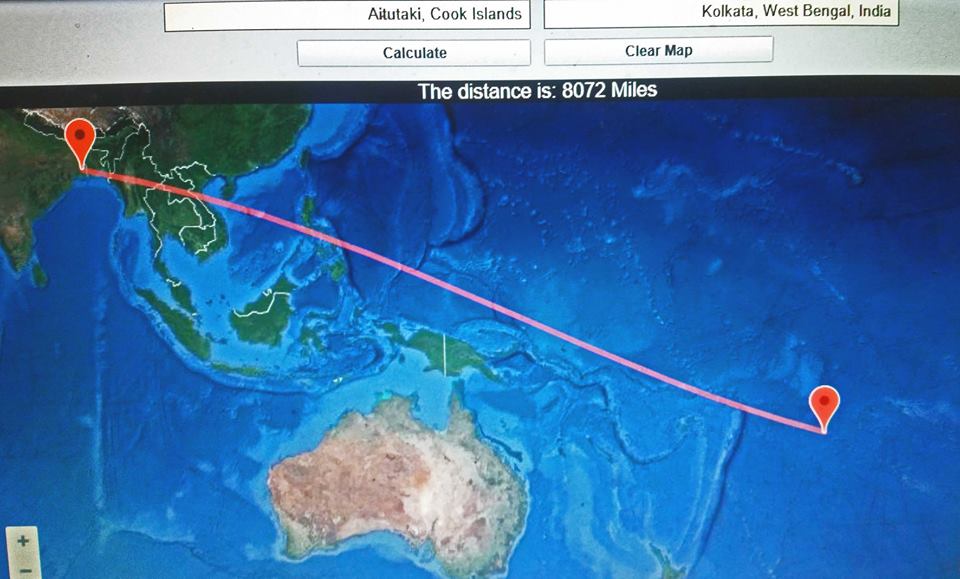
Many thanks to SWLing Post contributor, Gary DeBock, who shares the following notes from his Cook Islands Ultralight DXpedition:
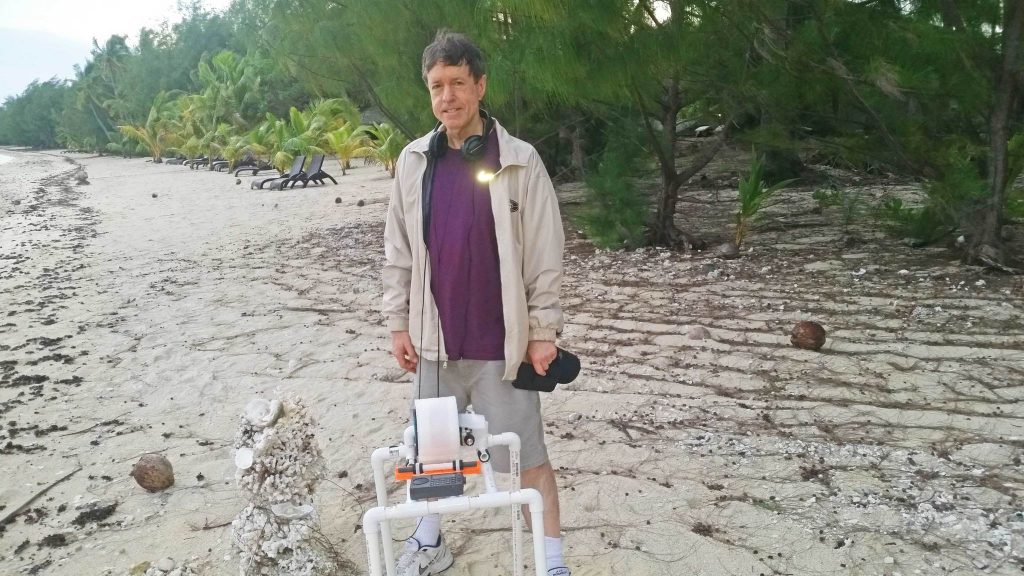
Checking out transoceanic DX propagation at an exotic ocean beach site can provide the hobby thrill of a lifetime– if a DXer is lucky enough to choose the ideal time, place and gear to make the chase. All of these fell into place in an amazing way during a 5-day trip to Aitutaki Island (2600 miles due south of Hawaii) with Ultralight radio gear, resulting in the reception of MW stations in India, Bangladesh, Mongolia and Cambodia– all at over 6,800 miles.
Because of extensive QRM from Australia and New Zealand the total number of Asian stations received was limited, but it was definitely a case of quality over quantity. Phenomenal gray line propagation around sunrise shut down Japanese signals almost completely, but boosted up those from the exotic countries in east and south Asia. Korean station reception was limited to the big guns, which was also primarily true for Chinese signals. Except for the ANZ pest QRM, the conditions seemed custom-designed for a west coast DXer to go after the exotic stations which rarely– if ever– show up in BC, Washington or Oregon (even though the Cook Islands’ distance to them is greater).
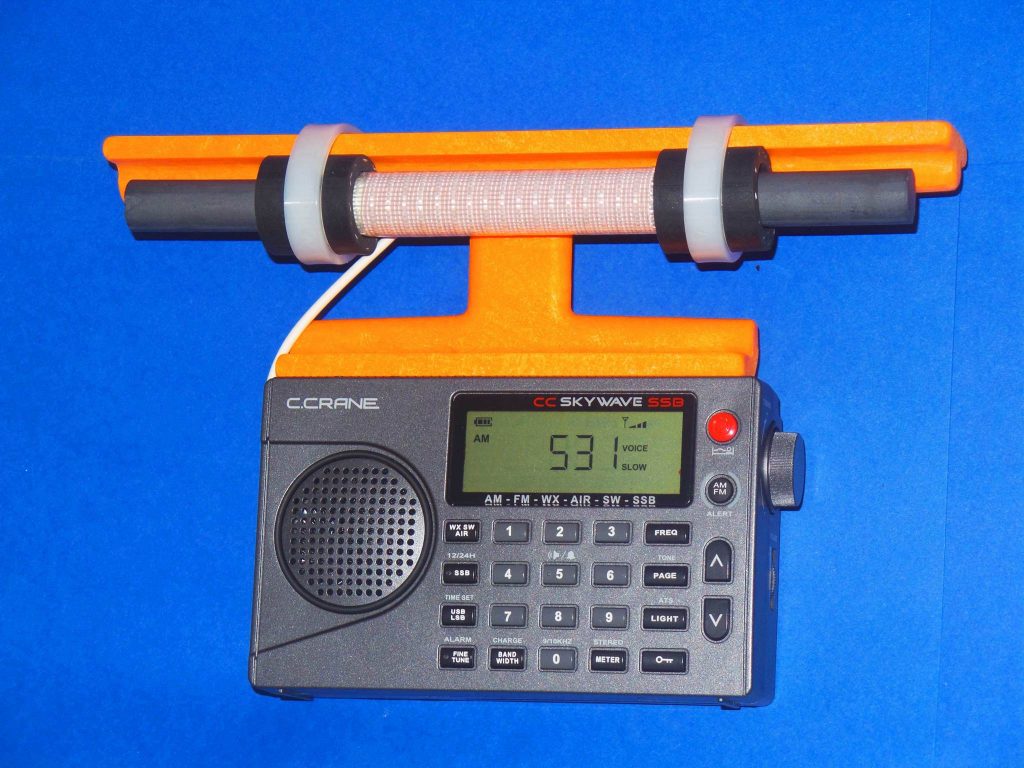
Ocean beach propagation at sunrise was strong enough to bring in both 693-Bangladesh and 1431-Mongolia at S9 levels almost every morning on my Ultralight gear, and allow both 657-AIR and 918-Cambodia to break through ANZ QRM on April 12th. No doubt many more of these exotic stations could have been logged except for Australian QRM on 576, 594, 872, 883 and 1566, but this only added to the thrill of the chase. The overall results were exceptional for a DXer using only a 7.5 inch loopstick Ultralight radio and 5 inch “Frequent Flyer” FSL– all designed to fit within hand-carry luggage, and easily pass through airport security inspections. Thanks very much to Alokesh Gupta, Hiroyuki Okamura, Jari Lehtinen, Chuck Hutton and Bruce Portzer, who all assisted in the identification of these stations!
657 All India Radio Kolkata, India, 200 kW (8,075 miles/ 12,995 km) Recorded by accident during a sunrise check of the Korean big guns at 1641 on April 12, reception of this longest-distance station went unnoticed until file review after return to the States. The female speaker (in the Bengali language) is the third station in the recording, after the female vocal music from Pyongyang BS and the Irish-accented male preacher from NZ’s Star network. Her speech peaks around 40 to 50 seconds into the recording. The isolation of the Star network at the 55 second point was done by the Ultralight’s loopstick, not by the propagation. Thanks to Alokesh Gupta for the language and station identification:
Click here to download an MP3 of this recording.
657 Pyongyang BS Pyongyang, N. Korea, 1500 kW Like most east Asian signals the N.K. big gun sounded pretty anemic in the Cook Islands. Its female vocal music at 1641 on April 12th shared the frequency with NZ’s Star network (Irish-accented preacher) and AIR’s female Bengali speaker:
Click here to download an MP3 of this recording.
693 Bangladesh Betar Dhaka, Bangladesh, 1000 kW (7,960 miles/ 12,810 km) Probably the biggest surprise of the DXpedition, with S9 signal peaks on 4 out of 5 sunrise sessions. Frequently snarling with the Oz pest 3AW, it usually managed a few minutes on top of the frequency each morning from 1630-1700 UTC. Exotic South Asian music was the usual format, and was very easy to distinguish from the talk-oriented format of 3AW (and other Oz co-channels). This first appearance at 1652 on 4-10 featured a “Bangladesh Betar” ID by a male speaker at 8 seconds into the recording (thanks to Chuck Hutton for listening):
Click here to download an MP3 of this recording.
This was followed by a lot of exotic music until 3AW claimed the frequency just before the 1700 TOH:
Click here to download an MP3 of this recording.
The next day (4-11) the exotic station was back with S9 peaks, including this typical music and female speaker at 1625:
Click here to download an MP3 of this recording.
The exotic music from Bangladesh was in an S9 snarl with 3AW (and another Oz pest) from 1659 throughout the 1700 TOH on April 11th:
Click here to download an MP3 of this recording.
774 JOUB Akita, Japan, 500 kW Oddly enough, this was the only Japanese signal making it to the island during the entire trip. Mixing with a goofy-sounding 3LO announcer at 1613 on 4-11, the Japanese female speech concerns a “doobutsuen” (a “zoo” in Japanese, similar to what the frequency sounded like with the 3LO announcer):
Click here to download an MP3 of this recording.
819 KCBS Pyongyang, N. Korea, 500 kW The N.K. big gun managed a potent signal for its 3+1 pips across its “TOH” at 1630 on 4-12 but never could shake off RNZ’s Tauranga transmitter:
Click here to download an MP3 of this recording.
909 CNR6 Quanzhou, China, 300 kW Strong signal with CNR ID (1:08) and Mandarin speech by male and female announcers. NZ’s Star network was apparently off the air at the time, since it was a real blaster when transmitting:
Click here to download an MP3 of this recording.
918 RNK Phnom Penh, Cambodia, 600 kW (6823 miles/ 10,981 km) Breaking through the Shandong and Oz QRM at an ideal time to dominate the frequency, its sign off transmission with the National Anthem peaked just before the 1700 TOH on April 12. Female speech in the Khmer language and exotic music are featured just before the anthem (thanks to Hiroyuki Okamura and Jari Lehtinen for listening, and identifying the National Anthem):
Click here to download an MP3 of this recording.
Chuck Hutton’s improved audio file of the same reception (thanks):
Click here to download an MP3 of this recording.
918 Shandong RGD Synchros (Multiple) The dominant Asian signal on the frequency, it rarely allowed Cambodia to sneak through. Here it is with female Mandarin speech at 1647 on 4-11:
Click here to download an MP3 of this recording.
Shandong RGD’s transmitters were poorly synchronized, resulting in the two-tone time pips at the 1700 TOH on 4-12 (during Cambodia’s National Anthem at 1:40, in the MP3 linked below). Although actually from two different transmitters, the sound effect sounds similar to that of a “cuckoo clock,” resulting in some initial confusion about their source:
Click here to download an MP3 of this recording.
972 HLCA Dangjin, S. Korea, 1500 kW The South Korean big gun played the part on most mornings, including this S9+ Korean female speech at 1631 on 4-12:
Click here to download an MP3 of this recording.
981 CNR1 Synchros Changchun/ Nanchang, China, 200 kW/ 200 kW The first of three CNR1 frequencies which usually produced strong signals, this music // 1377 was received at 1624 on 4-12:
Click here to download an MP3 of this recording.
1377 CNR1 Synchros (Various) Overall this was not only the strongest Chinese frequency on the band, but was the strongest Asian station on the band as well. Awesome S9+ signals were typical each morning, as with this male speech and music at 1622 on 4-12:
Click here to download an MP3 of this recording.
Another potent signal from this Chinese blaster at 1640 on 4-12:
Click here to download an MP3 of this recording.
1431 Mongolia (Relay Station) Choibalsan, Mongolia, 500 kW This station was easy to receive on the first attempt, with very little competition on the frequency. It typically managed an S9 signal after 1630 daily with the BBC’s Korean service, which seemed to be broadcast during the peak sunrise enhancement time in Aitutaki’s ocean-boosted propagation. Here is BBC’s Korean male announcer at an S9 level at 1632 on 4-11, with the BBC interval signal at 47 seconds into the recording:
Click here to download an MP3 of this recording.
The Mongolian relay program prior to 1630 was also in Korean, with this female Korean speech at 1627 on 4-11:
Click here to download an MP3 of this recording.
1566 HLAZ Jeju, S. Korea, 250 kW A very poor signal was typical during this trip, with the Chinese service barely showing up under 3NE and two other DU English stations (probably 4GM and Norfolk Island). Whenever 3NE was in a fade it had a chance, since other two co-channels were running very low power. Here is the latter situation, with the weak Chinese barely audible under the DU English snarl at 1641 on 4-12:
Click here to download an MP3 of this recording.
1593 CNR1 Changzhou, China, 600 kW This was another Chinese blaster, with S9 signals typical every morning. Here it was at 1641 on 4-12 with male Chinese speech and music at 1377:
Click here to download an MP3 of this recording.
73 and Good DX,
Gary DeBock (DXing in Aitutaki, Cook Islands)
Amazing, Gary! Thank you for taking us along on your excellent Ultralight DXpedition. With a modest portable radio and a little antenna ingenuity, you’re enjoying some outstanding DX! You’re living proof of the point I was trying to make in a post yesterday!
Thanks again, Gary, and good DX!