Radio Waves: Stories Making Waves in the World of Radio
Radio Waves: Stories Making Waves in the World of Radio
Because I keep my ear to the waves, as well as receive many tips from others who do the same, I find myself privy to radio-related stories that might interest SWLing Post readers. To that end: Welcome to the SWLing Post’s Radio Waves, a collection of links to interesting stories making waves in the world of radio. Enjoy!
Many thanks to SWLing Post contributors Rich Smith, Kim Elliott, and Pete Eaton for the following tips:
The Maritime Mobile Service Net (MMSN) on 14.300 MHz came to the assistance of a sailing vessel on June 25. MMSN control operator Steven Carpenter, K9UA, took a call on 20 meters from Ian Cummings, KB4SG, the skipper of the Mystic Lady, then some 40 miles east of Florida. Cummings reported that his engine had failed as he was attempting to return to his home port of Stuart, Florida. He not only had insufficient wind, but a strong current was carrying the vessel out to sea.
Cummings had been unable to reach any station via his VHF marine radio, since he was too far from the coast. Assisting in the call was Robert Wynhoff, K5HUT, also an MMSN net control operator. Cummings said his vessel, with one passenger on board, was drifting northwest toward the South Carolina coast.
“A major concern was that the vessel was heading directly towards a lee shore,” the MMSN reported. “Lee shores are shallow, dangerous areas which are a hazard to watercraft. Vessels could be pushed into the shallow area by the wind, possibly running aground and breaking up.”
Carpenter contacted Cummings’ family, who had already called the Sea Tow marine towing service. Sea Tow advised Carpenter to tell the captain to head closer to shore by sailing west, if possible. Carpenter told Cummings that if he was unable to get nearer to shore, he would notify the US Coast Guard, which was already monitoring the situation.
As the MMSN reported, “The Mystic Lady was able to make some headway, but it was very slow. Members of the MMSN made additional calls via landline to the captain’s family as to the ongoing status of those on board. The family was concerned but relieved that communication was established and that all were well.”
Several hours later, the captain advised that the wind had picked up, allowing him to head close enough to shore for Sea Tow to reach the vessel and take it back to port.
The Pacific Seafarers’ Net, which monitors 14.300 MHz from the West Coast after the MMSN secures at 0200 UTC, kept in touch with the Mystic Lady into the night while it was under tow.
The tired, grateful captain later messaged the net, “A million thanks to everyone last night who helped rescue us on 14.300. Everyone chipped in as we drifted north in the Gulf Stream 60 miles headed to a lee shore. The MMSN net control and several others stayed with us for hours, phoned people, and were immensely helpful. The situation on board was dangerous. We are now safely under tow home. You folks are amazing!”
In operation since 1968, the MMSN monitors 14.300 MHz 70 hours a week to assist vessels and others in need of assistance. — Thanks to MMSN Net Manager Jeff Savasta, KB4JKL[…]
From 1985 to 2017, I was an audience research analyst at the Voice of America. During that time I was preoccupied by the fact that the BBC World Service had a larger audience than VOA. VOA had a larger budget, so money was not the issue.
In audience surveys, I inserted a question asking those who listened to BBC more often than VOA: “why?” The answer provided most often was trustworthiness of the news.
I asked a listener from Burma (now known as Myanmar) why he thought BBC is considered more trustworthy than VOA. He replied that VOA is more closely connected to the U.S. government than BBC is to the U.K. government. I asked how he knows this. He responded that it’s because VOA says so every day.
He was referring to the “disclaimer” at the beginning of the editorials that, by the 1980s, were heard daily on VOA’s English broadcasts: “Next, an editorial reflecting the views of the United States government.”
The daily editorial was a requirement handed down by VOA’s parent U.S. Information Agency. The editorials are drafted by the VOA’s policy staff, sent to the State Department for approval and finally broadcast after a sometimes lengthy back and forth.
Michael Pack, the new CEO of the U.S. Agency for Global Media, VOA’s present parent agency, is restoring the editorials to their previous prominence on VOA. In recent years, with diminished radio output, editorials were relegated to VOA’s little-viewed satellite television service and to a website separate from the main voanews.com. The revival of the editorials is a step in the repoliticization of VOA.[…]
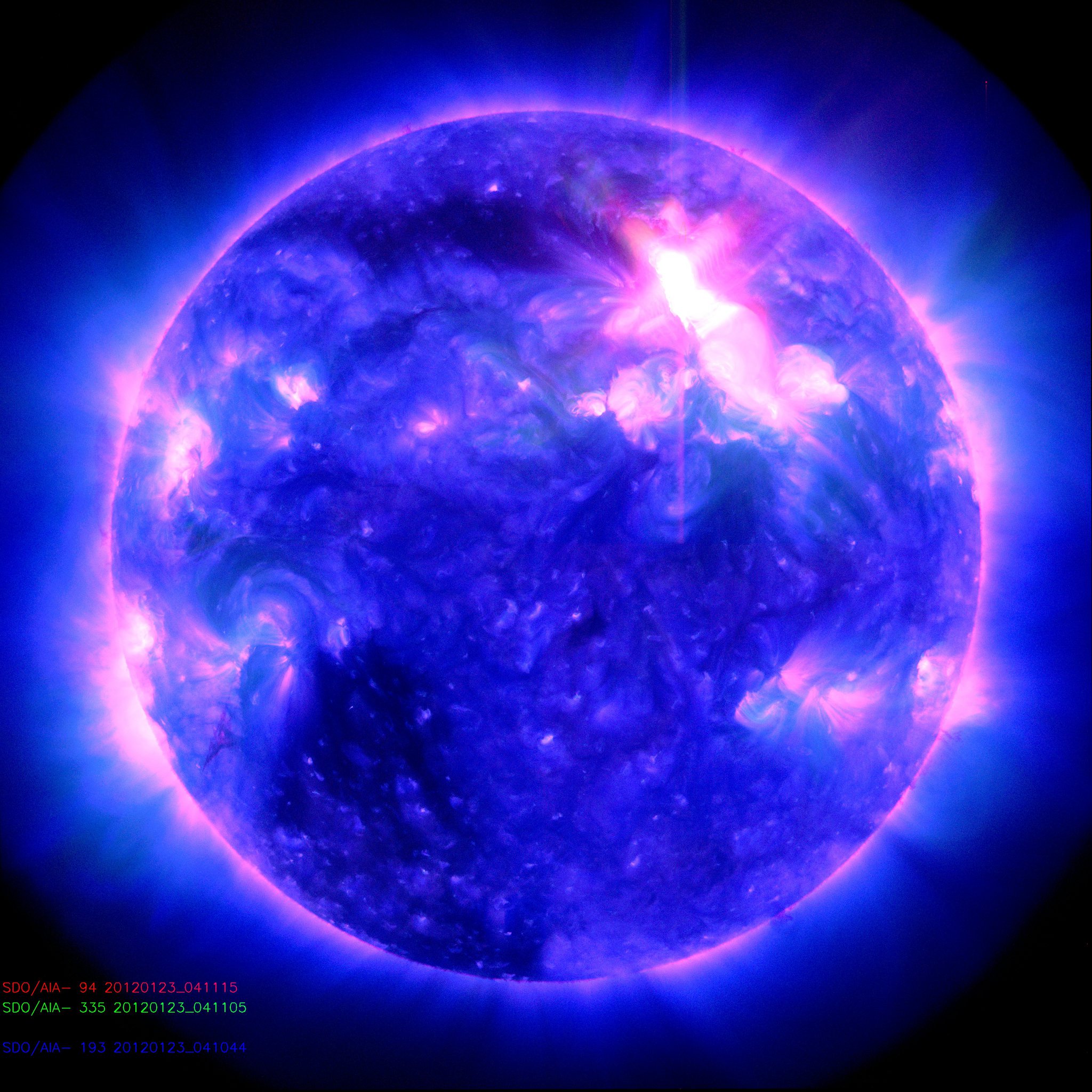
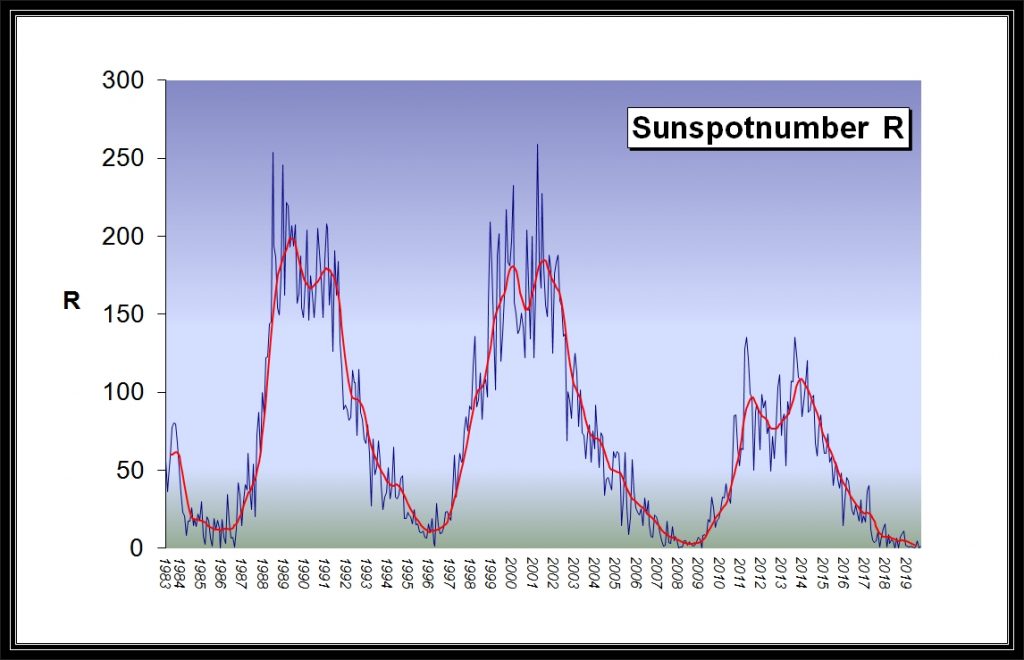
Scientists associated with the National Center for Atmospheric Research, the University of Maryland, NASA Goddard Space Flight Center, and other institutions are offering a “bold prediction” on how Solar Cycle 25 will play out. In a paper, “Overlapping Magnetic Activity Cycles and the Sunspot Number: Forecasting Sunspot Cycle 25 Amplitude,” they assert that the next sunspot cycle will be of major proportions. The forecast stands in stark contrast to the consensus of forecasters who predict that the magnitude of the nascent Cycle 25 may not be much different from the current unremarkable solar cycle, which appears to have reach its low point.
“From the dawn of modern observational astronomy, sunspots have presented a challenge to understanding — their quasi-periodic variation in number, first noted 160 years ago, stimulates community-wide interest to this day,” the abstract points out. “A large number of techniques are able to explain the temporal landmarks, (geometric) shape, and amplitude of sunspot ‘cycles,’ however, forecasting these features accurately in advance remains elusive.”
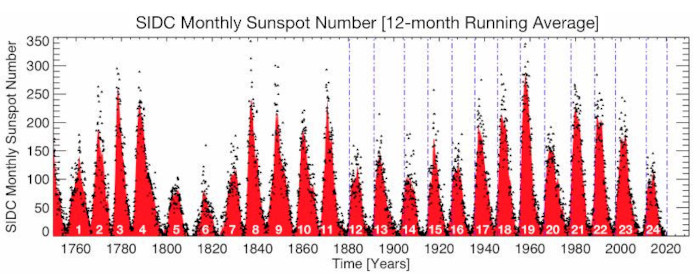
Monthly sunspot numbers since 1749. The data values are represented by dots, and the 12-month running average values are illustrated as a red shaded area. Vertical blue dashed lines signify the magnetic activity cycle termination times that trigger the rapid growth of sunspot activity.
The paper notes that recent studies have illustrated a relationship between the sun’s 22-year Hale magnetic cycle and the production of sunspot cycle landmarks and patterns, but not the amplitude of the cycle.
“Using discrete Hilbert transforms on 270 years of monthly sunspot numbers to robustly identify the so-called ‘termination’ events — landmarks marking the start and end of sunspot and magnetic activity cycles — we extract a relationship between the temporal spacing of terminators and the magnitude of sunspot cycles,” the abstract explains. “Given this relationship and our prediction of a terminator event in 2020, we deduce that Sunspot Cycle 25 will have a magnitude that rivals the top few since records began. This outcome would be in stark contrast to the community consensus estimate of Sunspot Cycle 25 magnitude.”[…]
Software-defined radio and cheap hardware are shaking up a hobby long associated with engineering
Will the amateur airwaves fall silent? Since the dawn of radio, amateur operators—hams—have transmitted on tenaciously guarded slices of spectrum. Electronic engineering has benefited tremendously from their activity, from the level of the individual engineer to the entire field. But the rise of the Internet in the 1990s, with its ability to easily connect billions of people, captured the attention of many potential hams. Now, with time taking its toll on the ranks of operators, new technologies offer opportunities to revitalize amateur radio, even if in a form that previous generations might not recognize.
The number of U.S. amateur licenses has held at an anemic 1 percent annual growth for the past few years, with about 7,000 new licensees added every year for a total of 755,430 in 2018. The U.S. Federal Communications Commission doesn’t track demographic data of operators, but anecdotally, white men in their 60s and 70s make up much of the population. As these baby boomers age out, the fear is that there are too few young people to sustain the hobby.
“It’s the $60,000 question: How do we get the kids involved?” says Howard Michel, former CEO of the American Radio Relay League (ARRL). (Since speaking with IEEE Spectrum, Michel has left the ARRL. A permanent replacement has not yet been appointed.)
This question of how to attract younger operators also reveals deep divides in the ham community about the future of amateur radio. Like any large population, ham enthusiasts are no monolith; their opinions and outlooks on the decades to come vary widely. And emerging digital technologies are exacerbating these divides: Some hams see them as the future of amateur radio, while others grouse that they are eviscerating some of the best things about it.[…]
Do you enjoy the SWLing Post?
Please consider supporting us via Patreon or our Coffee Fund!
Your support makes articles like this one possible. Thank you!
 Many thanks to SWLing Post contributor, Paul Evans, who writes:
Many thanks to SWLing Post contributor, Paul Evans, who writes: