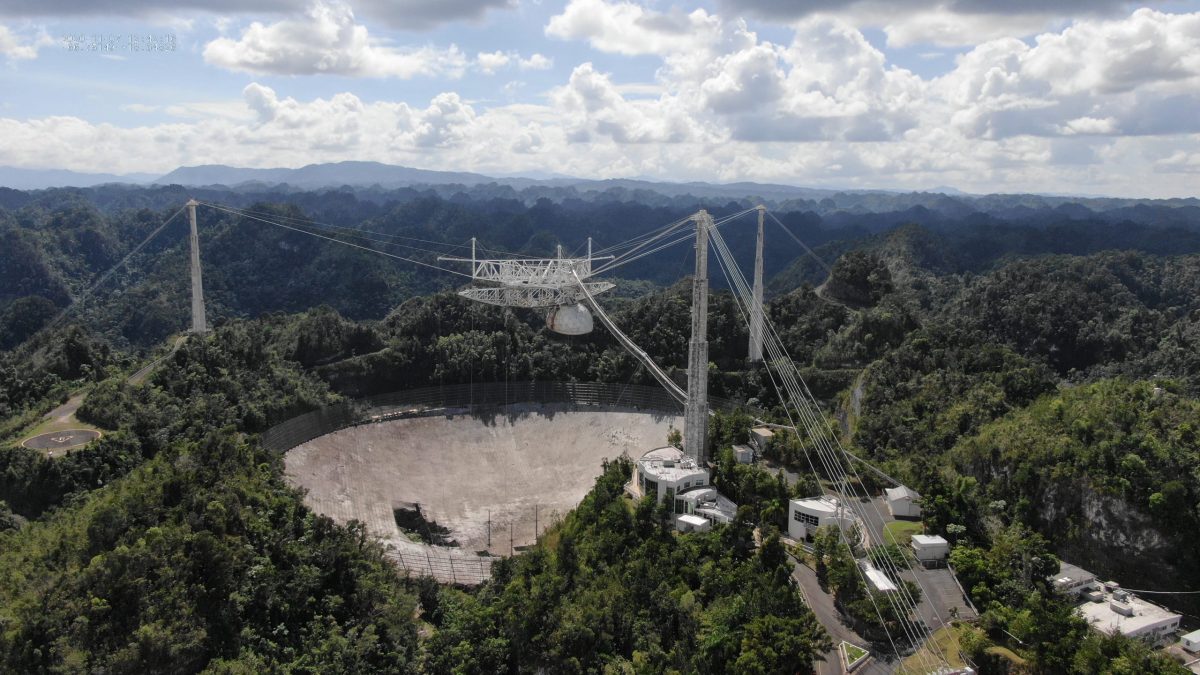
Arecibo Observatory’s 305-meter telescope in November 2020 (Credit: University of Central Florida)
Radio Waves: Stories Making Waves in the World of Radio
Because I keep my ear to the waves, as well as receive many tips from others who do the same, I find myself privy to radio-related stories that might interest SWLing Post readers. To that end: Welcome to the SWLing Post’s Radio Waves, a collection of links to interesting stories making waves in the world of radio. Enjoy!
Many thanks to SWLing Post contributors Ned Wharton, Pete Eaton, Zack Schindler, and Dave Zantow for the following tips:
Today, the National Science Foundation released video taken at the moment the Arecibo Radio Observatory’s cables failed, allowing its massive instrument platform to crash into the dish below. In describing the videos, the NSF also talked a bit about the monitoring program that had put the cameras in place, ideas it had been pursuing for stabilizing the structure pre-collapse, and prospects for building something new at the site.
A quick recap of the collapse: the Arecibo dish was designed to reflect incoming radio radiation to collectors that hung from a massive, 900-ton instrument package that was suspended above it. The suspension system was supported by three reinforced concrete towers that held cables that were anchored farther from the dish, looped over the towers, and then continued on to the platform itself. Failure of these cables eventually led to the platform dropping into the dish below it.
[…]The video of that collapse comes from a monitoring system put in place in the wake of the cable failures. Due to the danger of further cable breaks, the NSF had instituted no-go zones around each of the three towers that supported the cables. With no personnel allowed to get close enough to inspect the cables, the staff started monitoring them using daily drone flights, one of which was in progress during the collapse. In addition, a video camera was installed on top of the visitor’s center, which had a clear view of the instrument platform and one of the support towers.
Continue reading full article.
Lessons of a successful electronic business—an interview with Chas Gilmore, former Heath executive.
For those of you who do not know or remember, Heath Company was the largest kit company in the world. Heath designed and put practically every type of electronic product into kit form. Its products, called Heathkits, were exceptionally popular and many are still in use today.
Over the years, Electronic Design has published many Heathkit-related articles and blogs. Recently, I had a chance to talk with Chas Gilmore, who was a Heath executive. For those of you who fondly remember Heathkit and miss its products, here’s a look back at this amazing company and the lessons it offers.
Chas, what was your affiliation with Heath?
A recent physics graduate, I joined Heath in 1966 as an engineer in the Scientific Instruments department. This was a new group designing laboratory instruments supporting the Malmstadt/Enke, Electronics for Scientists program. The kit business was making great strides.
The audio department was about to introduce the AR-15 FM receiver/amplifier. It had rave reviews, putting Heath in the top tier of the Audio/HiFi market. At the same time, the Ham (amateur radio) department was updating the phenomenally successful SB-line of an HF SSB receiver, transmitter, and transceiver, and modernizing the popular $99 single-band SSB transceiver line[…]
Zack writes:
Found this interesting series at Radioworld called “Radio at 100”. It is 29 different articles about the history of broadcasting in the USA. A lot of your readers might enjoy these;
https://www.radioworld.com/tag/radio-at-100
Another great series at Radioworld that your readers might be interested in “Roots of Radio”:
https://www.radioworld.com/columns-and-views/roots-of-radio
Amateur radio licensees and candidates will have to provide the FCC with an email address on applications, effective sometime in mid-2021.
If no email address is included, the FCC may dismiss the application as defective.
The FCC is fully transitioning to electronic correspondence and will no longer print or provide wireless licensees with hard-copy authorizations or registrations by mail.
A Report and Order (R&O) on “Completing the Transition to Electronic Filing, Licenses and Authorizations, and Correspondence in the Wireless Radio Services” in WT Docket 19-212 was adopted on September 16. The new rules will go into effect 6 months after publication in the Federal Register, which hasn’t happened yet, but the FCC is already strongly encouraging applicants to provide an email address.
When an email address is provided, licensees will receive an official electronic copy of their licenses when the application is granted.
The Report and Order can be found in PDF format online at, https://www.fcc.gov/document/fcc-adopts-electronic-licensing-report-and-order
Under Section 97.21 of the new rules, a person holding a valid amateur station license “must apply to the FCC for a modification of the license grant as necessary to show the correct mailing and email address, licensee name, club name, license trustee name, or license
custodian name.” For a club or military recreation station license, the application must be presented in document form to a club station call sign administrator who must submit the information to the FCC in an electronic batch file.
Under new Section 97.23, each license will have to show the grantee’s correct name, mailing address, and email address. “The email address must be an address where the grantee can receive electronic correspondence,” the amended rule will state. “Revocation of the station license or suspension of the operator license may result when correspondence from the FCC is returned as undeliverable because the grantee failed to provide the correct email address.”
NNNN
/EX[…]
Do you enjoy the SWLing Post?
Please consider supporting us via Patreon or our Coffee Fund!
Your support makes articles like this one possible. Thank you!

 Many thanks to SWLing Post contributor, Franco (K4VZ) , who writes:
Many thanks to SWLing Post contributor, Franco (K4VZ) , who writes: