 Radio Waves: Stories Making Waves in the World of Radio
Radio Waves: Stories Making Waves in the World of Radio
Because I keep my ear to the waves, as well as receive many tips from others who do the same, I find myself privy to radio-related stories that might interest SWLing Post readers. To that end: Welcome to the SWLing Post’sRadio Waves, a collection of links to interesting stories making waves in the world of radio. Enjoy!
Many thanks to SWLing Post contributors Alan, Bill Mead, Bill Hemphill, and Gregg Freeby for the following tips:
The ACMA released an issue paper in May 2019 to hear from industry about the delivery of radio. We also wanted to consider if there needs to be any changes to support radio services into the future.
Following this, we conducted a public consultation, receiving submissions from across the industry. We found that live radio across different platforms is important to Australians. This is especially relevant during emergency situations, such as the recent bushfires. We also determined that a mix of platforms is crucial to bringing radio to listeners.
Our report identifies four broadcast spectrum planning priority activities to help support radio:
-
- converting commercial, community and national radio broadcasting services from AM to FM where available
- improving the coverage of radio broadcasting services where spectrum is readily available
- making digital radio channel plans for regional DAB+ where there is a planned rollout
- supporting trials of new broadcasting technology.
Report to the Minister Future delivery of radio (319.59 KB)
AUBURN — On Maine Big Z’s “The Breakfast Club,” Mark Turcotte interviewed local business owners, entertainers, activists, and once last summer, a mixed martial arts cage fighter and state senator one hour apart.
“Had to shift gears pretty quickly that morning,” quipped Turcotte, the morning show host since December 2018.
On Wednesday, he was abruptly down to two final shows.
Gleason Radio Group announced that its five stations will go off the air at 7 p.m. Sunday. They include Norway, Paris, Rumford, Mexico and Auburn.
“This feels like the end of an era in Maine radio,” Turcotte said.
Kathy Gleason has run the business with WOXO station manager Vic Hodgkins in the year since her husband, founder and former Auburn Mayor Dick Gleason, died.
“I feel that I tried very hard to keep it going and at the same time have it be for sale,” Gleason said. “It didn’t sell, it may sell. The coronavirus was kind of like the last straw as far as finances go.”
Hodgkins said a combination of low receivables and slow payments, combined with a projected drop in advertising because of COVID-19, has resulted in the need to close the stations.[…]
To address our unprecedented global and immediate need for access to reading and research materials, as of today, March 24, 2020, the Internet Archive will suspend waitlists for the 1.4 million (and growing) books in our lending library by creating a National Emergency Library to serve the nation’s displaced learners. This suspension will run through June 30, 2020, or the end of the US national emergency, whichever is later.
During the waitlist suspension, users will be able to borrow books from the National Emergency Library without joining a waitlist, ensuring that students will have access to assigned readings and library materials that the Internet Archive has digitized for the remainder of the US academic calendar, and that people who cannot physically access their local libraries because of closure or self-quarantine can continue to read and thrive during this time of crisis, keeping themselves and others safe.
This library brings together all the books from Phillips Academy Andover and Marygrove College, and much of Trent University’s collections, along with over a million other books donated from other libraries to readers worldwide that are locked out of their libraries.
This is a response to the scores of inquiries from educators about the capacity of our lending system and the scale needed to meet classroom demands because of the closures. Working with librarians in Boston area, led by Tom Blake of Boston Public Library, who gathered course reserves and reading lists from college and school libraries, we determined which of those books the Internet Archive had already digitized. Through that work we quickly realized that our lending library wasn’t going to scale to meet the needs of a global community of displaced learners. To make a real difference for the nation and the world, we would have to take a bigger step.[…]
The RAF knew how to cut the power on propaganda.
eichsmarschall Hermann Göring was beside himself with anger. Years before, he had told the people of Germany that no enemy aircraft would ever cross the country’s borders. Now, on January 30, 1943, a national day of celebration marking the 10th anniversary of Hitler’s rise to power, Göring was made to look like a buffoon.
Dodging in and out of slate gray clouds, Royal Air Force bombers from No. 105 Squadron howled across Berlin. With bomb doors open and Merlin engines at their limits, the wail from a trio of de Havilland Mosquitos mixed with blasts from anti-aircraft batteries below. If everything went as planned, all that noise was going to be on the radio.
In Berlin, amid the grim news from the battlefronts in North Africa and Stalingrad, the January 30 celebration was intended to take German minds off their fallen soldiers and reversals of fortune. The Nazis were going to have a parade. Göring, one of the most powerful figures in the National Socialist German Workers’ Party, was about to deliver a speech to kick off the opening ceremonies in the capital city. British operatives knew it all. They even found out what time the Luftwaffe commandant was due to step to the podium at the Air Ministry Building—exactly 1100.
Royal Air Force leaders had dispatched orders to a pair of Mosquito squadrons experienced in low-level attacks. “I was playing [cards] in the crew room when my driver first told me we were going on an op,” Sergeant Richard Charles “Lofty” Fletcher later told reporters. “I must admit I was a bit shattered when I found out it was Berlin.”
The 400-mph Mosquitos were undertaking the RAF’s first daylight bombing attack on Germany’s largest city. Their target was not the parade route or even the Reichsmarschall himself, but something bigger. It didn’t take a top-level English spy to figure out that Göring’s remarks would be transmitted to the far corners of the Third Reich. The bombers banked and streaked towards Berlin’s Haus des Rundfunks—the headquarters building of the German State broadcasting company.
Göring and the radio building were slightly more than four miles apart—a distance that the Mosquitos could cover, going all-out, in roughly 40 seconds. And the cacophony they brought with them traveled even faster. As the mics went live and Göring began to speak, the roar of impending catastrophe became audible over the radio.[…]
Do you enjoy the SWLing Post?
Please consider supporting us via Patreon or our Coffee Fund!
Your support makes articles like this one possible. Thank you!

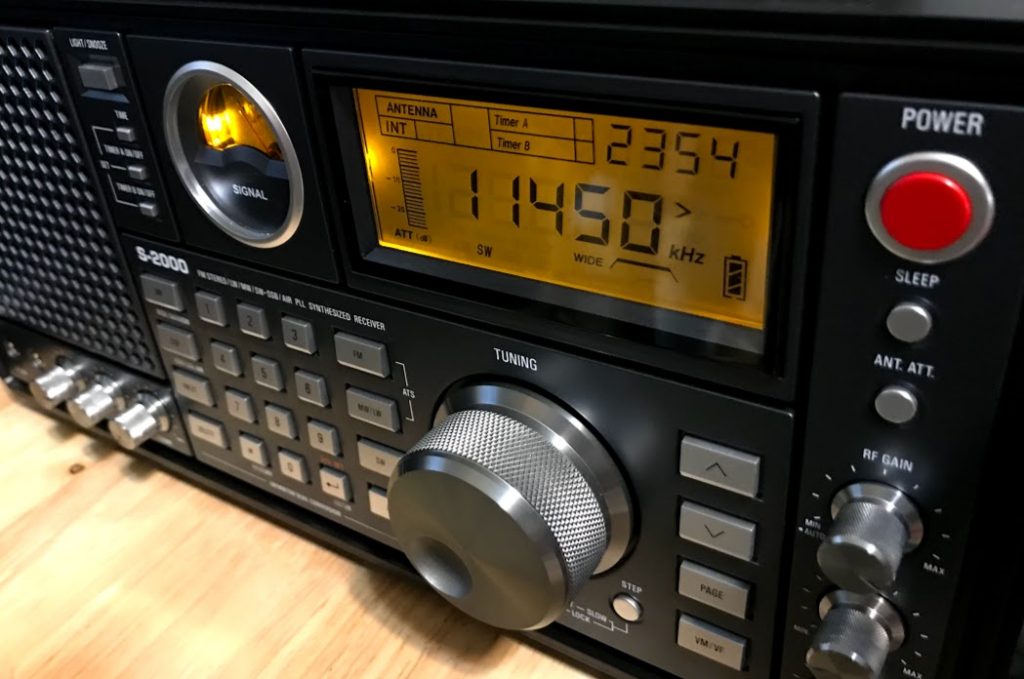
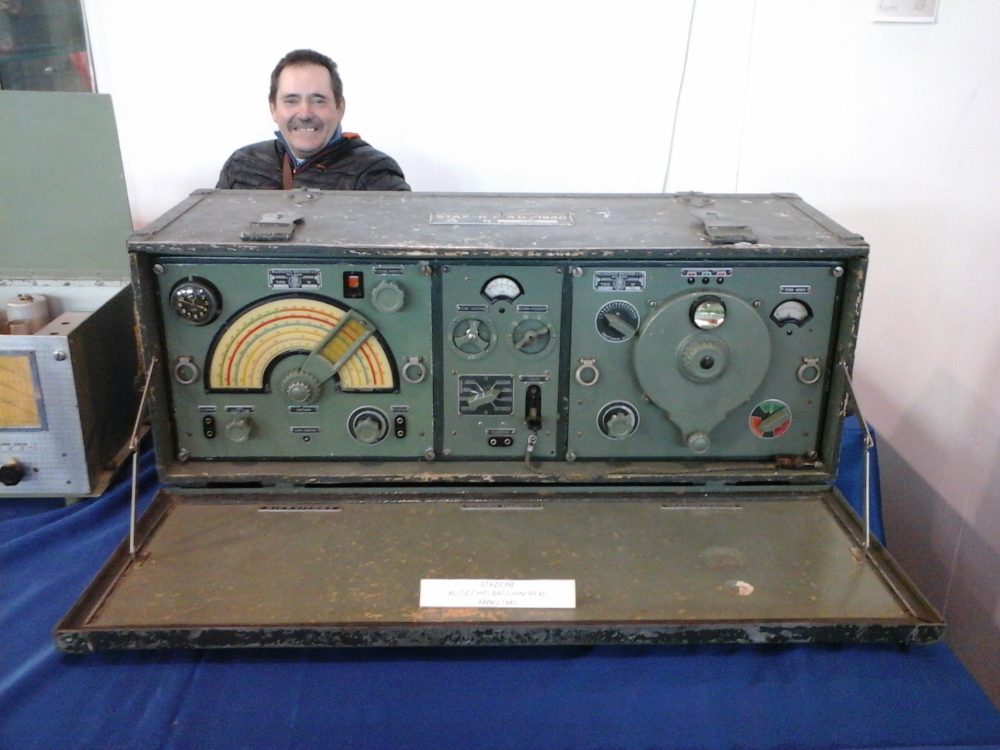
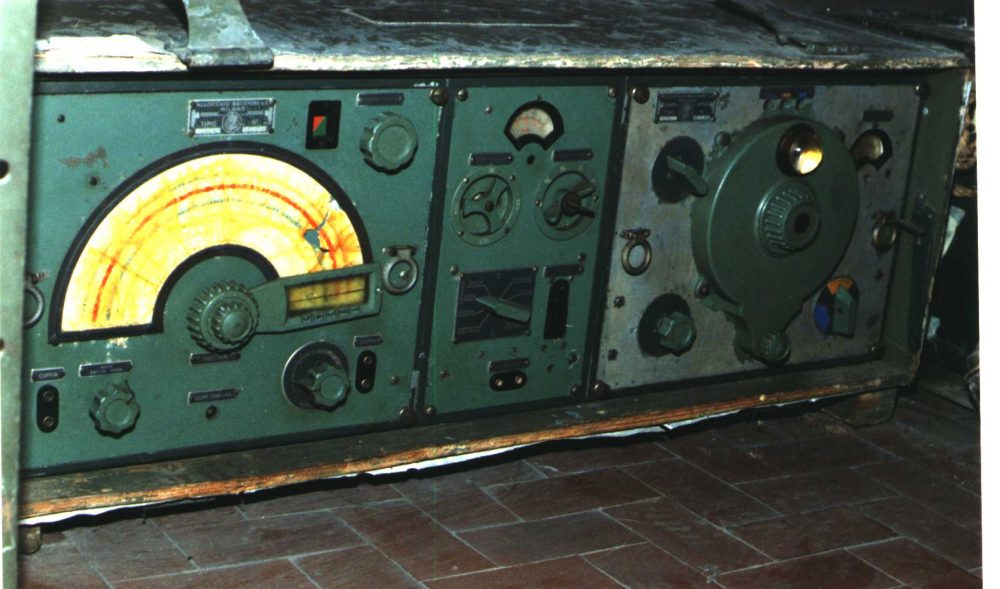
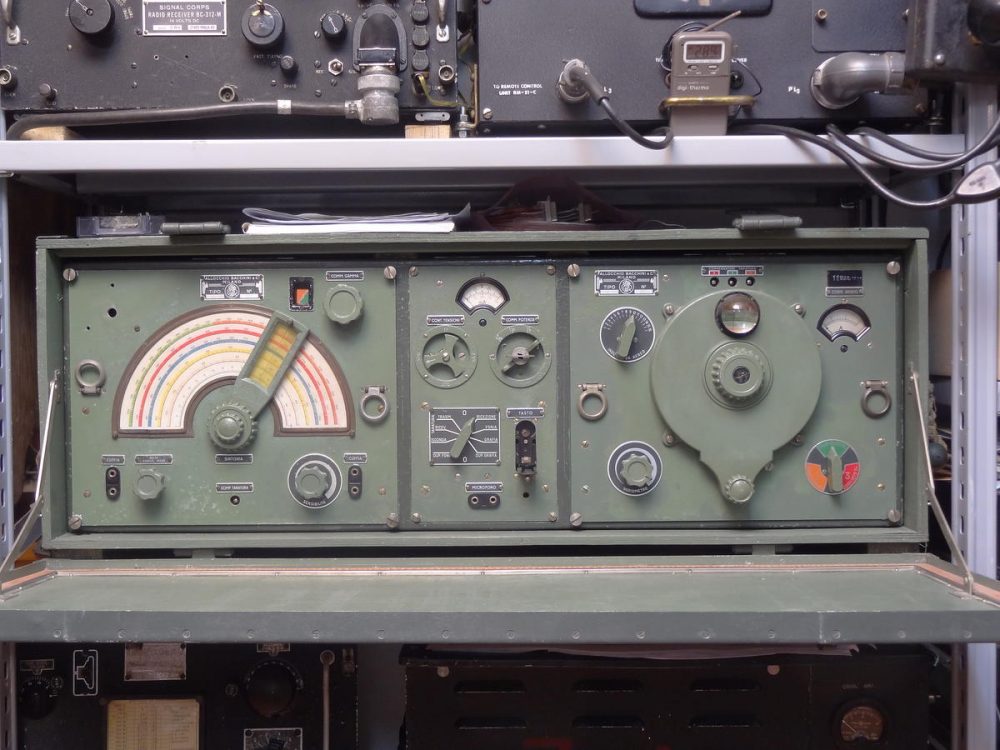
 Many thanks to SWLing Post contributor, Andrew, who correctly identified the radio Ed spotted in The Last Man On Earth as the Allocchio Bacchini RF4D. Andrew shared the following notes and links:
Many thanks to SWLing Post contributor, Andrew, who correctly identified the radio Ed spotted in The Last Man On Earth as the Allocchio Bacchini RF4D. Andrew shared the following notes and links: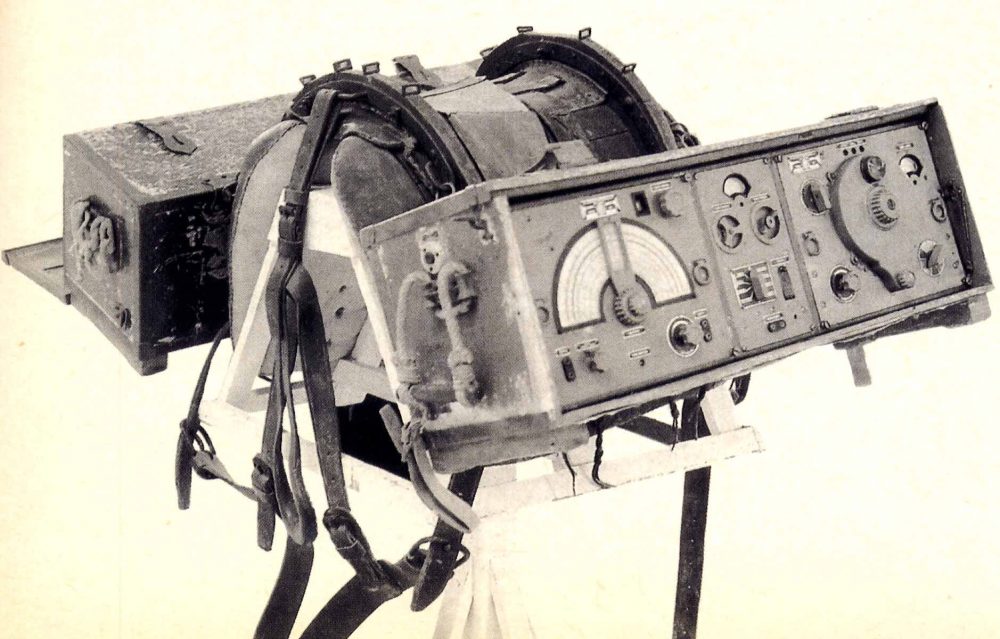 Wow! Thank you so much, Andrew! I would love someday to operate an original RF4D. What a fascinating WWII era radio. Thank you again for all of the details!
Wow! Thank you so much, Andrew! I would love someday to operate an original RF4D. What a fascinating WWII era radio. Thank you again for all of the details!







