Many thanks to SWLing Post contributor, Frank, in Germany, who shares the following guest post and review of the Deshibo RD1860BT:
Deshibo RD1860BT report
Hello Thomas,
Today I would like to report on a new portable world receiver. Unfortunately, new devices have not been found on the shelves of electronics retailers for a long time, but now in the depths of the world wide web. And that’s how I came across the Deshibo RD1860BT.
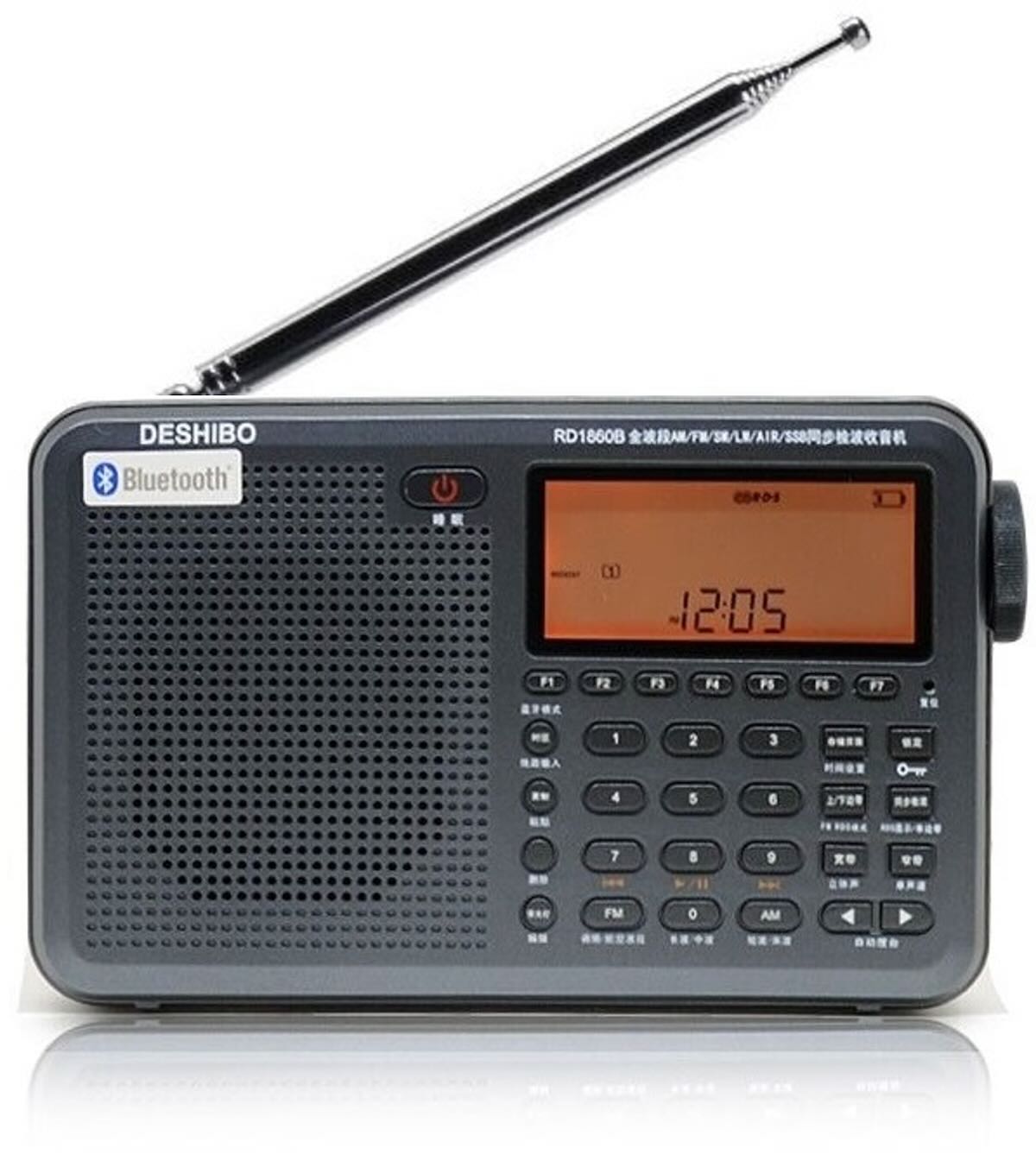
Deshibo is certainly known to many from their GA450 loop antenna. But Deshibo has also produced several radios, including the RD1780L, which is probably a little better known. New to the segment is the RD1860BT, which initially seemed like an old friend to me. An Eton Elite Executive? Yes, there are external similarities, but also differences.
Many months ago I had an Eton Elite Executive for a short time. I had heard of its excellent reception properties, which I can confirm, but the design is reminiscent of older receivers from the 80s, is relatively heavy, operation is sometimes a bit cumbersome, the protective cover does not protect properly. I find the device to be portable overall difficult. We didn’t become friends, so I sold it on to a Swede, who in turn became a friend.
I still missed the Eton. RDS on VHF is not found in any Tecsun , nor are there memory banks that can be written on.
Then I discovered the RD1860BT and couldn’t resist. First of all: the Deshibo is only labeled in Chinese for important function keys. But the friendly dealer on eBay provided me with an English manual before I bought it. That was the deciding factor, because I was sure that after a little use , the Deshibo could be operated blindly.
However, some questions have arisen in the user manual. Some things didn’t seem quite right, others were completely missing from the description. That’s why I decided to write my own manual on a journey of discovery of the new Deshibo. And so that it might also help others who might be interested in radio, I wrote it in English and attach it here.
Click here to download Frank’s version of the RD1860BT manual (PDF).
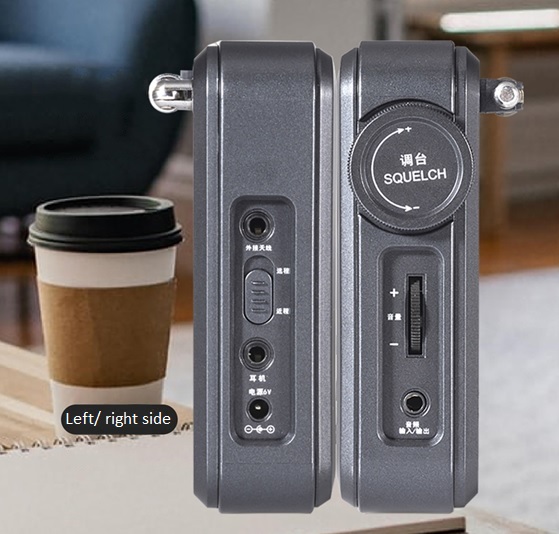
The Eton’s somewhat unsorted manual was very helpful, but I also added my own drawings. For example, I added an English-labeled keyboard as a back cover, so that the keys can be assigned without a long search.
Here you can already find the first differences to the Eton: the keyboard layout is a bit more orderly. Also, the Deshibo doesn’t have a metallic speaker grille (which frankly I don’t like about the Eton). The display, not the writing, is backlit in orange on the Deshibo . Most importantly, the Deshibo is a lot lighter than the Eton ( around 500g if I researched correctly). And that means: the structure of the Deshibo must be different. Continue reading