Many thanks to SWLing Post contributor, TomL, who shares the following guest post:
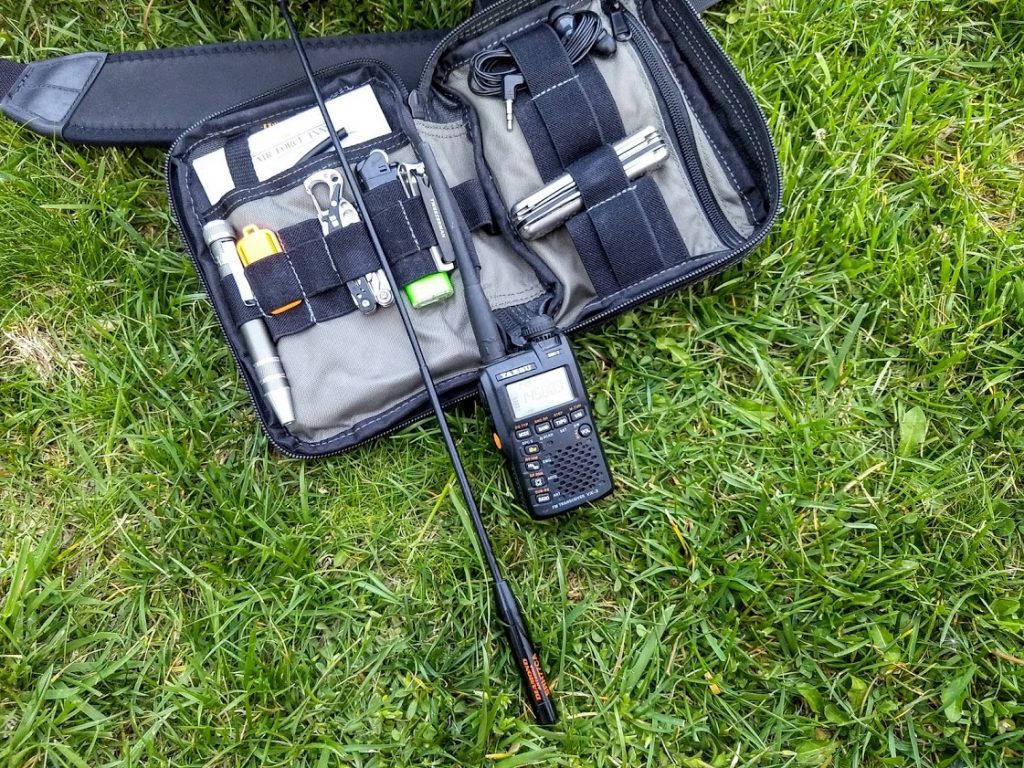
Backpack Shack 3 – Amplified Whip Antenna
by TomL
So, having enjoyed using the Ferrite Sleeve Loop I created last year, I have wanted something a little more sensitive and less bulky. I will eventually create a much BIGGER FSL antenna on the order of 2 feet long and perhaps 18 or 24 inches in diameter for indoor/attic use. But that is not a priority at the moment.
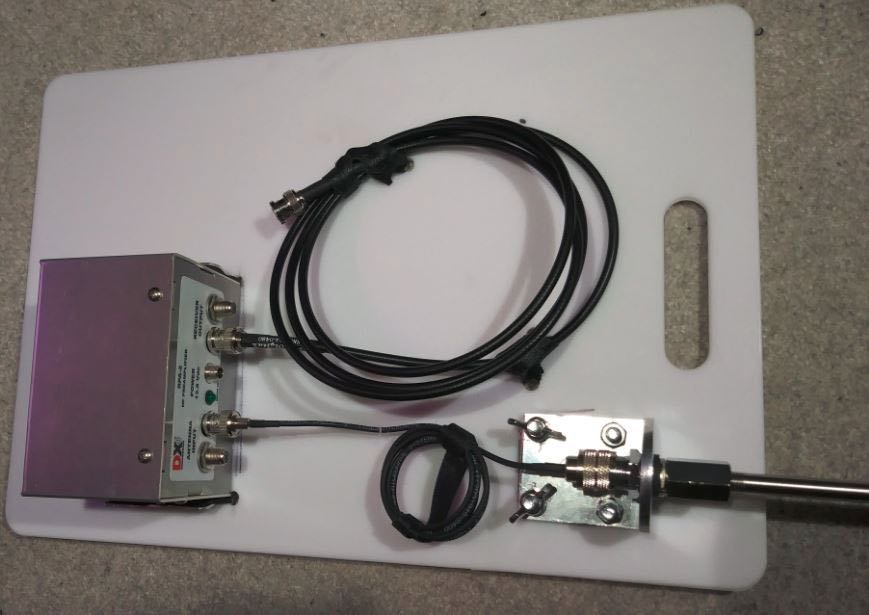
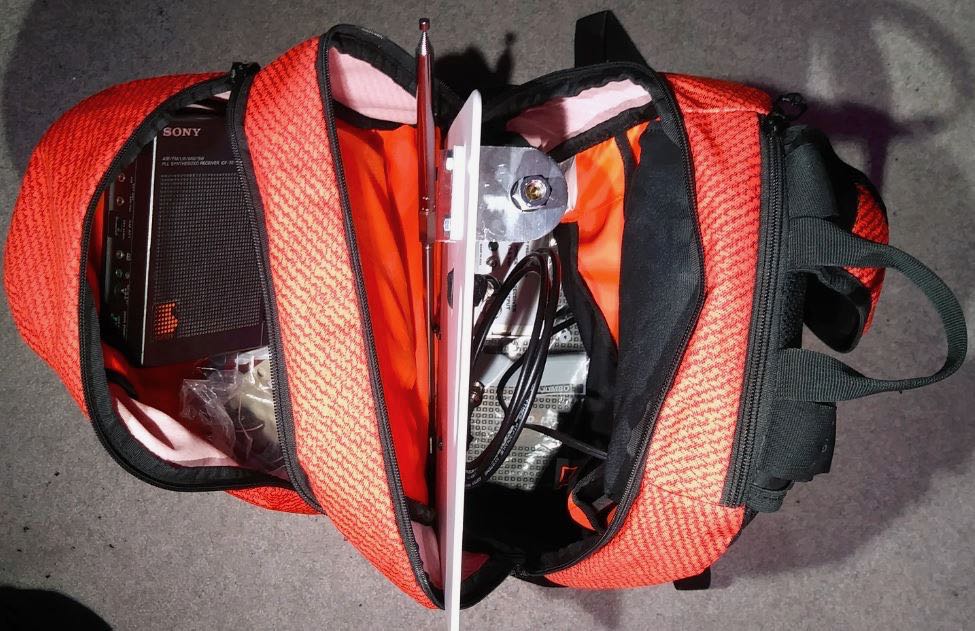
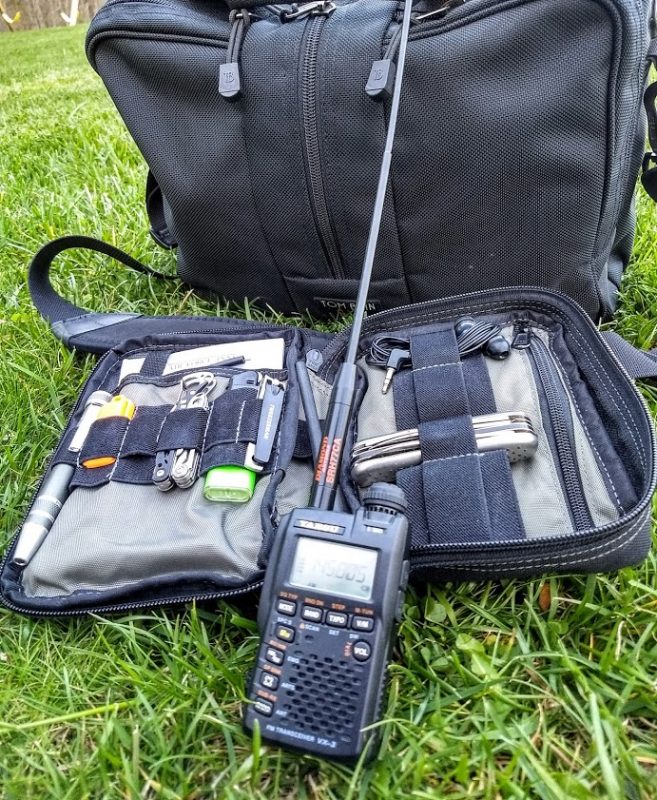
Since I already have the DX Engineering Pre-Amplifier and the very nice Cross Country Preselector from the loop project, I thought it might be useful to create an active whip antenna for it. And the cool looking Solar Red backpack needed something to do!
Power
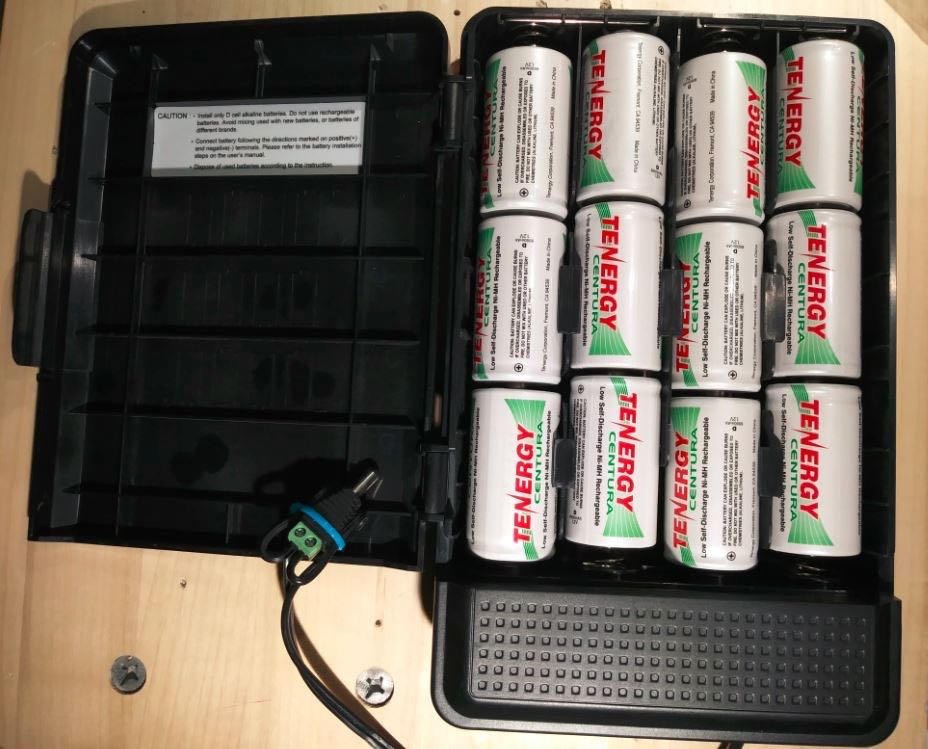
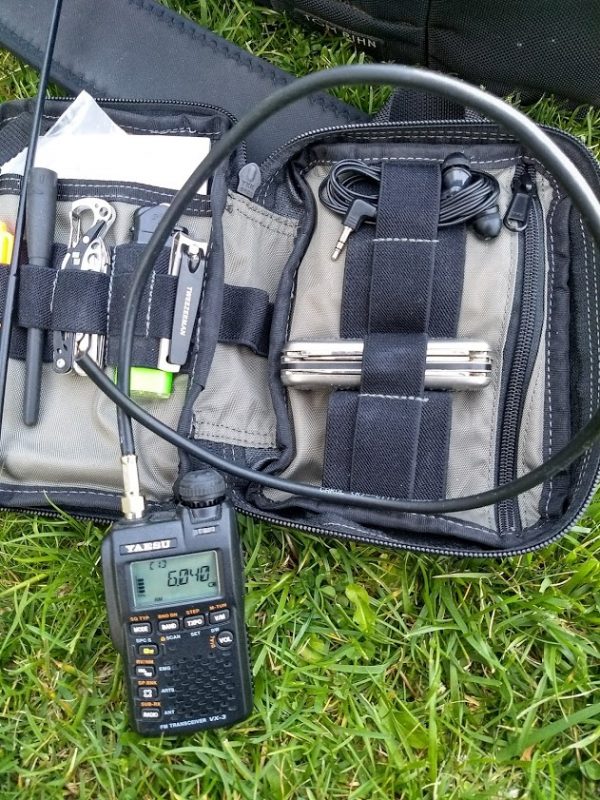
Now that the bulky loop was not taking up the main compartment of the backpack, I could think about what else to put in there, like a larger power pack. I scoured FleaBay for ideas and stumbled upon this contraption for backup power to network systems, the CyberPower CyberShield for Verizon.
This has 12 spaces for D-cell batteries and was mounted inside the demarcation terminal to provide backup power for things like cable systems and Copper-to-Ethernet networks. It is not waterproof, so would be inside the premises of the customer getting the internet/cable service. But my Pre-Amp needs 12-18Volts and would love to have nearly unlimited power. So, I bought a used one, cut the end off of the power lead and put on my own 2.1×5.5mm plug (carefully glued down and tie-wrapped). Then I filled it with 1.2Volt Tenergy D-cells.
Everything was just fine until I forgot to double check the polarity of the plug that I had wired onto the end. Plugged it into the DX Engineering Pre-Amp, flipped the power switch and fitzzz…. The Pre-Amp light went on, then off (permanently!).
So, my expensive mistake is that I start using the FREE multimeter I got from Harbor Freight and check the polarity before I connect homemade battery packs to anything!!
DX Engineering charged me $60 to fix my mistake and it is working fine now after I swapped the wires on the plug. Yes, their Pre-Amp is NOT reverse-polarity protected! Disappointing, since the price tag for that device is $148!!! The CyberShield now sits comfortably inside the bottom of the backpack.
Antenna
Now that the drama was over regarding the Power pack, I could think about the whip. I did not want a wimpy whip! (No one should rightly aspire to this, in my opinion). More FleaBay searches found me looking at Trucker parts. Loaded whips, magnetic mounts, 10 foot tall MFJ telescoping whips, etc was looking a bit expensive.
Besides that, I cannot fit a 10 foot tall telescoping whip into the backpack, I am limited to at most 18 inches (and that is at an angle to fit it in there). But I found an old-fashioned mirror mount that looked promising since it had a nice SO-239 connector at the bottom and standard CB antenna fitting on top of 3/8”-24.
Then I found the 44 inch SuperAntenna with the same threads; then found the replacement Stainless Steel Shafts for a Wilson antenna in different lengths (I ordered the 10 inch version to test). With a couple of rod coupling nuts and I was ready for testing!
Test Locations
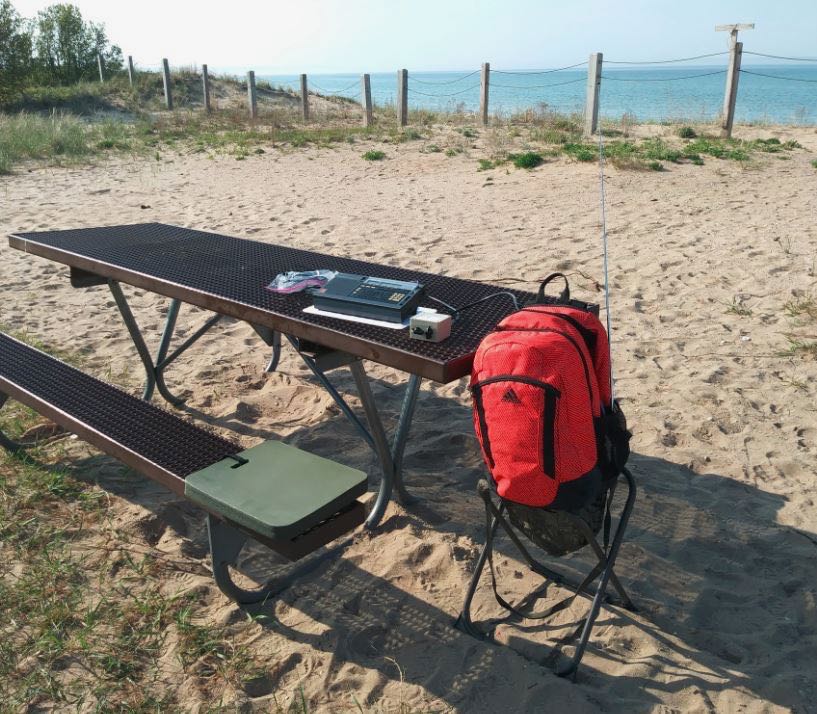
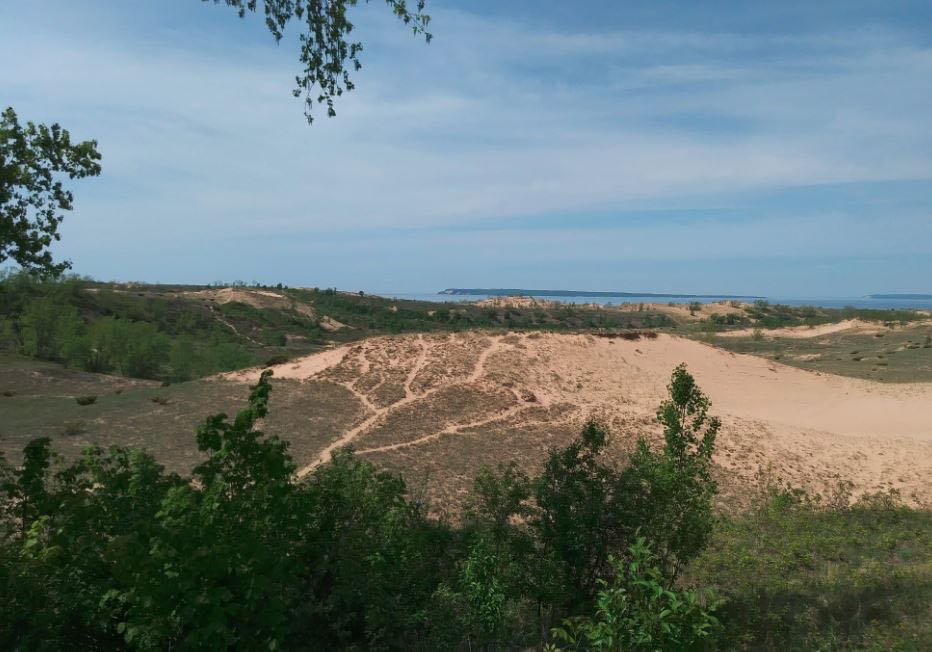
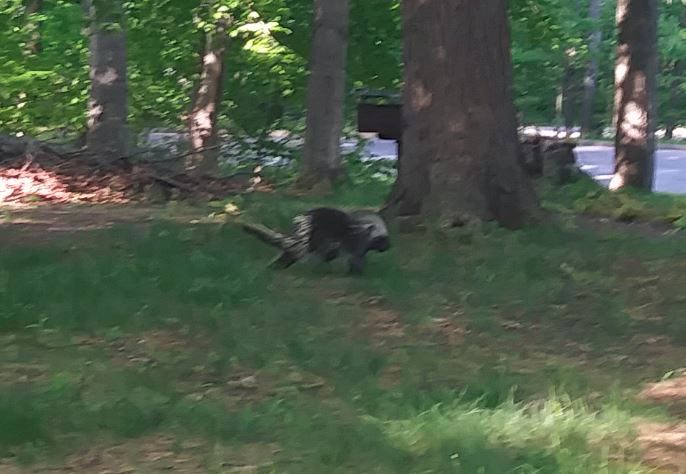
I had already scheduled a short vacation to Sleeping Bear Dunes on the thumb of Northwestern Michigan, so I took this test setup with my Sony ICF-2010. This area is a very nice remote National Lakeshore with minimal noise. I tried a beach setting and a couple of hilltop picnic areas (including meeting a local Porcupine) and had very nice reception at all locations. The hilltop locations are approximately 400 – 600 feet above the Lake (yes, the Dunes are THAT big there!).
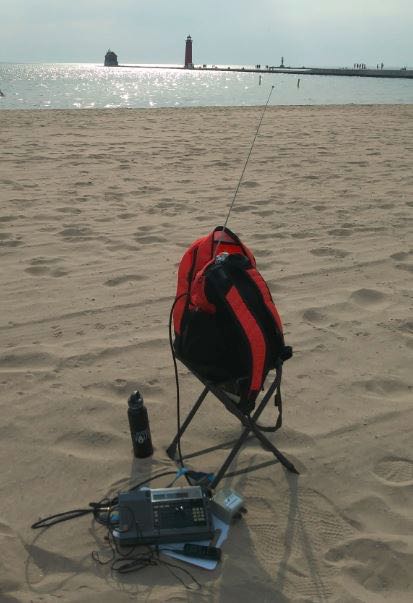
Later on, I went to Grand Haven, MI on the way home and stopped at their very lovely beach.
Reception was just as good as the hilltop locations at Sleeping Bear! In both areas, I was next to a large body of water (in this case, Lake Michigan) and makes for an advantageous place for DXing! I had also stopped at a Rest Area off the highway and that was a terrible place even though it was electrically quiet but nowhere near the big Lake. I guess the rumors are true about being near a large body of water somehow enhances reception of weak signals–?
I will submit recordings later since I lost the mini-B cable for the Sony digital recorder and had to order a replacement. However, this was a nice project that freed up some space inside the backpack. I will add an 18 inch extension to the whip that will give me a total length of 72 inches. Plus, it is mounted 12 inches up on the poly cutting board and I place the backpack on a small hunters folding chair that is about 24 inches tall. So, the tip will be about 9 feet off the ground.
Not pictured but I was also able to easily fit inside a used CCrane Twin Coil Ferrite antenna for mediumwave use that also performed very well. I noticed that the picnic benches at some locations are made of metal, so that gives me a future idea of trying to leverage that to use as a ground plane somehow. The battery pack is heavy but also gives great ballast to the backpack and will not tip over. Cannot wait for the Tecsun S-8800 to arrive so I can try leaving the radio inside the bag and just use the remote control to tune!
Happy Listening,
TomL
Parts List
-
- Trucker Mirror Bracket with SO-239 connector on the bottom
- 10 inch X 3/8-24 SS Antenna Shaft
- 18 inch X 3/8-24 SS Antenna Shaft
- Two SS 3/8-24 Coupling Nuts
- 44 inch SuperAntenna
- Thin Cutting Boards (using the largest one in the pack)
- CyberShield DBH36D12V
- Tenergy Centura Rechargable D cells
- DX Engineering Pre-Amp
- Cross Country Preselector
- Adidas XXL Excel Backpack (Discontinued Solar Red)
As always, I’m so impressed with your spirit of radio adventure, Tom! I love the fact that your goal is to make a field-deployable DX kit that isn’t cumbersome or time-consuming to set up on site. I imagine you only need a couple of minutes to open the pack and have it on the air.
Those DXing spots are stunning! I had no idea one could find 400-600′ dunes in NW Michigan–! With that said, I’ve heard that part of the state is one of exceptional natural beauty. If you could somehow turn the lake into a body of salt water–thus increasing ground conductivity–you’d really enhance that already impressive reception! I’m guessing that sort of project would be a bit outside your budget! Ha ha! That and the freshwater fish might protest!
To me, there is no better way to enjoy radio than finding a nice RF quiet spot in the great outdoors…no matter where you live in the world. On top of that, Tom, you’re constantly building, experimenting, documenting and sharing your findings–you’re a true radio zealot! Huzzah!
Post readers: Read Tom’s past contributions and articles by clicking here.