Many thanks to SWLing Post contributor, Adrian Korol, who shares the following announcement. Please note that this announcement has been machine translated–click here to read the original announcement in Spanish (PDF):

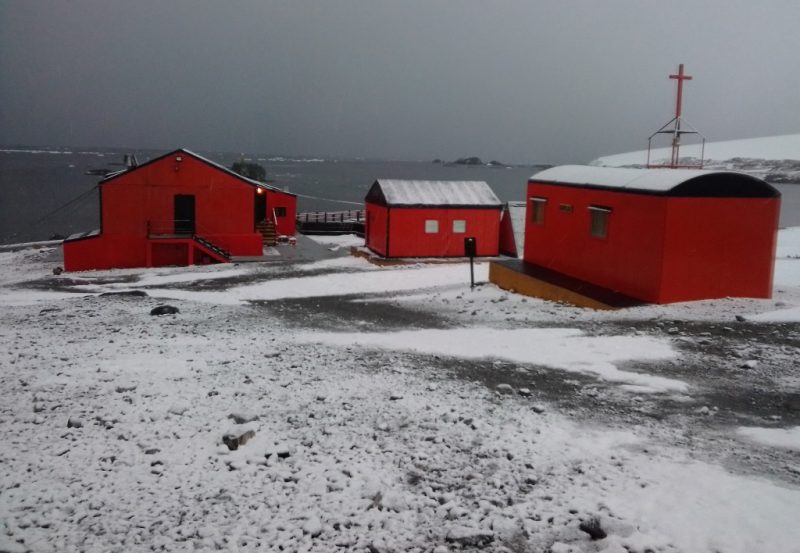
First Short Wave Emission of Radio Nacional Arcangel San Gabriel Radio LRA 36 From the Esperanza Antarctic Base
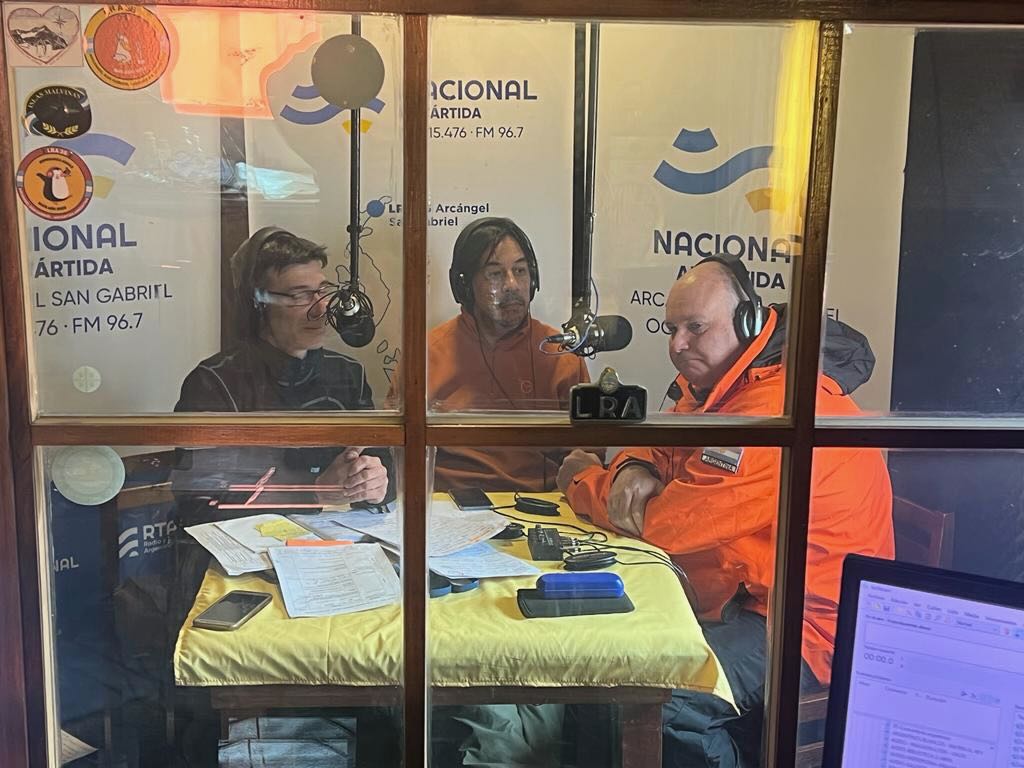
 Last Saturday, January 21, at 12:15 (15:15 UTC) Argentine time, the Antarctic shortwave radio station LRA 36 “Radio Nacional Arcángel San Gabriel”, located at Base Esperanza, began the program “Uniendo Voces”, from the cycle 2023 summer special of the RAE service, Radio Argentina abroad POR 15476 kHz (usb)
Last Saturday, January 21, at 12:15 (15:15 UTC) Argentine time, the Antarctic shortwave radio station LRA 36 “Radio Nacional Arcángel San Gabriel”, located at Base Esperanza, began the program “Uniendo Voces”, from the cycle 2023 summer special of the RAE service, Radio Argentina abroad POR 15476 kHz (usb)
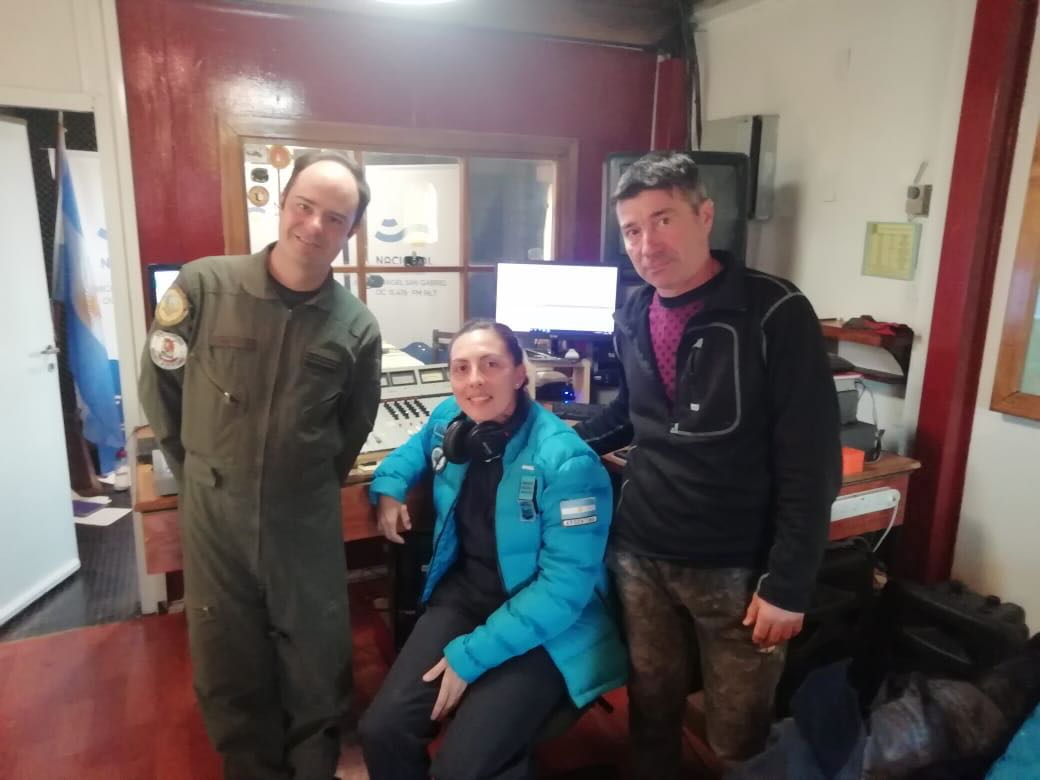
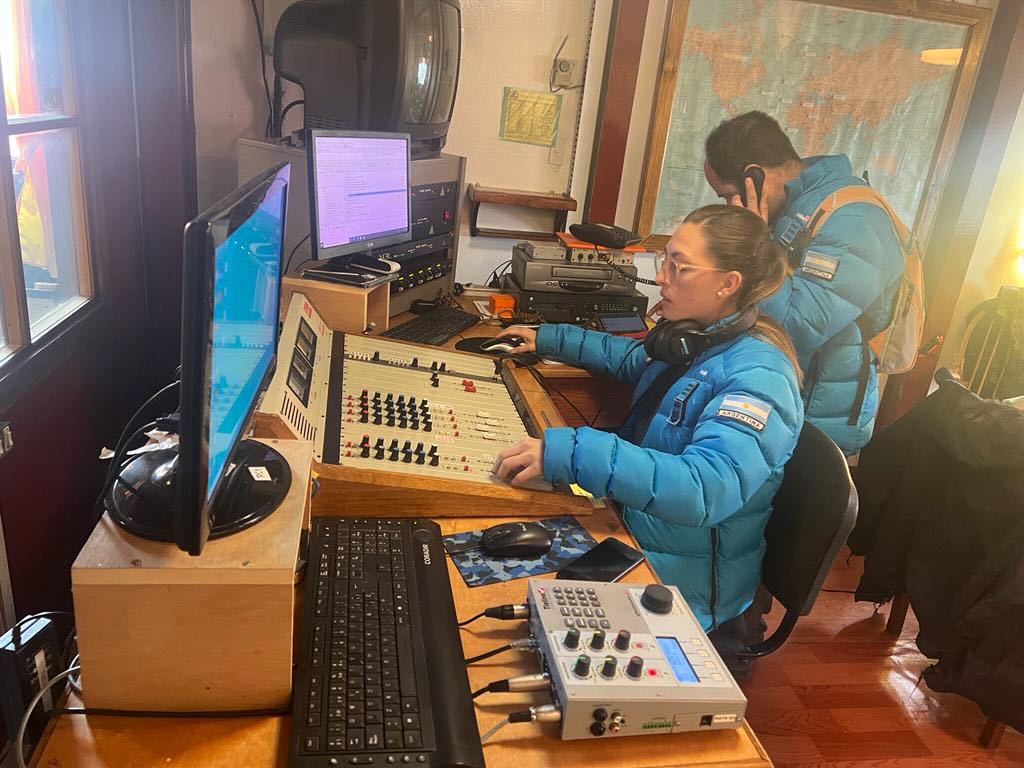
 The program was carried out by Juan C. Benavente, a member of the Joint Antarctic Command and a professor at the National University of Quilmes; Marcelo Ayala, a journalist from LRA 1 Radio Nacional Buenos Aires, and Principal Corporal Nicole Valdebenito in the technical operation, a member of the Antarctic staff of that Argentine base. The proposal and general coordination is in charge of the director of RAE, the journalist and host Adrián Korol, who for years has coordinated the annual broadcasts of LRA 36.
The program was carried out by Juan C. Benavente, a member of the Joint Antarctic Command and a professor at the National University of Quilmes; Marcelo Ayala, a journalist from LRA 1 Radio Nacional Buenos Aires, and Principal Corporal Nicole Valdebenito in the technical operation, a member of the Antarctic staff of that Argentine base. The proposal and general coordination is in charge of the director of RAE, the journalist and host Adrián Korol, who for years has coordinated the annual broadcasts of LRA 36.



In this first program, the Antarctic Joint Commander, Brigadier General Edgar Fernando Calandín; the head of the Esperanza base and current director of LRA 36, Lieutenant Colonel Gustavo Cordero Scandolo. For his part, the director of RAE spoke by telephone on the air before the closing of the program, emphasizing the importance and international repercussions of these wave broadcasts.

 The broadcast was followed by diexers, radio listeners and radio amateurs from Argentina, Uruguay, Chile, Brazil, Mexico, Costa Rica, the United States, Spain, Germany, Japan, Ukraine, Belgium and France. Online SDR receivers (kiwisdr and websdr) in Latin America were active during the transmission with all their channels occupied and tuned almost entirely to the LRA36 frequency.
The broadcast was followed by diexers, radio listeners and radio amateurs from Argentina, Uruguay, Chile, Brazil, Mexico, Costa Rica, the United States, Spain, Germany, Japan, Ukraine, Belgium and France. Online SDR receivers (kiwisdr and websdr) in Latin America were active during the transmission with all their channels occupied and tuned almost entirely to the LRA36 frequency.
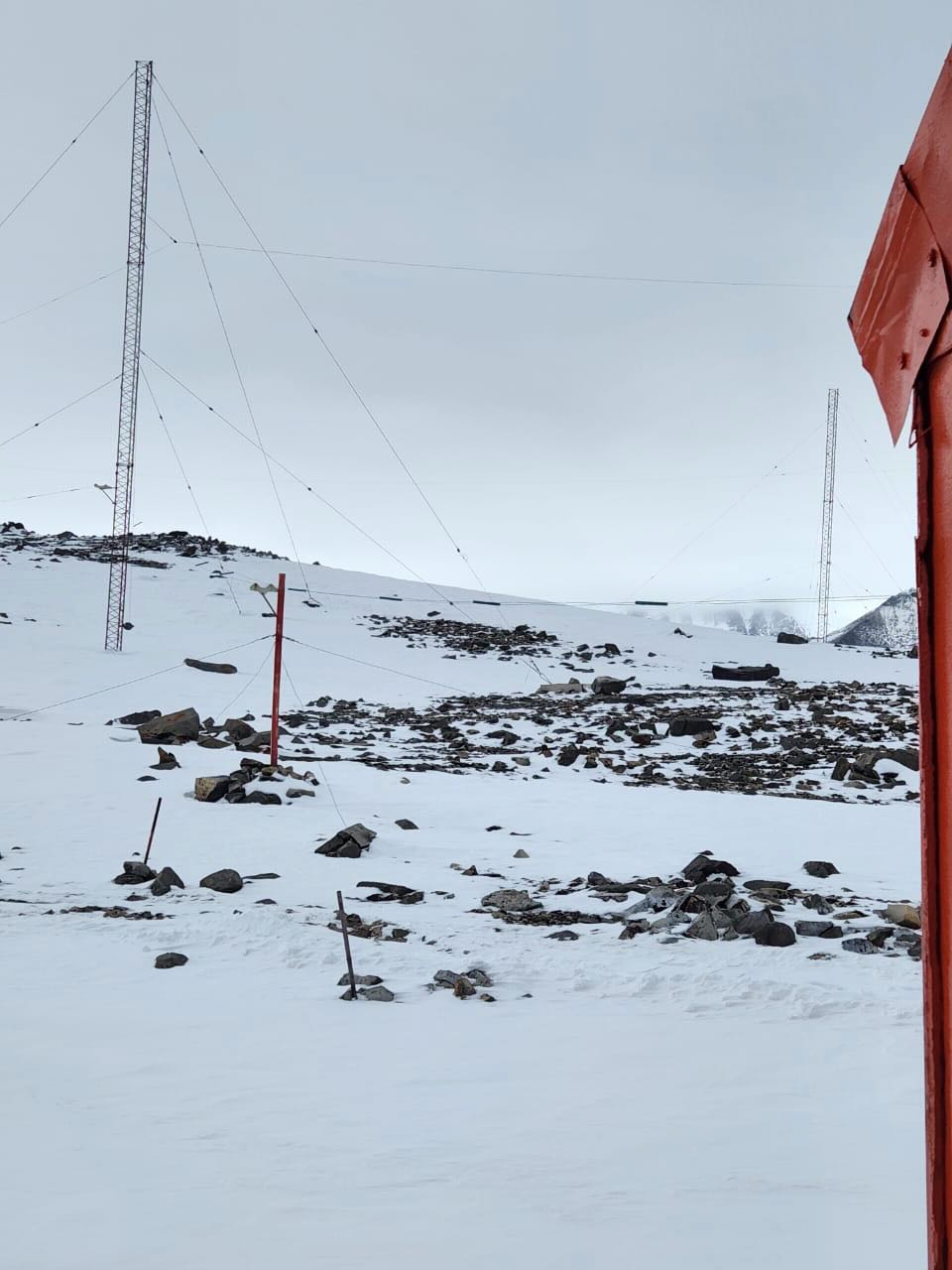
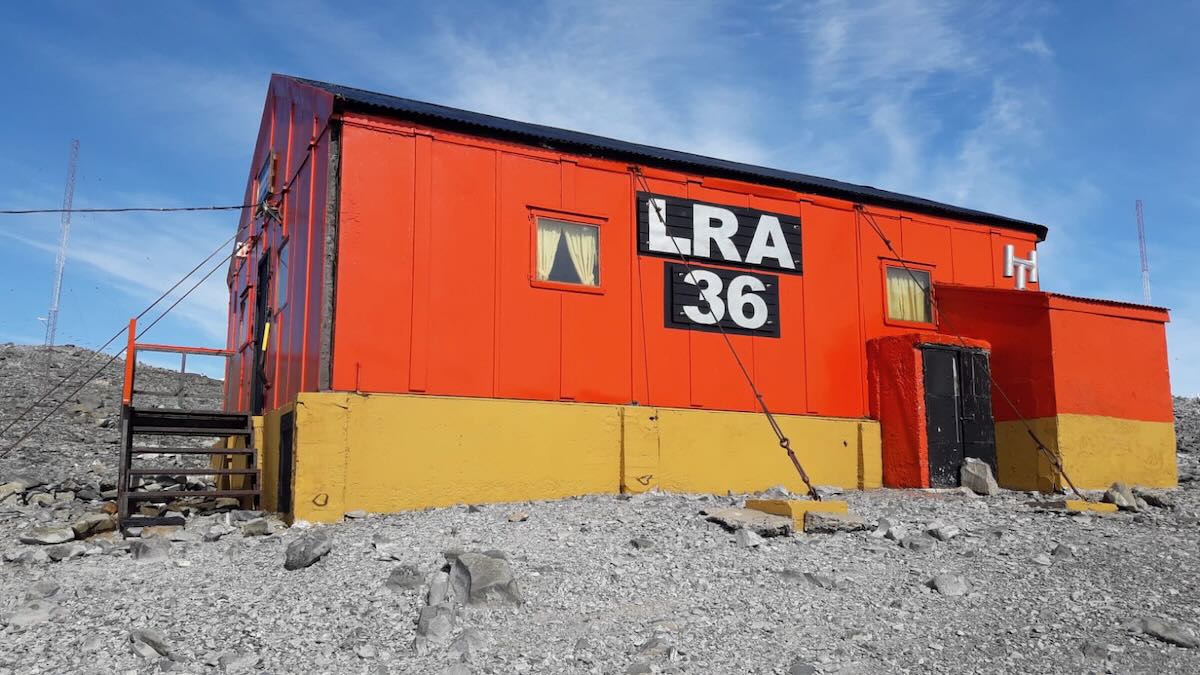
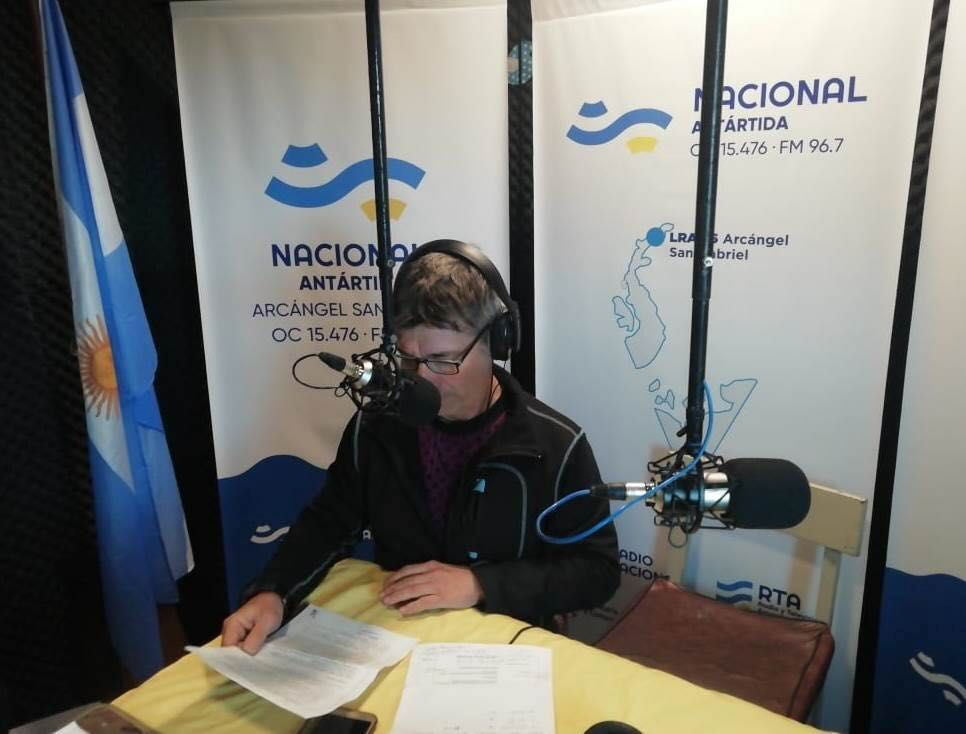 In addition, the Antarctic station LRA 36 is the only one that transmits on shortwave from Antarctica and also does so on FM for local coverage on the 96.7 MHz frequency, and on the Internet, from the site www.radionacional.com.ar/emisoras/Antarctica.
In addition, the Antarctic station LRA 36 is the only one that transmits on shortwave from Antarctica and also does so on FM for local coverage on the 96.7 MHz frequency, and on the Internet, from the site www.radionacional.com.ar/emisoras/Antarctica.
With the broadcast on Saturday, the start of the radio programming of the Special Summer Cycle is completed, which is part of the Antarctic Culture Agenda 2023 “Culture is Sovereignty”, an initiative for the sixth continent developed between the Ministry of Culture and the Ministry of Defense, through the Joint Antarctic Command (COCOANTAR).
The other radio activities in the cycle include the broadcast of “Panorama de Noticias”, hosted by journalist Marcelo Ayala, which is broadcast on LRA 1 in Buenos Aires, and the activation of station LU1ZV from Base Esperanza on amateur radio bands.
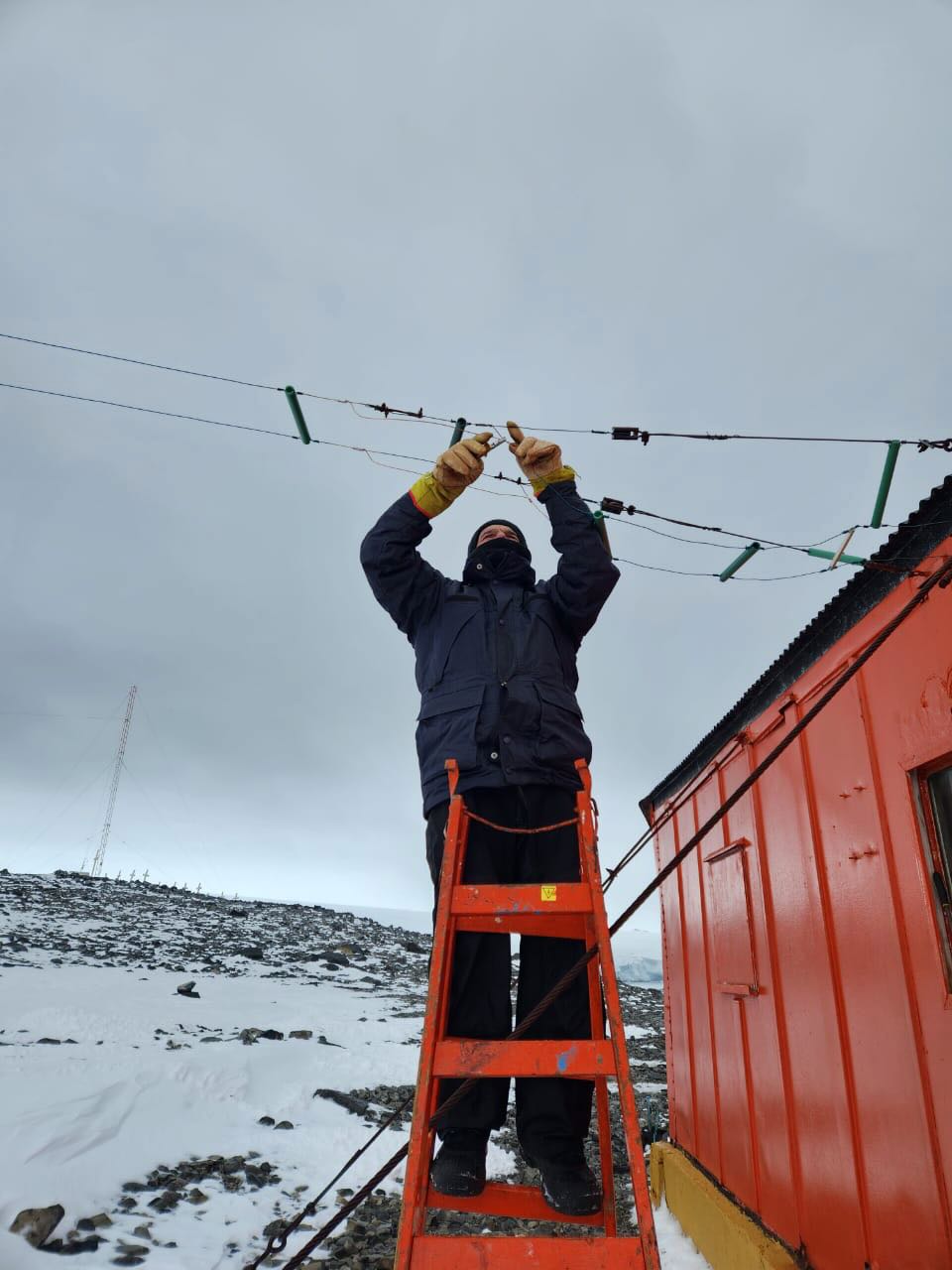
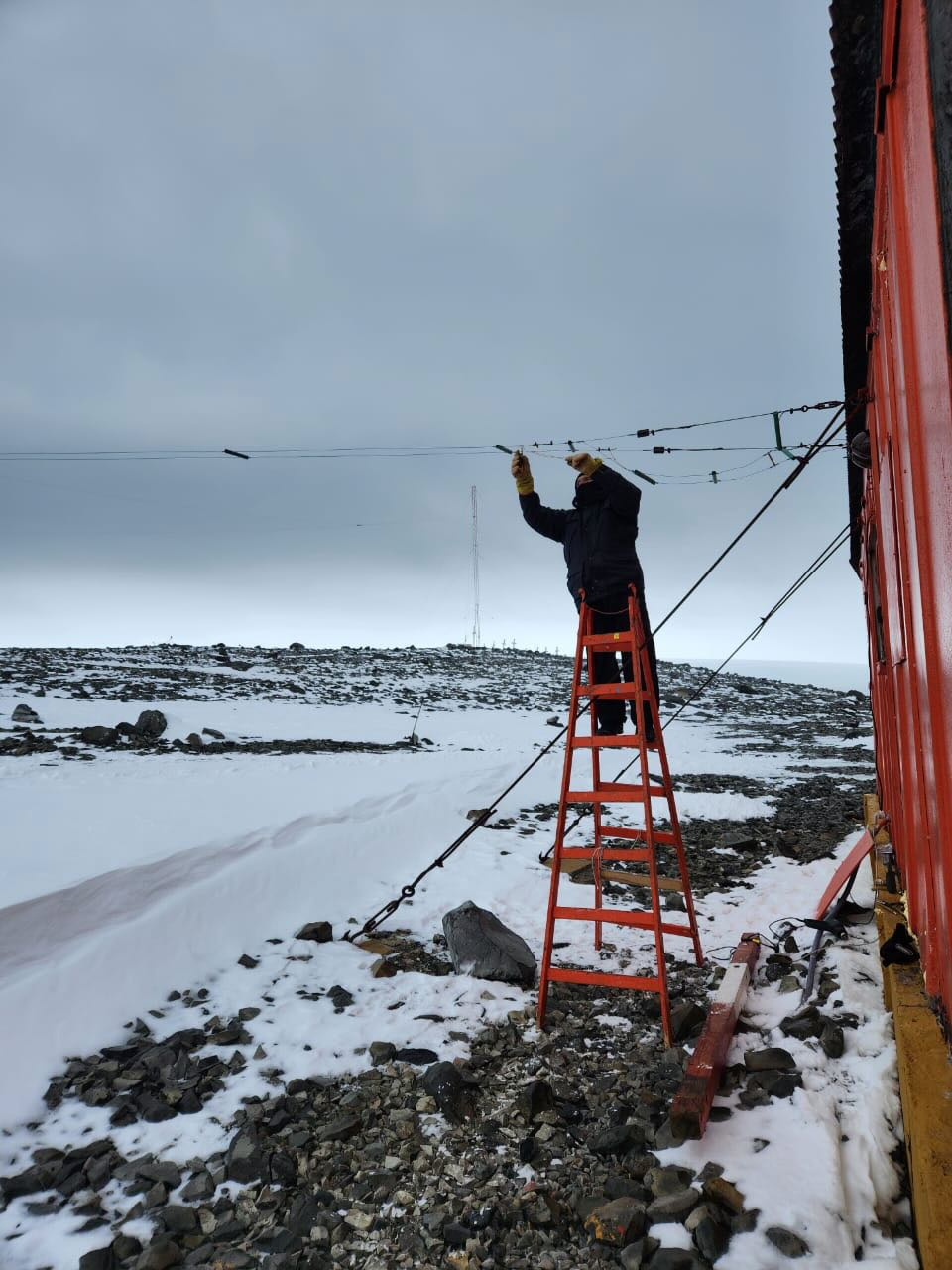
The airing was in charge of Nicole Valdebenito and Esteban Romero, members of the Navy and Air Force respectively.

ON SATURDAY, JANUARY 28, a new 90-minute broadcast will be made on short wave on 15476 kHz (USB) at 12 local time (15 UTC) with repetition at 4 local time (19 UTC)


















