 Many thanks to SWLing Post contributor Fred Waterer who shares this article from Radio World that takes a closer look at how online SDR networks have transformed shortwave listening. Even for those of us who regularly use Web SDRs, it’s an interesting perspective on how these global receiver networks continue to evolve and expand the reach of radio in the 21st century.
Many thanks to SWLing Post contributor Fred Waterer who shares this article from Radio World that takes a closer look at how online SDR networks have transformed shortwave listening. Even for those of us who regularly use Web SDRs, it’s an interesting perspective on how these global receiver networks continue to evolve and expand the reach of radio in the 21st century.
Tag Archives: KiwiSDR
Bob’s Radio Corner: Pairing a Phone or Tablet with a Radio
 Pairing a Phone or Tablet with a Radio
Pairing a Phone or Tablet with a Radio
By Bob Colegrove
The Internet is full of resources for radio listeners and hobbyists. There are numerous examples of general information, frequency, and schedule lists. There are also WebSDR sites, which allow you to compare reception experiences from around the world. All of these can be accessed quickly and easily by having them loaded on your phone or tablet operating side-by-side with your radio and having Wi-Fi or cellular access. We never had any of this when I was starting out.
I realize there are other ways to go about what I have described below, for example, merging station listings with SDR. This posting is for folks like me who are SDR-challenged. I listen to plain old radios. My modern-day experience with newfangled technology has been limited to hitchhiking on WebSDR sites for the last few years. It has served me well.
Ideally, I would like to generalize this topic to simply cover all phones and tablets. In truth, my experience has been limited to an iPhone and Kindle Fire tablets. They have worked very well as I shall explain. Perhaps you have paired a different phone or tablet with your radio, in which case, feel free to share your experience.
The choice of a phone or tablet is yours. Either works well. Your decision will be affected by what you have available and what is easier to use. If you intend to buy a new device and associate it with your radio, cost will be an additional factor.
A noteworthy device (the one I tend to favor) is a Kindle Fire. Mainly, they are cheap. The regular price of a 7-inch model is just under $60 and can often be purchased for less during Black Friday and Prime Day sales. It is versatile, possessing all the usual functions except for cellular access. Perhaps most importantly, it is virtually noise-free. For a while I struggled using Internet sources on a laptop computer. Even a good one located about 10 feet away from the radio antenna generates noise. On the other hand, I have taken a 7-inch Kindle Fire in hand and placed it against the resonant coil of a loop antenna. This abuse generated no more disturbance to the antenna than if it were a block of pinewood. I have noticed some slight noise from the 11” Kindle when the antenna is exposed this way, but when that tablet is held at arm’s length from the antenna, all is well. Recently, I have expanded this application to my iPhone and found its noise immunity matches that of the Kindle Fire 7.
Broadcast Schedules
The most useful Internet resources are the broadcast schedules. These are the comprehensive frequency-time-station listings that tell us where and when to tune. There are many good ones. My favorites are the EiBi listing http://www.eibispace.de/, and Dan Ferguson’s https://groups.io/g/swskeds/topics. For the latter you will need to request membership. SWskeds merges EiBi, Aoki (https://www1.s2.starcat.ne.jp/ndxc), HFCC (https://new.hfcc.org/index.php), as well as other sources into a single list.
Processing
The EiBi listing comes as a CSV-formatted text file, which can be imported into a spreadsheet. I have done some processing using spreadsheet functions to produce a customized listing. Processing the frequency-time-station lists is most conveniently done using a computer rather than the phone or tablet. Processing includes selecting, arranging, or filtering the downloaded data tailored to your needs. This might include adding a filterable column to indicate only stations that are on at the current time. Some users might favor filtering by country or station. The heavy lifting processing is done automatically whenever a new listing is published by simply dropping the new file into the existing spreadsheet. No, the functionality of a spreadsheet and ease of editing are not as good on a tablet as with the mouse and keyboard of a computer. My processing on the computer includes measures to optimized the screen view to the most essential information thus minimizing the amount of scrolling on the tablet.
After the files are downloaded and processed, they can be loaded on the phone or tablet in a couple of different ways. They can be directly transferred over a USB cable, or they can be transferred using a cloud server. The USB cable-transfer method may be difficult on some devices, particularly iPhones. The Kindle seems to be the more convenient device. Being an obedient Microsoft customer, I can also transfer the files from my computer to OneDrive, then pick them up on the Kindle or iPhone using the OneDrive and Microsoft 365 apps which are available for both phone and tablet.
Examples
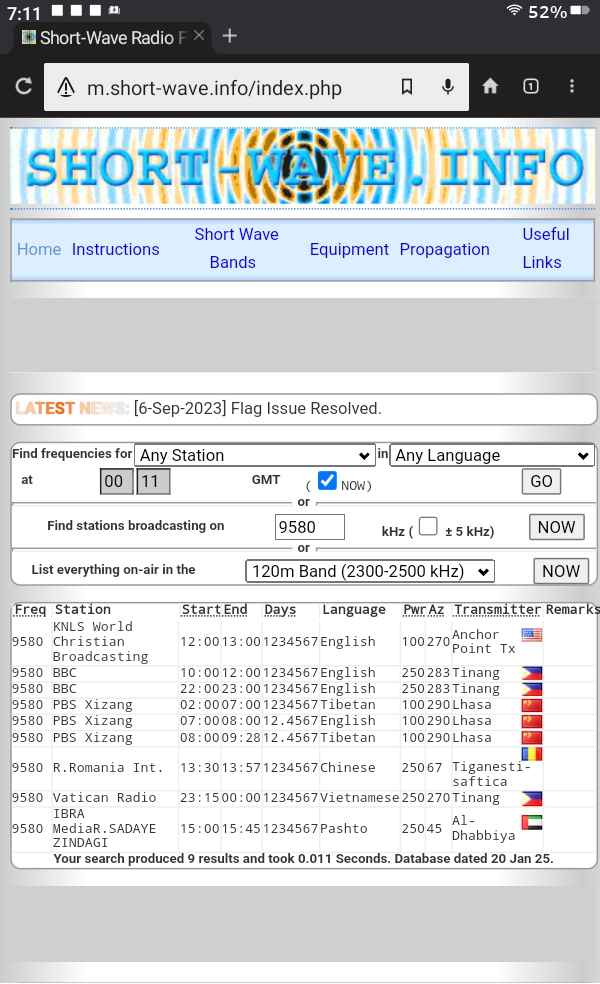
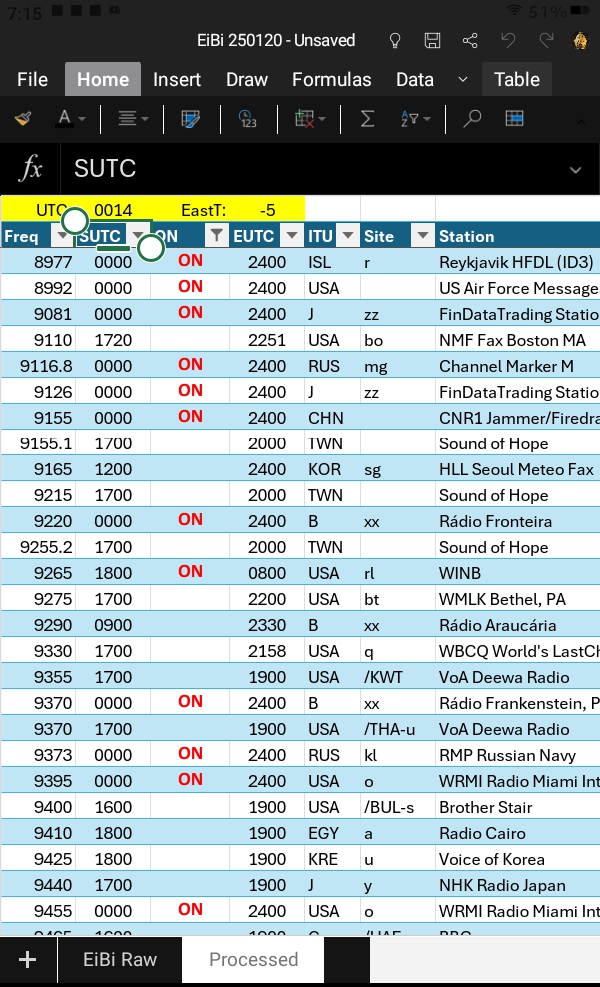
The screenshot below shows an EiBi example at 0014 UTC. Although the “ON” column filter is set to show only transmissions currently “ON,” it had not been manually updated on the Kindle for a couple hours and thus includes listings from a previous time. The EiBi database does not include transmitter power or beam information. However, the identification of countries and transmitter sites is extensive. These are determined by downloading and printing the README.TXT file on the EiBi site.
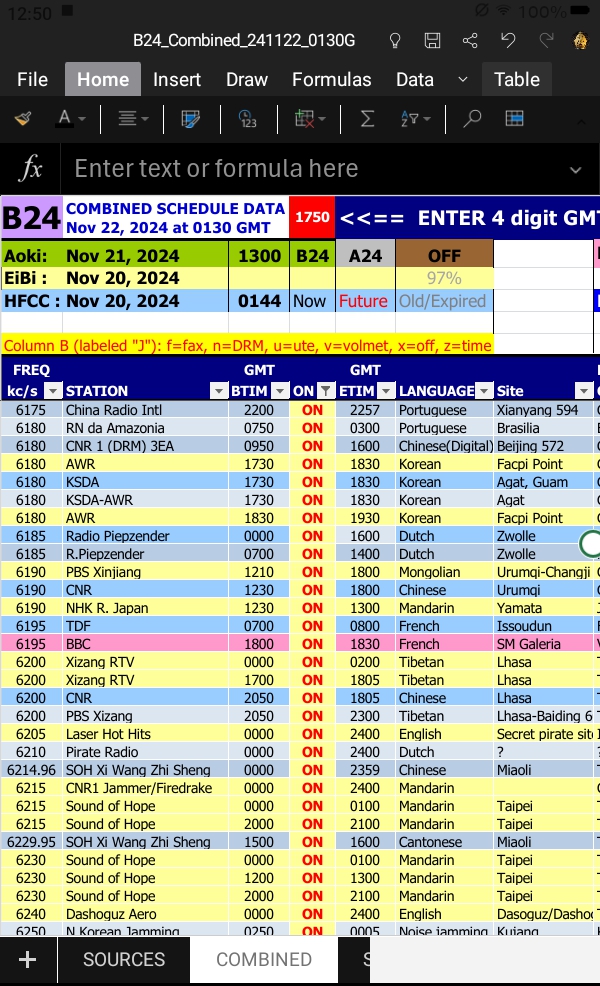
 The SWSkeds listing is available in both CSV and Excel formats. It contains several additional data fields, very importantly including transmitter power and beam direction when available. For this list, I make the simple conversion of the existing Excel data range tab, “COMBINED” to a table so I can easily apply filters. The screenshot below shows an example at 1750 UTC with the “ON” column filtered to “ON.”
The SWSkeds listing is available in both CSV and Excel formats. It contains several additional data fields, very importantly including transmitter power and beam direction when available. For this list, I make the simple conversion of the existing Excel data range tab, “COMBINED” to a table so I can easily apply filters. The screenshot below shows an example at 1750 UTC with the “ON” column filtered to “ON.”
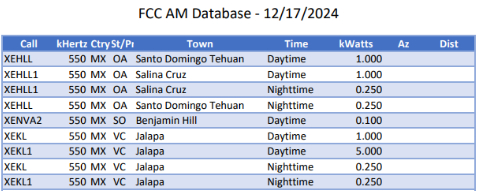
 Not to be left out, the complete medium wave broadcast station list for Region 2, the Americas, is easily downloadable at https://www.fcc.gov/media/radio/am-query. The entire database is formidable and contains nearly 600 pages in a printable format. Much of this bulk is due to the doubled size necessitated by giving both daytime and nighttime power separate entries for each station. A number of marginally useful data columns can be eliminated in spreadsheet processing. I have added formulas to calculate the azimuth heading and distance from my listening post (blanked out in the example below).
Not to be left out, the complete medium wave broadcast station list for Region 2, the Americas, is easily downloadable at https://www.fcc.gov/media/radio/am-query. The entire database is formidable and contains nearly 600 pages in a printable format. Much of this bulk is due to the doubled size necessitated by giving both daytime and nighttime power separate entries for each station. A number of marginally useful data columns can be eliminated in spreadsheet processing. I have added formulas to calculate the azimuth heading and distance from my listening post (blanked out in the example below).
 A variation of the downloadable file format is the direct-query site, SHORT.WAVE.INFO. Here you can simply enter queries by station, language, frequency, or band, and produce listings which match your criteria. Any listings which are currently on the air will be highlighted in red.
A variation of the downloadable file format is the direct-query site, SHORT.WAVE.INFO. Here you can simply enter queries by station, language, frequency, or band, and produce listings which match your criteria. Any listings which are currently on the air will be highlighted in red.
WebSDR
Finally, I would like to mention the WebSDR sites. While not used explicitly for broadcast schedules, these sites are great for anyone wanting to compare how well they are receiving signals relative to what others are experiencing. Granted, location and time of day are big factors that affect reception, but it is still useful to make these relative comparisons.
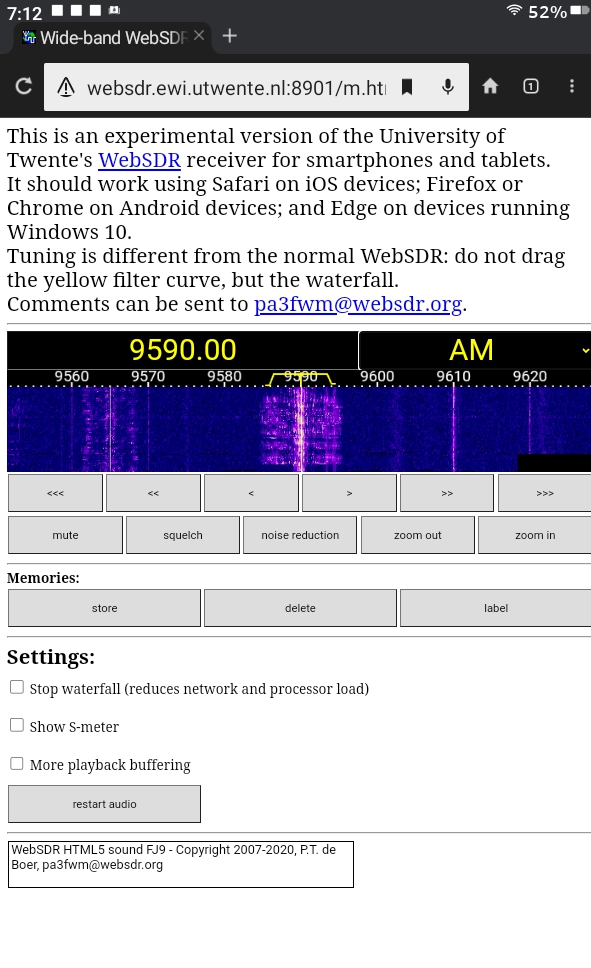
Home base is http://websdr.org/ which presents a catalog of many WebSDR sites by location. At the bottom of the page is a world map which pinpoints the location of each site. Most of these sites cater exclusively to hams; however, The University of Twente, Enschede, Netherlands (http://websdr.ewi.utwente.nl:8901/) covers 0.000 to 29.160 MHz unabridged. The screenshot below shows the tablet/phone version of the U. of Twente site. There are also two sites on the US East Coast which cover some non-hamband portions of the SW spectrum: http://na5b.com:8901/ in the Washington, DC area and http://websdr.k3fef.com:8901/ in Milford, Pennsylvania. The SHORT.WAVE.INFO and WebSDR sites can be directly accessed and queried over the tablet’s browser and a Wi-Fi or cellular connection.
Using the System
In my relentless pursuit to log the Nibi-Nibi Islands, I will load up one of the frequency-time-station listings and start my DX session. This typically includes a scan of a particular band, checking signals I can receive against the lists. If my interest peaks on a particular catch (usually a weak one), I will switch the tablet over to a WebSDR site to see how it is being received in Europe or along the East Coast of NA.
In summary, ready access to these Internet resources using a phone or tablet next to the radio has notable advantages:
- The frequency-time-station listings provide quick, reliable signal identification in most cases.
- The WebSDR sites confirm that my antennas are doing their job.
Am I done? I hesitate to stop here. The process of discovery is a marvelous human experience. The foregoing are merely starting points. Other applications might include sunrise-sunset calendars or maps or propagation forecasts. There are certainly other ways to do all this depending on your druthers. I know I am erring by omission and neglecting many other good resources. Let’s hear about yours.
Frank’s take on WebSDRs and the SWL Contest that encourages use of them
 Many thanks to SWLing Post contributor, Frank, who writes:
Many thanks to SWLing Post contributor, Frank, who writes:
Hi, I am Frank SWL F14368, organizer of the SWL Contest 2024. I have written an article [about the use of WebSDRs]. Maybe you like to share on your nice website for SWL ?
https://icomjapan.blogspot.com/2023/12/listen-world-for-free-on-your-computer.html
My contest is open to listeners who use a Kiwi or a WEB SDR. Not many contest accept this.
Thank you very much.
Best regards
73 de Frank SWL F-14368 / FØDUW
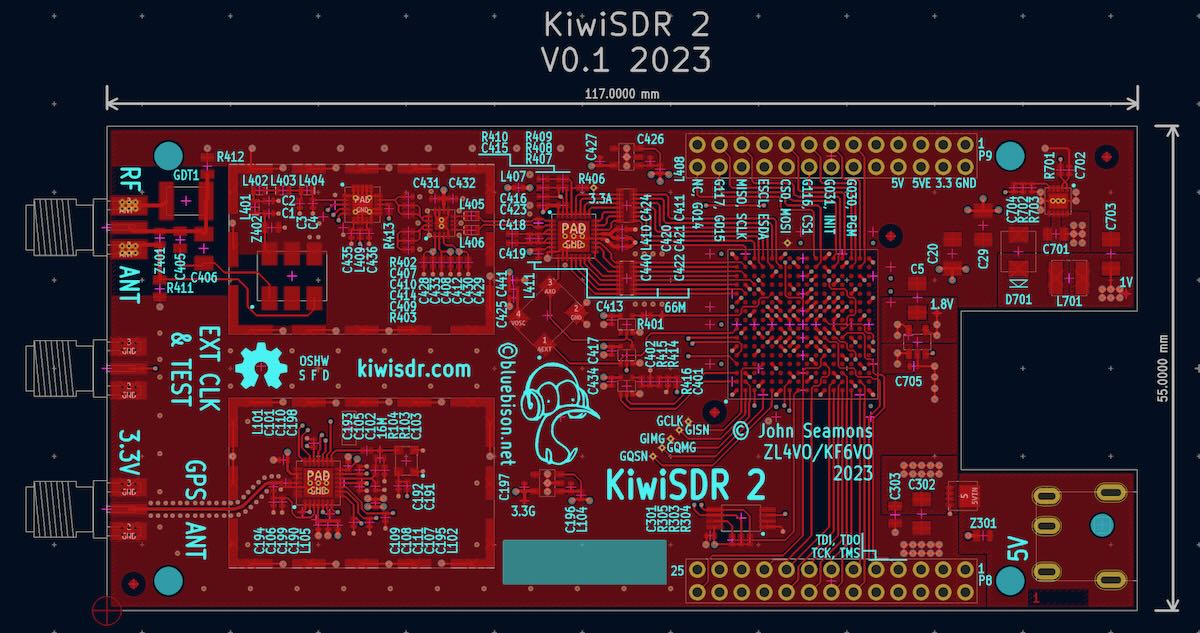
KiwiSDR 2 on the horizon…
A number of SWLing Post readers have shared a link to this post by KiwiSDR creator John Seamons on the KiwiSDR forum. In it, he (somewhat reluctantly) describes a new version 2 of the KiwiSDR that is in the works.
John writes:
I don’t like to announce something before it’s ready. But my hand is being forced.
So please consider this a pre-announcement. There are no guarantees.
The PCB and bill-of-materials (BOM) are finished and ready for prototype construction.
The problem is I don’t know WHO is going to build this or HOW. So I don’t know WHEN it might be available. And most importantly I don’t know what it might COST.
If YOU have specific ideas about these questions please email me. I’m especially interested in full-service manufacturing and distribution outside of China.
KiwiSDR 2 Goals:
Minimal changes. Fastest time-to-market with lowest possible risk. BUT since the PCB is going to be re-spun fix some of the known limitations that don’t add too much risk:
-
- New RF front-end:
- Balanced input via balun transformer
- Digital attenuator (per the advisory group: pSemi PE4312, 0 – 31.5 dB, 0.5 dB steps)
- Gas discharge tube (GDT) across input in addition to TVS diodes
- Static drain resistors (100K) from input connections to ground
- External ADC clock brought out on third SMA connector
- Self test loopback mode using a short cable between this SMA and antenna input
- New GPS chip to replace current one which is now EOL
- Reverse polarity protection (via P-FET) on 5V DC input
- TVS diode across 5V input
- New RF front-end:
I have an email advisory group. Many, many other changes and additions were considered and deferred. They have been put onto a list for the future.
Additional info as things progress.
Thank you.
Readers: If you have suggestions for John regarding a manufacturing and distribution facility outside of China, please connect with him on the KiwiSDR forum.
In my opinion, the KiwiSDR has been the most accessible and effective web-based SDR platform out there. I’m looking forward to version 2 and hope it becomes a reality in the near future.
Listening to Shortwave Australia this morning
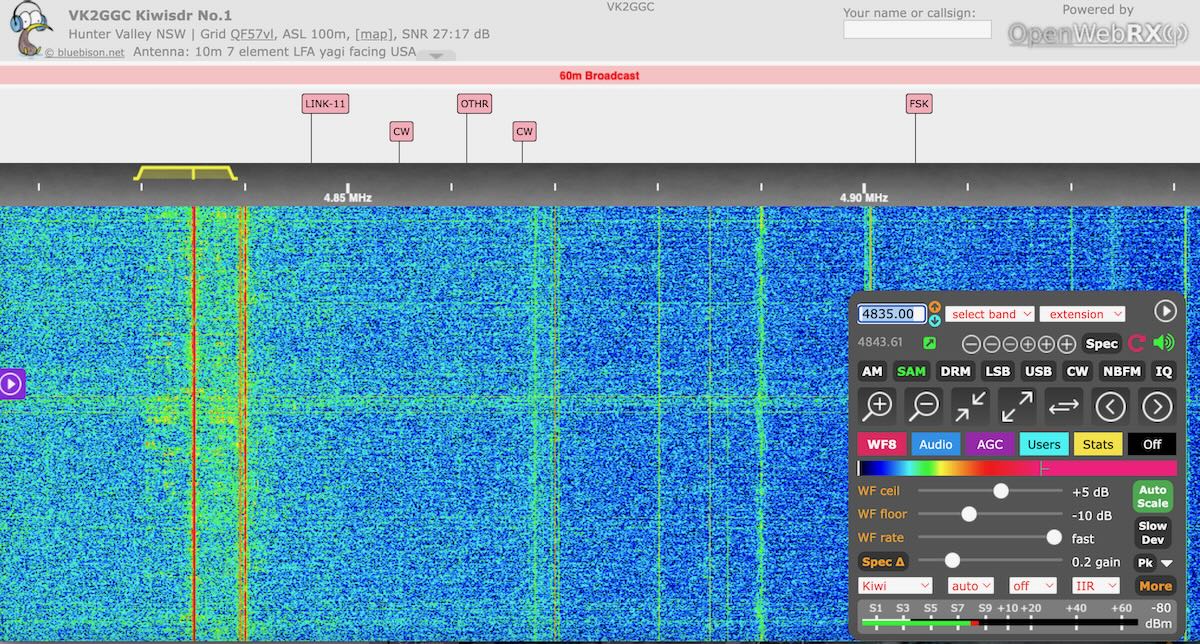 I’m traveling at present and staying in a hotel where, let’s just say, QRM is heavy.
I’m traveling at present and staying in a hotel where, let’s just say, QRM is heavy.
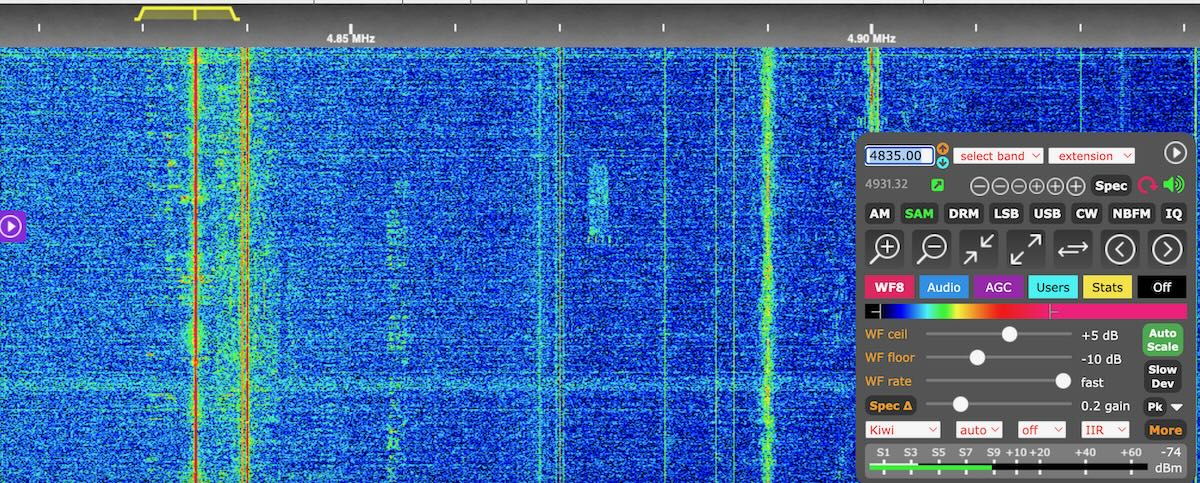
I decided to cruise the KiwiSDR network and found myself on the VK2GGC KiwiSDR in Hunter Valley NSW, Australia. As I was band-scanning, I stumbled upon Shortwave Australia on 4,835 kHz around 9:40 UTC.
It was great hearing this low power shortwave broadcaster on the air again! Check out the recording below with ID:
WebSDRs are such a wonderful resource when you truly need to escape QRM. It’s fun to travel the globe and tune through the bands like a local. Again, it’s great to hear Shortwave Australia again–I’m curious if anyone has logged them as DX from home.
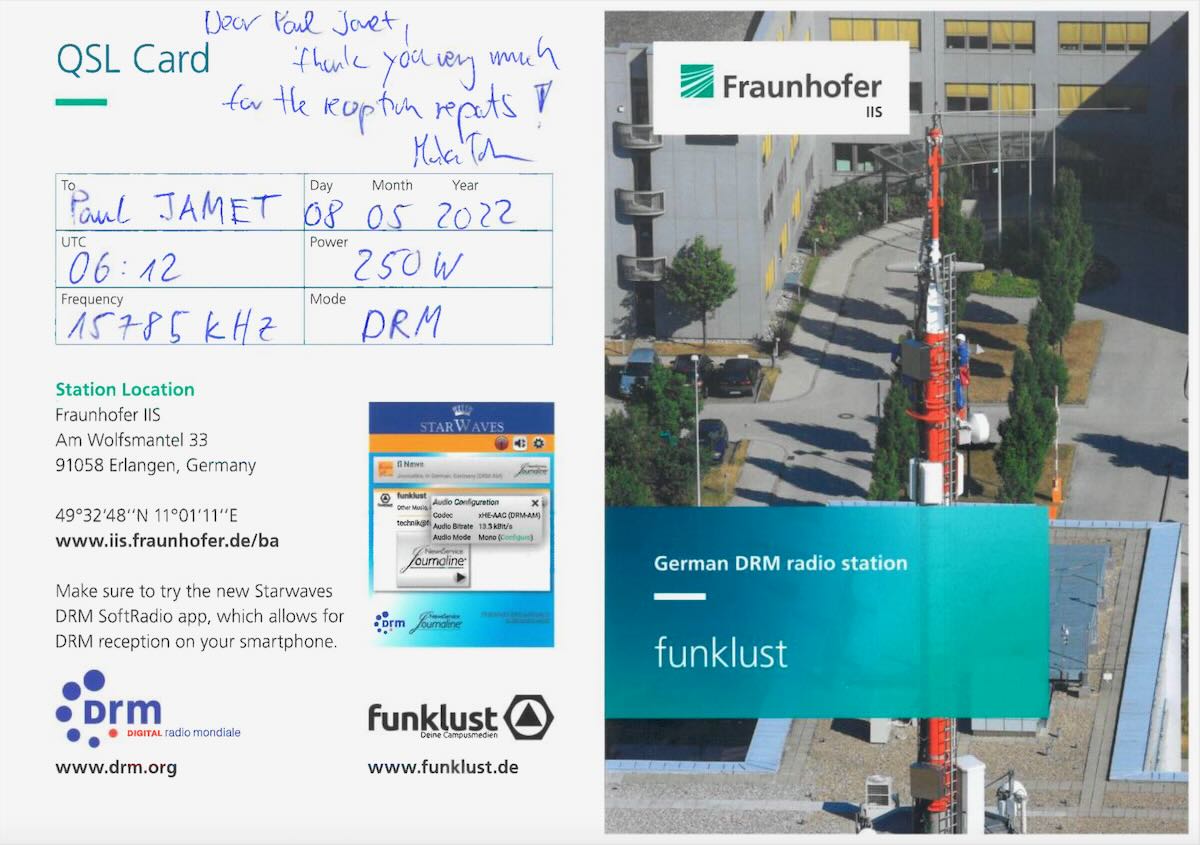
Paul receives a Funklust DRM QSL
 Many thanks to SWLing Post contributor, Paul Jamet, who writes:
Many thanks to SWLing Post contributor, Paul Jamet, who writes:
Hi Thomas,
I am reacting to the latest Radio Waves news items on the SWLing Post: Funklust is back on air with a boost
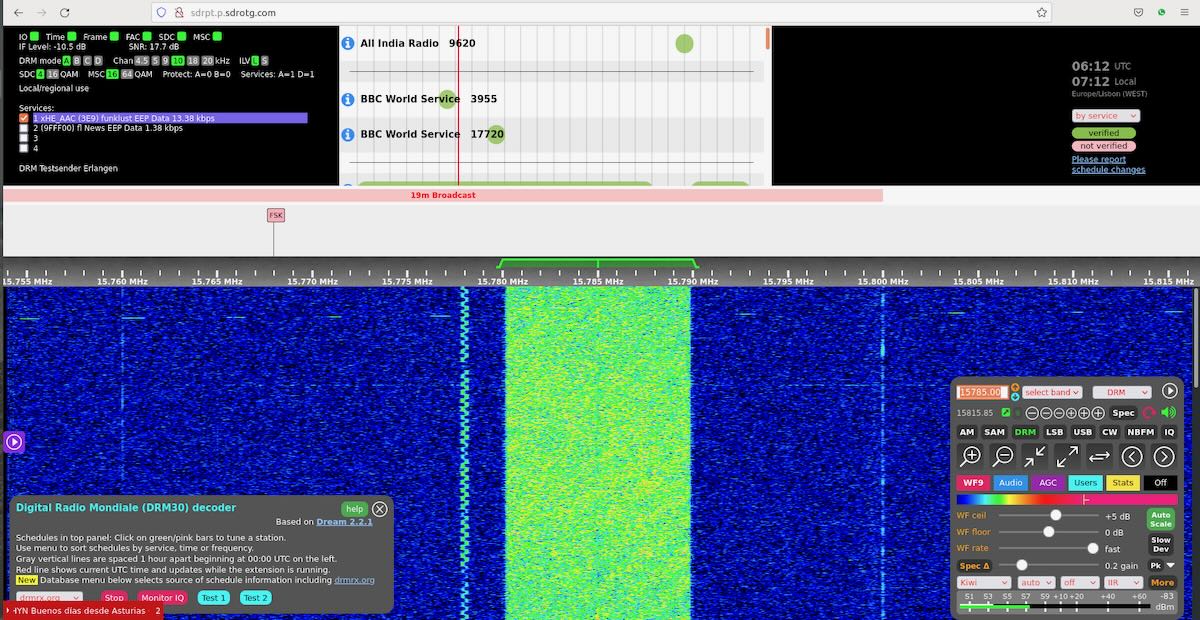
Connected to a Kiwi SDR installed in Portugal, I listened to this experimental station on its 15785 kHz DRM frequency and sent a listening report (in the form of an audio recording and a screenshot) to the Fraunhofer Institute in Erlangen, Germany:
[email protected]
I received a nice QSL!
Audio File:
KiwiSDR Screenshot:
The signal was picked up as far as New Zealand one told me. I think reception reports from all over the world would be very much appreciated …
Have a nice day. Best regards.
Paul JAMET
Radio Club du Perche
That’s brilliant, Paul. Thank you so much for sharing the recording and QSL info. Hopefully, they’ll continue to receive reports from across the globe. It might be fun, in fact, to see just how far one could DX this DRM broadcast via the KiwiSDR network. Frankly, good copy of Funklust’s 250W DRM signal in Portugal is pretty impressive!
HF Monitoring in Ukraine?
 Many thanks to SWLing Post contributor, Al Hearn, who writes:
Many thanks to SWLing Post contributor, Al Hearn, who writes:
Given the emerging situation in the Ukraine, I would appreciate any tips and suggestions that you might offer directly or on your blog as to what we might find interesting in terms of SWL — related broadcast stations, pirate stations, unencrypted government stations, ham nets, or numbers stations that might be monitored for increased activity. KiwiSDR could be an important tool in such monitoring.
Thank you for any information you can provide.
Al Hearn
WA4GKQ
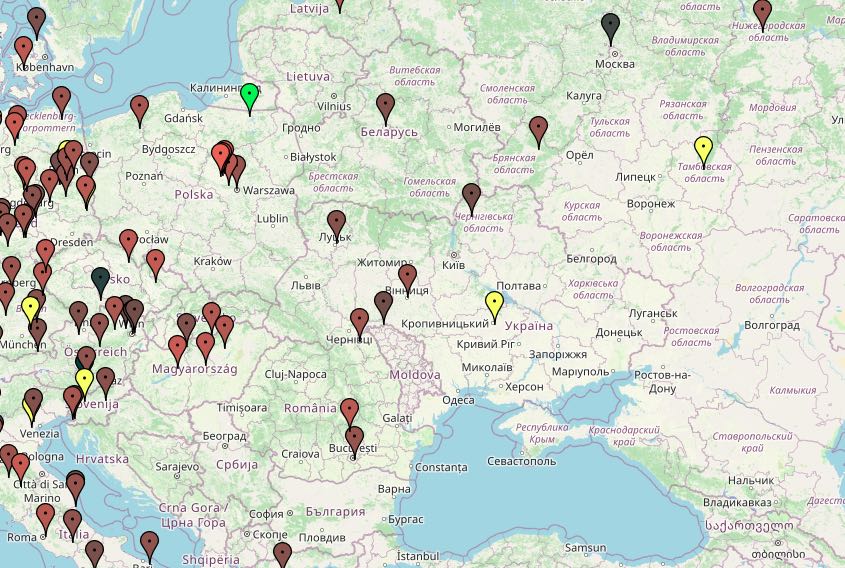
You are not alone in asking this, Al. Indeed, I’ve gotten a numerous inquiries as of late and as tensions continue to rise along the border.
There are numerous KiwiSDRs in the region and throughout Europe that should be positioned well for monitoring pirates, hams, etc. (see map at top of post).
A reminder that the RTL-SDR blog did share a note of caution recently for SDR users in the Ukraine.
Of course, the limiting factor to me is that I don’t speak the language, so I would appreciate any comments from and SWLing Post community members in the region. Have you noticed any new HF activity? What stations are you turning to for information?
Please comment.
I do hope for a peaceful outcome to all of this.