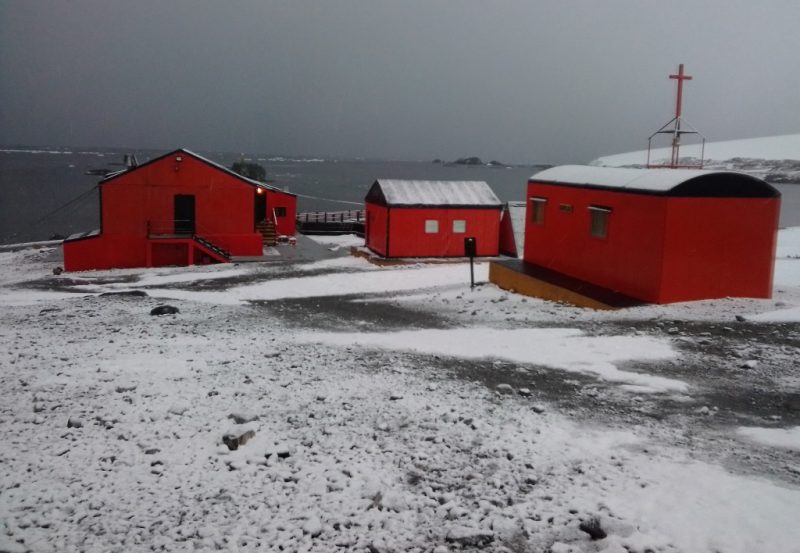
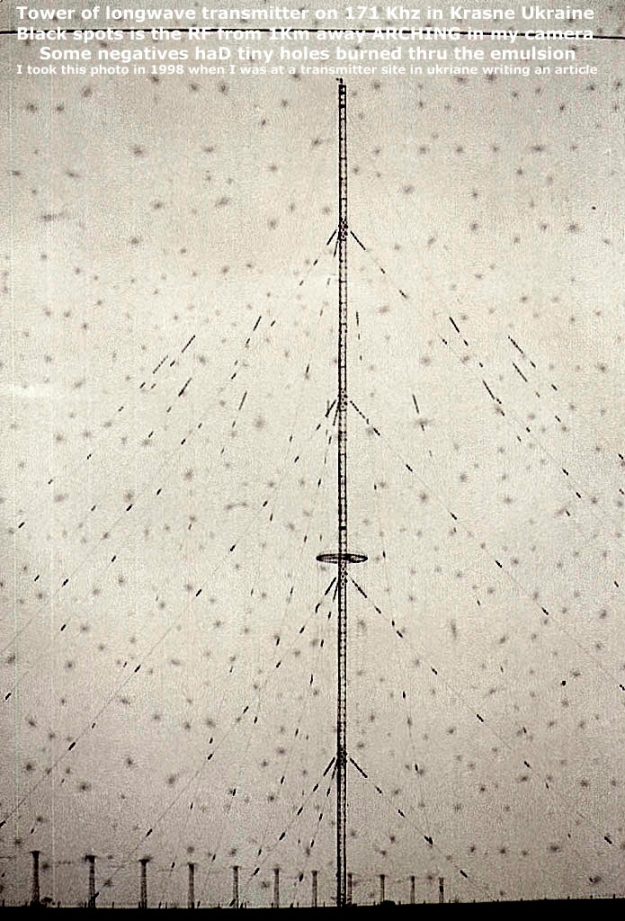
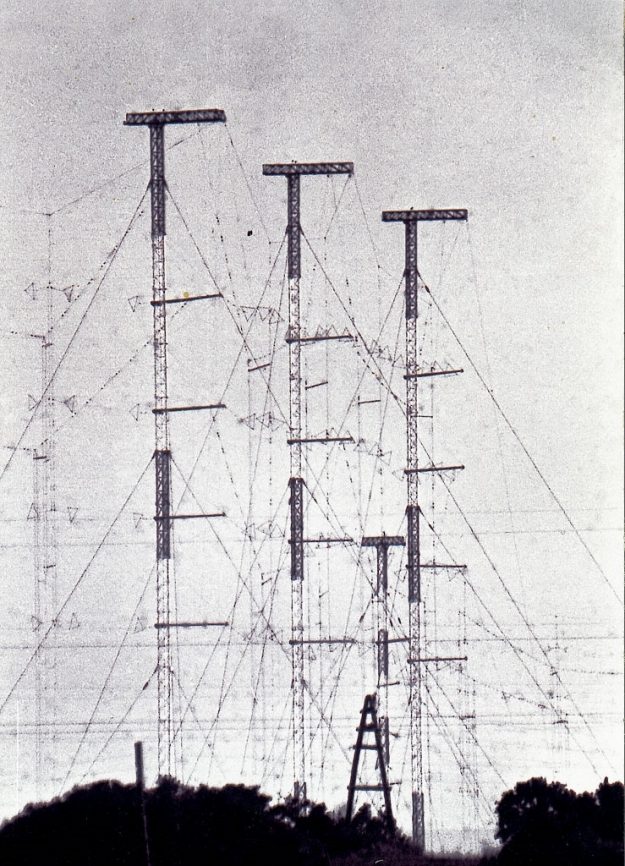
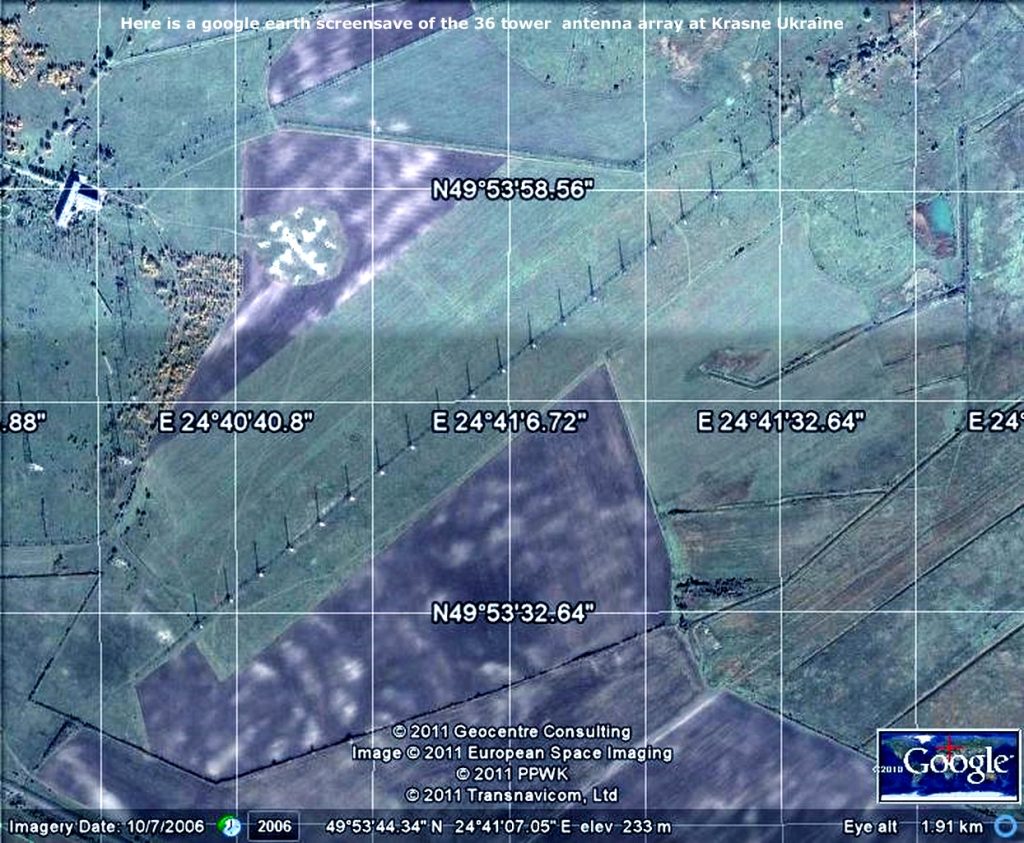
Source: Base Esperanza – Antártida
Many thanks to SWLing Post contributor, Tracy Wood, who writes:
I listened to LRA36 streaming this past Friday with their special show, including callouts to other Argentine scientific stations via satphone and lots of greetings by ham radio enthusiasts, both recorded and via live call-in.

Source: Base Esperanza – Antártida
…At the conclusion the announcer said they would be back this Monday at 1800 Buenos Aires time or 2100 UTC.
Details about last Friday’s broadcast:
http://www.radionacional.com.ar/continuan-las-emisiones-especiales-en-lra-36-arcangel-san-gabriel/

Source: Base Esperanza – Antártida
The audio stream is only up when LRA36 is on the air apparently but is at the Radio Nacional website under the audio streams listing:”
http://vmf.edge-apps.net/embed/live.php?streamname=sc_rad32-100131&autoplay=true
Thank you so much for sharing this, Tracy! It’s incredibly difficult for me to snag LRA36 broadcasts off the air, so it’ll be nice to have this stream link as well.
I also recently received a note about LU1ZV: the amateur radio station at the Esperanza Antarctic Base. What follows is a rough English translation of the press release. Click here to download the original press release in Spanish (MS Word Doc).

Source: Base Esperanza – Antártida
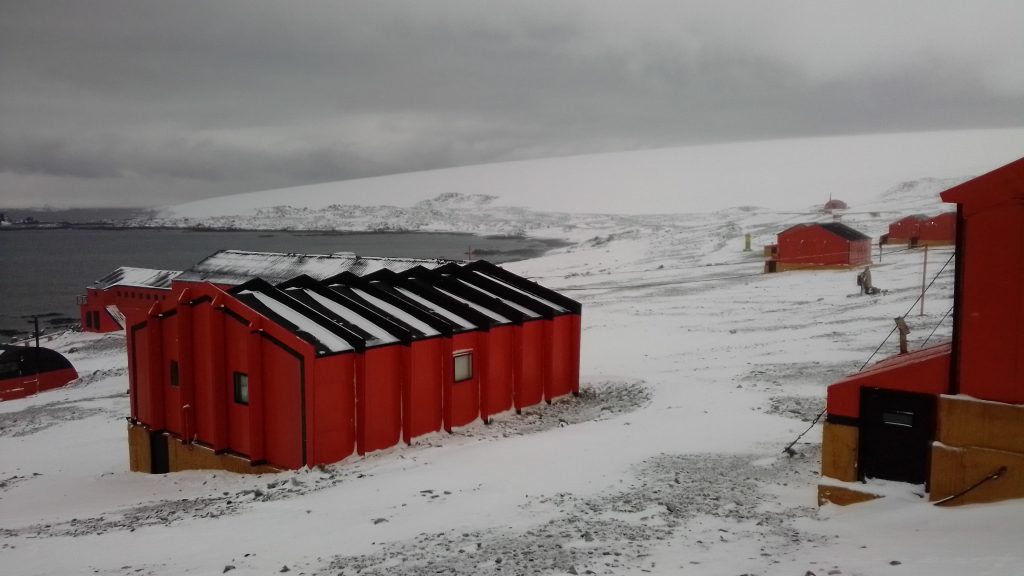
THE HAM RADIO ACTIVATION OF ESPERANZA ANTARCTIC BASE
Started on December 8, the activation of the LU1ZV amateur radio station of the Antarctic Base Esperanza, after years of being inactive.
The radio activity of LU1ZV has as primary objective to remember the 40th anniversary of the beginning of the transmission of the radio station LRA 36 “Arcángel San Gabriel” of the Esperanza Base, the first shortwave station in AM across Antarctica, which began broadcasting on October 20,1979. In addition, this activity seeks to maintain the continuity of emission of stations of radio amateurs from Antarctica.
The LU1ZV activation has registered more than 900 contacts with amateur radio stations
nationally and abroad, and in addition to covering all regions of the country, they have already

Source: Base Esperanza – Antártida
contacted twenty-two Argentine provinces.
Among the most relevant data that LU1ZV activity exhibits so far are the distant radio contacts (despite the low emission power) as in the case of Japan, Canada, Latvia, Ukraine and Finland among others. They have contacted most South American countries, several of Central American countries and all from North America.
Another outstanding contact was made with VP8HAL, the Halley VI scientific station of the British Antarctic Survey (BAS), located in the Brunt Ice Barrier, about 1,700 km SE of Hope.
The operation of LU1ZV is carried out from the study of LRA 36 and the rhombic antenna of the station, while the station isn’t operating. The amateur radio station activity adapts to the general schedule of the base and of LRA36, so activation times are reduced to a few hours during the evening – night.
The Head of Hope Base, Lieutenant Colonel Norman Walter Nahueltripay was present during some contacts and received greetings from radio correspondents.
This special activation also includes the project “Uniendo Voces” of the National University of Quilmes (UNQ) of the province of Buenos Aires, an initiative that included areas of interest to amateur radio and Antarctic activations, and which was presented to the
Antarctic Joint Command (COCOANTAR).
“Uniendo Voces” has participated in these radio activations since 2013 (in Marambio Base and Matienzo) to which the historical emission from Base Esperanza is now added, within the framework of a special initiative called “DX Radial Expedition Uniting Voices”.
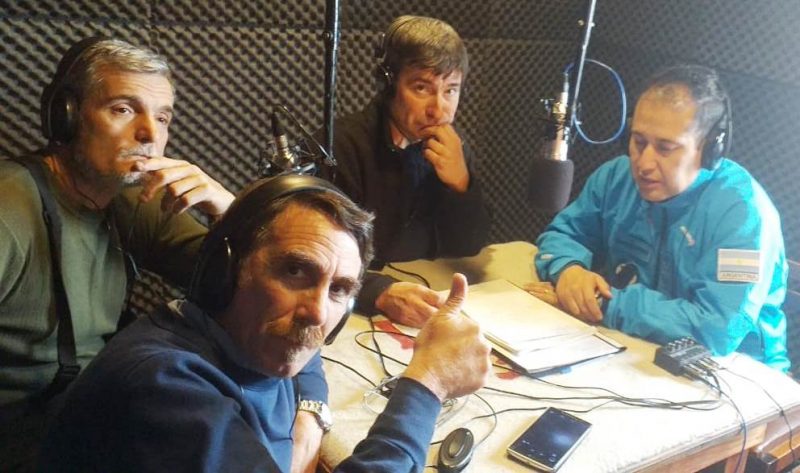
The amateur Radio Claudio García (LU1VC) member of the LRA 57 Radio Nacional de El
Bolsón (province of Chubut) and Juan C. Benavente (LU8DBS) of COCOANTAR and UNQ, perform the activation for which they had to move equipment to that Antarctic base.
The radio activation of Esperanza has the support and collaboration of Adrián Korol,
director of the Argentine Broadcasting Abroad (RAE) who expressed his emotion and
satisfaction for “this joint achievement with the Antarctic Command and the National University of Quilmes. “
Antarctic bases are licensed by amateur radio stations, and like all the activity, is regulated by the National Communications Agency (ENACOM). These radio activations have a “high symbolic and real value”, as Korol says, and they contribute, in addition to remembering ephemeris, to the promotion of sovereignty in the Antarctic region from the radio spectrum.
Likewise, the amateur radio activity contributes to the study of communications – such as
radio wave propagation conditions- and keeps an alternative communication service active and effective.
Many Argentine radio amateurs from different parts of the country are attentive to the
calls from LU1ZV and collaborate with the initiative.”
Along with the photos and LU1ZV press release above, I also received press releases from two special broadcasts that happened earlier. Click here and here to download the MS Word documents in Spanish.