Many thanks to SWLing Post contributor, Don Moore–noted author, traveler, and DXer–for the latest installment of his Photo Album guest post series:
Don Moore’s Photo Album: Costa Rica (Part Two)
by Don Moore
It’s been three months since the last time I put together one of these pieces because I was busy finishing my book, Tales of a Vagabond DXer [Note: SWLing Post Amazon affiliate link]. You may have seen the announcement about it here a few weeks ago. This series should appear more regularly in 2024 as I plan to concentrate on small writing projects for a while!
Back in August, we looked at five Costa Rican shortwave stations that I visited in 1990. This time I’m going to feature just one station, but a station with a very interesting story. My book has an updated and rewritten version of the article I wrote about it for Monitoring Times magazine in the early 1990s. But the book doesn’t have many photos as adding those significantly increases the price. So, here are the pictures and a little bit about the station.
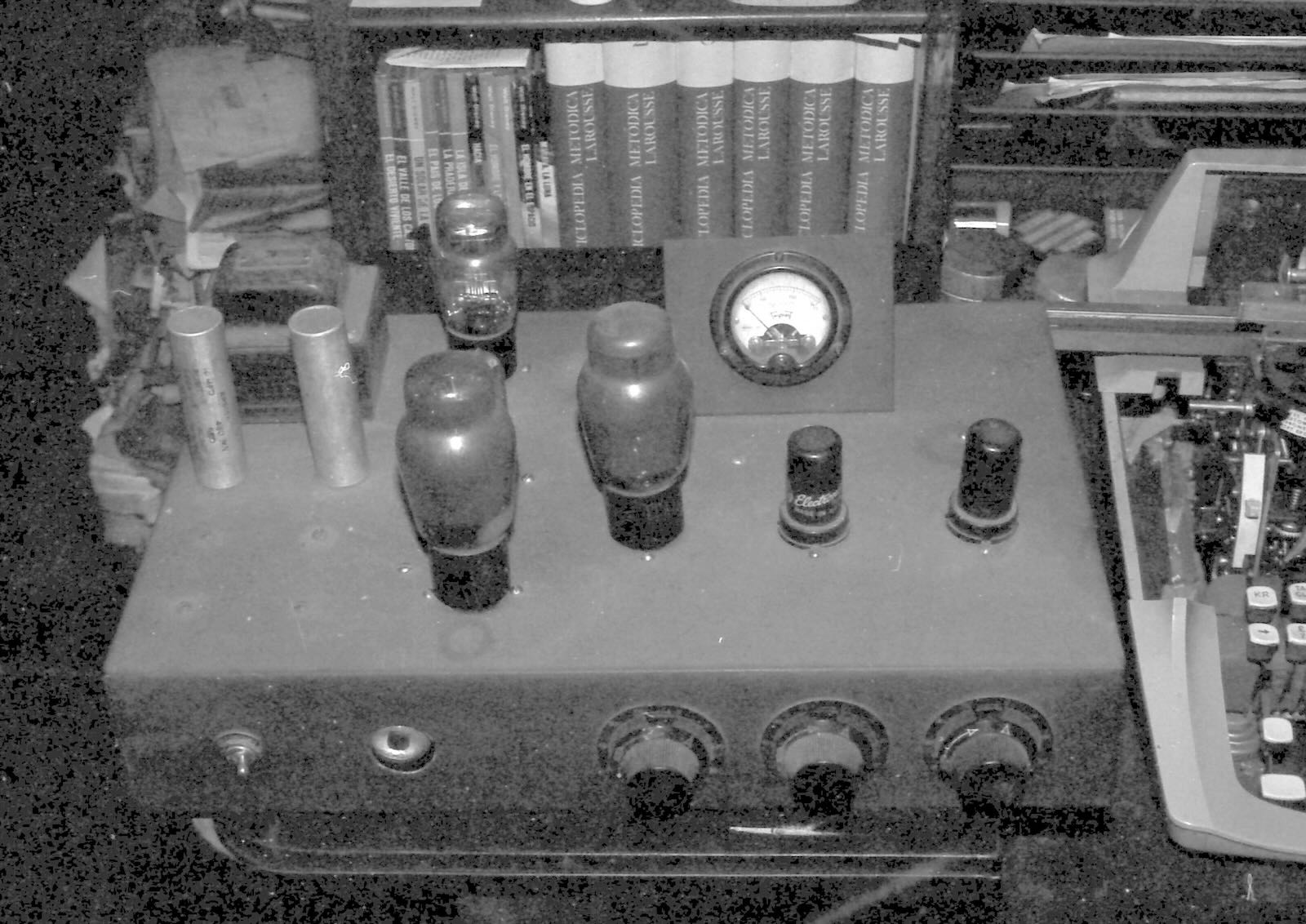
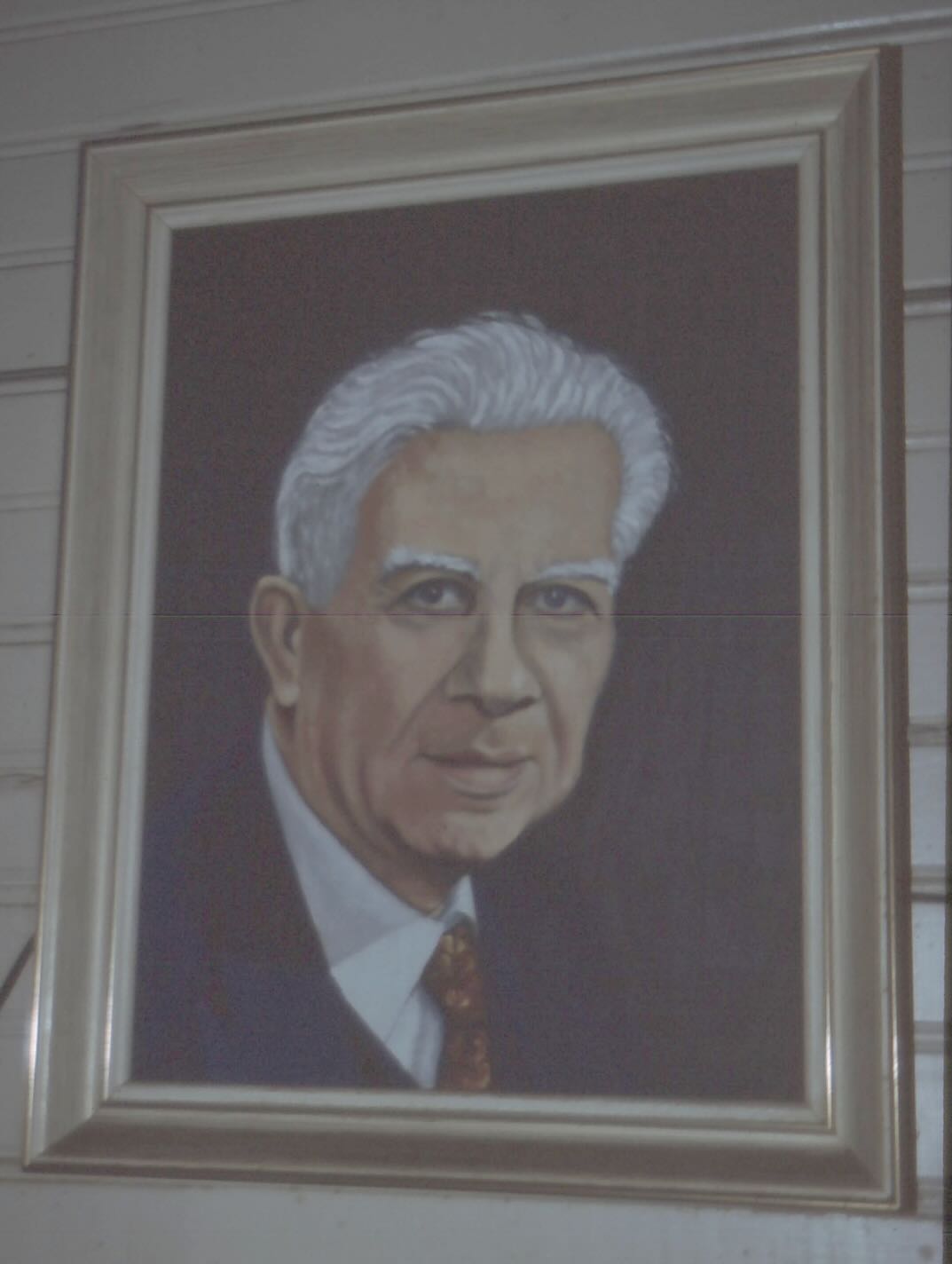
This seven-and-a-half-watt transmitter was the first transmitter for TI4NRH, the first shortwave broadcast station in Latin America. It was built by Amando Céspedes Marín in Heredia, Costa Rica in 1928. Don Amando operated a small medium wave station and hoped that by using shortwave he could reach listeners in all of Costa Rica. Instead, he gained an audience all around the world. His little TI4NRH became one of the most popular radio stations for shortwave listeners throughout the 1930s until he shut it down at the beginning of World War Two. This portrait of Don Amando was made around that time.
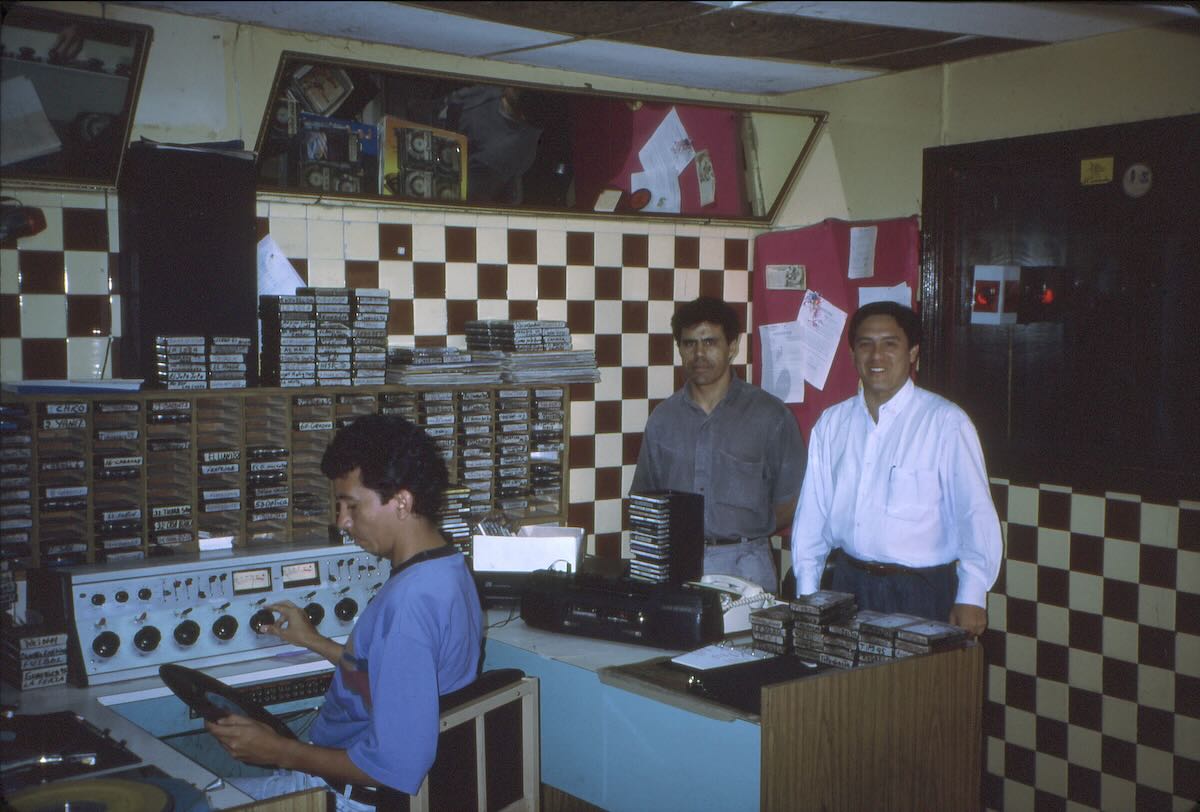
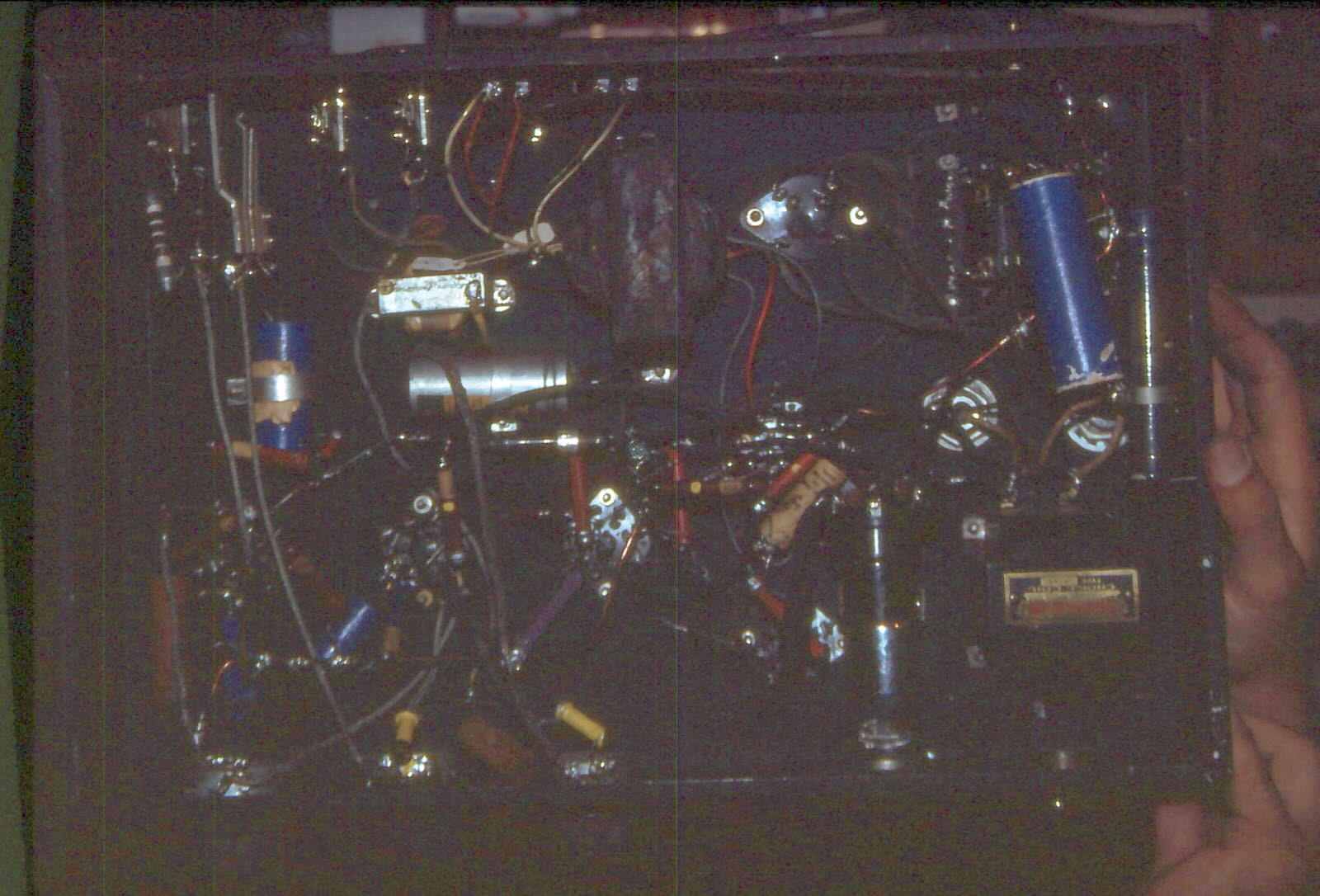
I remembered reading about TI4NRH in an old-timer’s article, so while I was in Costa Rica I went to Heredia hoping to find someone who could tell me where the station had operated from. I wanted to get a picture of the building. Instead, I found that everything was still there in the dimly lit backroom of the family house. (The pictures are grainy as the room was very dark.) Don Amando had passed away in 1976 but his never-married daughter, Lydylia, still lived there and treated the room as a shrine to her departed father.
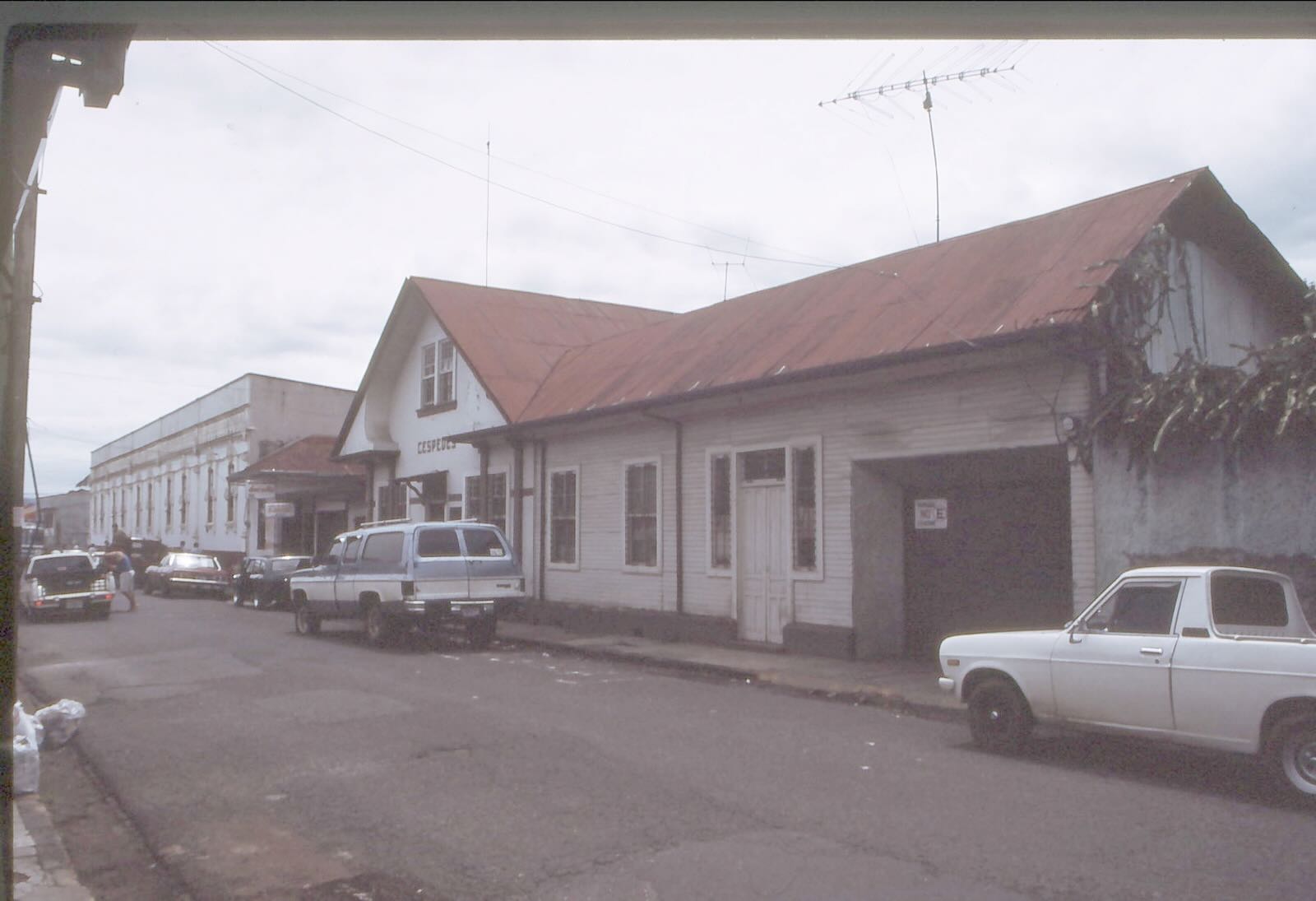
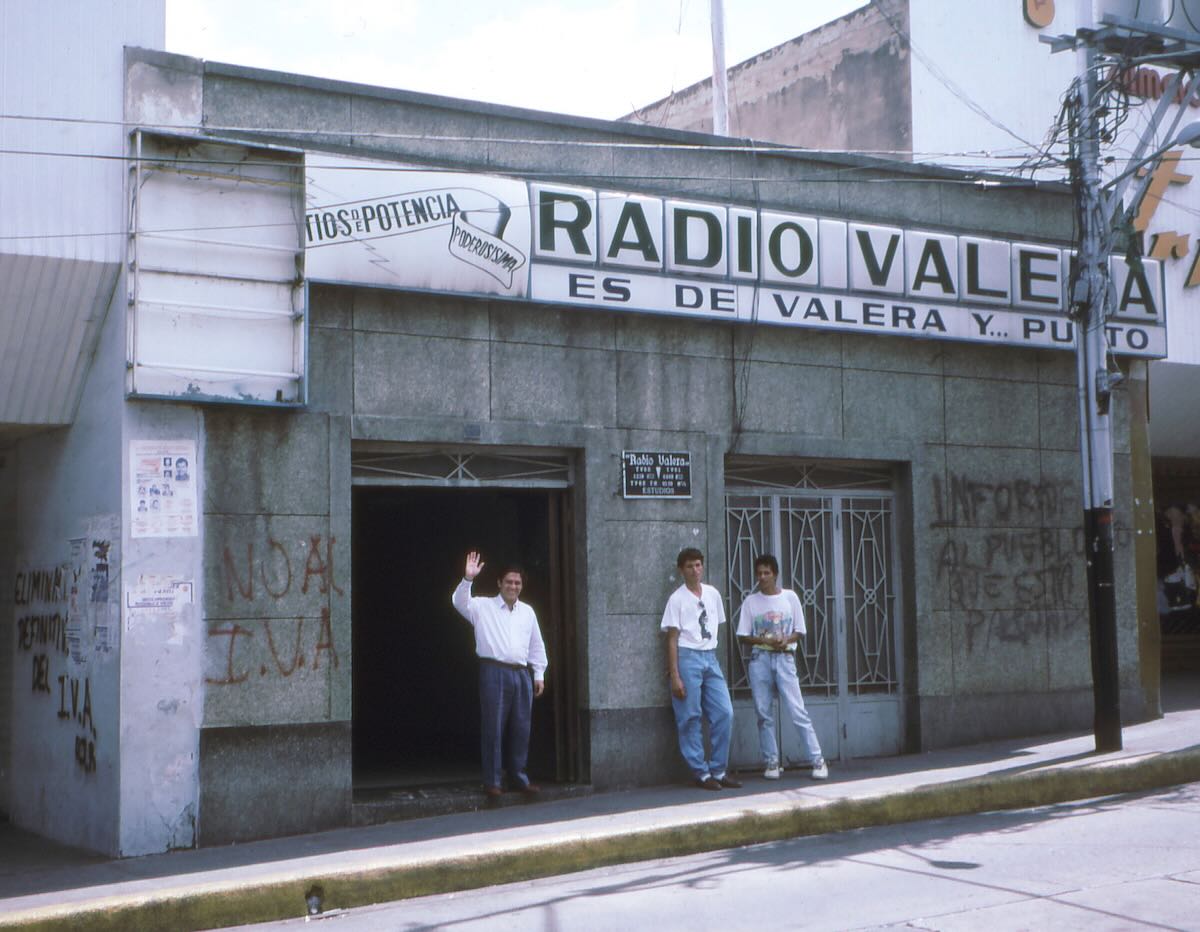
The Céspedes family house was on a side street a few blocks south of the main plaza in Heredia. The radio station was located in the middle section, behind the white door.
Plaque on the front door commemorating the building as the birthplace of radio in Costa Rica.
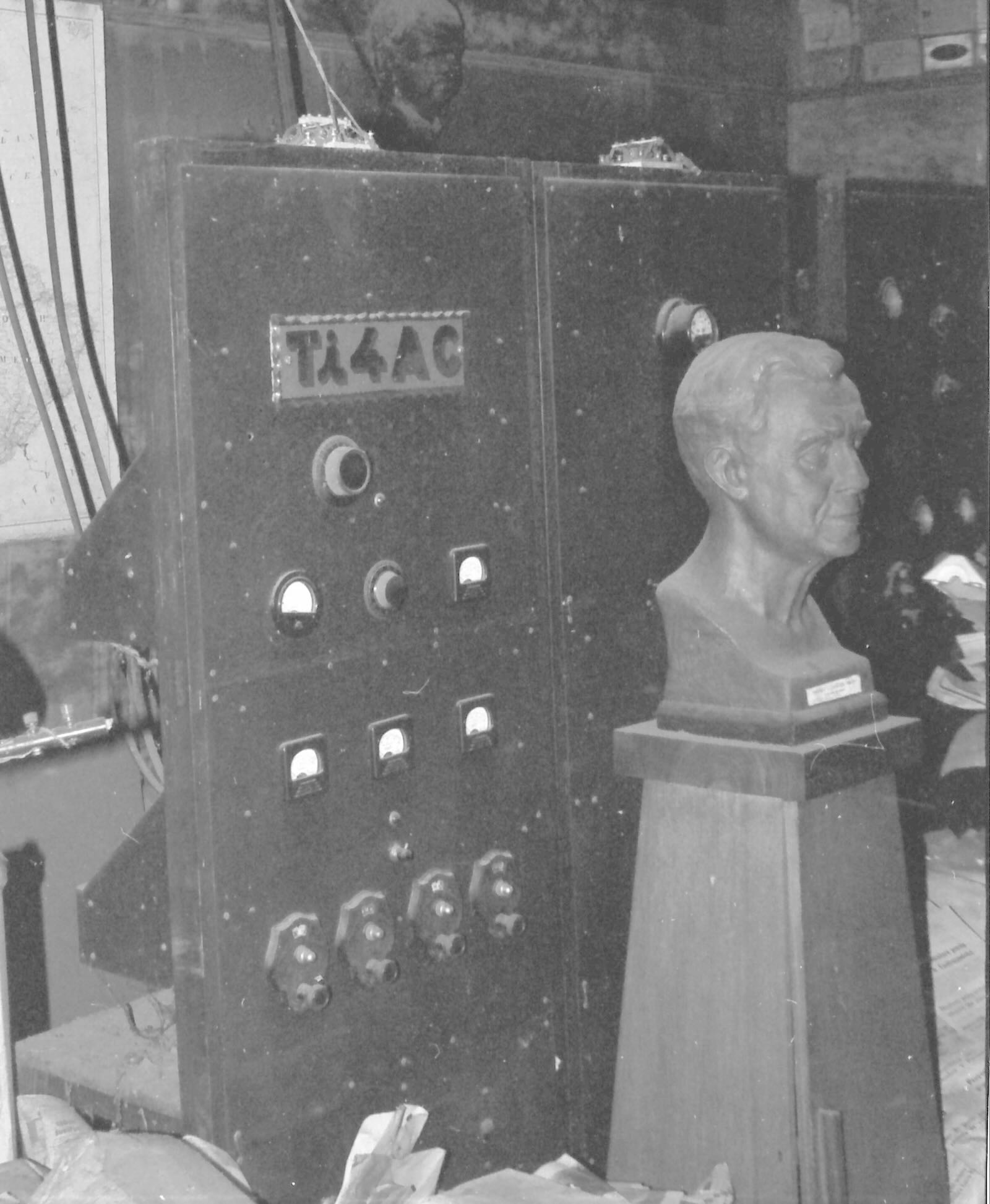
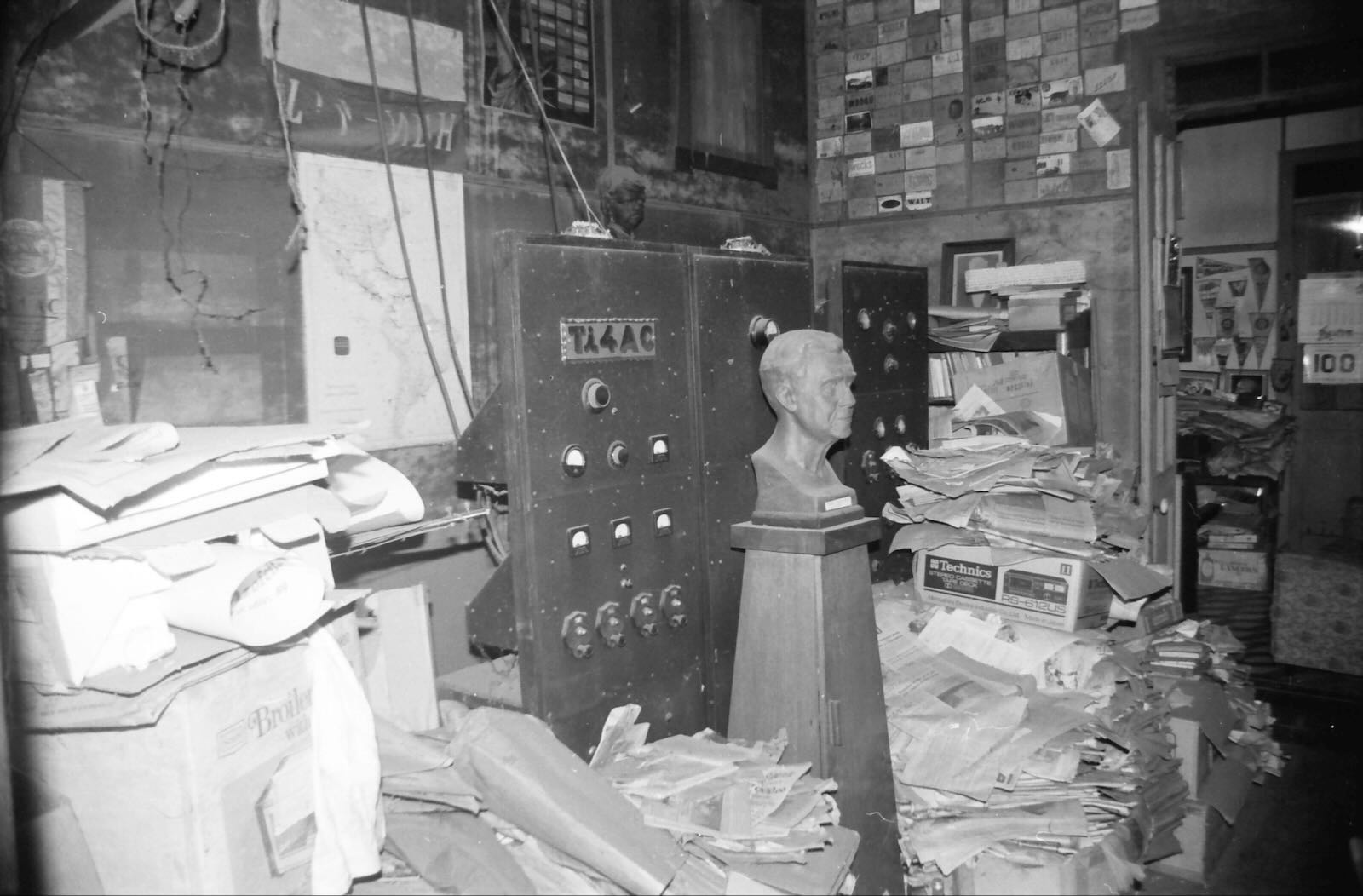
Financial support from listeners helped TI4NRH buy new transmitters and raise power. This 300-watt transmitter was the last one used.
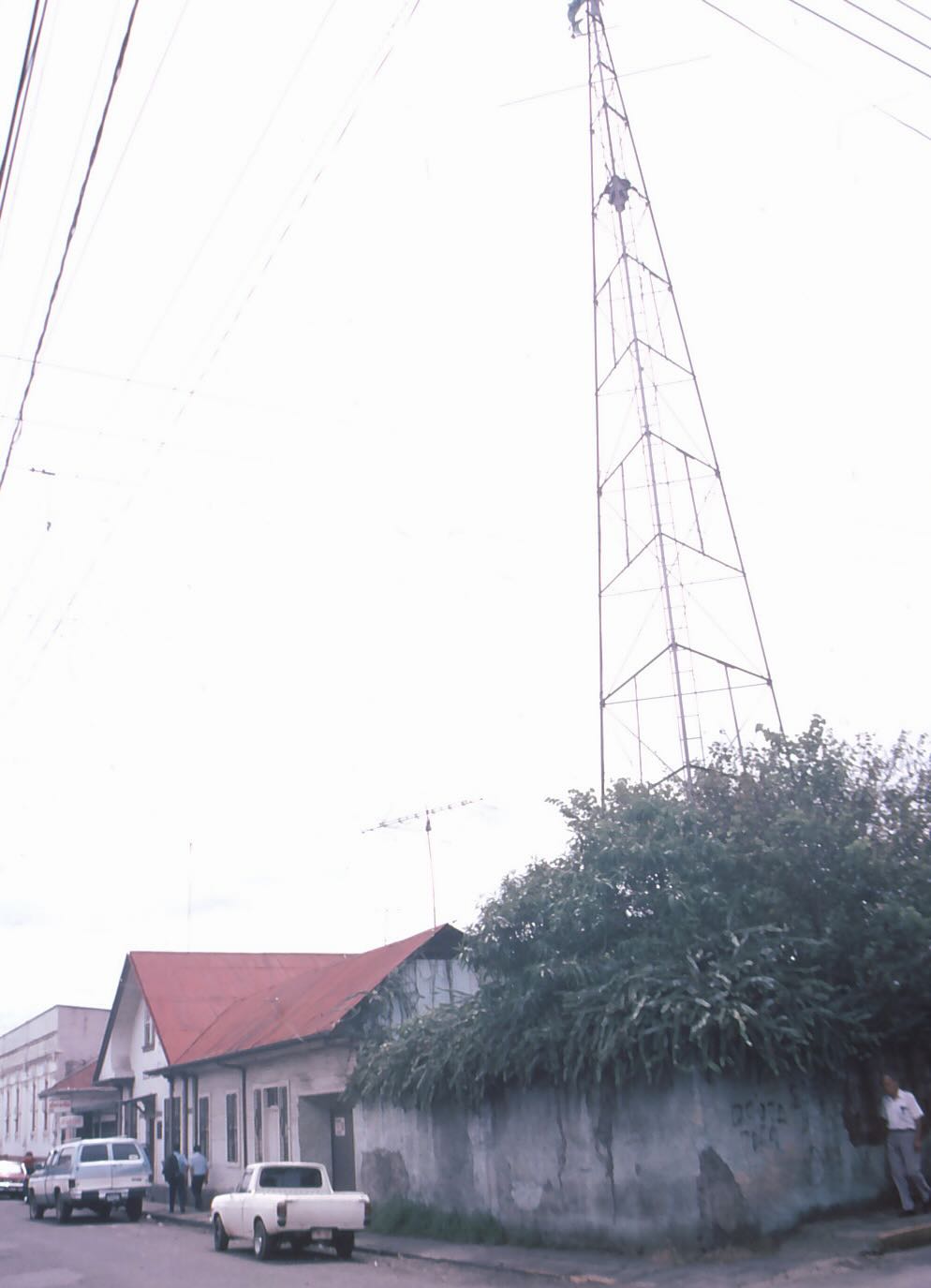
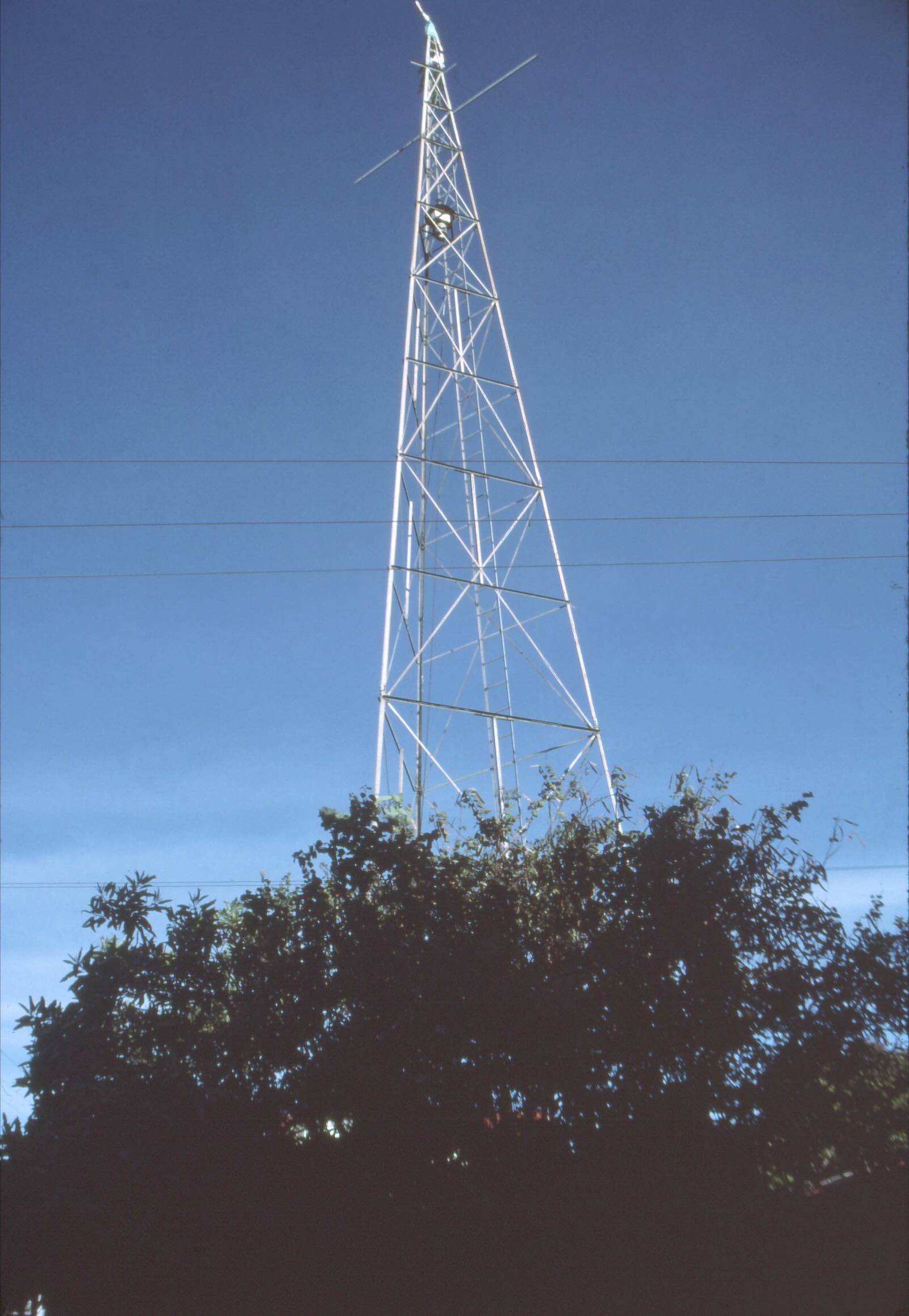
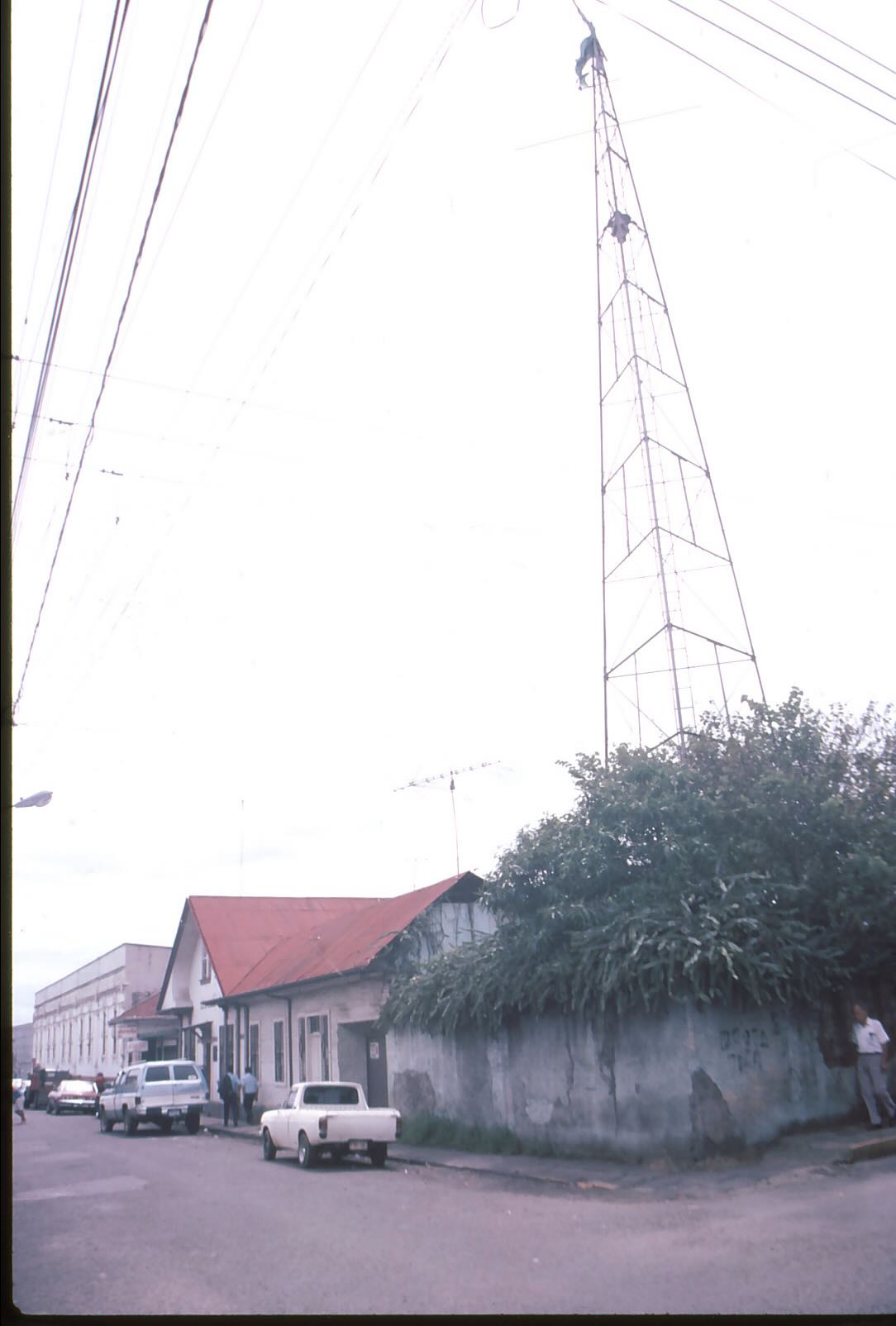
Radio amateurs in the USA and Canada raised money to buy and ship this antenna tower to TI4NRH in the late 1930s.
Nothing was removed after the station closed down but the space became a storage room for the family. This is how it looked in June 1990.
The bottom of that original 7 ½ watt transmitter. Unfortunately, the photo came out very dark in the dimly lit room.
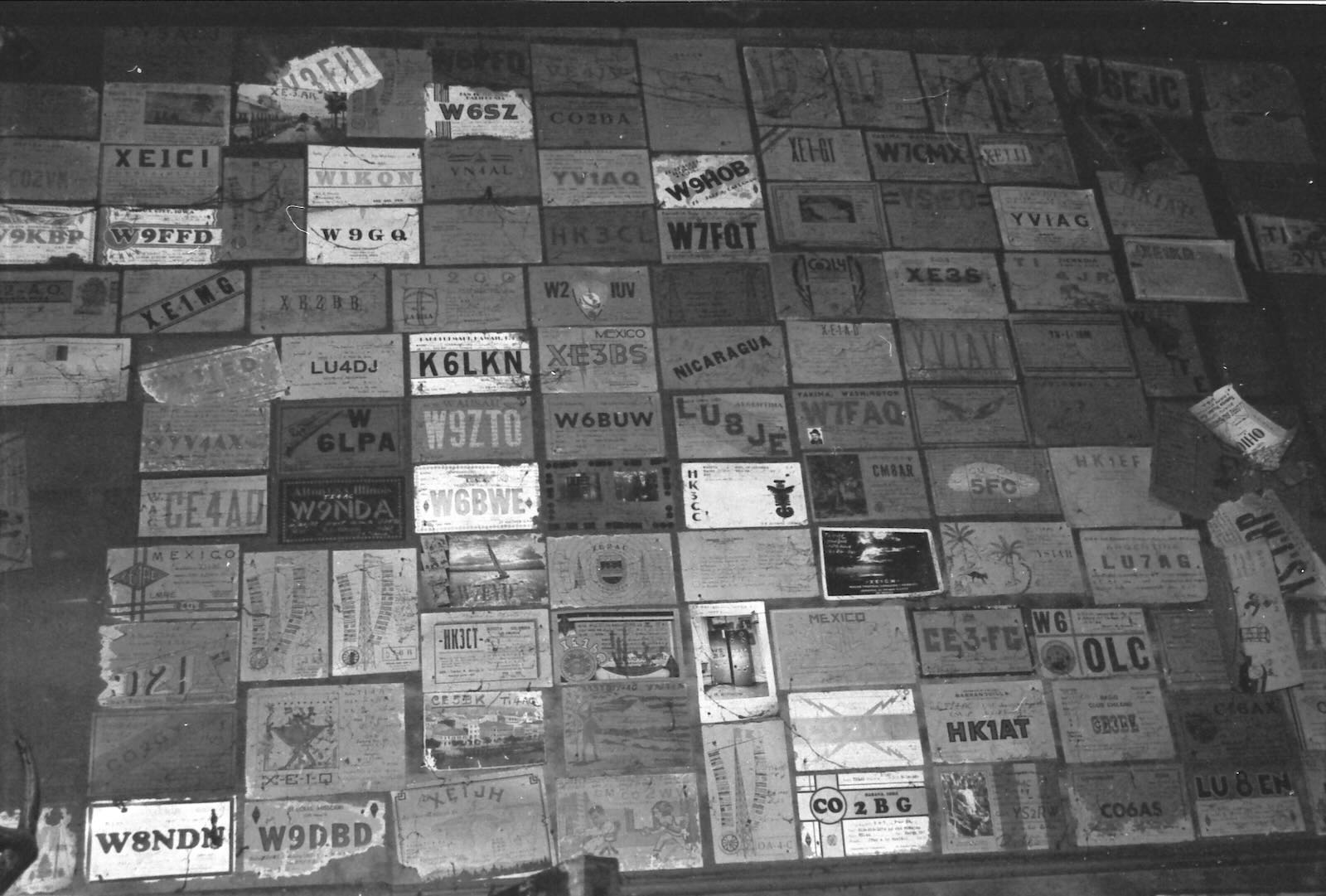
The walls were covered with yellowing 1930s amateur radio QSL cards.
This letter written by Arthur Kopf, an American working in the Panama Canal Zone, was the first report received by TI4NRH. That made it the first reception report ever written to a Latin American shortwave broadcast station.
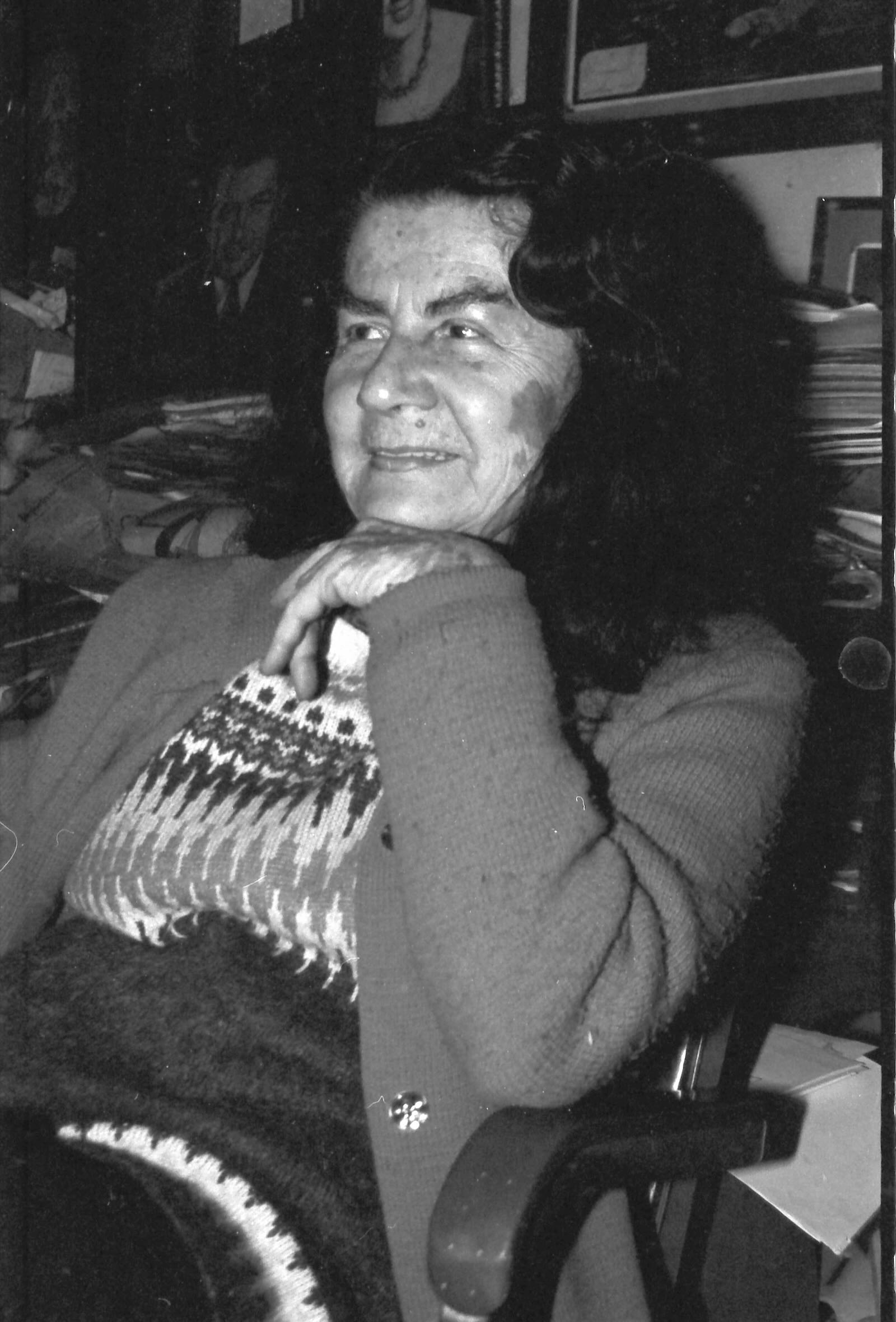
Don Amando’s daughter Lydylia was the guardian of her father’s legacy.
A view showing the house and neighboring antenna tower.
TI4NRH was only a hobby for Don Amando. He made a living by operating a print shop and photography studio. With financial support from the Zenith Corporation, he published a monthly radio magazine (primarily in Spanish) for several years in the 1930s.
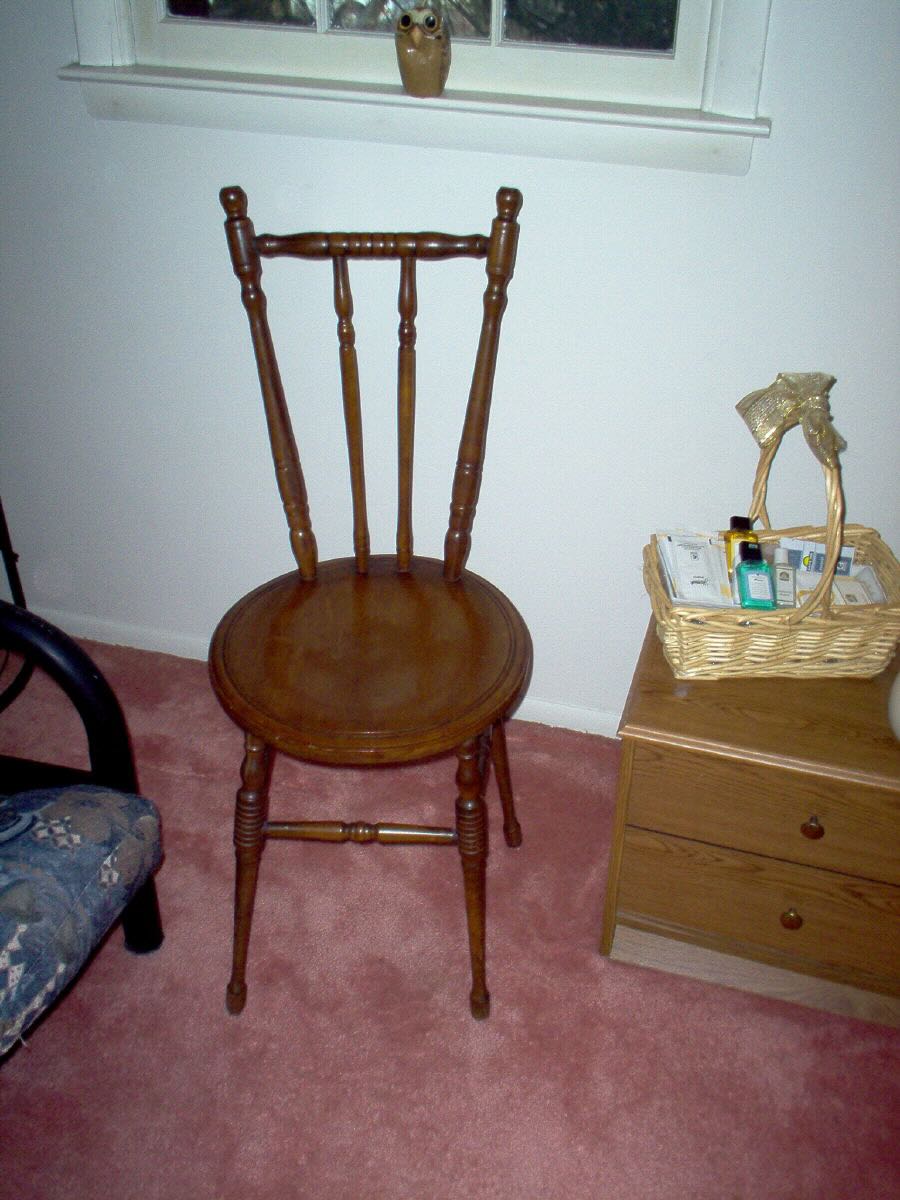
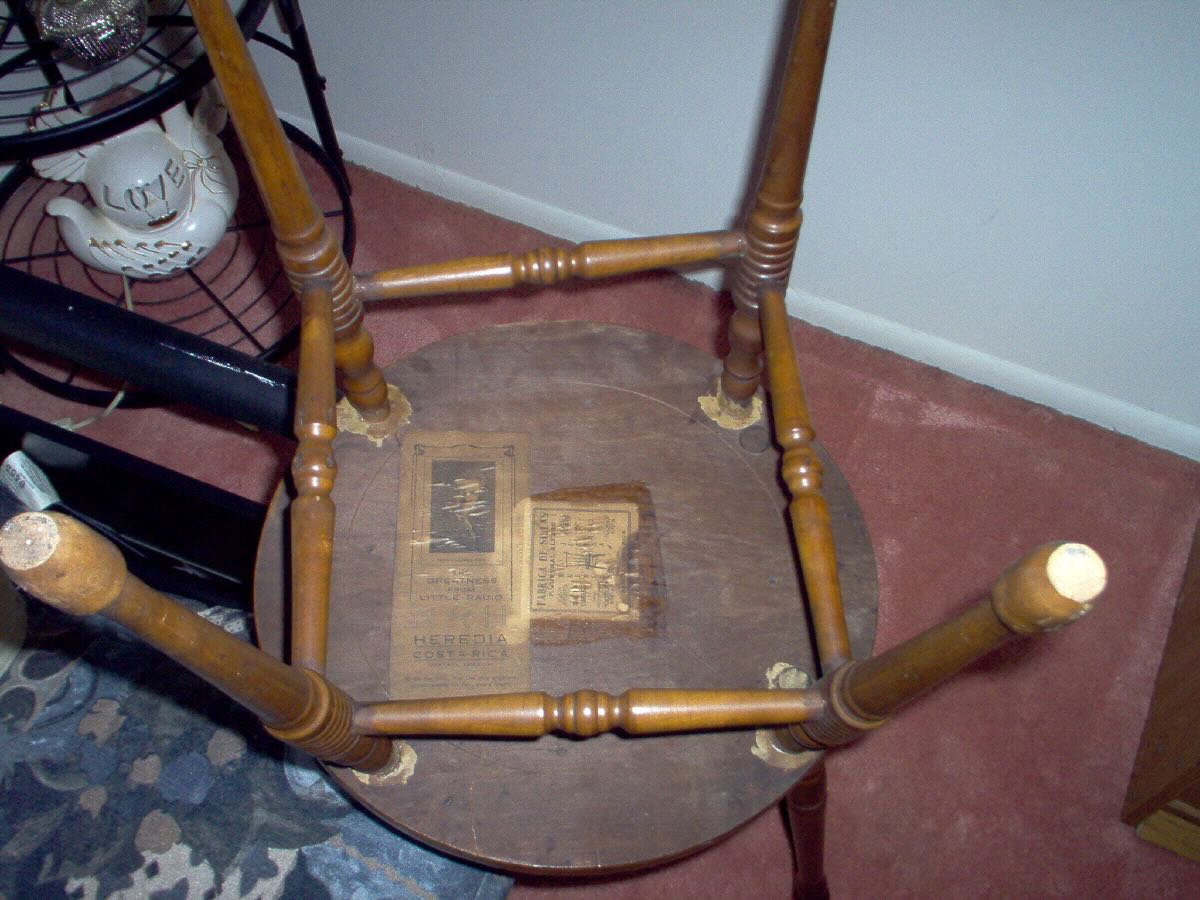
In 1928, Philadelphia DXer Charles Schroeder became the first North American DXer to log a Latin American SWBC station when he heard TI4NRH. He not only got a QSL for his reception, TI4NRH sent him a beautiful chair made out of Costa Rican tropical hard woods. The chair was sent in pieces with instructions for assembly and arrived in just twelve days. Mr. Schroeder passed away in 1956, but in 2005 I heard from Schroeder’s daughter, who still had the chair. She sent these photos.
Finding TI4NRH was like finding an unknown time capsule. It was one of the biggest highlights of both my DX career and my travels. And I always hoped to return. In the late 1990s I learned that Lydylia had passed away and that one of her nephews had moved into the house. Sometime around 2010 the antenna tower had become unsafe so the family had it torn down and sold for scrap. However, other than donating a few items to the city museum (something Lydylia had refused to do), the family continued to hold on to Don Amando’s legacy. In 2017, a group of Costa Rican radio amateurs visited the house and published their photos, which were much better than my old ones.
I would like to say that everything is still there for the next visiting DXers to see. But in looking for links to include in this piece I came across some very sad news. The house was demolished in July 2021. Apparently the next generation of the family (Don Amando’s great-grandchildren) had no interest in maintaining the old house and Costa Rica doesn’t have a good program to preserve historical sites. So the city of Heredia had the house torn down. The news article I found (which was very critical of the destruction) didn’t even know what had happened to the station memorabilia that had been in the house. So, unfortunately, this story does not have a happy ending.
LINKS
- The article about the destruction of the house.
- The 2017 visit by Costa Rican amateurs. Scroll through the photos by clicking on the dots or the white arrows.
- In 1990 I was given several copies of Don Amando’s URA magazine from the 1930s. Images can be downloaded here.
- The On The Shortwaves website of the Committee for the Preservation of Radio Verifications has some excellent material on TIRNRH.
- A six-minute video of photos and movies taken by Don Amando in the 1920s and 1930s (but nothing of the radio station): https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yXu-7k9Lql0
To see the exact location of where TI4NRH was, open Google Maps and search for the following coordinates: 9.995550958984419, -84.11618361000325 then switch from map view to satellite view.
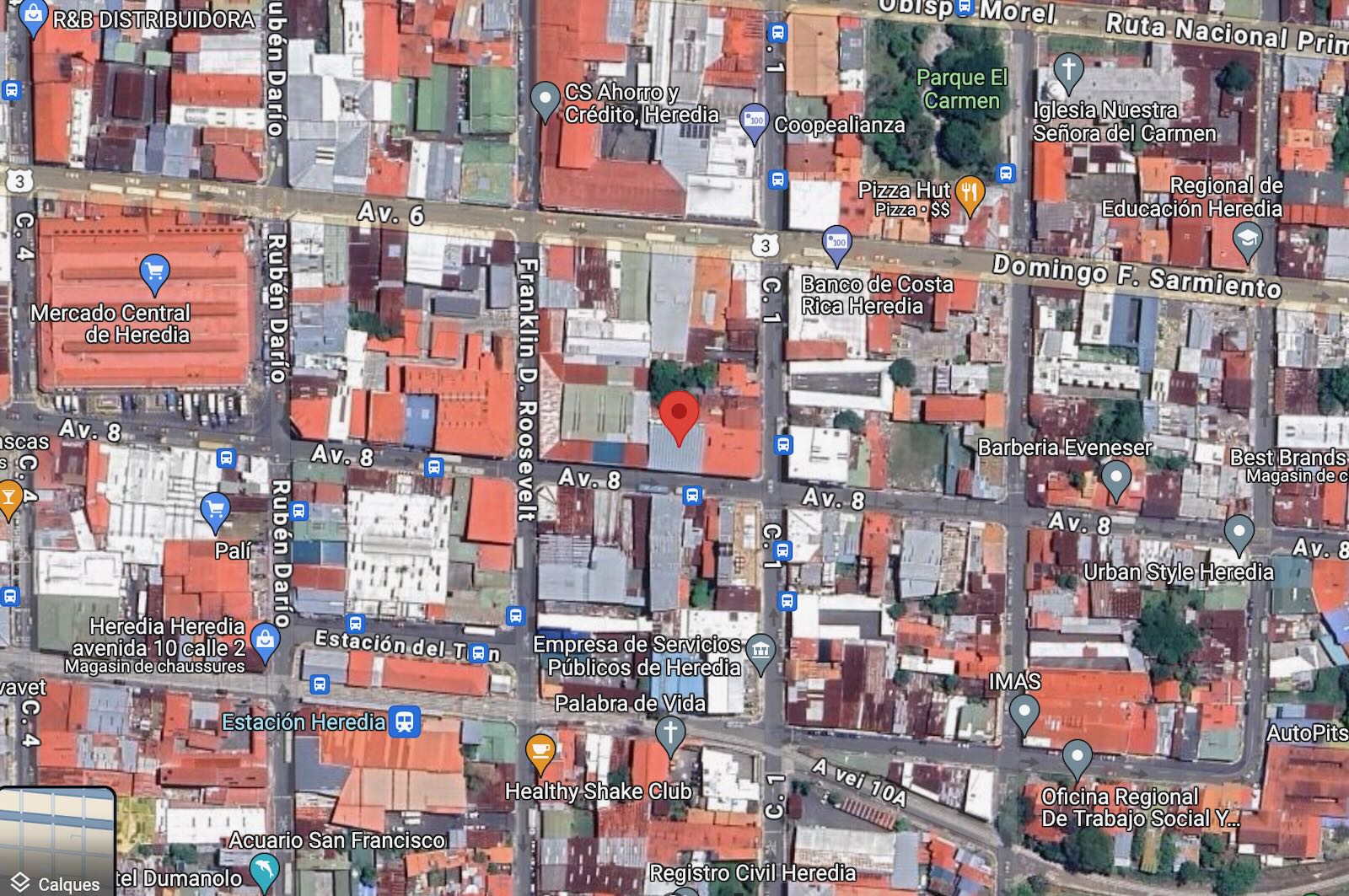 The main house was where the shiny tin roof is today (2024). Just to the right is another building with a red roof. That is where the wing with the station and the antenna tower were.
The main house was where the shiny tin roof is today (2024). Just to the right is another building with a red roof. That is where the wing with the station and the antenna tower were.