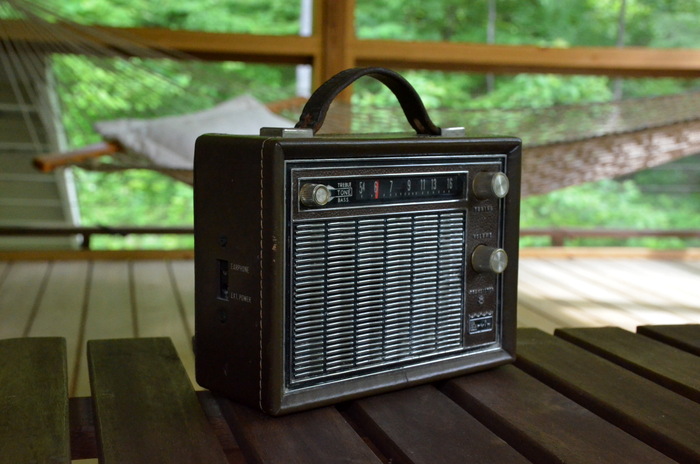
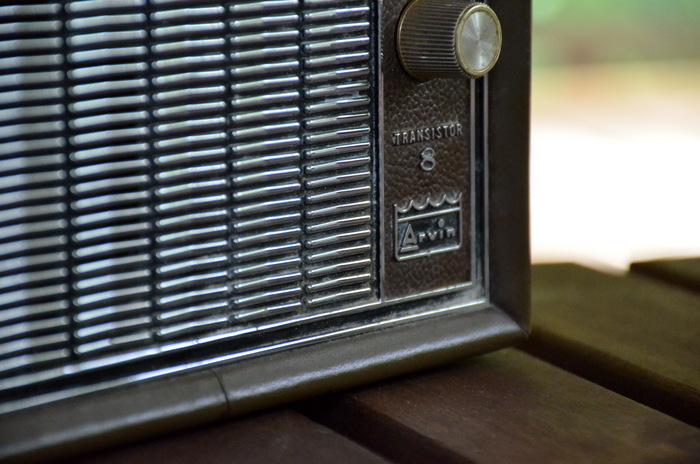
Though I believe I spent more money at the Dayton Hamvention this year than I have in all previous years, I only purchased one radio: the Arvin 68R58 eight-transistor.
Though I believe I spent more money at the Dayton Hamvention this year than I have in all previous years, I only purchased one radio: the Arvin 68R58 eight-transistor.
I spent a whopping $5 on the little Arvin in the Hamvention fleamarket. To be fair, the seller sold it for this modest price because he was not sure if the radio worked. But when I unsnapped the back leather cover, peered inside, and found the works remarkably clean, I suspected it might…
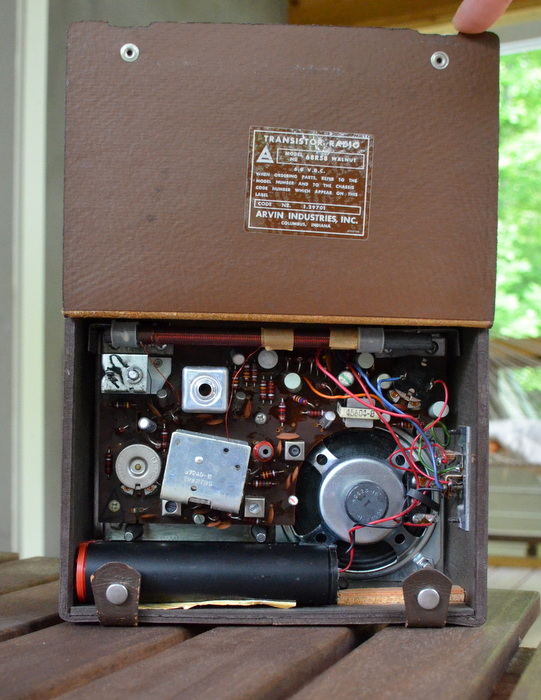 No original power supply was included, of course, and I was a bit concerned when I saw the somewhat out-of-character plastic battery holder. In the filtered fleamarket light, it appeared to me as if it required proprietary batteries–the holder appeared too small for C cells, and too large for AAs. There was no indication of the type of batteries it used, but since the spec read “6 volts,” I knew I could build a small AA battery holder, if need be.
No original power supply was included, of course, and I was a bit concerned when I saw the somewhat out-of-character plastic battery holder. In the filtered fleamarket light, it appeared to me as if it required proprietary batteries–the holder appeared too small for C cells, and too large for AAs. There was no indication of the type of batteries it used, but since the spec read “6 volts,” I knew I could build a small AA battery holder, if need be.
So, at $5 (I bargained him down from $10, based on the doubt of operation) it was a very low risk purchase, and a potentially a fun project.
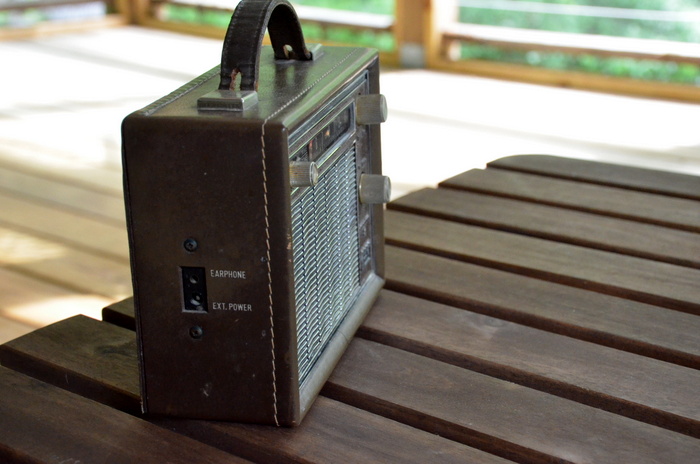

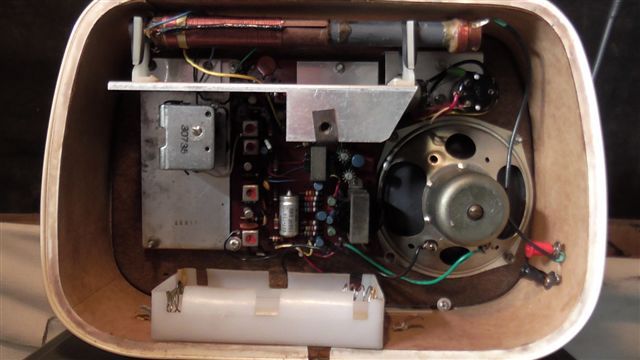
Back at home, I popped open the battery holder and looked inside…And I discovered the Arvin did, indeed, take four C cells. Simple enough! After inserting fresh batteries, I turned on the radio via the tone pot, and instantly heard beautiful, rich audio.
What I thought would be a project radio ended up being fully functional, and was, moreover, in tip-top shape.
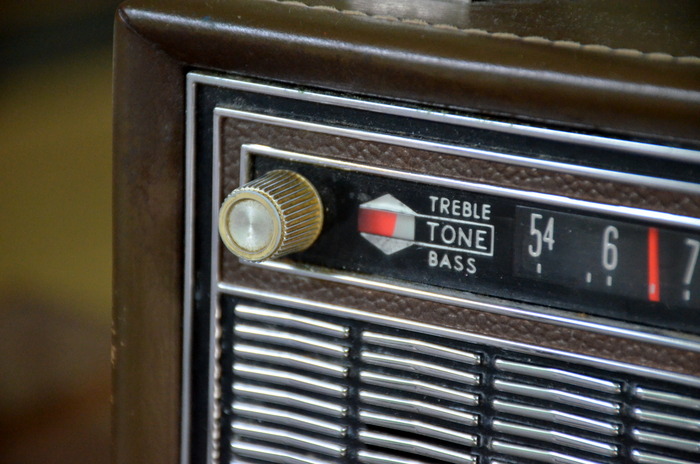

So far, I’ve been very impressed with the Arvin’s AM sensitivity and audio fidelity. No doubt the generous ferrite rod antenna is doing the trick on medium wave.
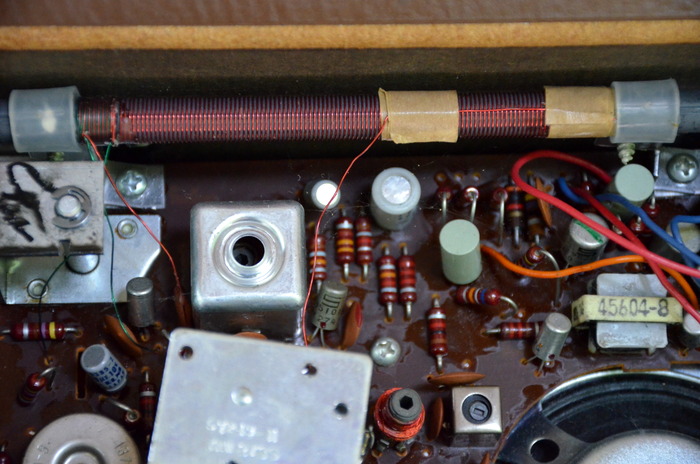

Last night, as I tuned through the AM broadcast band, I was able to null out unwanted stations and noise amazingly well. There is something to be said of transistor radios from this era–let’s just say, they’re classics.
 The Arvin has a simple set of controls: tone, tuning, and volume. There are no filter selections, of course, but I can tell that it’s quite wide; perhaps 8 or 9 kHz.
The Arvin has a simple set of controls: tone, tuning, and volume. There are no filter selections, of course, but I can tell that it’s quite wide; perhaps 8 or 9 kHz.
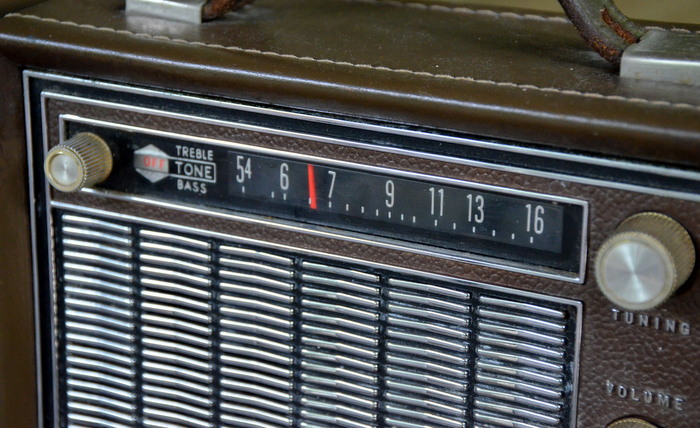 All in all, I’m very pleased with my little purchase, and the Arvin has become my new (vintage) bedside radio. Last night, I tuned in one of my favorite AM stations on 740 kHz, CFZM in Toronto, Canada. CFZM (a.k.a. “Zoomer Radio”) is not only a benchmark, but a right of passage for any worthy AM radio in my household. The Arvin passed the Zoomer test with colors flying.
All in all, I’m very pleased with my little purchase, and the Arvin has become my new (vintage) bedside radio. Last night, I tuned in one of my favorite AM stations on 740 kHz, CFZM in Toronto, Canada. CFZM (a.k.a. “Zoomer Radio”) is not only a benchmark, but a right of passage for any worthy AM radio in my household. The Arvin passed the Zoomer test with colors flying.
And, yes, it even soothed me to sleep.

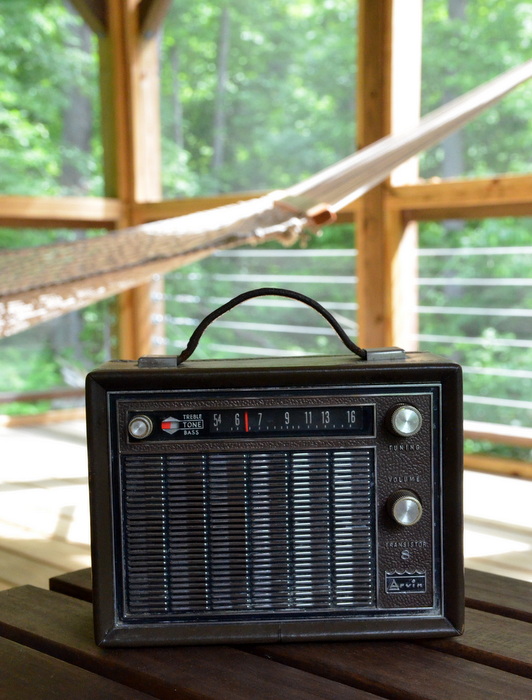
Now I only need to properly clean and restore the Arvin’s leather chassis and perhaps build a 6V-regulated linear power supply.

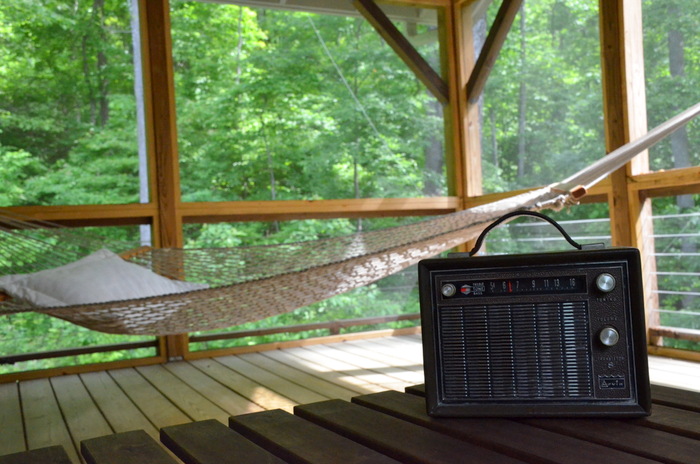
Next time you pass by a 1960s/70s vintage transistor, grab it! I’m certainly happy I did.
Now, I think I’ll turn on the Arvin, sip some dark beans, and put up my feet in the Pawley’s Island hammock…Cheers! Summer’s on the way.
 Want one of your own? A quick search reveals that the Arvin 68R58 can be found on eBay for quite reasonable prices. Click here to search eBay for an Arvin.
Want one of your own? A quick search reveals that the Arvin 68R58 can be found on eBay for quite reasonable prices. Click here to search eBay for an Arvin.






![Very early National portable with twin speakers, broadcast [band] and [shortwave. Works very well.](https://swling.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2015/06/NationalPanasonic.jpg)