Many thanks to SWLing Post contributor, Dan Van Hoy (VR2HF), who shares the following guest post:
Many thanks to SWLing Post contributor, Dan Van Hoy (VR2HF), who shares the following guest post:
ARISS FM Repeater May Be Back on Early December and a Short Ham Satellite Summary
by Dan Van Hoy (VR2HF)
I’ve recently had a lot of fun learning about the current batch of ham satellites and operating through some of them for the past several months with only a Diamond discone (and a short run of RG-213 double-shielded coax), Yaesu FT-817 (for SSB/CW) and TYT TH-9800 for FM satellites (more power, Scotty!). This simple set-up has yielded hours and hours of great fun. The last time I did satellite work was in the ’70s making contacts from my car through Oscar 6. If I had a car here in Hong Kong I might try it again!
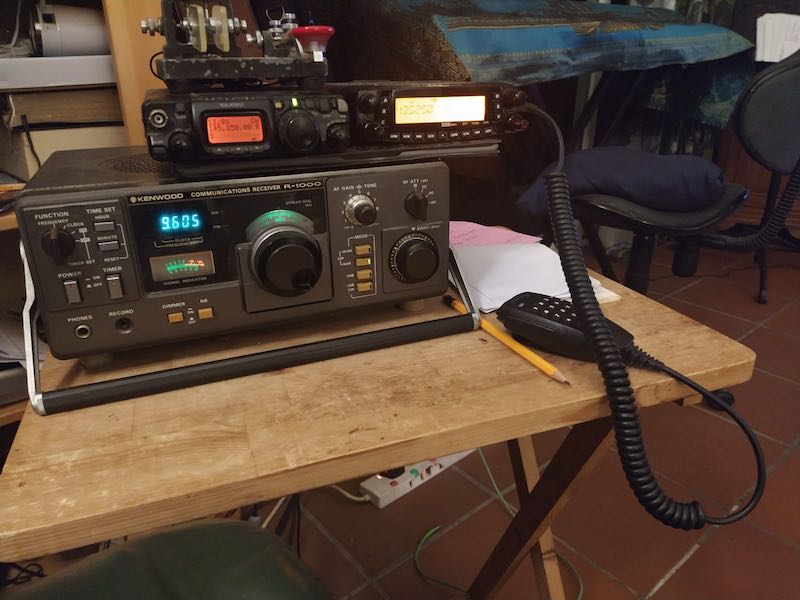
Here’s my living room TV tray and sofa shortwave and satellite station (no XYL in house at the moment).
ARISS FM Repeater
One of the recent highlights for both newcomers to satellite operations and old-timers was working the International Space Station’s (ISS) new FM repeater which came on the air in early September. It is a specially modified Kenwood D710-GA VHF/UHF transceiver. Unfortunately, it was only operational for about a month. For the past several weeks it has been used mostly in APRS mode.
The ARISS FM repeater runs five watts and sounds just like a regular terrestrial repeater in many ways. You can work it with any dual-band VHF/UHF FM rig and the right antenna. Full-duplex is not required, but it helps. Lower power requires some kind of gain antenna, but receiving can be done with simple antennas.
The ARISS organization just updated the schedule for the ARISS operation with this announcement:
“Next mode change (cross band repeater) targeting early December.”
YEAH! What a nice Christmas present!
Here’s a link to the full ARISS information page:
https://www.ariss.org/current-status-of-iss-stations.html
ARISS QSO with E21EJC
Here’s a Youtube video of one of my ARISS contacts with E21EJC. It was right after he came back from his DXpedition hauling microwave gear and dishes out to the Thai countryside to work the QO-100 geosynchronous satellite. I tell him “welcome home and have a good rest.” Kob really is “Mr Satellite!” He has posted hundreds of Youtube videos of satellite contacts.
In addition, here is video of their HS0AJ/P special “portable” station antennas for QO-100. 10 GHz RX dish (downlink) and 2.4 GHz TX dish (the big one). I listened to Kob and his friend make several QSOs via the QO-100 WebSDR:
Amazing the things we hams do just to spray some RF in the right direction!
Beyond the ARISS: A Ham Satellite Summary
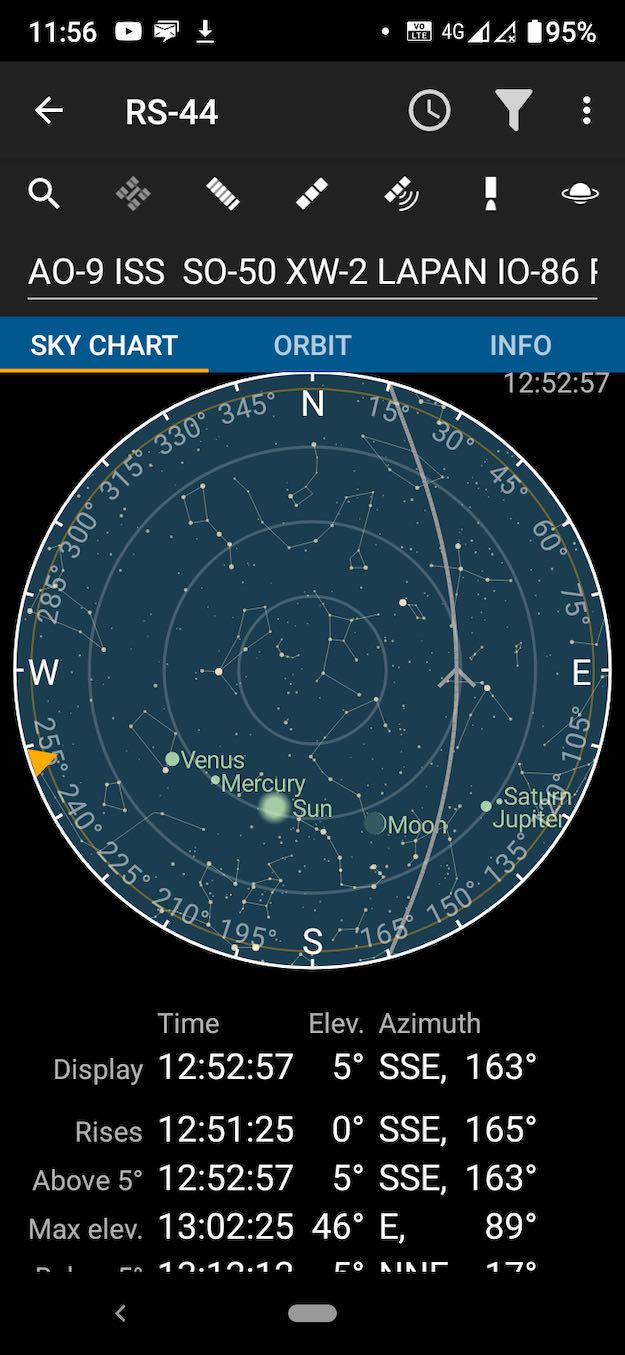
Presently, AO-91 is probably the most popular FM satellite, along with SO-50, AO-27 and PO-101. RS-44, a linear satellite for SSB and CW, is far and away the most popular for those modes. RS-44 is in a higher orbit providing less Doppler shift and longer contact times per pass. You can easily see from the Amsat status page which satellites are in operation and which are the most popular. Many of the ham satellites do not provide two-way communication capability, but still have beacons (CW and data) that can be heard (those are in YELLOW on the Amsat status page). Everyone with a ham callsign can contribute by by uploading a reception report of the satellites you hear or work.
Full-duplex on SSB/CW satellite work is very desirable but not mandatory. I have learned you can make contacts without it coupled with a little skill and some luck. Staying near the center of the satellite’s particular passband is helpful. Sadly, there are few full-duplex rigs available these days. One of the best may be the Yaesu FT-847 which can be found on the used market. Some satellite ops are using SDRs for RX and a ham rig for TX to achieve full-duplex. I’m going to try that soon using two Diamond discones and vertical separation.
For current status of all ham satellites and ARISS operation, go here:
https://www.amsat.org/status/index.php
Tracking
For tracking the ham sats and ISS, I like the Heavens-Above app (or Webpage: https://heavens-above.com/). The Pro version of Heavens Above is worth every penny. In the app, I put only the active satellites I am interested in in the search box. That way all the remaining unusable satellites will be ignored. Heavens-Above also lists the satellite operating frequencies for a quick reference.
One cool side note. With Heavens-Above, you can also see when ISS visible passes are available over your area (almost always near sunrise/sunset). Look for the passes with a magnitude greater than -3.0. If you have clear skies or a thin layer of clouds it’s quite a treat to see the ISS zoom overhead at 17, 000 miles per hour. When the ARISS repeater is operating, you can see and hear the ISS! The screen shot above is a visible pass at -3.9 magnitude, as bright as Venus.
Antennas
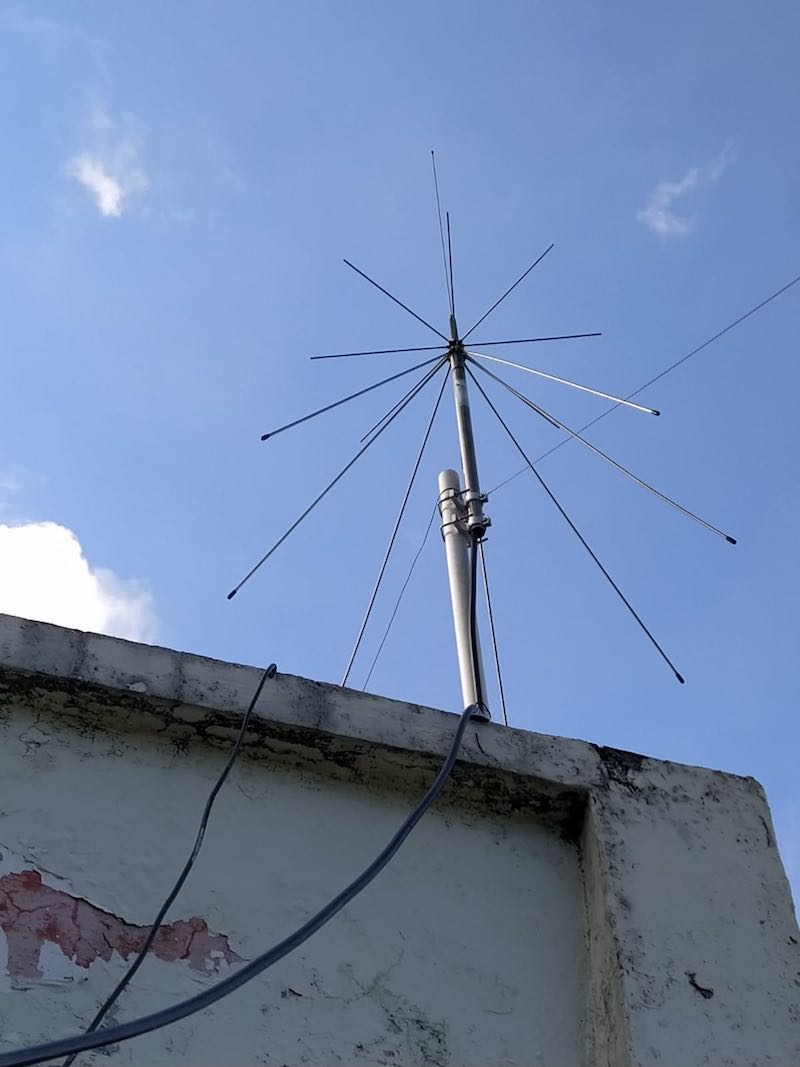
I have found my Diamond discone to work quite well for satellite operation. It’s probably the cheapest, simplest and most effective antenna you can use for this application If you really get interested in satellite work you can always spend the big bucks for AZ/EL rotators and beams as well as the software to run it all including tuning your rig to compensate for Doppler shift. Or you can buy quite expensive omni-directional antennas designed specifically for satellite use. So far, the KISS approach has worked well for me.
The Future Is Now
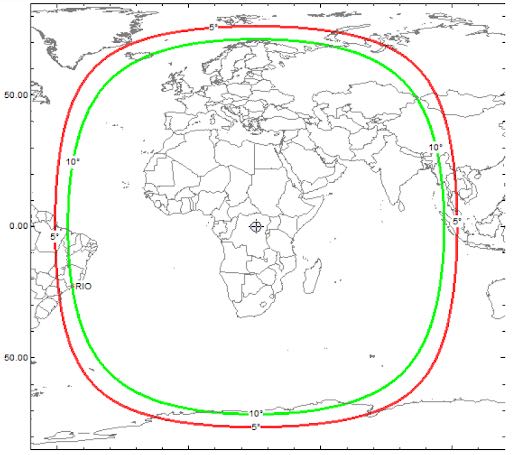
Finally, we can all get a taste of the future now by listening to the only ham radio geosynchronous satellite currently in operation, QO-100. It is centered on Europe and covers about 1/3 of the earth from Brazil to parts of Asia.
It was a thrill for me to listen (via the WebSDR listed below) to one of my new satellite colleagues, Mr Kob, E21EJC, who I call “Mr Satellite,” work Brazil and many other stations in the EU, the Middle-east and elsewhere through QO-100 during a special event operation from Thailand.
Anybody can listen to activity on QO-100 at the link below. When you get there just find the CLICK TO START SOUND! button. Then, click UNDER one of the signals in the waterfall and tune with the controls below. Weekends and holidays seem to be the best time to listen.
https://eshail.batc.org.uk/nb/
Because both the uplink and downlink frequencies are way up in the microwave bands, it’s not easy to get on QO-100, but, it appears to me, worth the effort. Maybe one day we will have two more QO-100-like birds linked together to cover the whole earth for 24/7 communication anywhere in the world. One can dream.
Full details about the QO-100 geosynchronous satellite can be found here:
https://amsat-uk.org/satellites/geo/eshail-2/
CQ Satellite!
When the propagation is bad, or actually anytime, ham satellites are a wonderful alternative to HF for having fun on the air.
Sorry, gotta go, RS-44 is just about here. CQ satellite, CQ satellite, de VR2HF…
Thank you so much for the satellite overview, Dan!
You’ve inspired me to get out of my comfort zone and try a little satellite work! The perfect project to do with my two daughters. I’m such a “below 30MHz” guy, I have to remind myself that there are actually some pretty amazing things you can do further up the band! When I purchase a discone antenna, I’m going to accuse you of being an enabler. Fair warning.
SWLing Post readers: Anyone else here tune to and track satellites? Please comment!