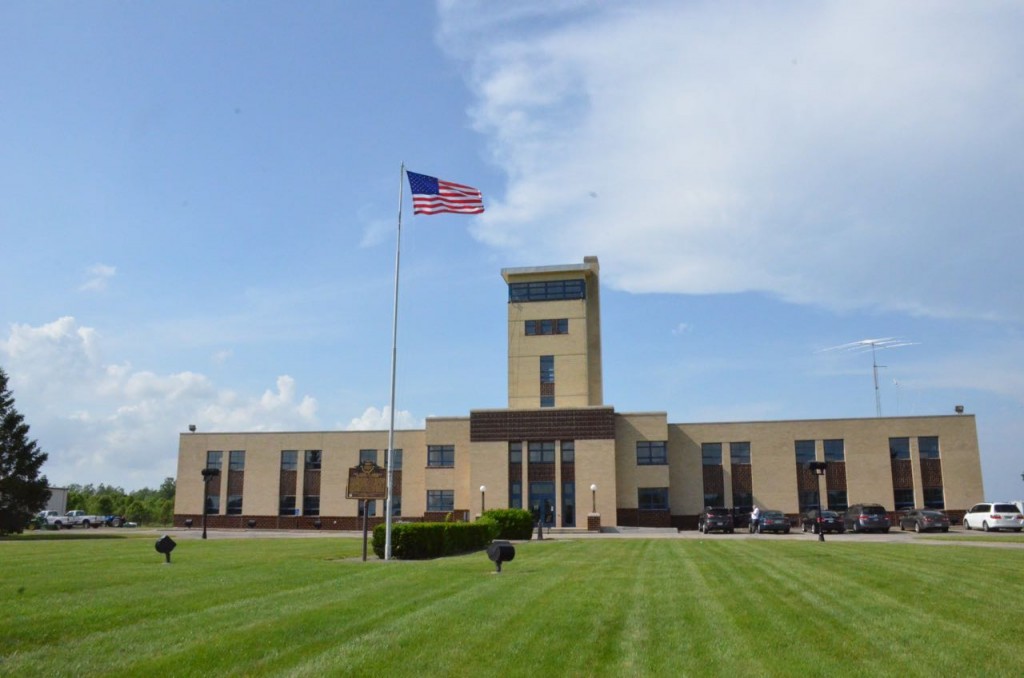
Immediately after packing up our table at the Dayton Hamvention, my buddies Eric (WD8RIF), Miles (KD8KNC), and I made the 30 minute journey to Bethany, Ohio, to visit the VOA Bethany museum.
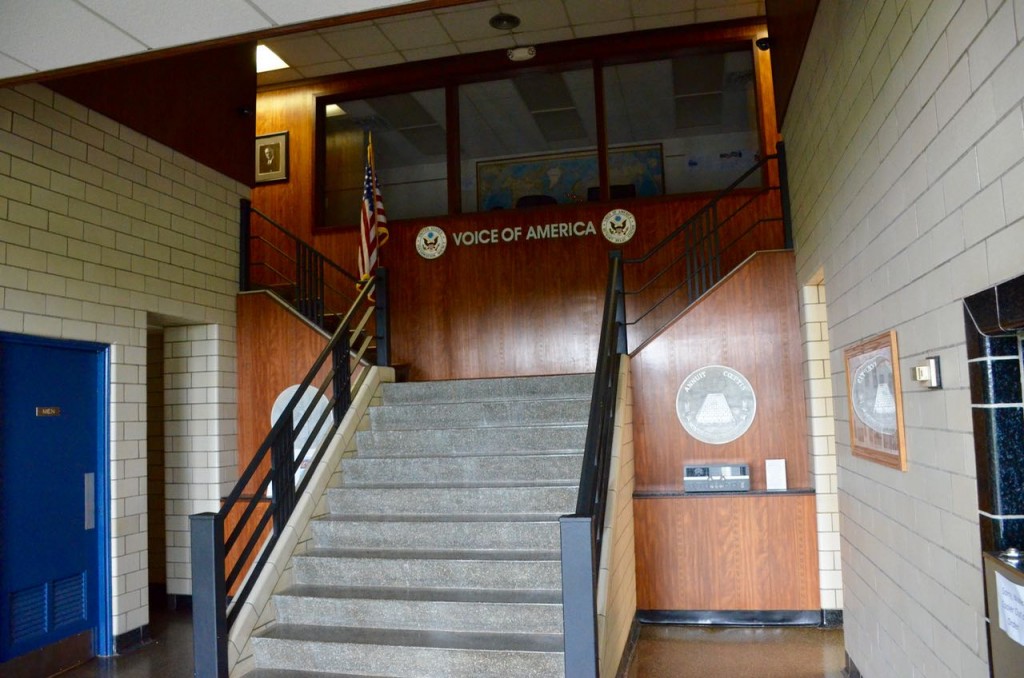
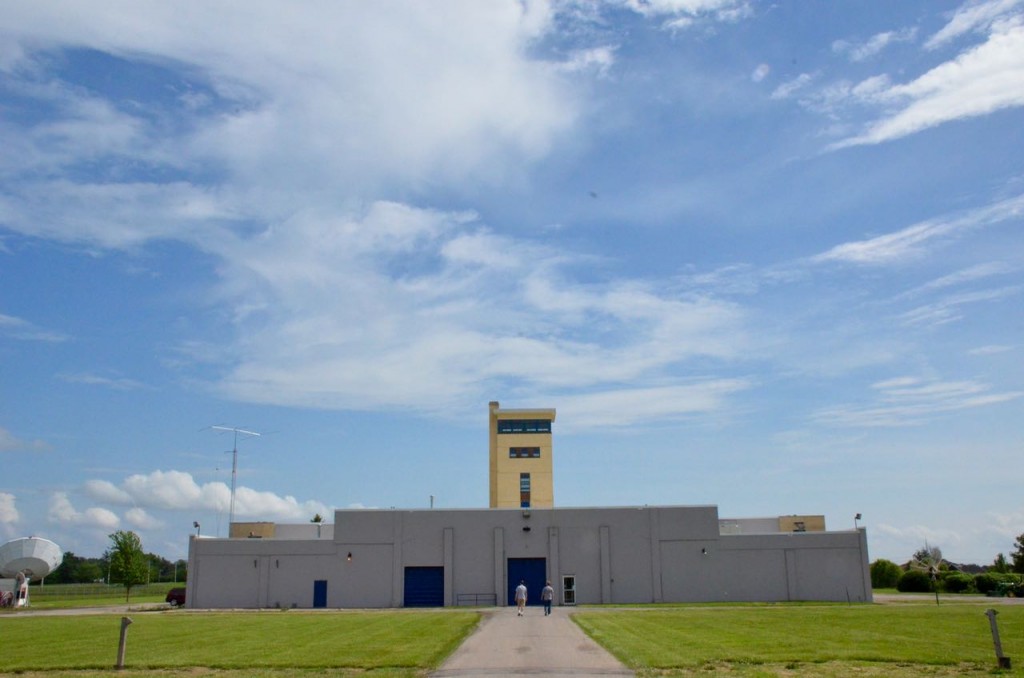
Main entrance and front lobby (above).
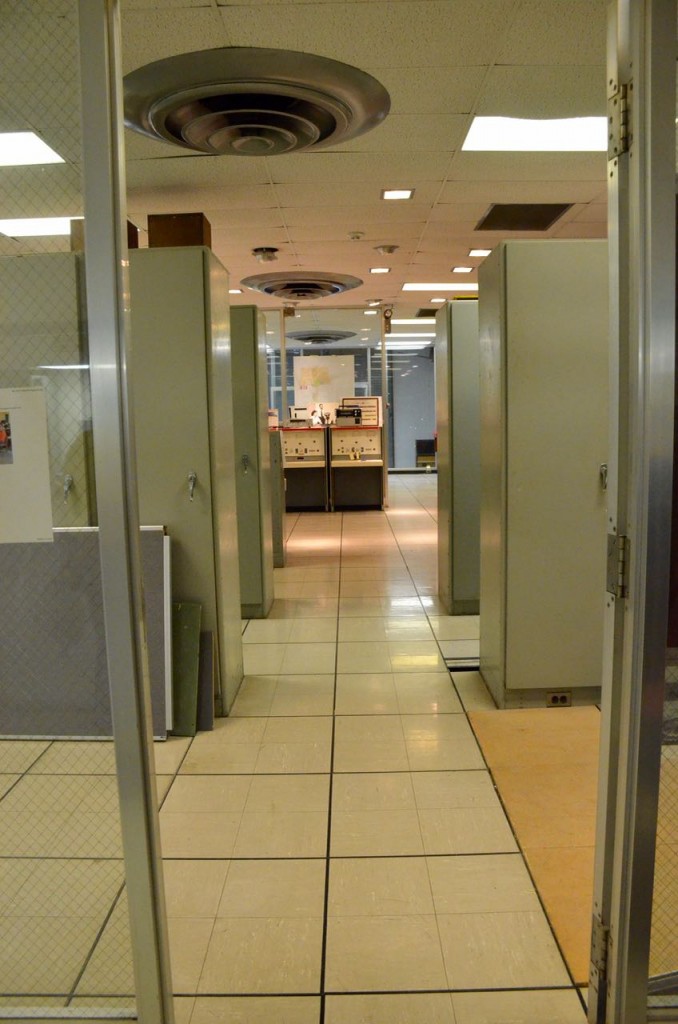

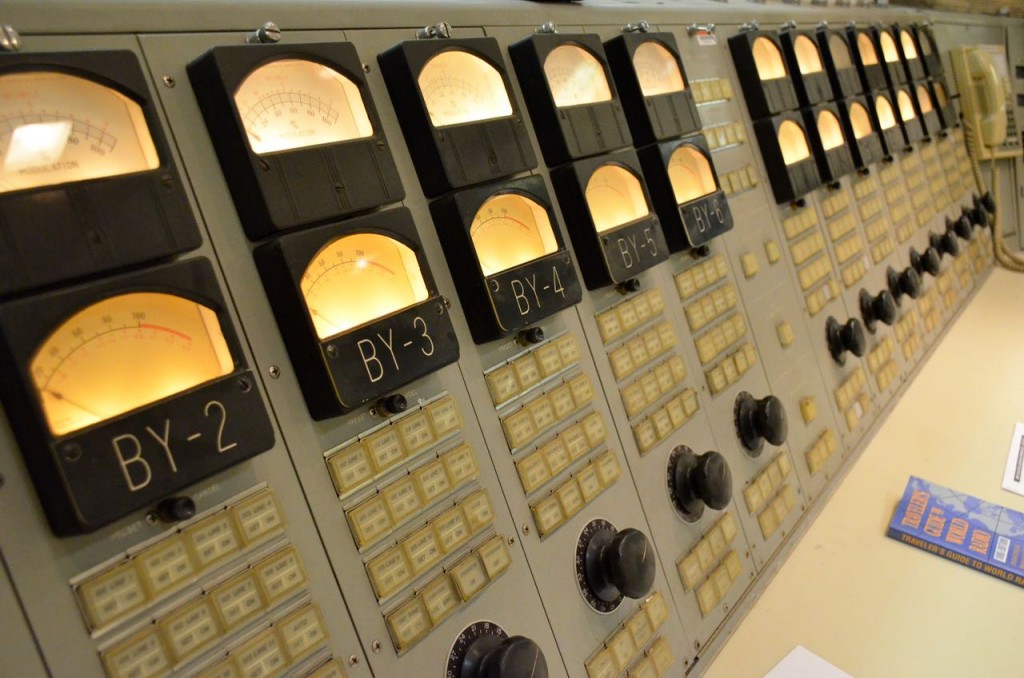
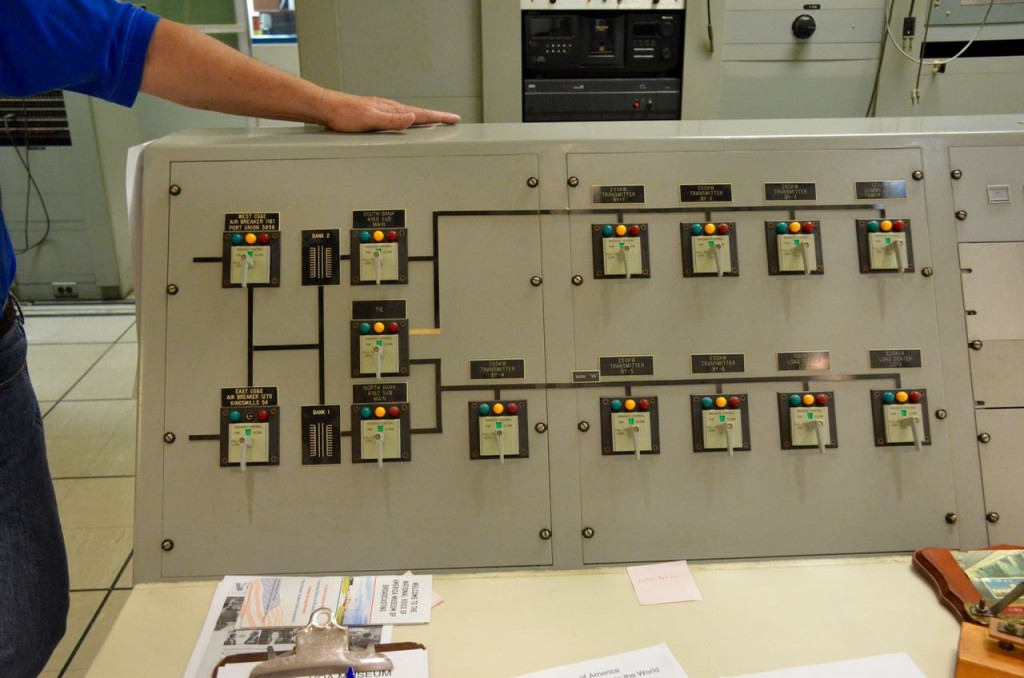
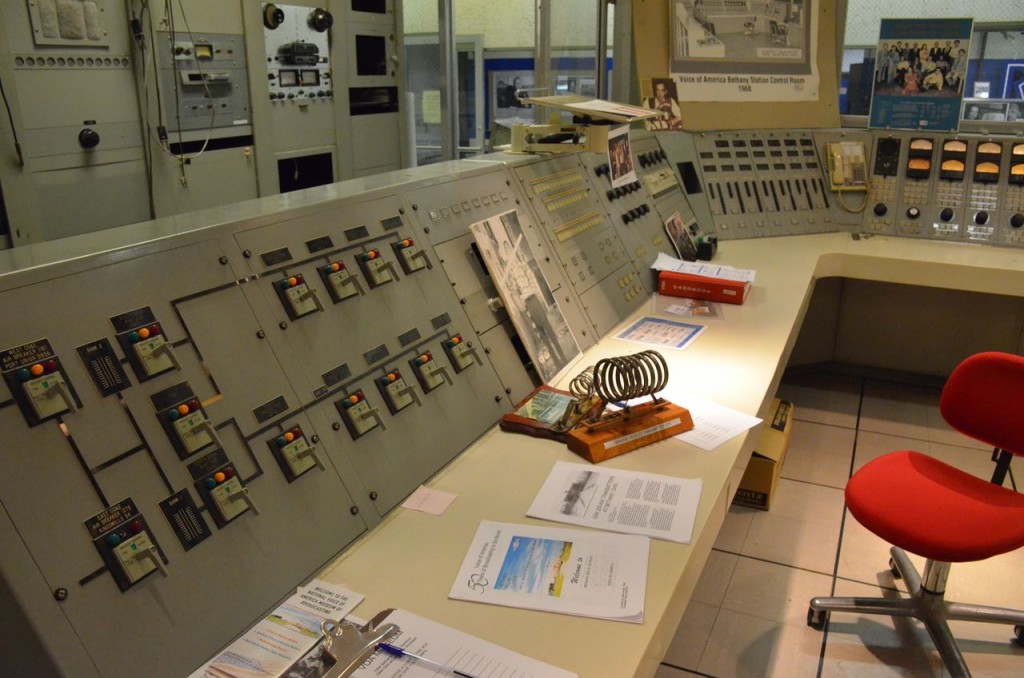
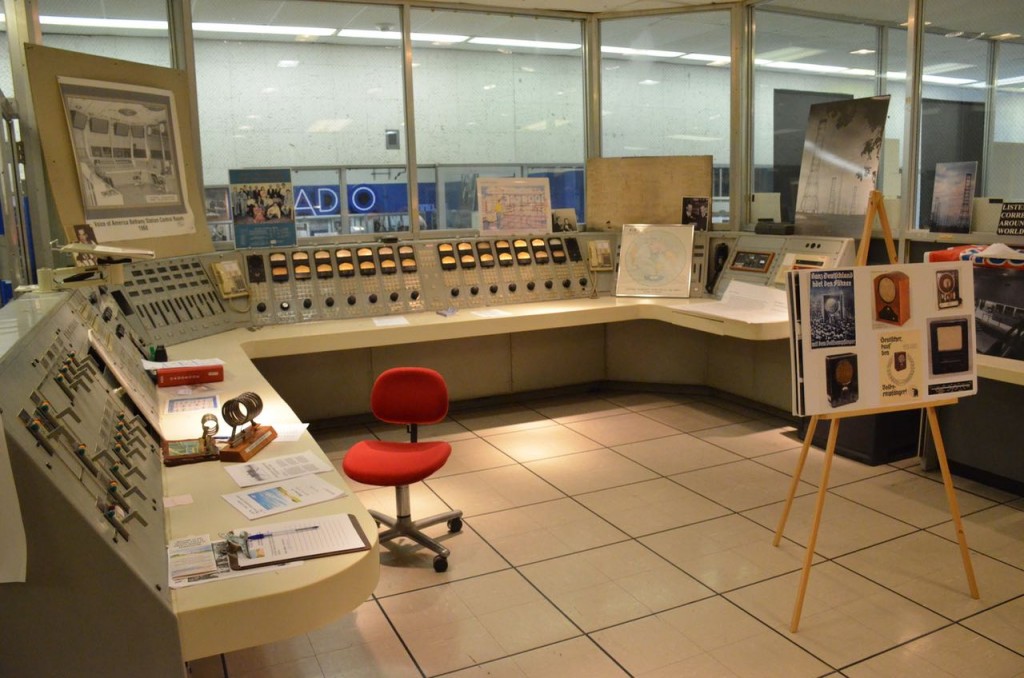
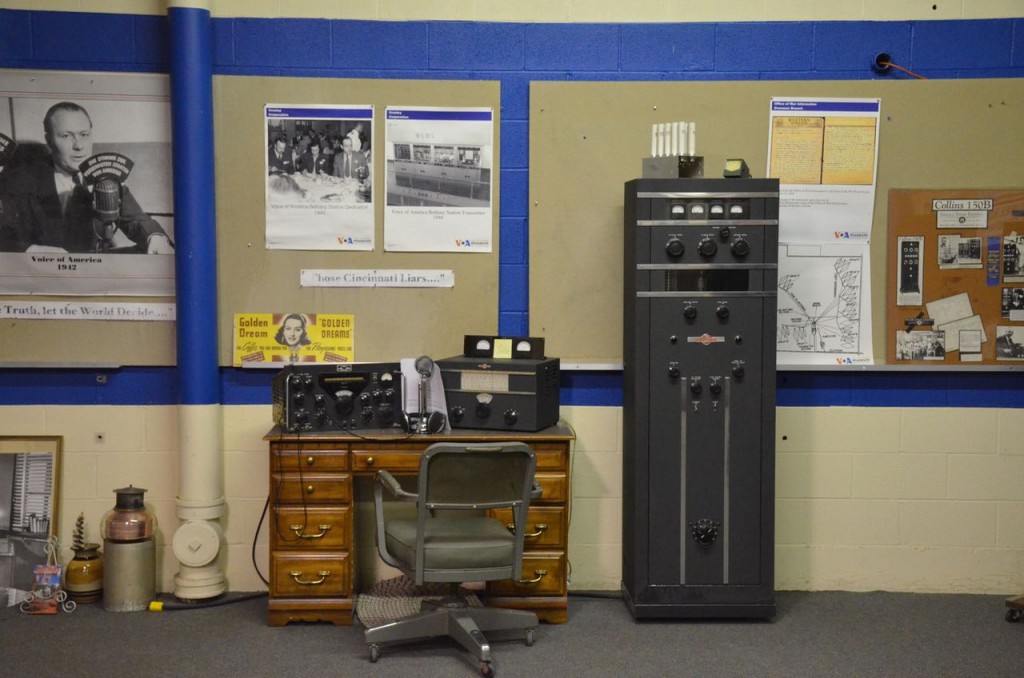
Entering the transmitter control room.
 Eric pointed out an article on the future of shortwave radio I published last year that the museum has posted in the hallway next to the control room (above). What an honor!
Eric pointed out an article on the future of shortwave radio I published last year that the museum has posted in the hallway next to the control room (above). What an honor!
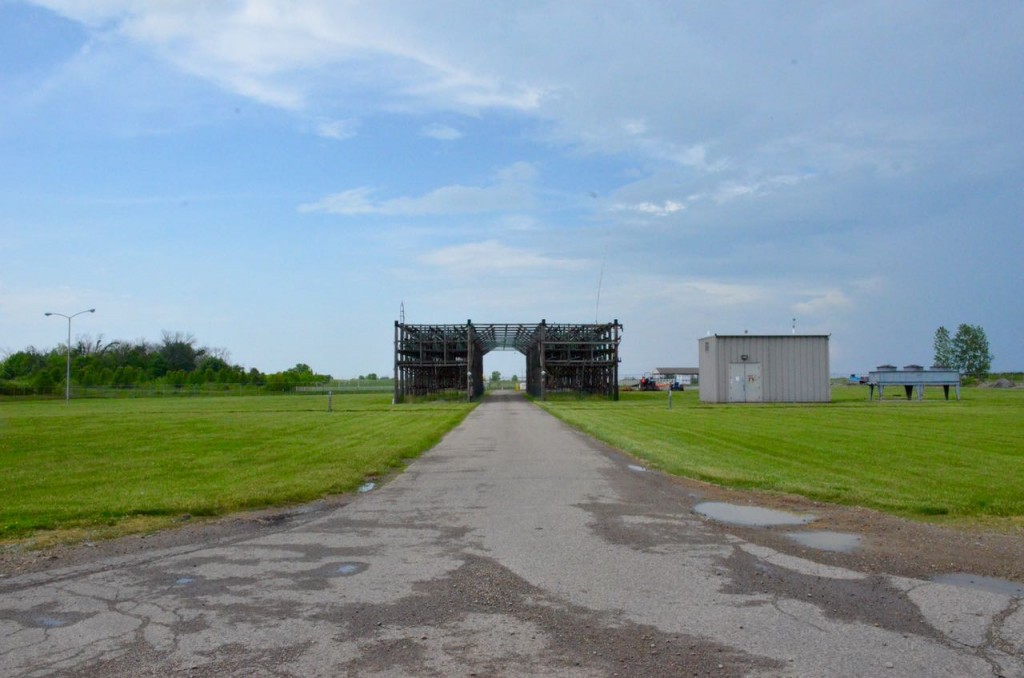
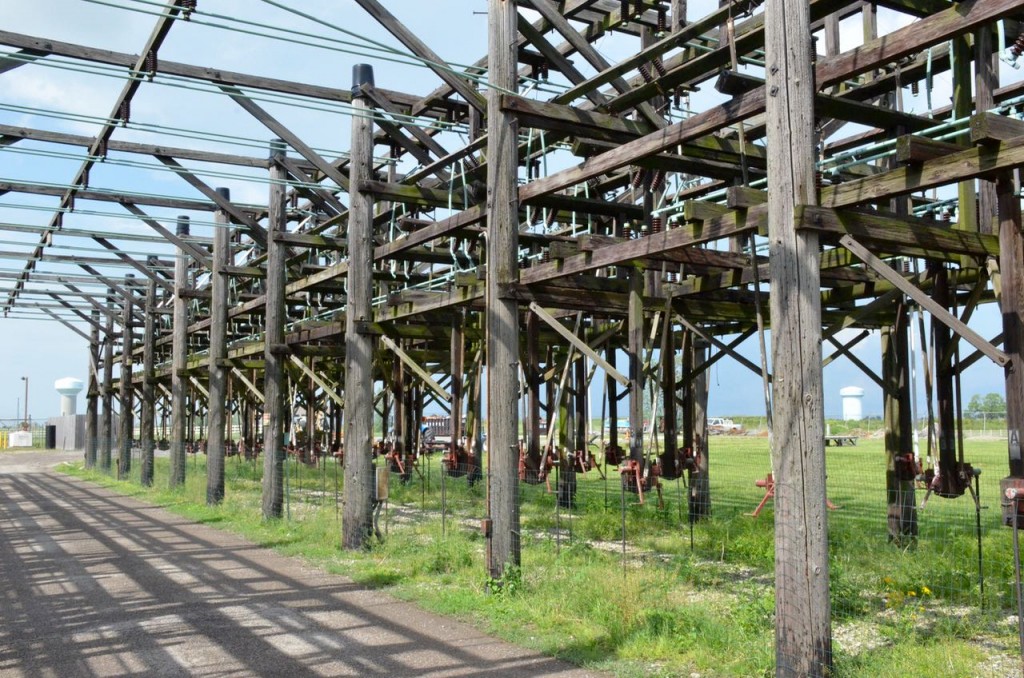
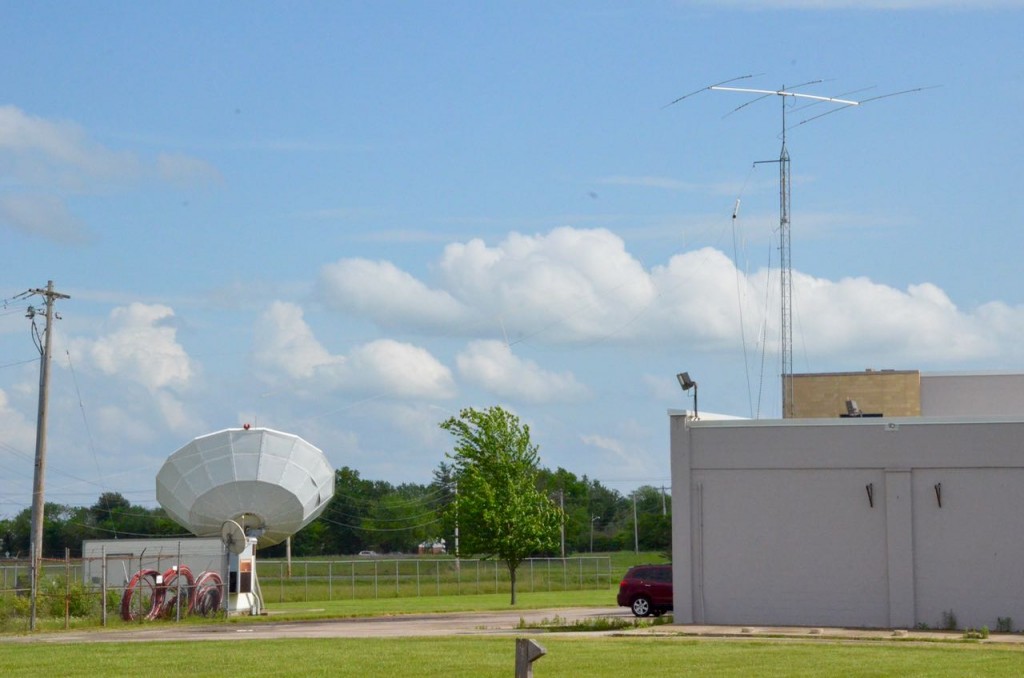
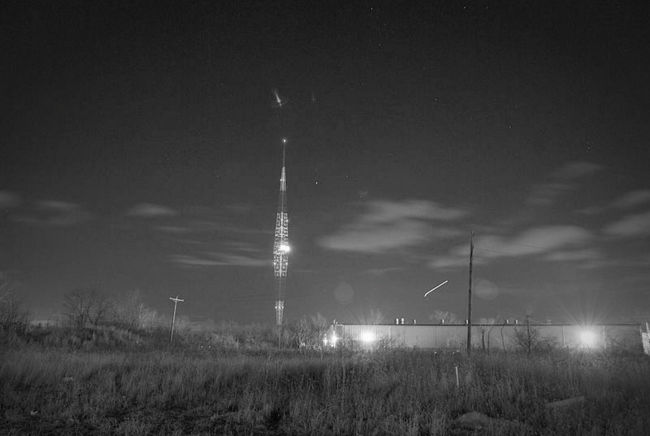
The antenna switching array behind the main building (following four photos).
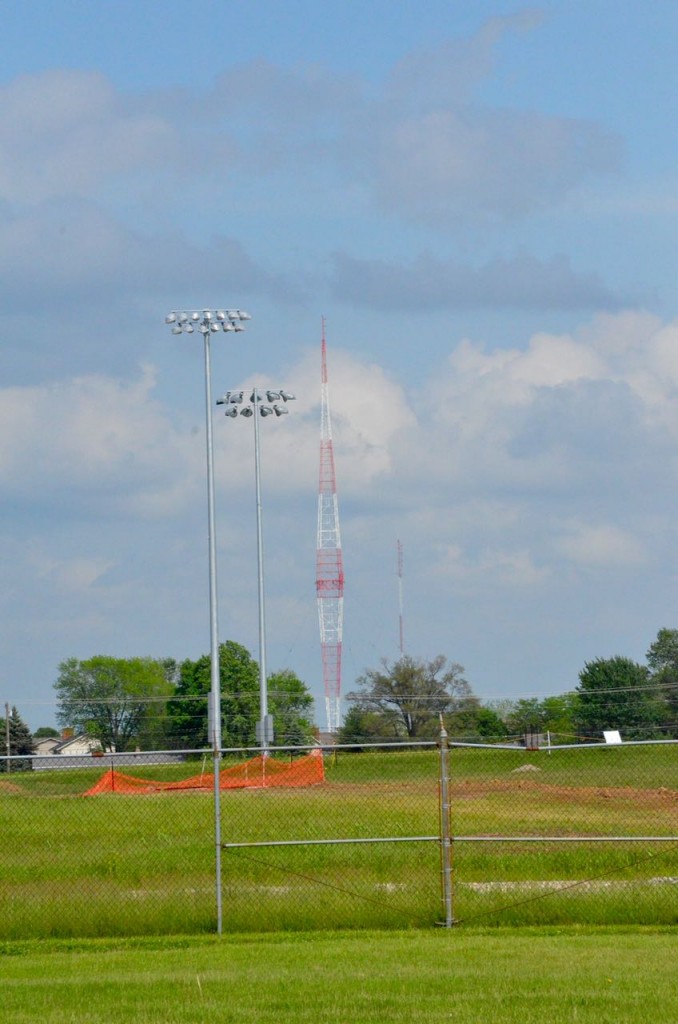
WLW (700 kHz) 800′ tower in the distance (above).
The satellite dish (above) was once used for VOA’s downlink/feed–now the West Chester Amateur Radio Association (WC8VOA) uses the dish for EME (Earth Moon Earth) contacts.
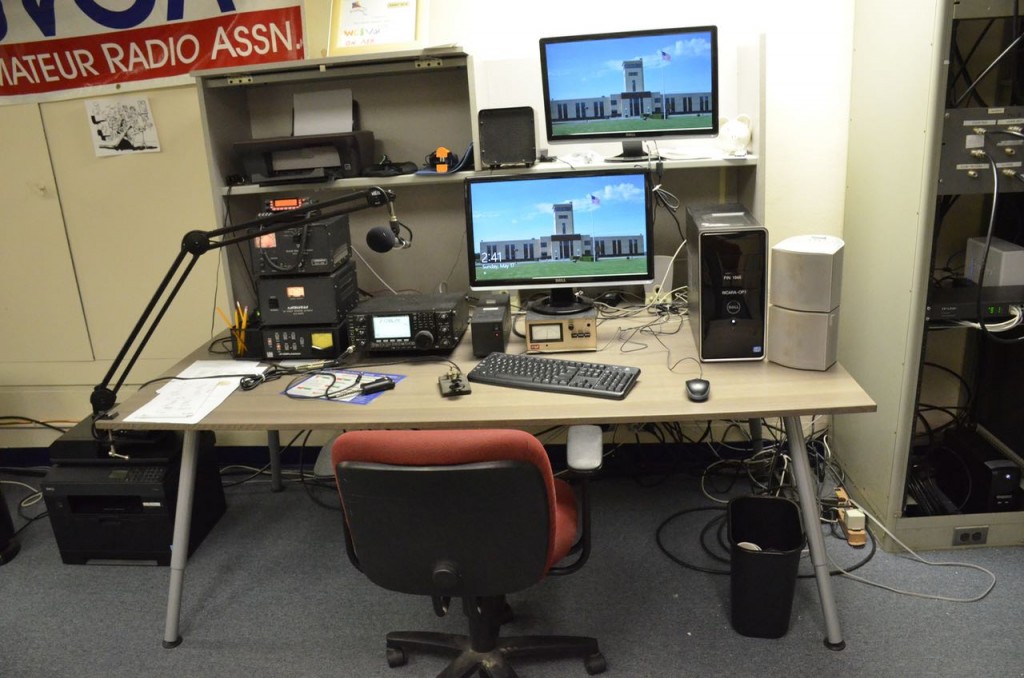
 Back inside, WC8VOA has four full amateur radio operating locations stocked with Icom, Yaesu and Kenwood gear. The club president told us that an antique amateur radio station will soon be added.
Back inside, WC8VOA has four full amateur radio operating locations stocked with Icom, Yaesu and Kenwood gear. The club president told us that an antique amateur radio station will soon be added.
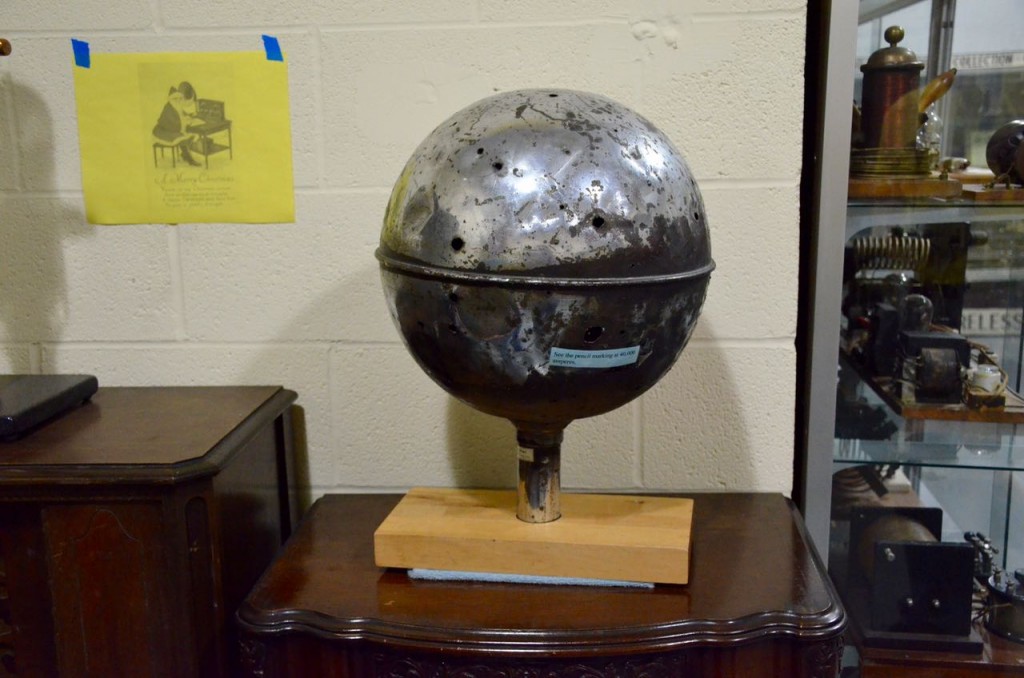
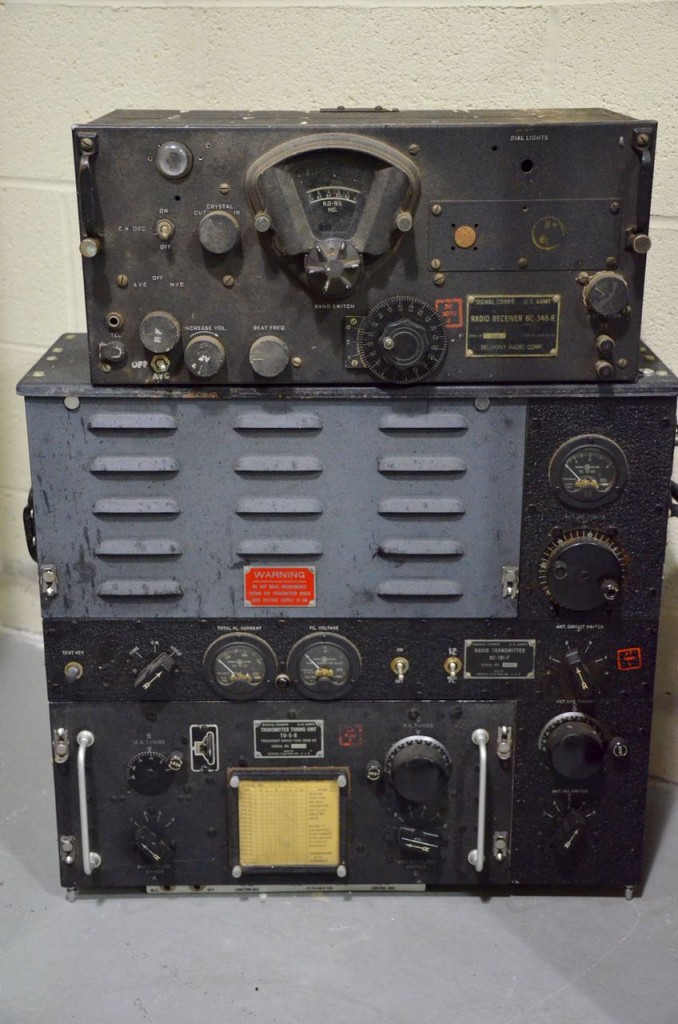
Our docent took us on a tour of two vaults filled with vintage radio equipment and then a museum devoted to the legacy of WLW. The item in the photo above is a corona ball from one of the original towers–notice the holes from lightning strikes.
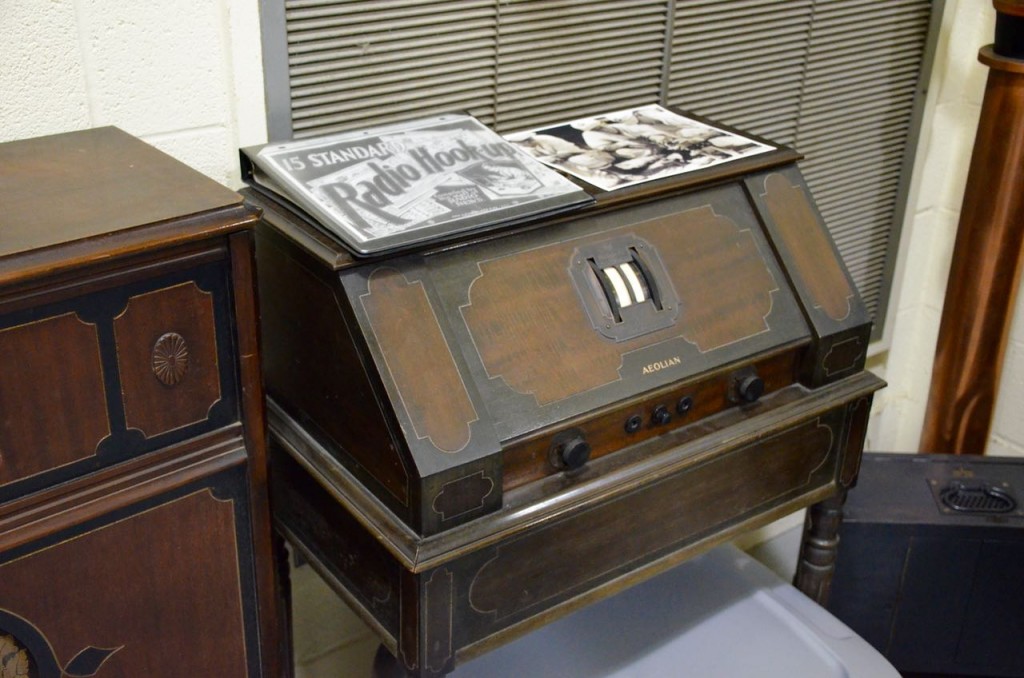
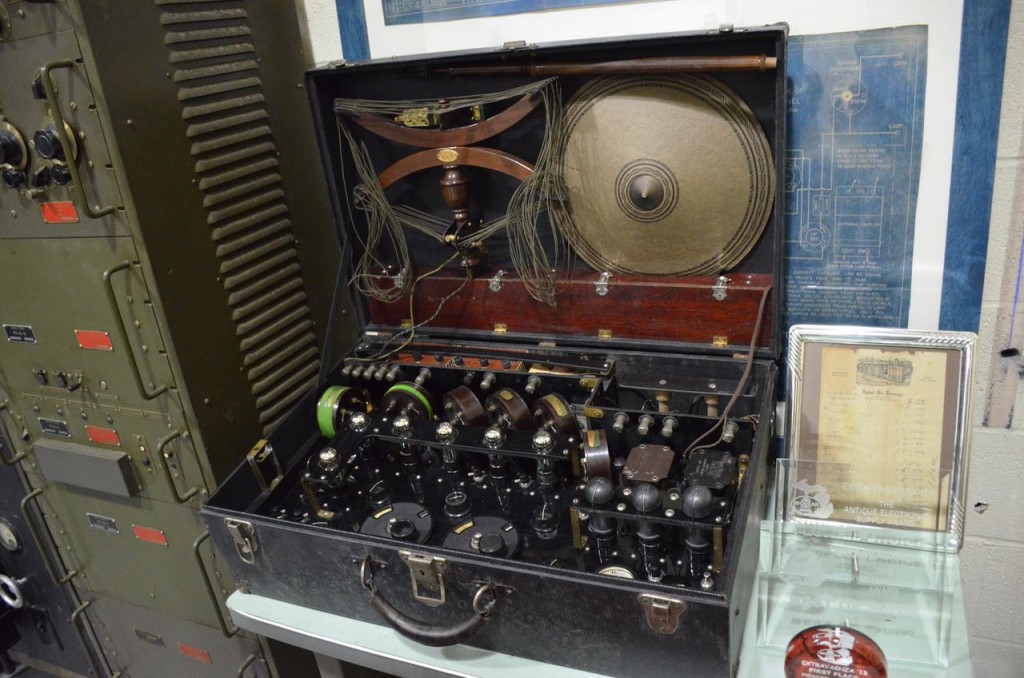
Example of an early radio kit (above).
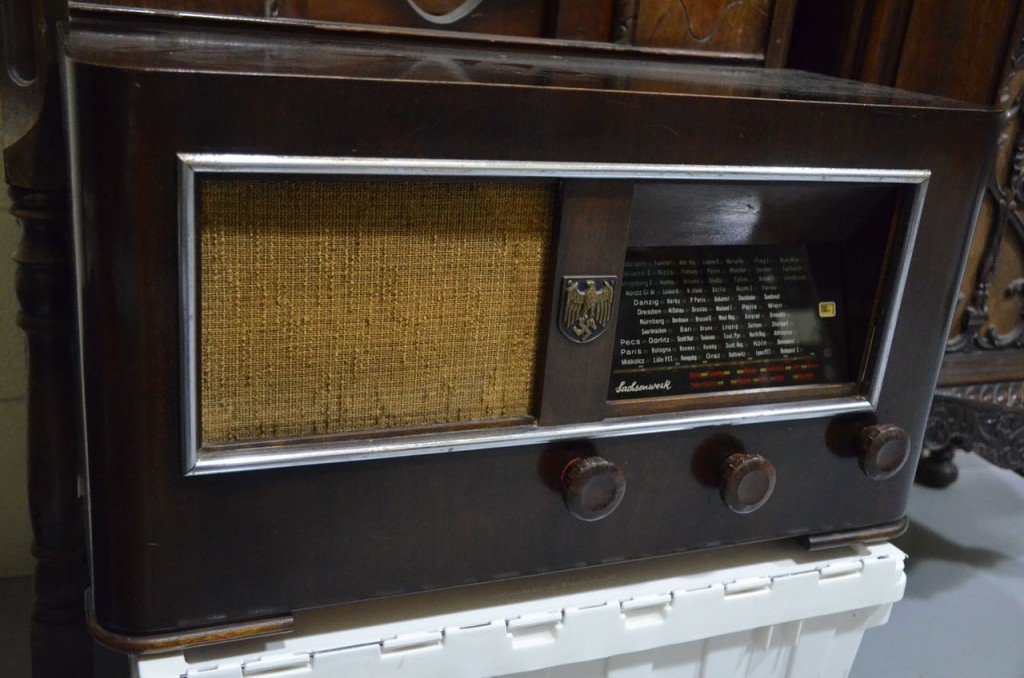
A rare Third Reich radio (above).
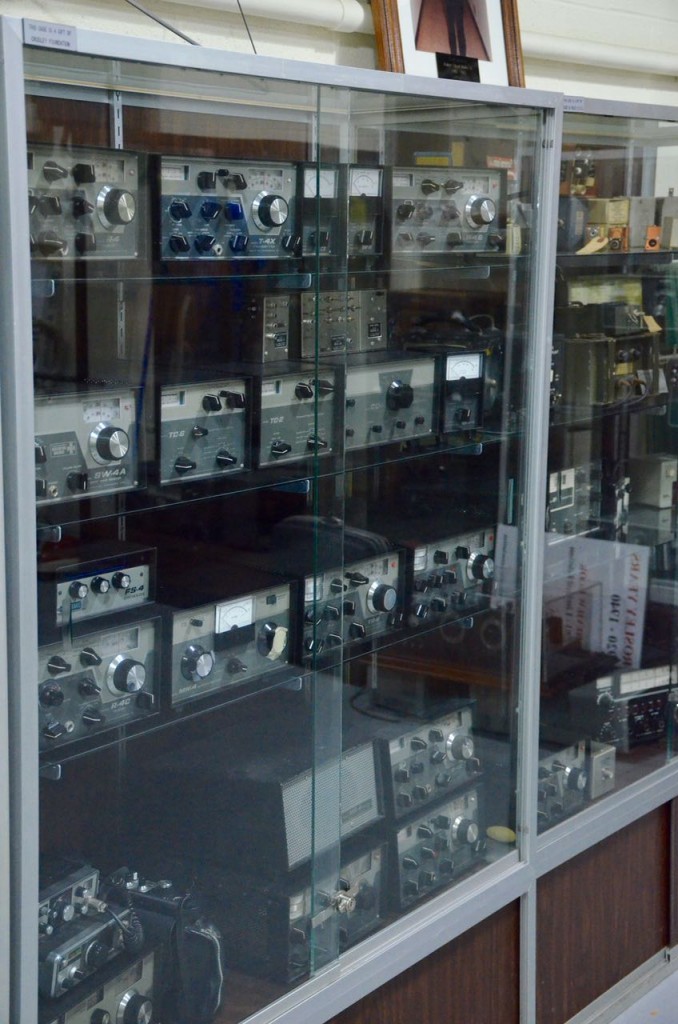
When Ohio-based R.L. Drake Company stopped manufacturing amateur radio equipment, samples of their full product line were donated to the museum.
The Museum is planning substantial renovations to restore the VOA Bethany Station and become a first class institution. During the restoration, the Museum is only open one day per month to the public: The third Saturday of each month from 1:00 PM – 4:00.