By Jock Elliott, KB2GOM
The XHDATA D109-WB is a small radio that hits a sweet spot on the price/performance curve, delivering a lot of performance for not a lot of money (probably less than $60 US, depending on the source).
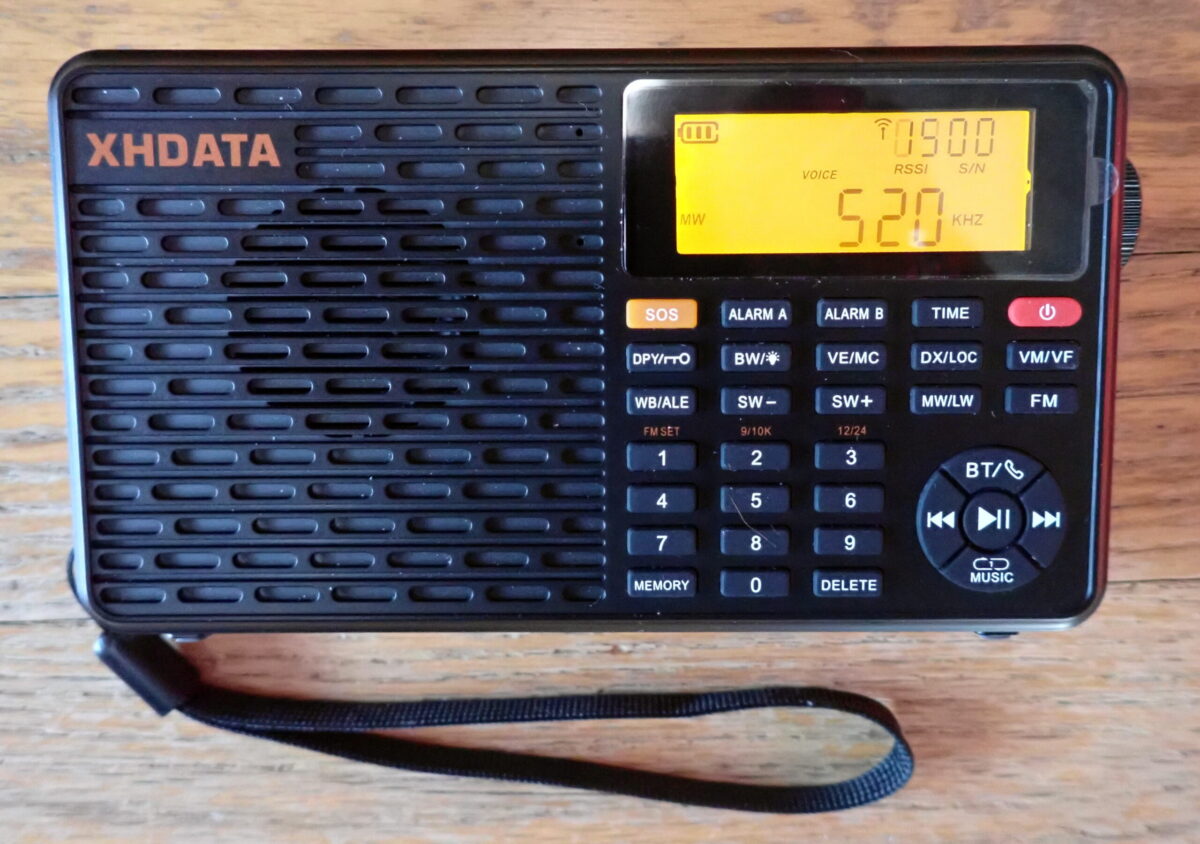
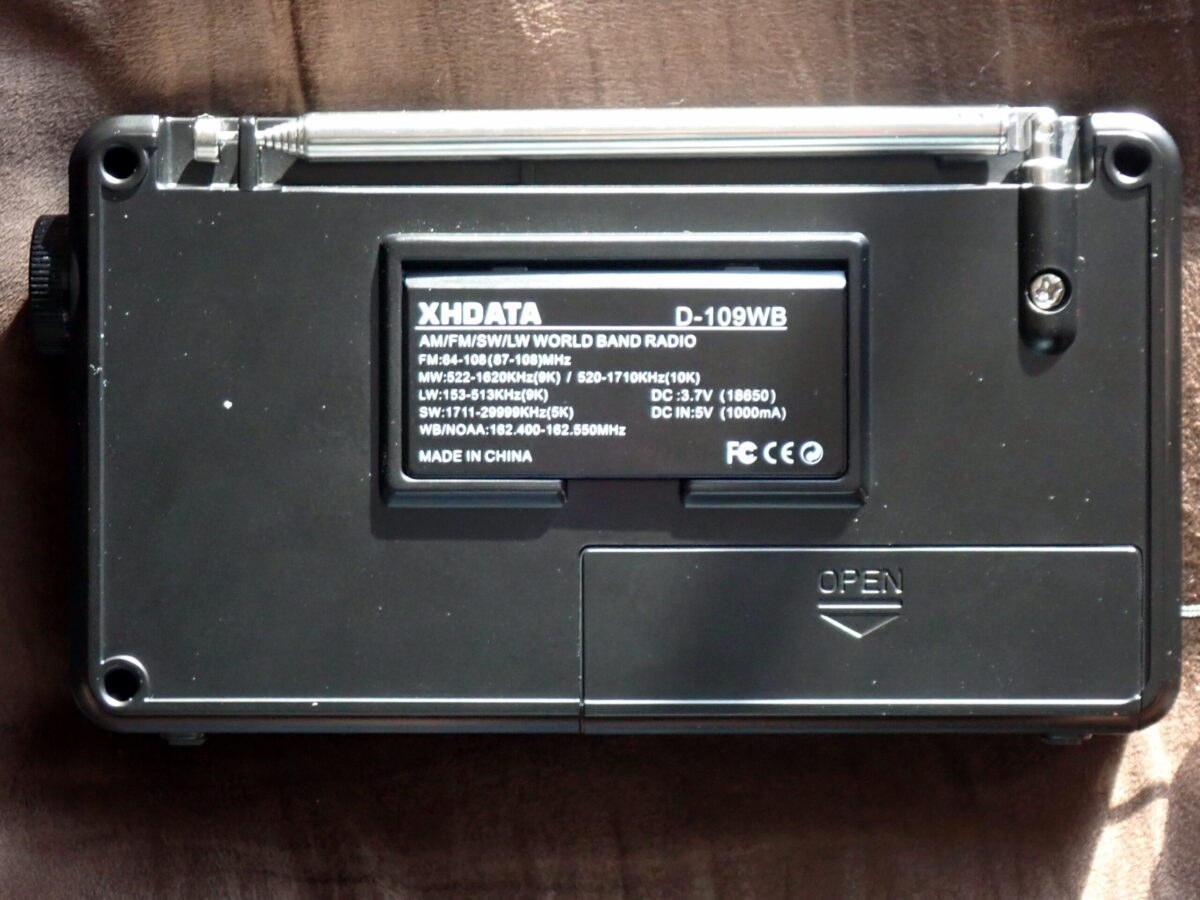
The D109-WB measures 5.9″L x 1.45″W x 3.07″H and weighs just over 10 ounces. It covers FM 64-108MHz, AM (medium wave) 520-1710KHz, LW 153-513KHz(9K), SW 1711-29999KHz, and seven NOAA Weather Radio channels 162.40-162.55MHz with alert function. It does not receive single-sideband signals. It offers 100 FM memories, 100 LW memories, 100 MW memories, and 300 SW memories. Further, it offers 1, 2, 3, 4, and 6 kHz bandwidths on MW and SW bands.
On the left side of the front panel is a plastic grill that fronts an inch-and-a-half speaker. On the right side is a small LCD screen with backlight that functions as information central for the D109-WB. Below it are 15 buttons (3 rows of 5 buttons each) that control various functions, including an “SOS Emergency Distress Sound and Light Alarm,” manual tuning and various auto scanning and auto memory storage schemes, band selection, DX/local receive mode selection, 9/10 kH MW spacing, clock alarms, bandwidth selection, a key lock/display switch, and a manual tune/memory mode switch, among others. Below those 15 buttons is a 3 x 4 numerical key pad for memory and direct frequency entry functions. To the right of the keypad are 5 buttons set in a circular pattern for controlling Bluetooth use and connectivity and MP3 playback (I did not test these last two functions).
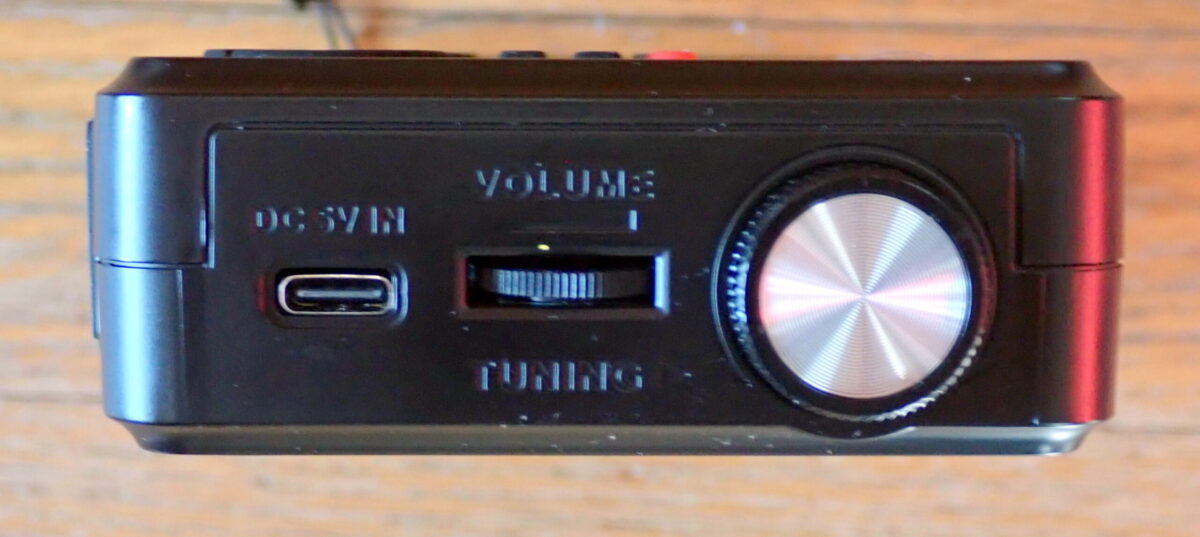
On the right side of the case, you will find a type-C socket for plugging in a cable to charge the 18650 battery, a wheel for volume control, and a tuning knob.
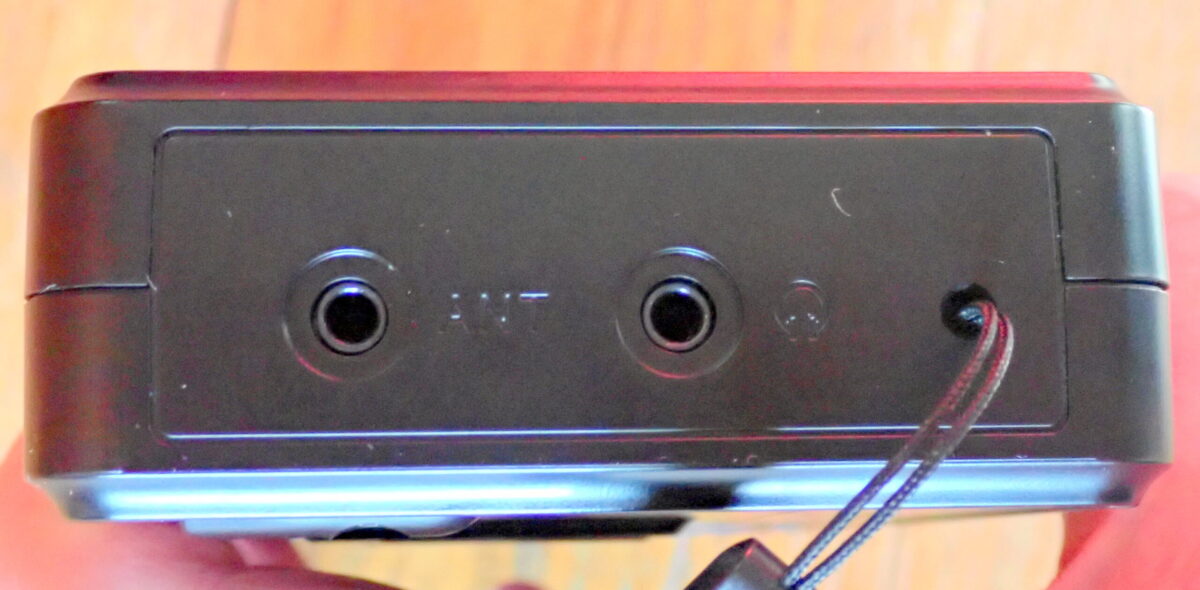
On the left side of the case are 3.5 mm headphone and external antenna jacks.
On the back panel is a flip-out support and a hatch for accessing the battery. On the top, there is a fold-over 21-inch telescoping antenna and, on the bottom, two anti-skid rubber feet.
In all, I found the D109-WB to be solidly constructed with fit and finish appropriate to a radio in its price class. The only serious deficit I found in the D109-WB was the extremely small type in the owner’s manual. Consult the photograph below to see what I mean.
The D109-WB was straightforward to operate, and I enjoyed it. One cute trick was variable-speed tuning: on MW, turn the knob slowly, and it will change frequency in 1 kHz increments. Turn the knob fast, and the tuning rate jumps to 10 kHz increments (or 9 kHz, if you have selected that tuning option). Variable-speed tuning works the same way on the shortwave bands, and on the FM band, the slow tuning rate is .01 MHz, and it jumps to .1 MHz when the knob is turned quickly. I had not experienced variable-speed tuning in any other radio, and I like it . . . a lot.
But what I was really wanted to know was how well did the D109-WB perform?
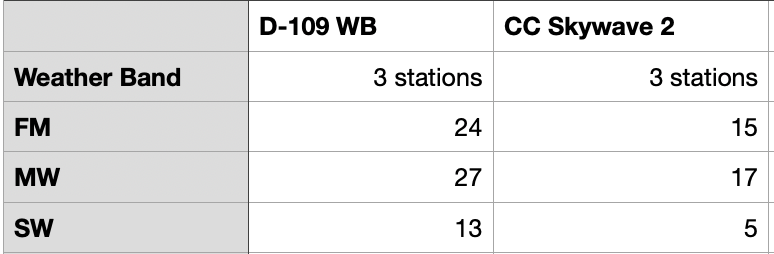
Now here’s the rub: I don’t have any test equipment . . . but I do own a CCrane Skywave 2. So I sat down on a bright sunny afternoon with the D109-WB and the Skywave 2 side-by-side and compared them. I found that both would receive two weather channels loud and clear and one more weather channel marginally. Then I tuned firm the medium wave band, then the FM band, running the two radios in parallel and found that there was nothing that I could hear on Skywave 2 that I could not also hear on the D109-WB, and vice versa. In other words, I found the electrical performance of the two radios to be very similar . . . except, of course, that the Skywave receives the AIR band, and the D109-WB does not.
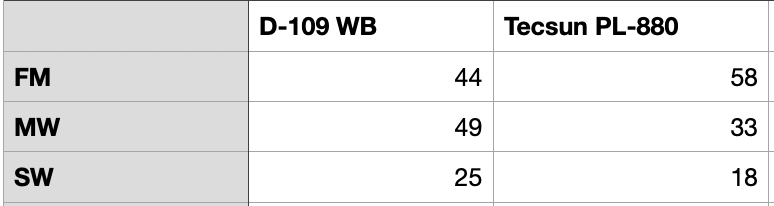
One of the things that I enjoy doing is to grab a radio, select a band, punch the SCAN button, and see what’s out there. Since I also own a Tecsun PL-880, I decided to run a scan on each band on each radio (D109-WB, Skywave 2, and PL-880) with its native whip antenna and see how many detectable signals I could find on each. By “signal,” I mean any place where the scan stopped where I could hear music, voices, or anything that sounded like a transmitted signal, as opposed to pure noise.
So here are the results of two different testing sessions on two different nights:
D109-WB vs. CCrane Skywave
D109-WB vs. Tecsun PL-880
A caution: before you start drawing conclusions from the results above about which radio is more sensitive than another, it is important to consider that those results may be heavily skewed by whatever “SCAN” algorithm is programmed into each radio. Further, the parameters of the SCAN algorithm for a particular radio are a black box to those who use the radio. What I can conclude from those results is that, if you want to be a lazy DXer like me and use the SCAN button for cruising the bands, the D109-WB will deliver pleasing results.
Since the D109-WB has a socket for plugging in an external antenna, I plugged in a 45-foot loop antenna. The D109-WB overloaded, but when I set the DX/local switch to local, the overloading went away but there was still a boost in signal-to-noise from the external antenna.
So, the bottom line: the XHDATA D109-WB delivers a whole lot of fun and performance at a very reasonable price, and I can easily recommend it for both newbies and old-timers alike.
In fact, if you want to turn a kid onto radio, here’s an idea: give the child a D109-WB and a paper atlas, explain how both work, then set that kid to work logging as many stations as possible and looking up where they are located. Heck, that sounds like fun to me.
Click here to check out the XHDATA D109-WB on Amazon.com
(note: this affiliate link supports the SWLing Post at no cost to you)