Source: Better Shortwave Reception, William I. Orr, W6SAI, Radio Publications Inc., Wilton, CT, 1st Edition, p. 25, 1957.
Tuning Single-Letter Cluster Beacons
by Bob Colegrove
Part of the allure of shortwave listening for me has always been vicarious visits to “those faraway places with the strange-soundin’ names.” After one has logged several big-time broadcasters, one begins to look for new challenges. Most of the so-called “utility” content which once occupied the space between the broadcasters and hams is now a vast open desert interrupted only with an occasional digital buzzsaw, a wide-band CODAR experiment, or some RTTY. But now and then you come across a signal that grabs your interest. In this case it happens to be a group of signals referred to as the Russian single-letter beacons. A good introduction to these beacons is here
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Letter_beacon
and here
https://www.hfunderground.com/wiki/Letter_beacon.
After many years, there is still some speculation as to the history, purpose and power of the single-letter beacons. Rather than repeat what has already been said, this posting focuses on my technique for monitoring a subset of these beacons called “cluster beacons.” They are called that because they are grouped close together, just 100 Hz apart, at ten different locations across the shortwave spectrum. A good tabular summary is at https://priyom.org/military-stations/russia/single-letter-beacons. Some stations may not currently be broadcasting or may be on at selected times.
These stations will neither captivate you with content or readily QSL. They are all continuous wave (CW) and are thus heard by turning on your radio’s beat frequency oscillator (BFO) or selectable sideband (SSB) detector. I am Morse-code-challenged – always have been. Fortunately, these stations all broadcast their single letter dits and dahs repeatedly and slowly. Having relatively low power, the challenge here on the East Coast of North America is just to pick them up through the band noise. Some nights are better, some not so good.
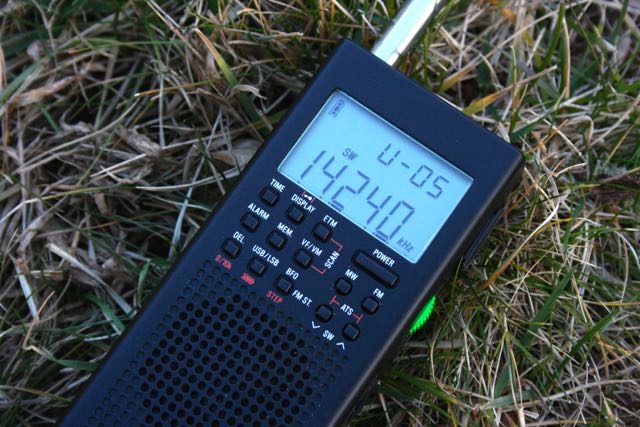
For purposes of this posting, I have focused on the stations around 7508 kHz. This seems to be the best cluster, at least at the current time and location. “D” is invariably the strongest and most consistent, with “P,” “S,” “C,” and “A” fading in and out at different times depending on the propagation.
To tune through the cluster, first tighten up your selectivity as narrow as possible – 500 Hz if you have it. Use the fine-tuning control – 10 Hz if you have it. The best way to catch these beacons is to sneak up on them.
- Approach upward from the low side of the cluster using USB, start tuning around 7508.3; or
- Approach downward from the high side of the cluster using LSB, start tuning around 7509.5.
- Try tuning in both USB and LSB to determine the better reception of the signal you are trying to hear.
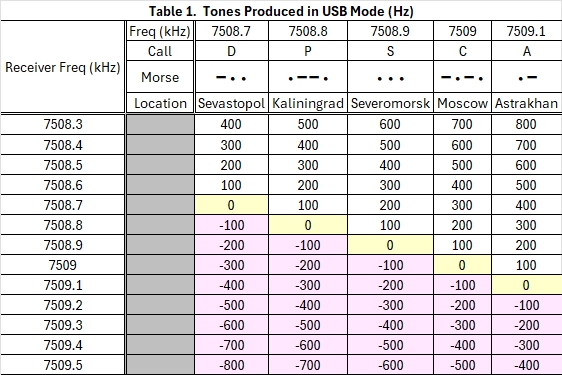
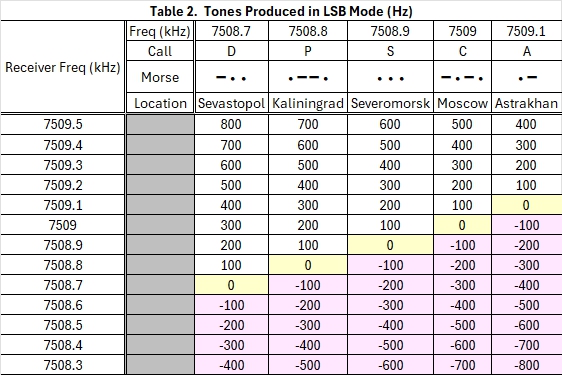
Depending on which signals are audible, you may hear two or three making it through the 500 Hz filter at the same time, each with a different pitch. The beacons will change pitch as you approach, going from a high pitch heterodyne to a lower pitch. When you reach zero beat with a station you will be directly on its frequency. Zero-beating a strong signal may help you hear a weaker one. Tables 1 and 2 show how this works for USB and LSB respectively. They indicate the heterodyne tone you will hear as you tune towards or away from each signal.
The negative value tones in the tables may not be heard if you are using a radio with selectable sideband (SSB). If your radio has a traditional BFO, you will hear a tone at either side of zero beat. In the tables, interpret the negative numbers for their absolute value, for example, |-100 Hz| = 100 Hz.
As part of the challenge for the 7508 kHz cluster, you may have to contend with interference from WRNO, 7505 kHz. When you finish this challenge, try it again on the 10781 kHz cluster.
Good DXing.