Radio Waves: Stories Making Waves in the World of Radio
Welcome to the SWLing Post’s Radio Waves, a collection of links to interesting stories making waves in the world of radio. Enjoy!
Note this article has been translated in English. Original in Ukrainian found here.
The police promptly responded to the call, but the SBU for some reason delays its response to illegal actions People’s deputy Mykola Knyazhytskyi announced this on Facebook .
“In Lviv, journalist Vitaly Portnikov, who hosts programs on Espresso and Radio Svoboda, found a eavesdropping device at home. It is a voice recorder with the ability to record for a long time. The police were called. They arrived quickly. The SBU was called. They are not going. As a member of the Verkhovna Rada, I ask the SBU to come immediately and disrupt case. We don’t know who installed this device and for what purpose: our services, foreign services or criminality,” the politician said.
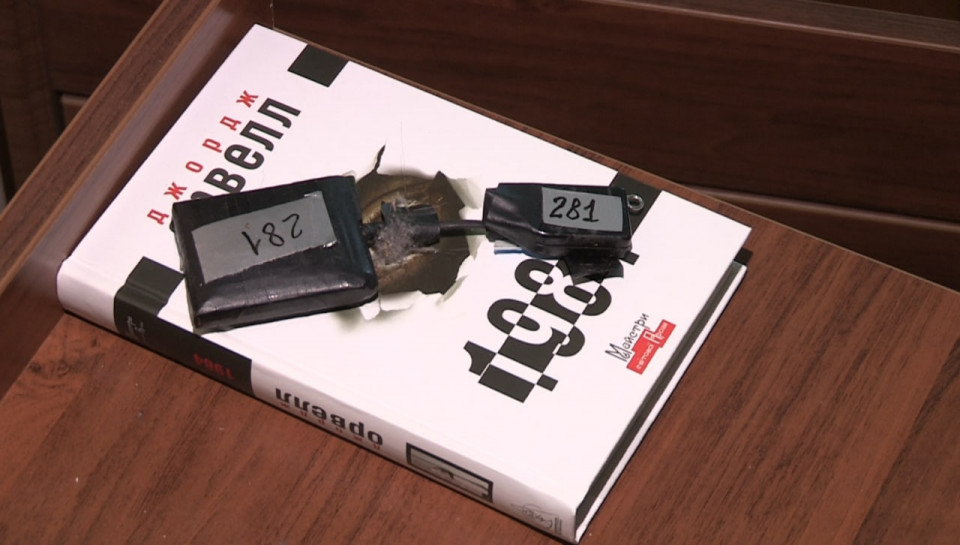

Image via Espreso
Vitaly Portnikov commented on the incident for “Espresso”:
“Today, while cleaning the apartment I lived in at the end of February, when the war started, I found a recording device under the bed. The device had an inventory number. I informed the law enforcement authorities about my discovery so that they could investigate this incident.”
The journalist added that he hoped for a high-quality investigation and clarification of all the circumstances of the case:
“After my statement, the investigators of the SBU of the Lviv region conducted an inspection of the premises and seized a device that is a device for listening and recording information. I hope that the relevant structures will conduct an examination and find out by whom and why this device was placed in my apartment.”
Vitaly Portnikov is a well-known Ukrainian journalist, publicist and political commentator. Cooperates with Radio Svoboda and Espresso. On the Espresso TV channel, he creates the programs “Political Club of Vitaly Portnikov” and “Saturday Political Club”. [Click here to read the full article at Espreso.]
This Episode explore three stories of cold war era radio in the USSR: Soviet Radio Jammers, the Russian ‘Woodpecker’ and the Soviet Radio Hooligans
[Click here to listen to the podcast via PodBean.]
We meet with Russian broadcaster Vladimir Raevsky to talk about radio jamming in cold war era Soviet Union.
As East and West super powers square up to each with nuclear weapons, a parallel invisible war is being fought in the airwaves. Continue reading →
 Many thanks to SWLing Post contributor, Adid, who writes:
Many thanks to SWLing Post contributor, Adid, who writes: