independent of it, doing its own robust and flexible routing. If the Internet was to go away, HAMNET would still be running. The same’s true of nearly all ham radio infrastructure: when everything else fails—power, comms, roads—ham radio is still there, and these days it can be a full-fat digital medium.[…]