Many thanks to SWLing Post contributor, Horacio Nigro (CX3BZ) who shares the following guest post which was originally published in his blog “La Galena del Sur” (in Spanish). Horacio recently translated his article into English for us:
Many thanks to SWLing Post contributor, Horacio Nigro (CX3BZ) who shares the following guest post which was originally published in his blog “La Galena del Sur” (in Spanish). Horacio recently translated his article into English for us:
1923: The first reception of a U.S. broadcaster in South America.
by Horacio A. Nigro, CX3BZ,
Montevideo, Uruguay, “La Galena del Sur”
On the night of October 30-31, 1923, Engineer Roland Raven-Hart, a British Army Major located in the Andes mountains on the Argentina-Chile frontier, heard a U.S. broadcast station (and thus an overseas station) for the first time in South America, an event that made the headlines in the specialized press of that time.
It was the first time that the famous KDKA, Pittsburgh, USA, was heard in South America.
Major Roland Raven-Hart was born in Glenalla, Ireland. He was trained as an engineer, and at the outbreak of World War I he enlisted in the the British Army. He was assigned to the General Staff, and served on sensitive missions in France, Belgium, Russia, Italy, Palestine, Sudan, Syria, Egypt, etc. At one point he installed an antenna on one of the pyramids of Egypt that allowed him to quickly communicate with the staff.

Ing. Roland Raven-Hart. (1889-1971). Major of the British Army. He was member of the Institute of Radio Engineers and the American Institute of Electric Engineers.
As a consequence of his outstanding performance, several allied governments gave him merit awards, such as Officer of the Order of the British Empire, Croix de Guerre from France, Order of St. Stanislaus of Russia, etc.
When peace was restored, and with the rank of major, he asked to be released to travel for rest and study in Buenos Aires, Argentina, where the Pacific Railroad Administration allowed him to study wireless. This continued after the Trans-Andean railway arrived in the mountain village of Los Andes, where he had installed his famous amateur radio station 9TC.
He had good DX, and on this date, achieved a distance record for broadcast reception between North and South.
In fact, the Argentinian “Revista Telegráfica”, a magazine edited in Buenos Aires, Argentina, reported the following news in its October 1923 edition:
REMARKABLE RECORD
At press time, we get the following report. The news could not be more sensational. It has been possible to receive a North American broadcasting station at a distance of approximately 8,300 kilometers!.
It is an event that marks a new era in our modern history of radio. Using the pseudonym “John English” is a distinguished engineer who deserves our absolute faith.
Indeed, “John English”, pseudonym of Roland Raven-Hart, reported:
Radiotelephony up to 8,300 kilometers. – Reception tests in Los Andes (Chile) and Puente del Inca (Mendoza). – Interesting observations.
In Los Andes (Chile) on the night of October 30-31 I received a complete program from a station announcing as “KDKA – Pittsburg ‘classical music, jazz and comedy, all in English. I think this must be a record, being a distance of more or less 8,300 kilometers.
The apparatus used is a “Western Electric”, with a high [frequency] amplification, detector and low [frequency]amplification, with a phone of the same brand.
The antenna was 20 meters long and 5 meters high on a zinc roof”.
He does not mention the frequency or wavelength. The Westinghouse station was operating on the frequency of 920 kHz at that time , but it is also likely that he received it on shortwave via station 8XS, which began simulcasting KDKA mediumwave in July 1923 on the 60 meter band.
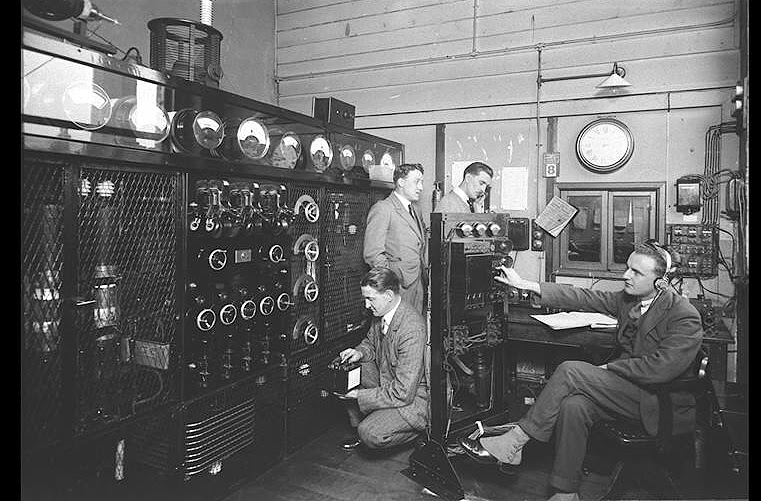

KDKA
Raven-Hart was enjoying reception at the time, but from local stations:
During the month of October I have heard the following stations, and will have much pleasure in giving news about the reception quality, etc. My address for letters: Supte. [abreviation of Super Intendent], Telégrafos F. C. T. Los Andes (Chile).
Buenos Aires ……. Radio Cultura, Radio Sud América
Montevideo ……… Paradizábal, R. Sudamérica
Tucumán ………….. Radio Club, San Pablo, « R. P. F. »
Rosario ……………. Radio Club
San Juan ………….. “340” , Pekam
Villa Maria ………… Radio Coen .
Bahia Blanca ……… Dr. Cattaneo ( CW . Telegrafía ) .
As promised, I detail the results of my tests at my facilities for October 17- 21 from Puente del Inca ( Mendoza ), with a “Western Electric” receiver, one tube for high frequency reception, detector, and one tube for low frequencies.
The weather was variable, cloudy and snowing on the 21st. Static was relatively strong on days 17-19, but there was little static on the 20th and 21st.
Radio Cultura and Radio Sudamérica [Buenos Aires] were also heard during the day, the first with the headphones on the table.
Sociedad Radio Argentina, 1100 kilometers away, was received well at night.
From Montevideo, 1300 kilometers, I got Paradizábal and Radio Sudamérica, and also the following:
Radio Club of Villa María (Cordoba ), 650 kilometers;
Radio Club de Tucumán, 850 km;
Station 340, San Juan, 200 kilometers, daytime, and Radio Pekam;
Station 394, Rio Cuarto (Cordoba), (initial number somewhat dubious ), 550 km
Radio Club of Rosario de Santa Fe, 900 km;
Radio Chilena de Santiago de Chile, with headphones on the table and at a distance of 120 meters [sic](1) ;
A. B. C., Viña del Mar (Chile).
My antenna is too long, allowing me to listen to only a few amateurs, but I will try again.
As always, during their conversations various radioamateurs did not give their names.
I think it is interesting to make three observations: 1) there are stations on the frequencies of Radio Sud América, Radio Cultura and Paradizábal, causing heterodynes, so it is impossible to receive one station without the other; 2) several of th smaller stations produce noise from the generator, or the rectified AC, that is louder than the music they broadcast, with horrible results; and 3) several stations produce carrier waves equal to or stronger than that of Radio Cultura, but the modulation is so low that the voice is barely heard.
In my view, there are stations that could double their transmission range if they paid more attention to their modulation than to the current at the antenna.
I do not mention the stations, but I’ll be glad to answer directly to the abovementioned amateur stations if they contact me at: “Superintendent of Telegraphs. F. C. Transandino. Mendoza.”
-John English

Broadcasting station HA9, Villa María, Córdoba, Argentina. “one of the best of the countryside”. (1925).
Mr. Raven-Hart, was in fact an active chronicler of the pioneering radio activity that had been developed at that time in the Southern Cone of America.
By the end of May 1926, he returned to Europe, spending some time in Spain and Italy. Then, he travelled to the U.S., where he was received by the organized amateur radio community in this country as a representative of the South American hams, in recognition of the 9TC success. He returned to Buenos Aires in 1927.
It is worth mentioning his impressions on his European tour. He summarized the status of radio in Europe in two words: “Little news”. However, he commented on the “new” Loewe brand of vacuum tubes, which he had the opportunity to test, “as detector and dual audio frequency amplification at the same time”, with results that he described as wonderful. He also found good broadcast programming. As to the receiving apparatus in use, he considered that it was“inferior to that used in the U.S. and Argentina and much more complicated”.
In 1932 he retired from his engineering profession, and traveled to Ceylon (now Sri Lanka) to do canoeing. Actually, he navigated more than 15,000 miles of the rivers in the world, using a folding canoe.

One of the books authored by R. Raven-Hart
During World War II, Roland James Raven-Hart was one of the 766 Argentine volunteers serving the Allied cause.
Roland’s life was undoubtedly an exciting global adventure. It is said that he was a friend of Colonel T. E. Lawrence (“of Arabia”) working for the Intelligence Department, and he seems to have been at least partly responsible for convincing the famous writer Arthur C. Clarke (author of “2001 A Space Odyssey”), a communications engineer colleague, to settle and live in Ceylon:
En route from Australia the ship docked in Sri Lanka (then Ceylon), where Clarke met Major R. Raven-Hart, OBE. “A remarkable linguist and lover of exotic places, cultures and customs,” said Clarke. “It was my first introduction to the fabulous Orient. I’ve been here, more or less, ever since”.
He was the author of several books, especially about his canoeing activities, and he wrote an article in collaboration with composer Lennox Berkeley entitled “Wireless Music”.
In December 1923 KDKA would be rebroadcast in Great Britain, and had even been received in Hawaii, and later, on March 25, 1924, KDKA broadcast entirely in Castilian for the South American nations .
In early 1924 it would be heard for the first time in Uruguay.
Sources:
-Originally published in my blog “La Galena del Sur”, (in Spanish).
-Special acknowledgment goes to Mr. Jerry S. Berg, USA, for helping with the best translation of the original article.
Amazing story, Horacio! Thank you for taking the time to translate this fine article into English!
[The] Pacific Islands News Association (PINA) is concerned with the decision of the Australian Broadcasting Corporation (ABC) to shut down its Shortwave Radio Services to the Pacific by the end of January next year.