The remote South Atlantic island of Tristan Da Cunha (Image via Google Earth)
Many thanks to SWLing Post contributor, Dan Robinson, who shares the following guest post:
Ultra-Rare Tristan da Cunha QSL: The Art of the Hunter-Killer QSL Pursuit
by Dan Robinson
Those in the QSL collecting community are likely to have noticed the recent appearance on Ebay of one of the rarest QSL cards in existence.
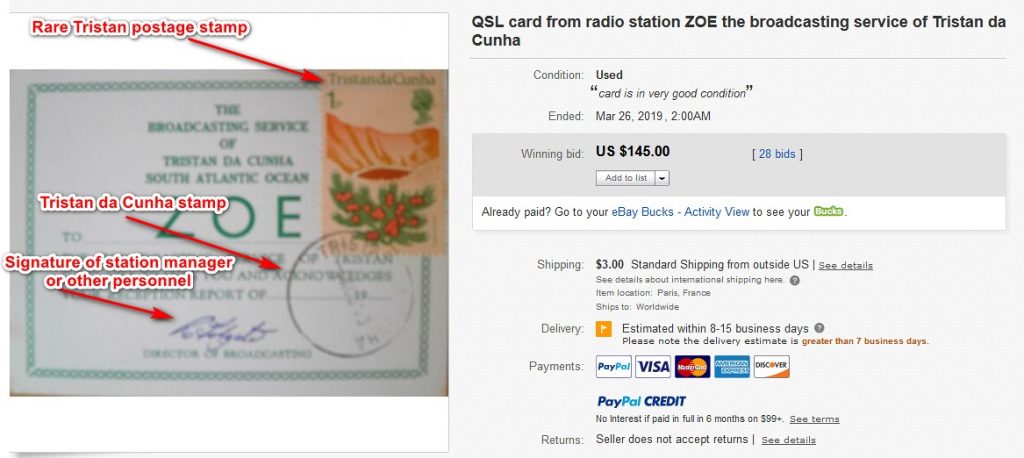
The QSL from Tristan da Cunha showed up around March 19th with a six day auction window, by a seller in France who also listed a number of other older QSLs.
For a description, the seller wrote: “QSL card from radio station ZOE the broadcasting service of Tristan da Cunha 1973. A very rare and sought after QSL. Seldom seen on Ebay. . .”
Understatement to be sure. Along with QSL letters directly from Biafra, the breakaway state in Nigeria many decades ago, QSLs from Tristan da Cunha are pretty much NEVER seen.
ZOE Tristan was a station intensively sought by thousands of DX’ers when it occupied the 90 meter frequency of 3,290 kHz with a power of only 40 watts.
Only a handful of DX’ers ever heard and QSL’ed Tristan. In this story still accessible online–three persons from South Africa are described as having received QSLs, along with two others, in the UK and in Florida, USA.
As a young DX’er, I remember reading the entry in the WRTH and the feeling of frustration with the reality that it was impossible to hear with my receivers, largely due to its limited broadcast time and hour of transmission which I recall was 2000 UTC.
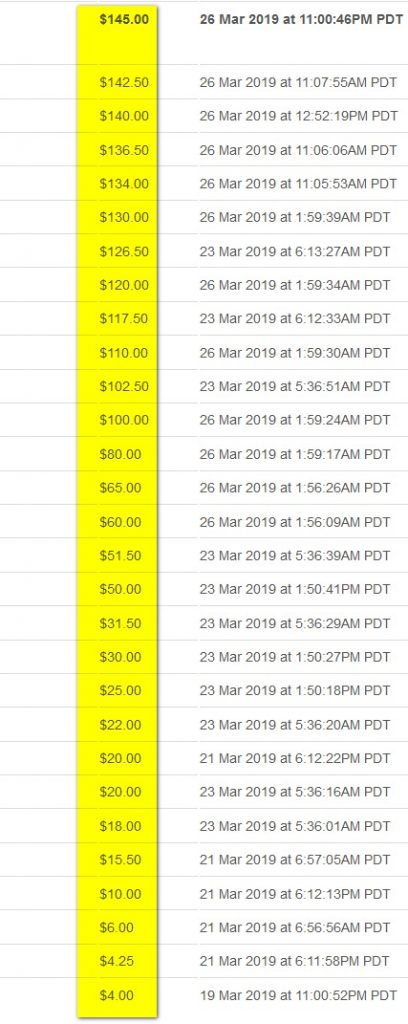
eBay bid history
As the hours ticked away in the auction, the number of bids increased. The ending time fell in overnight hours EDT. This increased chances of obtaining the card for a lower price, though bidders in other parts of the world would surely be stationed at their PCs and on their phones in the final hours of the auction.
I have been one of the most active QSL hunters in the world, and there are specific strategies involved in competing for QSLs.
For purposes of this article, I’ll just note that these involve constant attention, especially toward the end. As an auction nears conclusion, it’s important to “test” the bid level to assess the likelihood of the item selling at that or a much higher price.
Some cards or verification letters have the potential to bring hundreds of dollars. I assessed that this Tristan card could bring as much as $500-$1,000 depending on whether someone had “gone high” with an automatic “knock out” bid using either the Ebay system or other auto-bidding site.
As you can see in the image, from a starting price of $4.00 on March 19th the Tristan card had reached only $50.00 several days later on March 23rd. The $100 mark was reached on March 26th. One bidder retracted his $150 bid at one point.
On the final day March 26th, it was anyone’s guess how high the Tristan card could go. The card only inched up in small bid increments, surprising given its rarity.
If one assumed that any of the four bidders involved placed a “knock-out” auto-bid, and if two had placed such a bid, in the final seconds the Tristan QSL could quickly shoot up from the $142.50 level to whatever the extremely high maximums would be.
Due to the rarity of the card, my bid fell in the “knock out” category. I went to sleep reasonably confident, but concerned the competition could drive the price of the card through the roof.
When I awoke the next day, I was relieved — the Tristan card, complete with its original postage stamp, rubber stamp mark, and signature by the station, was mine. The price: an astoundingly low $145.

Such is the excitement involved in being a “hunter-killer” QSL card collector. As I noted in SWLing Post last year, I now own three of the world’s rarest QSLs.
These include possibly the last remaining QSL letters sent directly from Radio Biafra, a QSL from Portuguese Macao, and now this wonderful ZOE Tristan da Cunha card.
That is–actually two ZOE QSLs. About a decade ago, while scanning Ebay listings for QSLs, I was astounded to see a ZOE card listed as part of a group of amateur radio QSLs being offered by a seller in Europe.
I couldn’t believe what I was seeing. Until that point I had seen not a single ZOE QSL appear since the Ebay market for QSLs began to heat up in the late 1990s

(Source: SWL Card Museum)
This particular card, which you can see posted at the excellent “SWL Card Museum” site has “ZOE” printed in large letters, like the card that I recently won, a date of reception as “June 1, 1977” but no signature.
The card did arrive with the original envelope in which it was sent to a European DX’er, complete with a postage stamp and postal mark for Tristan.
Why that particular ZOE card was not signed by someone at the station, and why it was placed in an envelope rather than post marked on the card itself, remains a mystery.
Back to the story noted above, about the group of South African DX’ers who were among the few worldwide to have heard Tristan da Cunha.
In that article, the author notes that two other DX’ers, one in the U.S., one in Europe, had received QSLs from Tristan.
With a bit of online sleuthing, and help from some fellow DX’ers, I was able to determine that one of those two, Dave Sharp, is indeed still with us.
In response to an email inquiry, Dave provided the following history:
“I forget when exactly I heard the station, but it was 1984 or just prior, as I was still in high school. I was in Florida at the time and was using a rotatable three element beam ham antenna. [I] heard threshold talk from a woman with a deep voice and this apparently matched to voice of the Radio Tristan announcer at the time.
[I] received a reply from Pat Patterson, the Tristan postmaster and a Ham radio operator himself. Since my reception report was tentative, I felt a QSL wouldn’t have been issued if they hadn’t been reasonably confident of reception.
I received a personal letter, stamp bulletin, and a small QSL, bright green on white background, with “ZOE” across the front.
Long story, but many of my personal belongings were lost over the years and this includes my entire QSL collection (which had been left in possession of my sister).
Needless to say, I received a fair bit of ridicule after coming forward with the QSL. To emphasize, my report was tentative and they decided to issue a reply.”
It remains to be seen if other ZOE/Tristan da Cunha QSLs will surface in the future, and of course it is unknown how many of the cards that were sent out to the few DX’ers who heard, or claim to have heard, the station, still exist.
Wow! Thank you for shedding light on the history of ZOE Tristan Da Cunha QSLs. At those meager power levels, from such a remote location, and during that broadcast window, I can see why ZOE must be one of the rarest of QSL cards. I’m happy to know you obtained the card, too, Dan as you have such a long history of properly archiving and sharing your cards. As you just did. Thank you!















