(Source: Deutsche Welle)
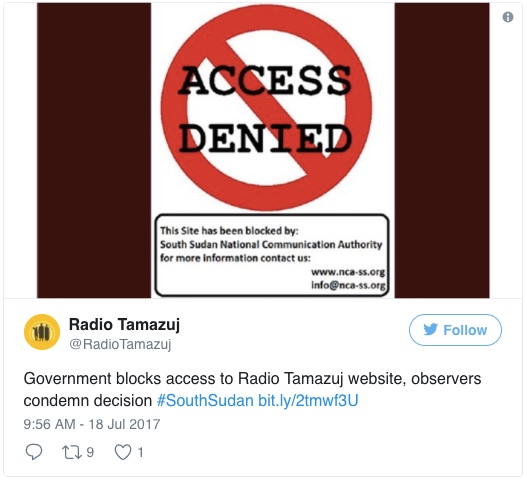
Internet and mobile phone users in South Sudan are not able to access the websites of at least four independent media outlets. The government has grown increasingly hostile to the media since civil war began in 2013.
The South Sudanese government has blocked access to the websites of Dutch-backed Radio Tamazuj, as well as the popular news blogs Nyamilepedia and Paanluel Wel. Internet users said that the website of the Paris-based Sudan Tribune was also affected on some mobile phone and Wi-Fi networks.
Radio Tamazuj and the Sudan Tribune are reputable sites which have been critical in their coverage of South Sudan’s government, which has grown increasingly hostile towards the media since civil war broke out in 2013.
The government is justified in blocking the websites to protect citizens from outlets that “disseminate subversive material,” South Sudan’s Minister of Authorities Michael Makuei Lueth told the US-based Committee to Protect Journalists (CPJ).[…]
Continue reading at Deutsche Welle online.
Fortunately, the South Sudan communities I’ve worked with through Ears To Our World have access to shortwave radio which is not affected by an Internet block.
No doubt, shortwave radio is the ultimate free speech medium, as it has no regard for national borders, nor for whom is in power (or not in power) at any moment.
Shortwave radio may be a sunsetting technology, but it’s also the most accessible and effective vehicle of the free press. What other technology can thoroughly blanket the globe with news and information yet can also be be received with a simple $20 battery-powered portable device?
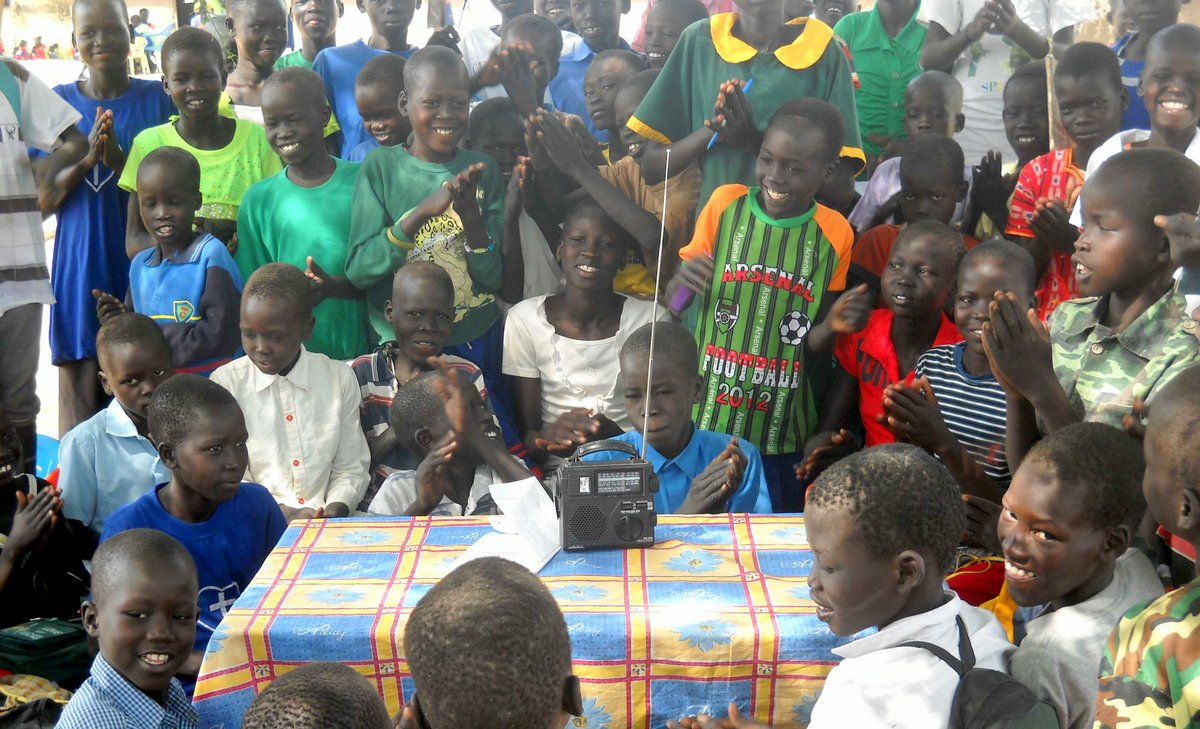

This photo was taken in South Sudan, after Ears To Our World distributed radios in this rural community for the fourth year running. We’ve been distributing radios in South Sudan through our partners there since 2009.
Check out these recent comments from the head of DW regarding the importance of international broadcasting. Thanks for the tip, Rich!