Many thanks to SWLing Post contributor, Alan, for his recent article in Radio World titled “The Modernization of Broadcast Radio.” In it, Alan argues that the proposed “AM Radio for Every Vehicle Act” in the U.S. should go beyond preserving legacy systems and instead embrace Digital Radio Mondiale (DRM) as the future of terrestrial broadcasting. Drawing comparisons with digital transitions in countries like Norway, Switzerland, India, and China, Alan highlights the potential to reduce transmission costs, increase coverage reliability, and enhance emergency communications — all while offering a path to modernize U.S. broadcasting infrastructure.
Tag Archives: Alan Hughes
Radio Waves: NAB and DRM Compete for US Digital, 1937 Radio School, iPhone over AM Radio, and “War of the Waves”
Radio Waves: Stories Making Waves in the World of Radio
Because I keep my ear to the waves, as well as receive many tips from others who do the same, I find myself privy to radio-related stories that might interest SWLing Post readers. To that end: Welcome to the SWLing Post’s Radio Waves, a collection of links to interesting stories making waves in the world of radio. Enjoy!
Many thanks to SWLing Post contributors Alan, Paul, Bruce Hardie, Josh Shepherd, and Paul Evans for the following tips:
NAB, DRM Spar Over AM Digital for U.S. (Radio World)
Digital Radio Mondiale says its technology deserves to be tested in the United States
The Federal Communications Commission has been hearing from the National Association of Broadcasters and other interested parties about whether to allow AM band stations to turn on all-digital transmission, and under what parameters.
In addition to publicly filed comments, the NAB, which supports the idea, has made presentations to FCC staff about certain specifics — including whether the FCC should allow Digital Radio Mondiale to be tested in this country. NAB says it should not.[…]
Remote learning isn’t new: Radio instruction in the 1937 polio epidemic (The Conversation)
A UNICEF survey found that 94% of countries implemented some form of remote learning when COVID-19 closed schools last spring, including in the United States.
This is not the first time education has been disrupted in the U.S. – nor the first time that educators have harnessed remote learning. In 1937, the Chicago school system used radio to teach children during a polio outbreak, demonstrating how technology can be used in a time of crisis.
[…]In 1937, a severe polio epidemic hit the U.S. At the time, this contagious virus had no cure, and it crippled or paralyzed some of those it infected. Across the country, playgrounds and pools closed, and children were banned from movie theaters and other public spaces. Chicago had a record 109 cases in August, prompting the Board of Health to postpone the start of school for three weeks.
This delay sparked the first large-scale “radio school” experiment through a highly innovative – though largely untested – program. Some 315,000 children in grades 3 through 8 continued their education at home, receiving lessons on the radio.
By the late 1930s, radio had become a popular source of news and entertainment. Over 80% of U.S. households owned at least one radio, though fewer were found in homes in the southern U.S., in rural areas and among people of color.
In Chicago, teachers collaborated with principals to create on-air lessons for each grade, with oversight from experts in each subject. Seven local radio stations donated air time. September 13 marked the first day of school.
Local papers printed class schedules each morning. Social studies and science classes were slated for Mondays, Wednesdays and Fridays; Tuesdays, Thursdays and Saturdays were devoted to English and math. The on-air school day began with announcements and gym. Classes were short – just 15 minutes – providing simple, broad questions and assigning homework.
The objective was to be “entertaining yet informative.” Curriculum planners incorporated an engaging commercial broadcasting style into the lessons. Two principals monitored each broadcast, providing feedback to teachers on content, articulation, vocabulary and general performance. When schools reopened, students would submit their work and take tests to show mastery of the material.
Sixteen teachers answered phone calls from parents at the school district’s central office. After the phone bank logged more than 1,000 calls on the first day, they brought five more teachers on board.[…]
Listening to an iPhone with AM Radio (Hackaday)
Electronic devices can be surprisingly leaky, often spraying out information for anyone close by to receive. [Docter Cube] has found another such leak, this time with the speakers in iPhones. While repairing an old AM radio and listening to a podcast on his iPhone, he discovered that the radio was receiving audio the from his iPhone when tuned to 950-970kHz.
[Docter Cube] states that he was able to receive the audio signal up to 20 feet away. A number of people responded to the tweet with video and test results from different phones. It appears that iPhones 7 to 10 are affected, and there is at least one report for a Motorola Android phone. The amplifier circuit of the speaker appears to be the most likely culprit, with some reports saying that the volume setting had a big impact. With the short range the security risk should be minor, although we would be interested to see the results of testing with higher gain antennas. It is also likely that the emission levels still fall within FCC Part 15 limits.[…]
“War of the Waves: Radio and Resistance during World War II.” (American Economic Journal: Applied Economics)
Abstract: We analyze the role of the media in coordinating and mobilizing insurgency against an authoritarian regime, in the context of the Nazi-fascist occupation of Italy during WWII. We study the effect of BBC radio on the intensity of internal resistance. By exploiting variations in monthly sunspot activity that affect the sky-wave propagation of BBC broadcasting toward Italy, we show that BBC radio had a strong impact on political violence. We provide further evidence to document that BBC radio played an important role in coordinating resistance activities but had no lasting role in motivating the population against the Nazi-fascist regime.
You can find a pre-print at: https://www.econstor.eu/bitstream/10419/202840/1/1016161859.pdf.
Do you enjoy the SWLing Post?
Please consider supporting us via Patreon or our Coffee Fund!
Your support makes articles like this one possible. Thank you!
Radio Waves: Radio Marti DRM, Push for Shepparton Museum, APRS on the History Channel, and Radio’s “Major Cultural Opportunity”
 Radio Waves: Stories Making Waves in the World of Radio
Radio Waves: Stories Making Waves in the World of Radio
Because I keep my ear to the waves, as well as receive many tips from others who do the same, I find myself privy to radio-related stories that might interest SWLing Post readers. To that end: Welcome to the SWLing Post’s Radio Waves, a collection of links to interesting stories making waves in the world of radio. Enjoy!
Many thanks to SWLing Post contributors Alan Hughes, Michael Bird, Zack Schindler, and Dennis Dura for the following tips:
Radio Marti Begins Shortwave DRM Transmissions (Radio World)
Radio Marti began Digital Radio Mondiale (DRM) shortwave transmissions on Feb. 4. Part of the U.S. Agency for Global Media (USAGM), Radio Marti broadcasts news and other programs to Cuba. The DRM shortwave transmissions are from USAGM’s Greenville, North Carolina, site.
USAGM has transmitted in DRM before. There were some transmissions from Briech, Morocco, in the early 2000s. Greenville tested DRM in 2009 in partnership with what was then known as HCJB Global Technology. So why are they back now after an absence of over a decade?
“We want to experiment a bit with different modes and services available on DRM. We also want to help push the development of low-cost receivers and the best way to do that is to put some transmissions on the air, explains Gerhard Straub, director of USAGM’s Broadcast Technologies Division.[…]
Push for museum at Shepparton’s Radio Australia site (Shepparton News)
Amateur radio enthusiasts are pushing for the former site of Radio Australia in Shepparton North to be upgraded and retained as a national museum of radio broadcast history.
Members of the Shepparton and District Amateur Radio Club and The Vintage Radio Club of North East Victoria are due to present a 25-page proposal to an anonymous consortium of buyers said to be interested in acquiring a 258ha block of land along Verney Rd.
The block includes two buildings and several large broadcast towers on the former site of Radio Australia. The site is currently owned by BAI Communications.
The Shepparton club’s assistant secretary, Geoff Angus, said the proposal would be presented to Greater Shepparton City Council for forwarding to the consortium.[…]
APRS usage seen on the History Channel “Secret of Skinwalker Ranch”
Zack Schindler writes:
I have been watching a show about paranormal activity on the History Channel called The Secret of Skinwalker Ranch. In the episode this week they hired a professor to do a balloon launch with some RF sensors. In this episode they also showed the APRS.FI webpage and I was able to read his callsign from an APRS tracker, KM4MRH.
The professor used an APRS tracking device. On the right side of the page link below you can click on Other SSID’s to see other balloon launches he has done. Normally when there is a balloon launch you can see the data from it going up and down. This page shows the Skinwalker balloon launch data transposed over a map. https://aprs.fi/#!call=a%2FKM4MRH-3&timerange=3600&tail=3600
Sadly they are using these for measuring RF fields rather than these.
In a Crisis, Radio Should Be Bigger Than Ever — So Why Isn’t It? (Rolling Stone)
Terrestrial music stations have a major cultural opportunity right now, but employees say a muddied strategy is standing in the way
Radio personality Kevin Ryder was “baffled” by KROQ’s “cold, heartless attitude” when he and his morning-show team were fired at the end of March. The station has long been an alternative/rock staple in Los Angeles, the second-largest market in the country, and Ryder had been on the air for more than 30 years.
“The new people in charge now weren’t here for the building of the world-famous KROQ,” Ryder, one-half of the popular Kevin & Bean Show, said on air when the station let him go, live one final time. “I don’t think it means anything to them. It’s a numbers business, and there’s no family aspect to it anymore. It’s only numbers, but this place was built without numbers. It was musicians, artists, and the special relationship between music, the station, and our fans.”
AM/FM radio provides localized, round-the-clock information and entertainment via friendly neighborhood voices — so in theory, it’s the perfect platform in a global crisis that forces hundreds of millions of people to stay home. But Ryder is one of many in the radio community — including on-air hosts, music directors, program directors — who have been shocked by sudden job losses in recent weeks as COVID-19 has spread across the U.S., and news out of the industry has been one bad thing after another. Why is terrestrial radio missing the opportunity here — and how should it be fighting to get back on top?[…]
Do you enjoy the SWLing Post?
Please consider supporting us via Patreon or our Coffee Fund!
Your support makes articles like this one possible. Thank you!
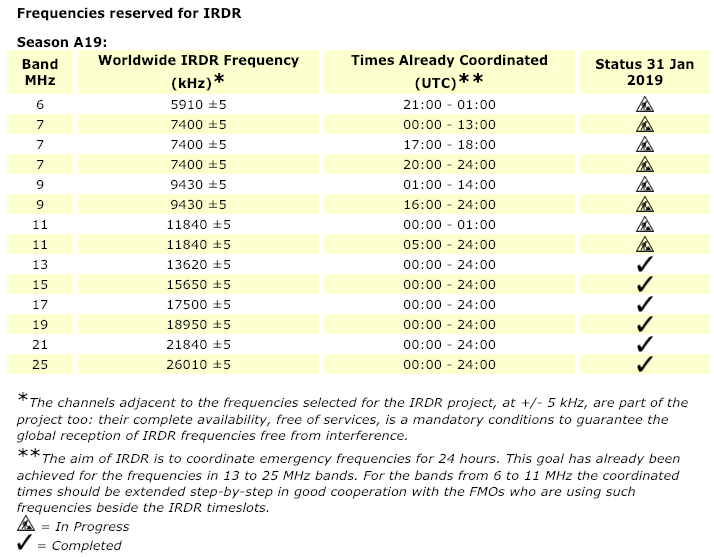
Frequency coordination news and IRDR updates
Many thanks to SWLing Post contributor, Alan Hughes, who shares this article by WRMI’s Jeff White in Radio World magazine. Besides covering updates in the A19 broadcast season, and Radio Exterior de España’s increased broadcasts, Jeff notes frequencies and updates for the International Radio for Disaster Relief initiative.
For more information about the IRDR, check out the information below taken from this page on the HFCC website:
International Radio for Disaster Relief (IRDR)
Humanitarian Aspects of HFCC ActivitiesFrom its infancy since 1920s shortwave radio has been associated with its potential of being a communication tool in emergencies. This use of shortwave radio is still very much present among amateur radio enthusiasts for example, who discovered its long distance properties early in the twentieth century. Amateur radio provides a means of communication on shortwaves and other frequencies “when all else fails”. This role of amateur radio is well recognised, valued and appreciated both by the public and by the world institutions managing and regulating the use of the radio spectrum.
In contrast the huge technical potential of international shortwave broadcasting that operates transmitter facilities tens, or hundred times, more powerful than those of amateur radio, remains almost unused in emergencies. At the moment when local and even regional communication and information networks are needed most, they are destroyed or overloaded and the population suffers from an information blackout. Shortwave radio is capable of remaining the only source of information.
Although the life-saving role of radio broadcasting is widely recognised by the public, and confirmed by surveys conducted after the recent disasters – and even acknowledged by world leaders – no concrete projects have been ever designed and no regulatory framework has been developed.
That is why the HFCC – International Broadcasting Delivery in co-operation with the Arab States and Asia-Pacific broadcasting unions are working on an International Radio for Disaster Relief (IRDR) project that is based on the system of online co-ordination of frequencies managed by the HFCC in accordance with International Radio Regulations.
The HFCC is aware of the humanitarian aspects of international broadcasting. It pointed out in 2012 – as the UNESCO partner for the preparation of the World Radio Day – that terrestrial shortwave radio in particular is still considered as a powerful communication and information tool during emergency situations. Read more >>
Receivers are inexpensive and require no access fees. Shortwave radio is important for people living in remote and isolated regions of the world. It reaches across the digital divide to the most disadvantaged and marginalised societies. This is also in keeping with the Declaration and Action Plan of the World Summit on the Information Society.
The annual edition of the World Disasters Report of the International Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies (IFRC) issued in October 2013 stressed again that with only 6 percent of people in low-income countries using the internet in 2011 the digital divide is still stark, and access to low cost media technology is really the key.
The HFCC is a strong advocate for incorporating terrestrial broadcasting permanently on the disaster risk reduction agendas of the ITU and other UN agencies and institutions. It submitted two documents for the ITU-R Working Party 6A November 2013 meeting:
HFCC – The Importance of Terrestrial radio in International Broadcasting
HFCC – The International Radio for Disaster Relief ProjectBoth documents are annexes in Section 8 of the ITU-R Study Group 6 Report BT.2266 “Broadcasting for public warning, disaster mitigation and relief”. The report can be downloaded via this link.
A workshop was held during the November 2013 meeting addressing these issues. The web site of the Emergency Broadcasting Workshop can be accessed here. The web site also contains copies of all the presentations that were made at the workshop, and a Video interview with Christoph Dosch, Chairman of ITU-R Study Group 6 (Broadcasting service)
The HFCC has applied for membership in the CDAC (Communicating with Disaster Affected Communities) Network in keeping with the conclusion of the debate on emergency communication during the Bratislava B13 Conference. Read more >>
The HFCC is staying in touch with the Information and Communication Sector of the UNESCO agency on the preparation of the World Radio Days that are celebrated each year on February 13th.
Humanitarian aspects of terrestrial broadcasting were also on the agenda of the Global Kuala Lumpur conference in January 2014. Read Opening Remarks.
The “Tecsun Radios Australia Q-3061” DRM Shortwave Radio
Many thanks to SWLing Post contributor, Alan Hughes, who notes that Tecsun Radios Australia have announced a new DRM stand-alone receiver: the Q-3061.
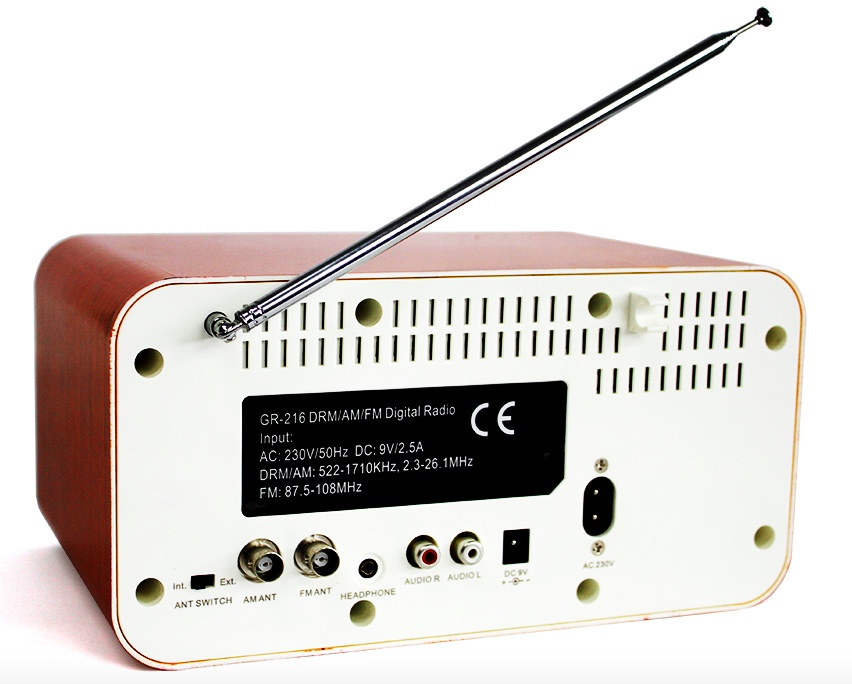
When I first received Alan’s tip, I was surprised that I had not been been given some advance notice or even a hint about Tecsun developing and producing a DRM radio. Then I saw the Q-3061 product image and it looked to be a spitting image of the Gospell GR-216 DRM radio. A quick look at the radio’s back panel and the connection with the GR-216 was confirmed.
 Reading through the product description, it appears they worked with Gospell to badge this for Tecsun Radios Australia’s primary markets:
Reading through the product description, it appears they worked with Gospell to badge this for Tecsun Radios Australia’s primary markets:
“The Tecsun Radios Australia Q-3061 DRM Shortwave Radio is for experienced shortwave users. There a limited number of DRM signals available in our region although the total number of DRM broadcasts are increasing. This radio is squarely aimed at radio enthusiasts and DXers, most signals require an external antenna, experience, and patience. We recommend our Tecsun Radios Australia Q-3061 DRM Shortwave Radio be used in conjunction with our Tecsun Shortwave and AM Outdoor Antenna for the best results (this is the setup we have in our Brookvale NSW office).
The Tecsun Radios Australia Q-3061 DRM Shortwave Radio is the culmination of several years work. Tecsun Radios Australia has worked in close co-operation with the manufacturer providing testing results from locations across the Pacific, including Samoa, Vanuatu, Solomon Islands, Fiji, and New Zealand. Reception of DRM signals in Australia requires many factors to be optimised, because we are outside the traditional coverage area of most broadcasters. Nevertheless, with an optimised antenna, correct selection of DRM broadcaster, schedule and good propagation conditions DRM signals can be received. New DRM broadcasters are appearing every month.”
After the product description they also include this disclaimer:
Note: This DRM radio has no association with Tecsun of China and is an exclusive initiative and product of Tecsun Radios Australia
The price is $500 AU or approximately $357 US.
To recap, this isn’t a new Tecsun DRM radio, rather it’s a rebadged GR-216 for the retailer/distributor Tecsun Radios Australia.
Click here to read about the Q-3061 at Tecsun Radios Australia.
Click here to read a review of the Gospell GR-216 DRM receiver.
Do you enjoy the SWLing Post?
Please consider supporting us via Patreon or our Coffee Fund!
Your support makes articles like this one possible. Thank you!