I recently discovered an article on the excellent blog, LifeHacker, which describes the contents of the CIA’s Escape and Evasion Survival Kit.
The kit’s contents currently include:
- Leatherman Squirt PS4
- Slim Line Lock Pick 13
- Tension Wrench Short Twist Flex
- Omni-Glow Mini Type A Glow Sticks
- Suunto Clipper
- Photon X-Light Micro Light
Lifehacker believes the small bag used is the Maxpedition M-2 Waistpack. I like Maxpedition packs: they’re very durable, typically military grade, and reasonably affordable. But the M-2 is small–quite small.
This led me to thinking about über-portable shortwave radios I would carry in such a small pack for survival purposes. If I were a foreign operative, ideally, I’d want a shortwave radio that has SSB mode, in case my home country’s numbers station broadcast in SSB.
In reality, there are very few good radios that are so compact they could fit in the M-2 Waistpack.
A few that came to mind were the Tecsun PL-310ET or Tecsun PL-380, but the fit would be very tight, if at all; both radios are slightly wider and taller than the M2’s main pocket, which measures 5 x 3 x 1.5 inches. I then remembered the Kaito KA1102 that I owned a few years ago–a very portable radio, but it, too, would be too large at 143 x 88 x 28.50 mm.
But then, it hit me: there is one radio, which, though no longer on the market, would fit the bill (and the pocket)…
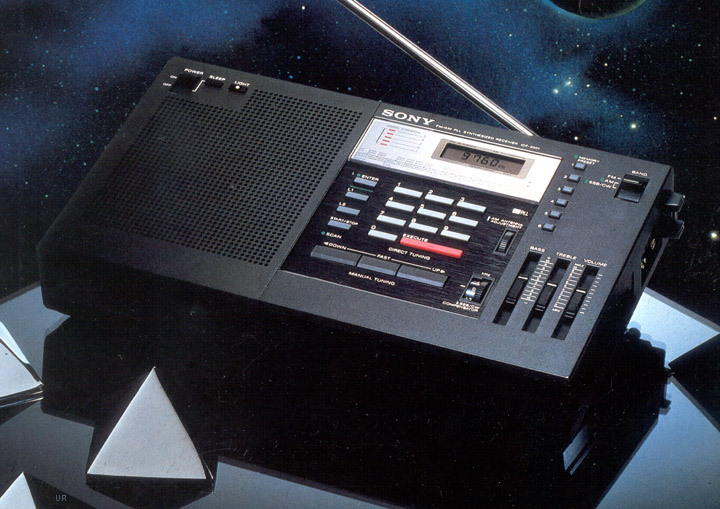
The Holy Grail of über-portable receivers: The Sony ICF-SW100
I have never owned an ICF-SW100, but I’d love to. Occasionally they show up on eBay, but prices range from $300-$800 depending on condition. That’s simply too pricey for my budget. Universal Radio has acquired used units in the past on rare occasions; these have sold between $200-400.
Then there are the lucky few, like my radio-listener buddy, The Professor. Remarkably, he tracked down (and knows I’ll never forgive him for it) an ICF-SW100 on Craig’s List for about $50! That was a steal.
Performance is superb for a radio this size. Not only does it have SSB mode, but selectable sideband sync detection.
One note of caution, should you be lucky enough to acquire one: the ribbon cable that connects the lower portion of the radio with the display (especially in the mark 1 production units) is known to fail. Fortunately, there are a number of videos (like this one) which walk you through replacement.
Click here to search eBay for a used Sony ICF-SW100.
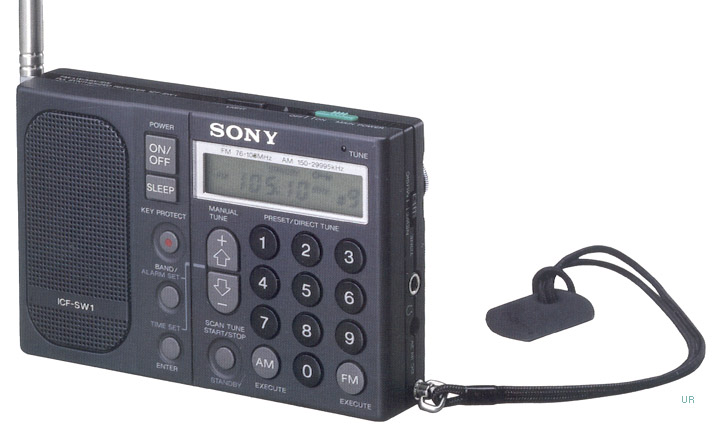
Honorable mention: the Sony ICF-SW1S
The ICF-SW100 predecessor, the ICF-SW1S (above), would easily fit in the M-2 Waistpack–it measures a mere 4.75 x 2.785 x 1 inches. Like its younger brother, it is highly sought after on the used radio market, and usually fetches $300+. The ICF-SW1S does not have a sync detector and lacks SSB mode. Still, as a broadcast receiver, it is truly superb for its size.
If you purchase a used ICF-SW1S, do ask the seller if all 6 original electrolytic capacitors have been replaced. If not, you may have to replace them in short order as the originals were known to fail. While not a repair for the faint of heart (as parts are quite small), there are several instructional sites and videos to help you. Alternatively, you can send your ICF-SW1S to Kiwa to be professionally re-capped.
Click here to search eBay for a used Sony ICF-SW1S.
Any others–?
Do you know of any other high-quality shortwave portables out there compact enough to fit in the M-2 Waistpack? Let us know!
The hunt is on…!







 Many thanks to SWLing Post reader, Richard Cuff, who shares this link to a numbers station piece
Many thanks to SWLing Post reader, Richard Cuff, who shares this link to a numbers station piece