Radio Waves: Stories Making Waves in the World of Radio
Welcome to the SWLing Post’s Radio Waves, a collection of links to interesting stories making waves in the world of radio. Enjoy!
Many thanks to SWLing Post contributors Troy Riedel, Dennis Dura, and Richard Cuff for the following tips:
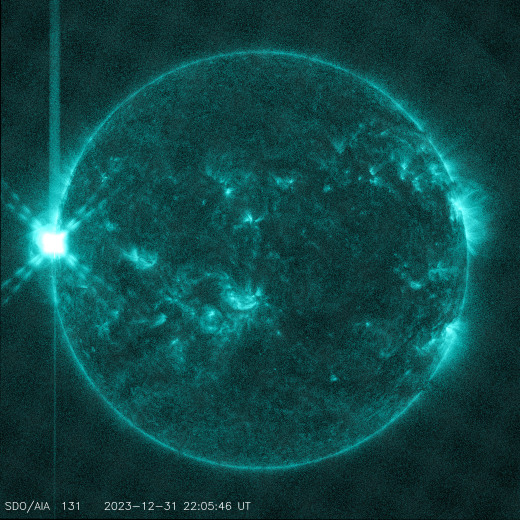
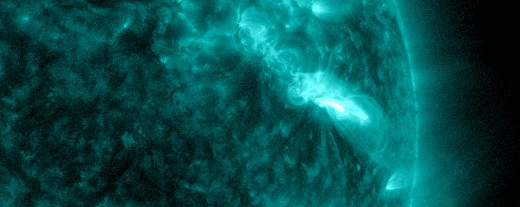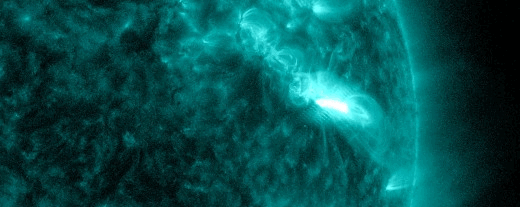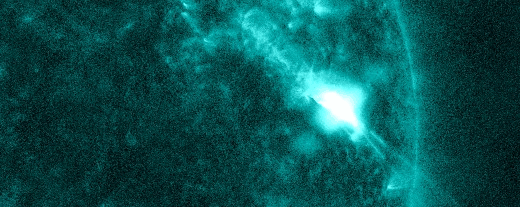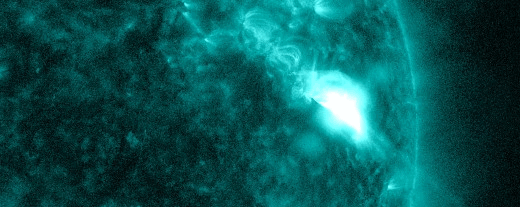
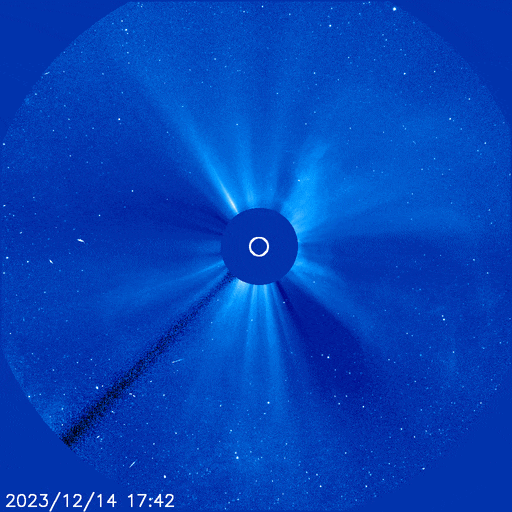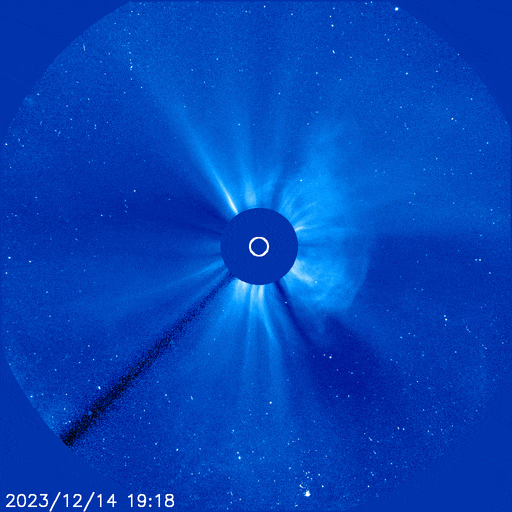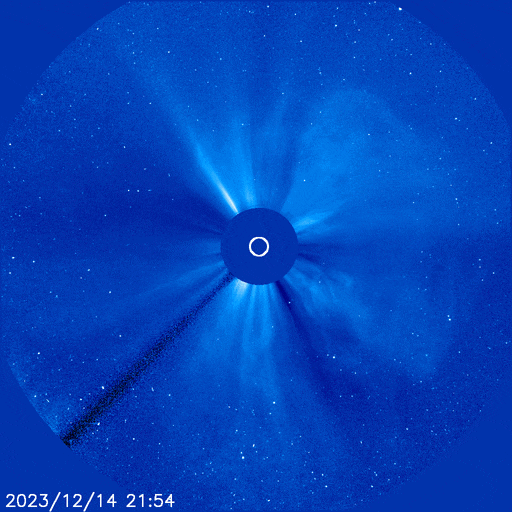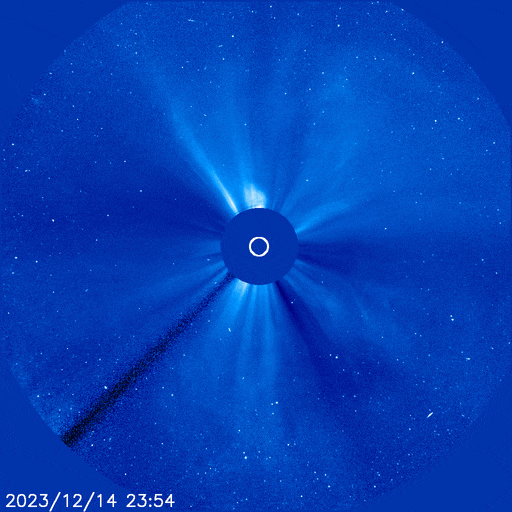
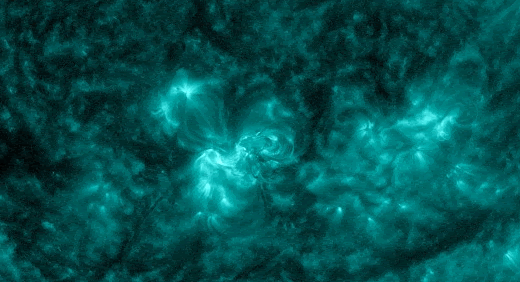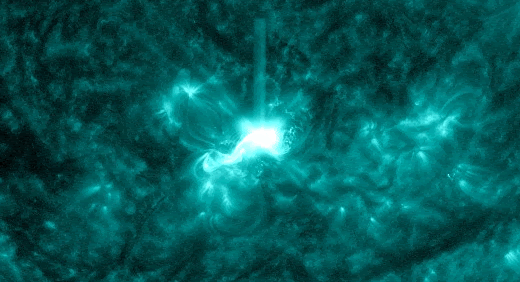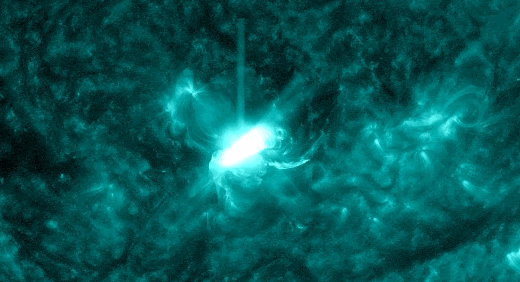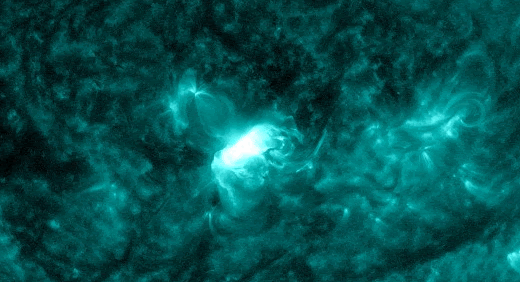
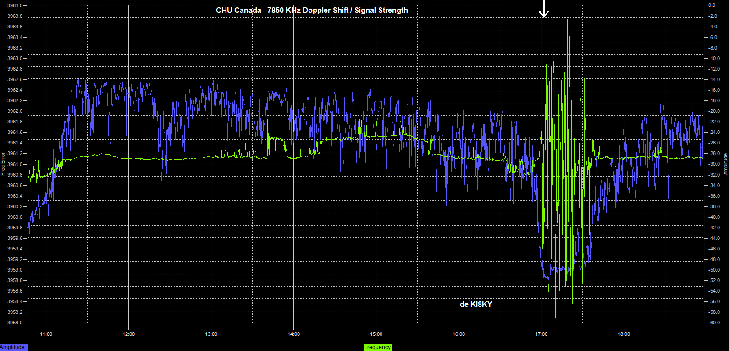
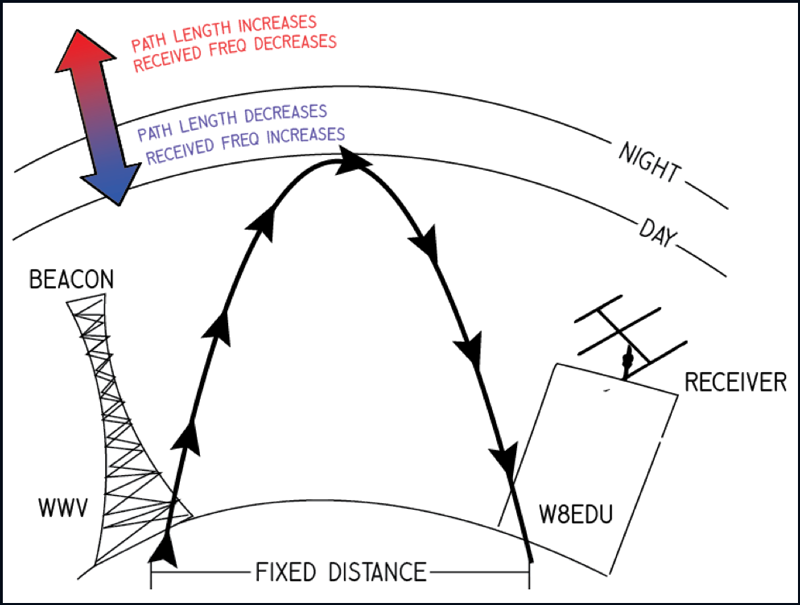
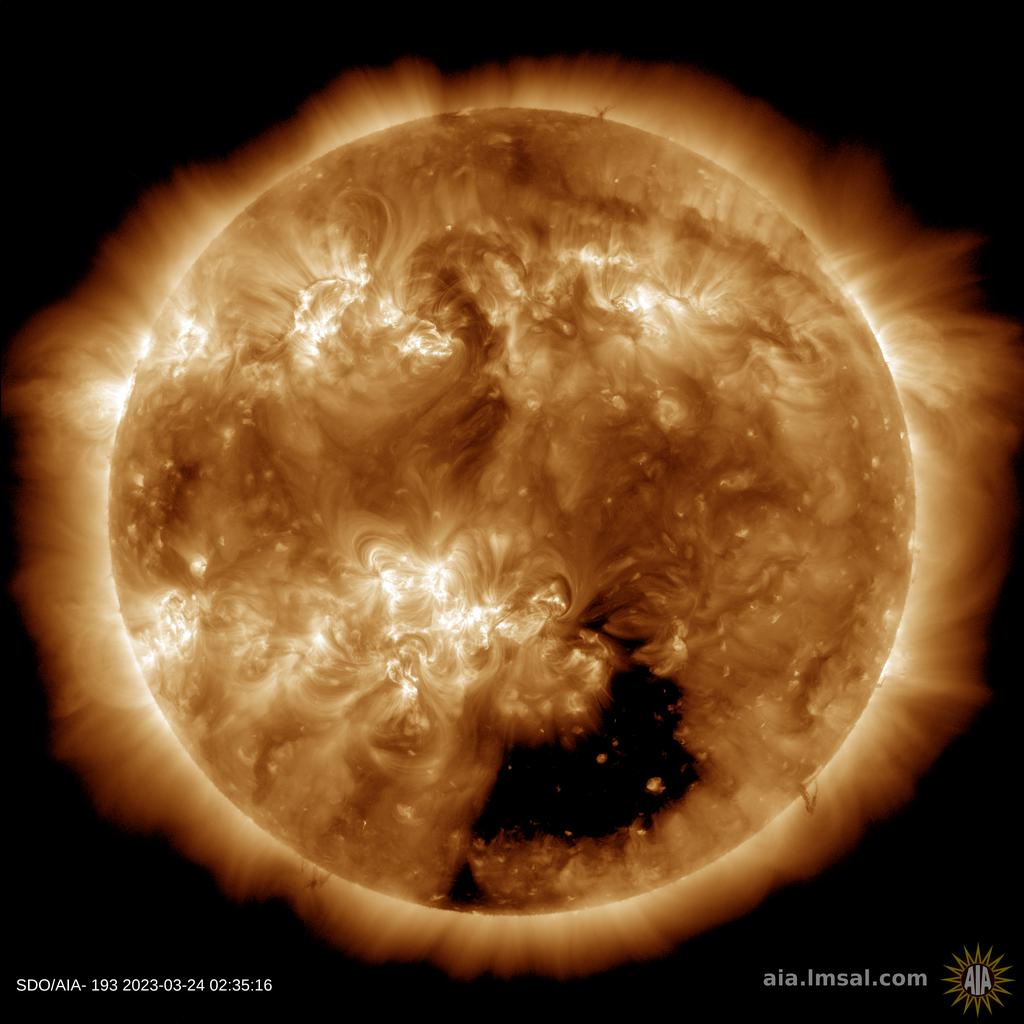
The powerful solar storm supercharged auroras as far south as Colorado and New Mexico.
The most powerful solar storm in nearly six years slammed Earth today (March 24), but strangely, space weather forecasters didn’t see it coming.
The geomagnetic storm peaked as a severe G4 on the 5-grade scale used by the U.S. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) to assess the severity of space weather events. The storm’s unexpected ferocity not only made auroras visible as far south as New Mexico in the U.S., but it also forced spaceflight company Rocket Lab to delay a launch by 90 minutes.
Geomagnetic storms are disturbances to Earth’s magnetic field caused by solar material from coronal mass ejections (CME) — large expulsions of plasma and magnetic field from the sun’s atmosphere. It turns out that this particular geomagnetic storm was triggered by a “stealth” CME which — as the name suggests — is rather tricky to detect. [Continue reading…]
Gottheimer also supports federal spending on AM infrastructure to assure continuity of service
A congressman from New Jersey wants the government to add AM radio to the list of safety equipment that carmakers must include in their vehicles.
Rep. Josh Gottheimer has called on the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration to “add AM radio to the Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standards to require that all automakers, including EV manufacturers, include AM radio as a stock feature in their vehicles. Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standards are the minimum safety standards that a manufacturer must meet when making a vehicle — including requirements related to airbags, brakes, seatbelts, tires, controls and displays.”
The National Association of Broadcasters welcomed his effort.
Gottheimer, a Democrat who represents a district along the state’s northern border, held a news event next to a Tesla dealership in Paramus, N.J., along with New Jersey Broadcasters Association Executive Director Jordan Walton. [Continue reading…]
An AI-generated radio DJ could be coming to your local radio station.
RadioGPT, a GPT-4-powered radio content generator from media company Futuri, is set to debut next month in radio stations in the US and Canada, Axios Cleveland reported.
Powered by the same tech that ChatGPT draws upon, RadioGPT aims to man radio airtime spots with AI-generated scripts and voices, as well as tailored local news content.
You can listen to a demo from the company that gives you a preview of what the AI-generated DJ voices sound like — which tell listeners that they are, in fact, fully AI — sprinkled between curated songs. The page includes snippets of RadioGPT-generated voices presenting news, weather, and traffic updates.
“Anything a radio human can do, I can do better,” one of the AI hosts can be heard saying in between songs. “Every voice you hear is 100% AI.” [Continue reading…]
The FCC is using its new powers to ask from the maximum fine from an Ecuadorian pirate radio station that’s run for more than 15 years.
The Federal Communications Commission (FCC) is using a new law to fine a pirate radio station operating in New York City for more than $2 million. For 15 years, Impacto 2, which has been operated by two brothers, has broadcast Ecuadorian news, culture, sports, and talk-radio on 105.5 FM in Queens. The feds have tried to shut it down repeatedly, but have never succeeded.
The FCC announced the fine in a press release last week. “The Commission proposed the maximum penalty allowable, $2,316,034, against brothers César Ayora and Luis Angel Ayora for pirate radio broadcasting in Queens, New York,” the release said. The FCC also said it was trying to seize $80,000 in equipment from a man broadcasting pirate radio in Eastern Oregon.
The Ayoras have been on the FCC’s radar since 2008 when they started broadcasting Impacto 2 for the Ecuadorian community in Queens: “The brothers César and [Luis] Angel Ayora in September 2008 founded the first Ecuadorian FM radio station in New York City. . . The station never sleeps, because a team of communication professionals are working for you 24 hours a day,” their website, which is currently down, said. The station is broadcast over the internet and has moved around the FM spectrum several times over the years. [Continue reading…]
Do you enjoy the SWLing Post?
Please consider supporting us via Patreon or our Coffee Fund!
Your support makes articles like this one possible. Thank you!