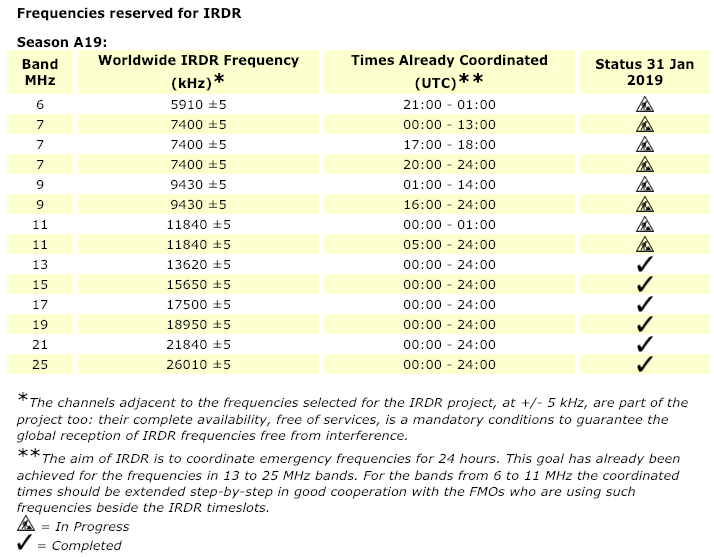
Many thanks to SWLing Post contributor, Alan Hughes, who shares this article by WRMI’s Jeff White in Radio World magazine. Besides covering updates in the A19 broadcast season, and Radio Exterior de España’s increased broadcasts, Jeff notes frequencies and updates for the International Radio for Disaster Relief initiative.
For more information about the IRDR, check out the information below taken from this page on the HFCC website:
International Radio for Disaster Relief (IRDR)
Humanitarian Aspects of HFCC Activities
From its infancy since 1920s shortwave radio has been associated with its potential of being a communication tool in emergencies. This use of shortwave radio is still very much present among amateur radio enthusiasts for example, who discovered its long distance properties early in the twentieth century. Amateur radio provides a means of communication on shortwaves and other frequencies “when all else fails”. This role of amateur radio is well recognised, valued and appreciated both by the public and by the world institutions managing and regulating the use of the radio spectrum.
In contrast the huge technical potential of international shortwave broadcasting that operates transmitter facilities tens, or hundred times, more powerful than those of amateur radio, remains almost unused in emergencies. At the moment when local and even regional communication and information networks are needed most, they are destroyed or overloaded and the population suffers from an information blackout. Shortwave radio is capable of remaining the only source of information.
Although the life-saving role of radio broadcasting is widely recognised by the public, and confirmed by surveys conducted after the recent disasters – and even acknowledged by world leaders – no concrete projects have been ever designed and no regulatory framework has been developed.
That is why the HFCC – International Broadcasting Delivery in co-operation with the Arab States and Asia-Pacific broadcasting unions are working on an International Radio for Disaster Relief (IRDR) project that is based on the system of online co-ordination of frequencies managed by the HFCC in accordance with International Radio Regulations.
The HFCC is aware of the humanitarian aspects of international broadcasting. It pointed out in 2012 – as the UNESCO partner for the preparation of the World Radio Day – that terrestrial shortwave radio in particular is still considered as a powerful communication and information tool during emergency situations. Read more >>
Receivers are inexpensive and require no access fees. Shortwave radio is important for people living in remote and isolated regions of the world. It reaches across the digital divide to the most disadvantaged and marginalised societies. This is also in keeping with the Declaration and Action Plan of the World Summit on the Information Society.
The annual edition of the World Disasters Report of the International Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies (IFRC) issued in October 2013 stressed again that with only 6 percent of people in low-income countries using the internet in 2011 the digital divide is still stark, and access to low cost media technology is really the key.
The HFCC is a strong advocate for incorporating terrestrial broadcasting permanently on the disaster risk reduction agendas of the ITU and other UN agencies and institutions. It submitted two documents for the ITU-R Working Party 6A November 2013 meeting:
HFCC – The Importance of Terrestrial radio in International Broadcasting
HFCC – The International Radio for Disaster Relief Project
Both documents are annexes in Section 8 of the ITU-R Study Group 6 Report BT.2266 “Broadcasting for public warning, disaster mitigation and relief”. The report can be downloaded via this link.
A workshop was held during the November 2013 meeting addressing these issues. The web site of the Emergency Broadcasting Workshop can be accessed here. The web site also contains copies of all the presentations that were made at the workshop, and a Video interview with Christoph Dosch, Chairman of ITU-R Study Group 6 (Broadcasting service)
The HFCC has applied for membership in the CDAC (Communicating with Disaster Affected Communities) Network in keeping with the conclusion of the debate on emergency communication during the Bratislava B13 Conference. Read more >>
The HFCC is staying in touch with the Information and Communication Sector of the UNESCO agency on the preparation of the World Radio Days that are celebrated each year on February 13th.
Humanitarian aspects of terrestrial broadcasting were also on the agenda of the Global Kuala Lumpur conference in January 2014. Read Opening Remarks.