Many thanks to SWLing Post contributor, Jonathan Marks, who shares the following article and notes in response to our previous post regarding WWII German broadcasts into Australia. Jonathan writes:
Many thanks to SWLing Post contributor, Jonathan Marks, who shares the following article and notes in response to our previous post regarding WWII German broadcasts into Australia. Jonathan writes:
[F]ound the attached on a German radio history site. Zeesen was well heard around the world, especially once the power was boosted to 50kW. Bearing in mind the broadcast bands were much quieter, I would expect signals to be heard in Australia/NZ.
The following article is a machine translation into English. Click here to read the full, original piece at Radio-Museum.de.
Shortwave transmitter Zeesen
Zeesen was an independent municipality until 2003, today it is a district of Königs Wusterhausen. In 1927, the German “shortwave transmitter”, the “Weltrundfunksender Zeesen”, was inaugurated in Zeesen. It was in operation until 1945. Then the facilities were dismantled by the Russians and the broadcasting houses were blown up.

Source: FunkAmateur 4/94; pp. 268-270)
From the history of German shortwave broadcasting: The “World Radio Station” Zeesen
GERHARD DAMM – DL1RWD
From 1929 to 1945, one of the most powerful shortwave radio stations of the time worked in Zeesen, on the southeastern outskirts of Berlin. Our article informs you about the prehistory, technical equipment and development of this “wide-range radio station” as well as about its political significance.
The official opening of the shortwave broadcasting service in Germany in 1929 was preceded by numerous activities to explore the usefulness of shortwaves for international operations.
This exploration also included the work of individual internationally renowned scientists, but also that of radio amateurs, primarily from the USA. The industry, including national postal administrations, including the German one, only showed interest in the use of shortwaves after their usefulness began to emerge as a result of the above-00 investigations. Until then, frequencies in the long and medium wave range were used. Fortunately for the radio amateurs, who had been granted the “useless” short waves. Who knows whether there would otherwise be shortwave amateur radio today and thus worldwide radio traffic.
Marconi conducted his first experiments with directional shortwaves in 1916, followed by Franklin in England, who experimented with shortwave voice transmissions in 1919. On the part of the radio amateurs, it was the Americans whose broadcasts were first received in Europe on 8 December 1921. Leon Deloy, a French radio amateur, bridged the Atlantic from Europe to the USA in 1923. And this without a “radio weather forecast”.
And as is so often the case in the history of technical inventions and developments, chance helped those involved to get started. On the occasion of the opening of a commercial radio station in Argentina, the reception of the German long-wave transmitter in Nauen failed due to strong atmospheric interference. A Telefunken engineer involved referred to the fact of the success of American radio amateurs in the use of shortwave. It may sound strange, but these events prompted telefunken to develop a shortwave transmitter and put it into operation in Nauen. With 800 W RF power, telegraphy connections with South America ran from July 1924.
These and other successes prompted the then Deutsche Reichspost. to deal with targeted experiments on the application of shortwaves to the broadcasting service. You have to know about that. that other European countries. e.B. in Englandthe BBC, in the mid-20s had begun with the trial broadcasting of radio programs in the shortwave range. Shortwave broadcasting therefore became not only a technical but also a national prestige issue.
From the location Königs Wusterhausen, which was previously used for radio broadcasts – the official opening of the German radio took place on 15 October 1923, the Deutschlandsender began its operation on 11 August 1925 on from 1 September 1926 radio broadcasts on shortwave.
The transmitter, built by Telefunken. radiated its power of 250 W via a simple oblique wire antenna. which was integrated into the existing antenna support masts.
Originally planned. on the then already existing central tower (popularly: the thickness) additionally put on a vertical spotlight. However, this ultimately failed due to political conditions. In the wake of the First World War, Germany was prohibited, among other things, from erecting buildings that would have exceeded the height of the Eiffel Tower. And this would have been the case in Königs Wusterhausen.

Partial view of the first KW antenna star with 70 m towers.On the far left, the 70 m wooden tower with the KW omnidirectional radiator, in the middle a 210 m mast for LW (1934)
The radio transmitter in Königs Wusterhausen was no longer expandable at that time, already the Deutschlandsender 11 (LW) had gone into operation in 1927 on the site of the aviation company SchütteLanz (airship construction and airfield) in Zeesen acquired by the Reichspost. In 1928, for example, the Reichspost commissioned the construction of a high-power shortwave transmitter on this airfield in Zeesen. The contract was awarded to Telefunken.
Telefunken built the first KW transmitter in House 4 (Houses 1 to 3 were located in Königs Wusterhausen) at the location of Deutschlandsenders 11. The power of this KW transmitter was quite respectable for those times, it was 5 kW, later 8 kW. The transmitter was built in seven stages and consisted of the crystal oscillator, followed by amplifier and multiplier stages. The power amplifier contained an RS 225 in the 5 kW version and two RS 225 in the 8 kW version, which were operated with an anode voltage of 10 kV. The modulation took place in the driver stage. The antenna part was designed for the frequency range from 3 to 20 MHz and was used to adapt the modest, 75 m long single-wire vertical antenna, which led to one of the two 210 m masts for the Deutschlandsender.
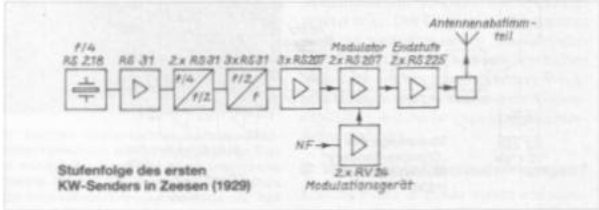
Ten machine sets (plus ten as a reserve) were required for the entire power supply of the KW transmitter. These consisted of high-voltage converters and DC generators. e.B. for heating. The end tubes were pressure-cooled with rainwater. After the official commissioning, the transmitter initially operated on two frequencies: 6.02 and 9.56 MHz. Higher frequencies were not released for broadcasting until 1932.
The wide range of the station at that time, which was in no way inferior to the stations Eindhoven (Netherlands) and Schenectady (USA), led to the naming “World Broadcasting Station” or World Broadcasting “Short Wave Transmitter” at the opening on August 26, 1929. In 1930, the antenna system underwent significant improvements. The construction of a 70 m high wooden tower(!) complemented the vertical wire spotlight. Quadruple dipoles in four directions were placed around the tower. This dipole combination achieved a favourable vertical opening angle and an elevation angle of 10′. The antenna gain is said to have been 9 dB.
The first directional antenna, commissioned for North America in January 1932, achieved a horizontal bundling of 30′. The performance gain was just under 17 dB! It consisted of a group of 24 dipoles plus reflectors. By 1934, ten such directional antennas had been attached to eleven steel lattice towers, each with a height of 70. They supplied the areas of North, Central and South America, East Asia and Africa in the frequency range from 6 to 17 MHz.
A second quartz-controlled transmitter with 5 kW was added in 1932. It was designed in eight stages, used two RS 255 tubes and was modulated like transmitter 1 with direct current.
While the stations had previously broadcast state programs of other stations, from 1933 a separate programming was carried out by the then Reichsrundfunkgesellschaft. It was specially intended for listeners abroad and was fully dedicated to the socio-political situation in Germany.
What a miracle that this also led to the further equipment of the transmitter in Zeesen. In 1935, another KW transmitter of the type “Nauen” (50 kW) with a telephony power of 12 kW began its operation. This transmitter worked in the power amplifier with two RS 257 switched in push-pull, a further development of the previously used RS 225.
As a special feature, it had a double equipment with oscillating circuits (variometers), which had to be retuned during frequency changes. Pre-tuning significantly reduced the frequency changeover period.
The switching between day and night frequencies as well as other frequency changes suitable for the most favorable propagation were already carried out on the basis of forecasts of the Reichspostzentralamt.
The broadcasting station in Zeesen experienced a special technical upswing in preparation for the 1936 Olympic Games in Berlin. In addition to the existing transmitter house 4, houses 5 and 6 were built. Among other things, they consisted of a 500 m 2 transmitter hall, which could accommodate four transmitters with 40 kW of power, which Telefunken and Lorenz built. These bore the well-known name “OlympiaSender”. A combination of parallel and push-pull switching of four RS 257 transmitter tubes made the high transmission power possible, which was later increased to 50 kW. In addition, anode BModulation was applied. The transmitters were built in seven stages and allowed quartz and VFO operation.

Olympiasender” (50kW) in Zeesen (1935/36)
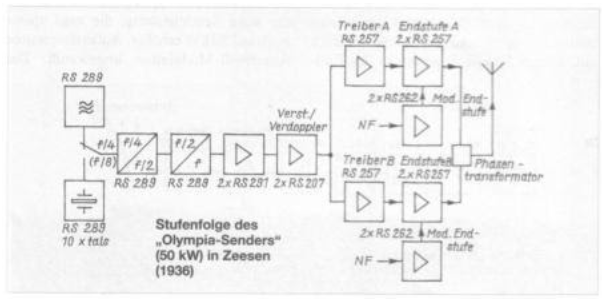
In addition to the expansion of the number of transmitters, an expansion of the antenna systems was necessary. A further 13 steel lattice towers were added, which, in contrast to the existing eleven 70 m towers, had a height of 100 in. This made it possible to achieve an even stronger vertical bundling by eightfold dipole stocking.
During the first years of the war, rhombus antennas were already being built in Zeesen, which had already been tried and tested in other radio services. Compared to the frequency-dependent dipoles, these are characterized by a relatively large frequency bandwidth and good radiation bundling.
In addition, the construction with wooden poles is possible because of the low installation height, which is probably also a question of materials in times of war. The construction also did not require the technical and material effort as with the already operated 70 and 100 in high steel lattice towers.
In 1939, the realization of a technical development in antenna construction, which was certainly spectacular for the time, was added. On one of the 70 m towers of antenna star 1, an extendable vertical radiator with self-tuning was installed, which enabled radiation over a wide frequency range (5 to 30 MHz) by changing its length. This antenna was called “Pope’s Finger” in insider circles, as such a construction had previously been erected at Vatican Radio.
 In its last stage of expansion, the “World Broadcasting Transmitter Zeesen” consisted of the following systems: nine 50 kW shortwave transmitters, a 12 kW shortwave transmitter, a LW Transmitter with two 210 m masts, 24 dipole walls at eleven 70 m and thirteen 100 m towers, the vertical spotlight “Papstfinger”, the 70 m wooden tower with omnidirectional radiator and four rhombus antennas. Three transmitter houses, a diesel house and a network substation completed the technical equipment on this former airfield.
In its last stage of expansion, the “World Broadcasting Transmitter Zeesen” consisted of the following systems: nine 50 kW shortwave transmitters, a 12 kW shortwave transmitter, a LW Transmitter with two 210 m masts, 24 dipole walls at eleven 70 m and thirteen 100 m towers, the vertical spotlight “Papstfinger”, the 70 m wooden tower with omnidirectional radiator and four rhombus antennas. Three transmitter houses, a diesel house and a network substation completed the technical equipment on this former airfield.
On April 26, 1945, the “Weltrundfunksender Zeesen” ceased its broadcasts. The operator removed important individual parts on command. The plants remained undamaged in order to be able to put them back into operation in the event of a “reconquest”, which, as is well known, did not come of anything. The Soviet troops dismantled the transmitters and antenna systems in the summer of 1945 and blew up the buildings.
After the founding of the GDR, a military KW broadcasting station began operation on part of the former broadcasting site, the part of the former location of sender house 4 for the long-wave Germany transmitter and the first KW antenna star, which is currently also being dismantled. The rest of the site was and is used economically.
In addition to this purely technical consideration of the world radio station of the Zeesen, by the way, a short political consideration should not be missing. While the shortwave broadcasting service and the establishment of the transmitter in Zeesen (there were also KWS broadcasting centers in Elmshorn near Hamburg, Ismaning near Munich and Oebisfelde west of Berlin) were first a technical and national prestige question – as I said, other countries within and outside Europe had already begun with the introduction of shortwave broadcasting for foreign broadcasts – it became more and more a worldwide propaganda instrument with the seizure of power by the National Socialists in 1933. Especially during the Second World War, this importance grew. All the belligerent states had recognized the role of foreign broadcasting. The international etheric war arose.
Before the Second World War, the main task was to bind Germans to their homeland abroad? thus the “German shortwave transmitter” developed into the so-called ranged gun in the ether”. One spoke of the “wave artillery of radio and its transmitter batteries”. The “Deutsche Kurzwellensender/ Weltrundfunksender Zeesen since 1936 world top performance in technical terms, was ideally suited for this political task. Some insiders I know even spoke of the “V 3″.
Reactions abroad ranged widely. They were enough, for example.B from Germans abroad: _’Do you know how a German feels. when in the evening greetings from home. from our dear fatherland, flooding through a German house in the African bush…” or: During the day we are in Brazil. but when the call sign of the German shortwave transmitter sounds, then we feel like in our heirnat” or: .. Through these broadcasts I have gained an indestructible faith in the new Germany and its leader … – up to: “This shortwave system represents the greatest potential propaganda weapon. that the world has ever seen…”
Despite all the jubilation for technical progress, it is important to consider. how it can be abused. In the case of the former “dreamy fishing village of Zeesen” south of Berlin in connection with Schütte-Lanz and airship and aircraft construction in the First World War, followed by the “world radio transmitter Zeesen- as a ranged gun” in the Second World War
Literature
(1) Archive of the author (information provided by former employees)(2) 50 Jahre Kurzwellen-Rundfunk, Sonderdruck 1979 [3] Wortschlacht im Äther, Morgen die ganze Welt, Deutsche Welle
Click here to read this and more articles on Radio-Museum.de.
 Many thanks to SWLing Post contributor, Jonathan Marks, who recommends this video tour of the Czech Radio Building from Radio Prague’s Facebook page.
Many thanks to SWLing Post contributor, Jonathan Marks, who recommends this video tour of the Czech Radio Building from Radio Prague’s Facebook page.