Reginald Aubrey Fessenden (October 6, 1866 – July 22, 1932)
Some of you may recall that last year, I posted an announcement about WG2XFQ; this station annually airs Brian Justin’s longwave broadcast honoring Reginald Fessenden’s famous Christmas Eve’n 1906 AM voice transmission. I had been lucky enough to capture a recording of this commemorative event on WG2XFQ in 2013.
Just yesterday, I was contacted by SWLing Post reader, George Stein (NJ3H), who had just discovered my recording–and, in turn, shared his own recording of the WG2XFQ transmission. In George’s message, he casually mentioned that he has a close family link to the original Fessenden Christmas Eve broadcast, which I find of great interest. George writes:
“My grandfather, Adam Stein, Jr., was Fessenden’s chief engineer and was present for the Christmas Eve broadcast from Brant Rock, Mass in 1906. He is also mentioned in the Fessenden biography by Helen Fessenden, of which I have a copy…
In scientific journals from that time…it was reported that my grandfather’s voice was the first heard across the Atlantic (Machrahanish, Scotland) in Nov/Dec 1906. This occurred during testing at Brant Rock and was picked up by Fessenden’s man in Scotland.”
All I can say is, Wow! This is an amazing bit of history. Of course, I sent a reply to George asking for more information and permission to post this, which he kindly granted. George continues with an excerpt from S. Belrose, Communications Research Centre Canada:
“In November 1906, Fessenden and colleagues were conducting experimental transmissions using his newly-developed HF alternator, between stations at Brant Rock and Plymouth, Massachusetts. The station at Brant Rock was modulated by a carbon microphone connected in series with the antenna lead.
About midnight, on an evening early in November, Mr. Stein was telling the operator at Plymouth how to run the dynamo. His voice was heard by Mr. Armor at the Macrihanish, Scotland station with such clarity that there was no doubt about the speaker, and the station log book confirmed the report.
Fessenden’s greatest triumph was soon to come. On 24 December, 1906, Fessenden and his assistants presented the world’s first radio broadcast. The transmission included a speech by Fessenden and selected music for Christmas. Fessenden played Handel’s Largo on the violin. That first broadcast, from his transmitter at Brant Rock, MA, was heard by radio operators on board US Navy and United Fruit Company ships equipped with Fessenden’s radio receivers at various distances over the South and North Atlantic, as far away as the West Indies. The wireless broadcast was repeated on New Year’s Eve.”

The Brant Rock staff and operators: Fessenden is seated in the middle and to his right is his son (Reginald Kennelly), holding Mikums, his cat. Mr. Pannill is on the far left. Standing next to him is Jessie Bent, the secretary. Mr. Stein is on the far right. (Radioscientist)
[Above] A picture of Fessenden’s team at Brant Rock, Mass in 1906. Radio pioneer Charles Pannill is shown in the picture. My grandfather, Adam Stein, Jr., who was Fessenden’s chief engineer, is also shown in the picture.
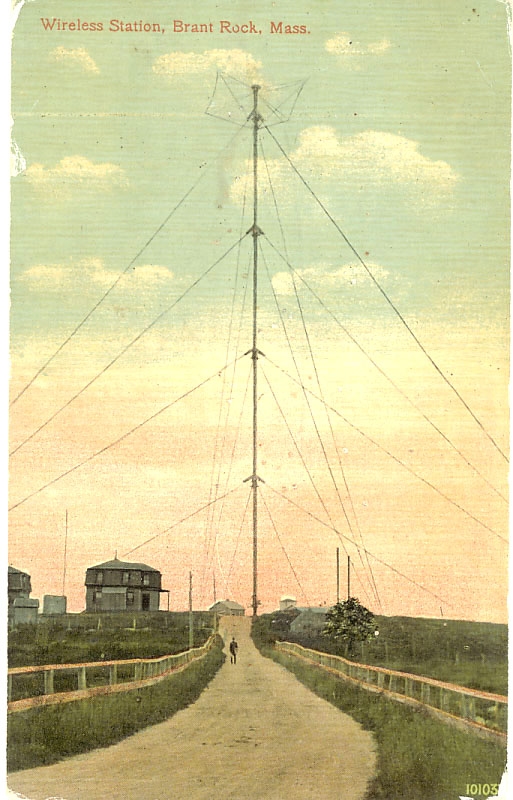
A postcard showing Fessenden’s wireless antenna in 1906 at Brant Rock.
George continues:
In December 2006, a special event amateur radio station, W1F, was on the air from Brant Rock to commemorate 100 years since Fessenden’s Christmas Eve and New Year’s Eve broadcasts. Stephan Barreres, K2CX, put a team together for the special event. I was fortunate to be included with the fine team he had assembled.
All that remains of the Fessenden antenna is the tower base.
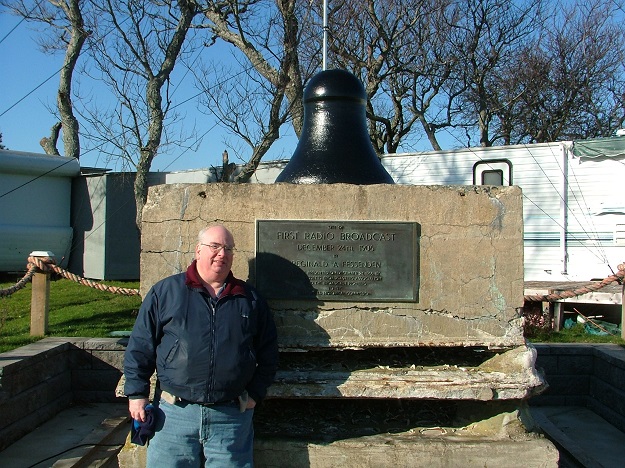

The picture was taken in Dec 2006, with NJ3H standing in front.

The plaque on the base was provided on the 60th anniversary of the 1906 broadcast.
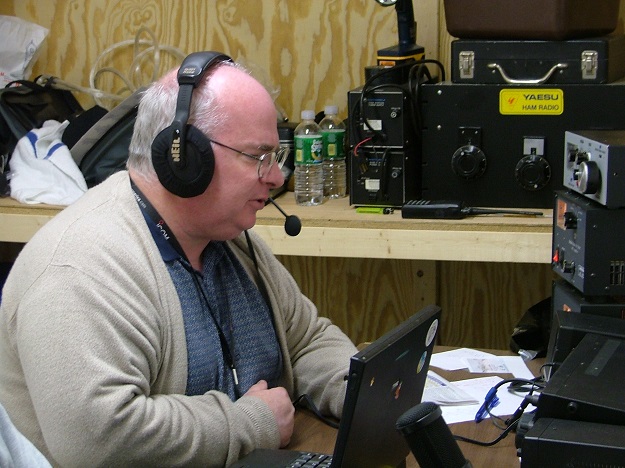

NJ3H at the operating position of W1F, 30 December 2006
The following is George’s audio and screen cast while he received the Christmas Eve reenactment broadcast on 25 December 2013; WG2XFQ broadcast from Forest, VA by WA1ZMS, this recording was made by George in Stephens City, VA on a Microtelecom Perseus SDR and a Wellbrook loop.
For those of you not familiar with Reginald Fessenden, I encourage you to read about him; he was a Canadian inventor who performed pioneering experiments in radio, including the use of continuous waves (CW) and the early—and arguably the first—radio transmissions of voice and music. Check out some of our archived posts on Fessenden and read more about him at this online Fessenden museum.
George, again, many thanks for sharing a little history about your grandfather and your own way of honoring his work.












