Many thanks to SWLing Post contributor, Bob Colegrove, who shares the following:
Many thanks to SWLing Post contributor, Bob Colegrove, who shares the following:
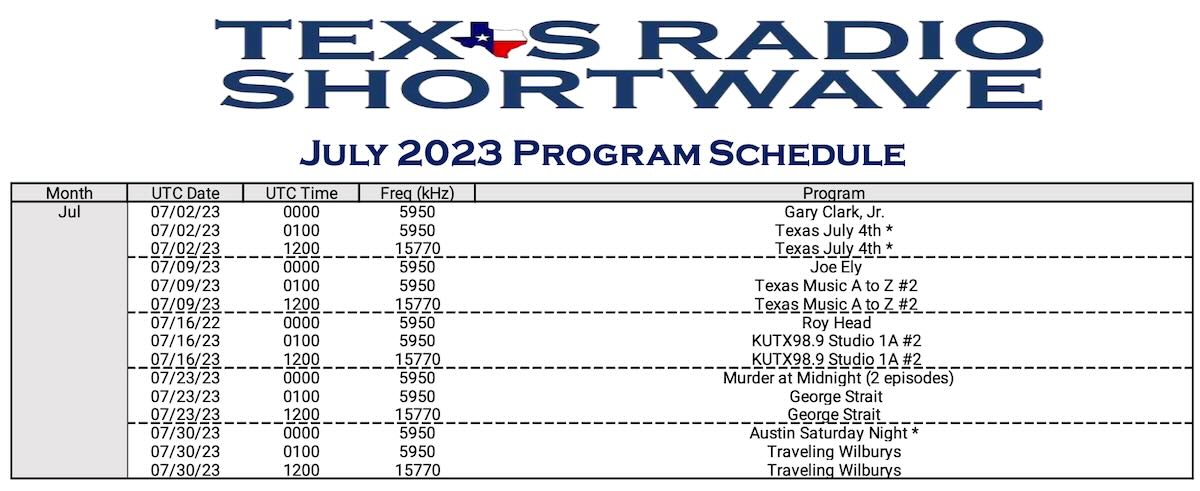
Power Play – Here Come the Lithiums
by Bob Colegrove
I have belonged to several radio-oriented user groups in recent years and can’t help noticing how often the subject of batteries comes up. It’s almost a sub-hobby within the hobby. There are a couple of reasons for this, first is the unending quest for the ultimate cost-effective, everlasting battery, and second, it’s a rare opportunity for most of us to tinker in an increasingly complex world of technology.
Lithium batteries offer a sustainable voltage output well into their discharge cycle and can deliver a higher rate of current than alkaline batteries. They are somewhat lighter in weight than alkaline batteries – 2.5 oz. versus 5 oz. for D-cells.
Considering the fast pace of technology, lithium batteries have been with us for a comparatively long time, this in the form of cell phone and camera power, not to mention a host of electric appliances. Most of these batteries have limited purpose, that is they have been developed and packaged for just a few applications, thus resulting in an incredible variety of sizes and shapes, and no doubt a host of frustrations due to obsolescence. It’s somewhat reminiscent of the early days of transistor radios which ran on a wide array of zinc-carbon batteries.
Perhaps I have been asleep at the wheel, but it has only come to my attention recently that lithium chemistry has begun to backfill the standard battery sizes we have long been familiar with, namely AAA, AA, C, D, and even the PP3 standard 9 volt.
I have been running along quite successfully for more than 10 years on AA NiMH technology on several portable radios. Although these run at a slightly lower cell voltage of 1.25 Vdc, the one-for-one substitution of these for alkaline chemistry has seldom been a problem in terms of performance. In most cases, newer radios are provided with an alkaline/NiMH-NiCad setting to compensate for the difference in voltage. Even the venerable Sony ICF SW7600GR, for which alkaline batteries are assumed, seems to operate equally well either way.
My problem has always been the larger power consumers running on D-cells – the Sony ICF 2010 and Grundig Satellit 800 to cite two examples. A fresh set of NiMH batteries put the 2010 on the cusp of poor performance. Lithium batteries having a sustainable single-cell voltage of 1.5 Vdc now provide a possible alternative to a steady diet of costly alkaline cells. Even more attractive, some are equipped with a USB-C connector and can be recharged without a dedicated charger.
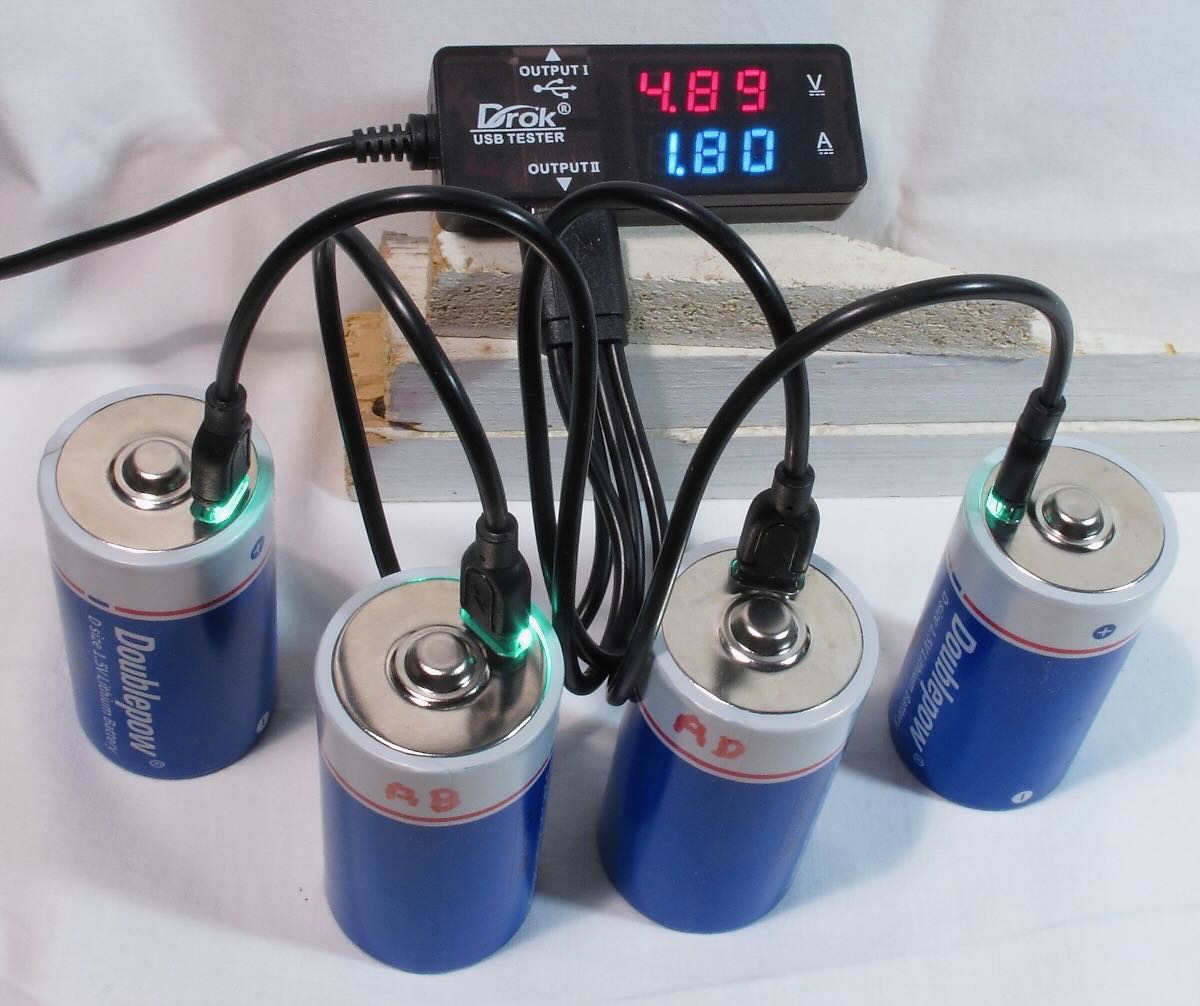

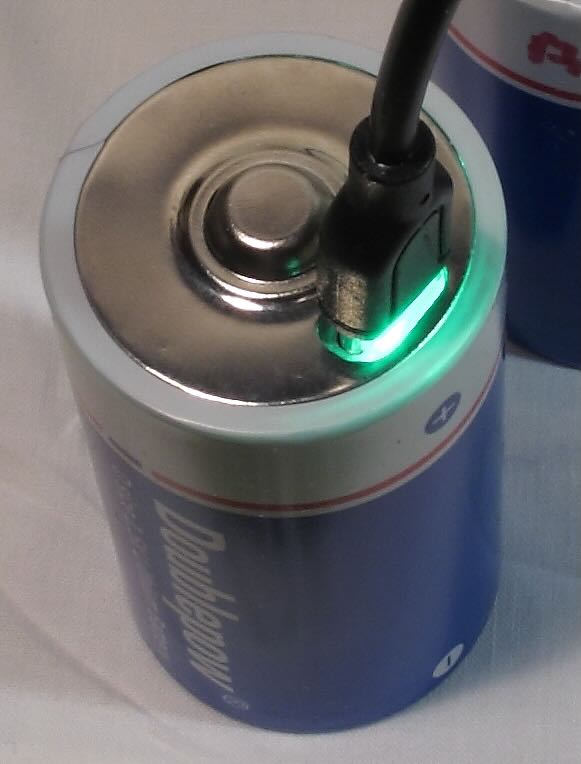
In the figure above, a set of four lithium D cells are connected simultaneously through a 4-lead USB-C harness and USB charger (not shown). Many of the brands include the harness with a set of batteries. I have added a USB multimeter, which I find very useful to monitor the progress of the charge, but this is not necessary. This particular meter can also show accumulated capacity. However, it should be noted that, unless batteries are charged one at a time, charging rate and capacity will show the total values for the number of batteries being charged. I would also recommend that the USB charger be rated at least 3 amps. In the figure below, one of the USB-C leads is connected at the top of the battery. The built-in LED flashes during charge and remains on when the charge is complete.
 Cost is an equally important consideration. There is a lot of hype in the marketing department about how many times these batteries can be recharged. The key compound preposition here is “up to,” and as long as they use those words, they can make the number anything they want to. That said, it simply won’t take more than a few cycles for the cost-benefit cusp to be reached in favor of lithium batteries.
Cost is an equally important consideration. There is a lot of hype in the marketing department about how many times these batteries can be recharged. The key compound preposition here is “up to,” and as long as they use those words, they can make the number anything they want to. That said, it simply won’t take more than a few cycles for the cost-benefit cusp to be reached in favor of lithium batteries.
I am just getting started with this. Although the batteries came highly recommended for the portable radio application, I can make no judgment at this time as to their ultimate quality or convenience. It just seems like the next logical way to go.
There are some things to remember when choosing lithium batteries. Not all lithium batteries are rechargeable, particularly smaller sizes. Some do not come with the built-in USB-C charging jack, so a separate charger intended for lithium batteries will be required. D size batteries are also available at 3.6 Vdc/cell. There may be other options, so watch out. Be sure to thoroughly check the features of any batteries you consider.
I would close by warning that lithium batteries come with safety caveats regarding their transport, handling, use, charging, and disposal. These precautions are all well stated in the literature, which should be followed with an abundance of caution. Of note is the fact that not all chargers support lithium batteries, and their capability should be checked as well.
Click here to check out these Lithium D Cells on Amazon.com (SWLing Post affiliate link), or explore other brands.