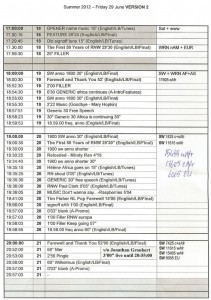
I have recorded hours of the Voice of Greece on shortwave since they were supposed to shutdown weeks ago. This update, via EnetEnglish, describes a re-branded TV service; Greek Public Television (EDT):
(Source: EnetEnglish.gr)
Greek Public Television (EDT), the replacement station for ERT which was shut down last month, has commenced broadcasting a basic signal.
A screen depicting the new station’s name and somewhat uninspiring logo appeared at about 8.30am on Wednesday morning, against a backdrop depicting a globe and waves of colour.
The decision to commence the signal follows the vote on Tuesday night, at committee, of a bill establishing New Greek Radio, Internet and Television, or Nerit, the new national broadcaster.
The bill received only the support of the coalition parties, New Democracy and Pasok, with all other parties against. Debate on the new legislation will be completed on Thursday.
Despite the move, ERT staff at the station have entered their second month of continuous broadcasting via a livestream hosted by the European Broadcasting Union, which has demanded that the station reopen.
[…]ERT staff are asking whether EDT has been approved by the state’s broadcasting regulator, the Greek National Council for Radio and Television (ESR). They also ask who is paying the staff working in EDT and on what kind of contracts.