(Image: AntiqueRadios.com)
(Source: Nuts and Volts)
In 1935, the Zenith Radio Corporation produced a stunning radio receiver called the Stratosphere model 1000Z. The set used 25 tubes and three loudspeakers — more than any other radio to date. An amazing (for the time) 50 watts drove its three speakers — one 6 inch dynamic high-frequency and two 12 inch dynamic low-frequency speakers.
Standing 50-1/2 inches tall, the Stratosphere sold for $750.00 — more than many automobiles; in comparison, a new Ford cost $652.00. At that price, it’s no wonder that only about 350 sets were produced during the four years that the Stratosphere was offered.
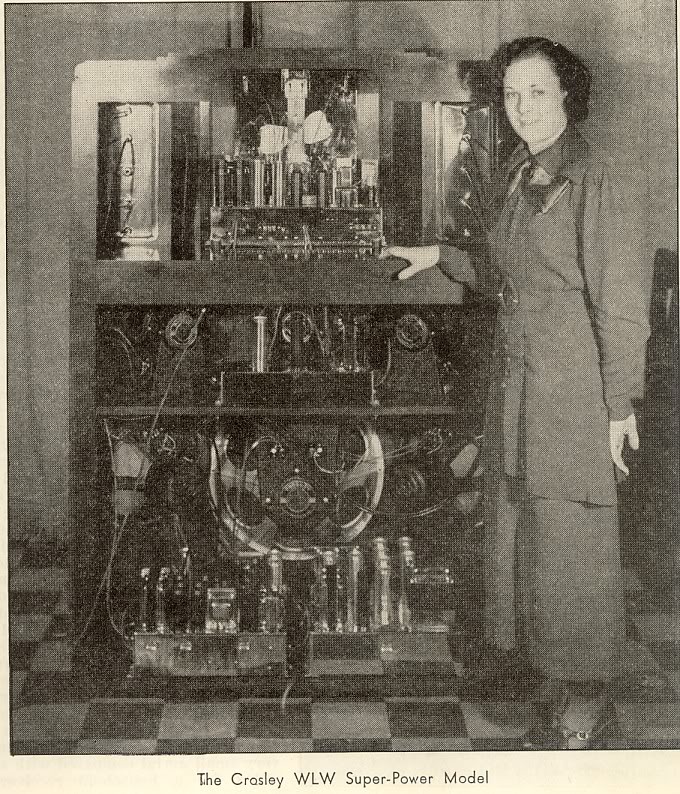
This achievement impressed Powel Crosley, Jr. — the President of the Crosley Radio Corporation — who praised it as a fine example of quality in radio construction, but it used “only” 25 tubes and three speakers! Crosley — who also owned the 500,000 watt powerhouse radio station, WLW — was inspired to surpass Zenith by bringing the world the largest and most powerful radio receiver yet known.
[…]Out of the numerous [engineering conferences were held throughout the winter months] and Crosley’s imagination came the basic specifications: the radio would be a superheterodyne receiver with no fewer than 30 tubes, six loudspeakers, four chassis; a suitably impressive cabinet would house it. More intricate than any set ever built, it would naturally have the highest possible quality and richness of tone.
[…]In its completed form, the WLW Model Super-Power Radio Receiver indeed surpassed the Zenith Stratosphere model. It had 37 tubes, six speakers, and 75 watts of power. The cabinet stood 58 inches tall, 42 inches wide, and 22 inches deep. Everything inside the cabinet that could be was chromium-plated. The transformer coils, tubes, and speaker frames were finished in black and each chassis had its own serial number plate.
Continue reading the full article at Nuts and Volts…
Regular SWLing Post readers know that I’m a bit of a vintage radio nut, so I thought I’d do a little digging to see if any WLW Model Super-Power Radio Receivers had been sold or auctioned recently. I was curious what sort of price they’d fetch.
Let’s just say, some owners demand a high price…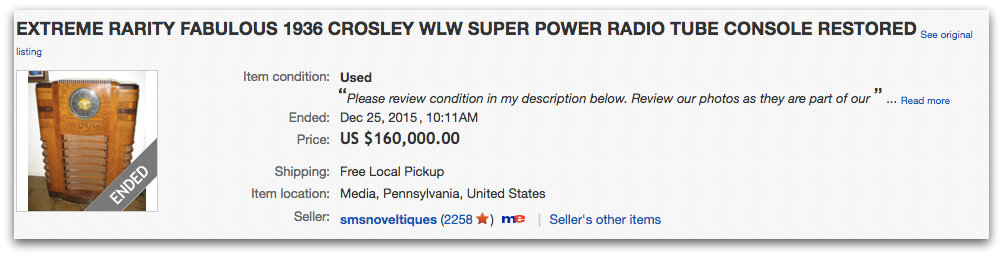
This unit was put up for sale on eBay for $160,000 US last year! While I know the Crosley WLW receiver is rare, that price was obviously over the top as is wasn’t sold. Still, the seller included some great photos of this near-mint model:
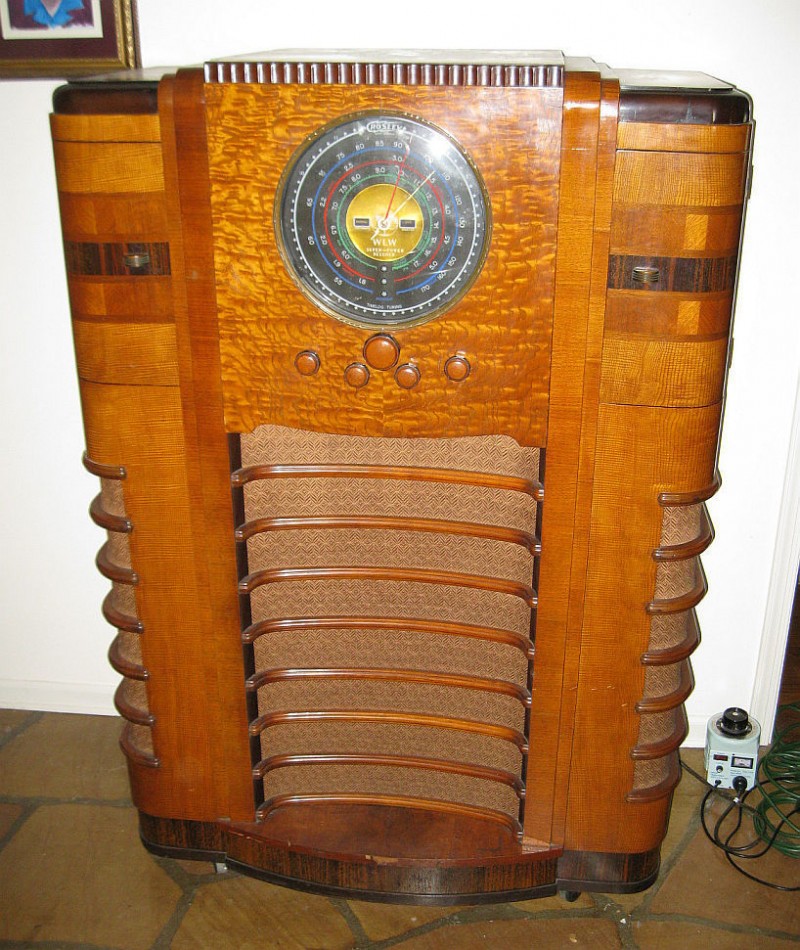
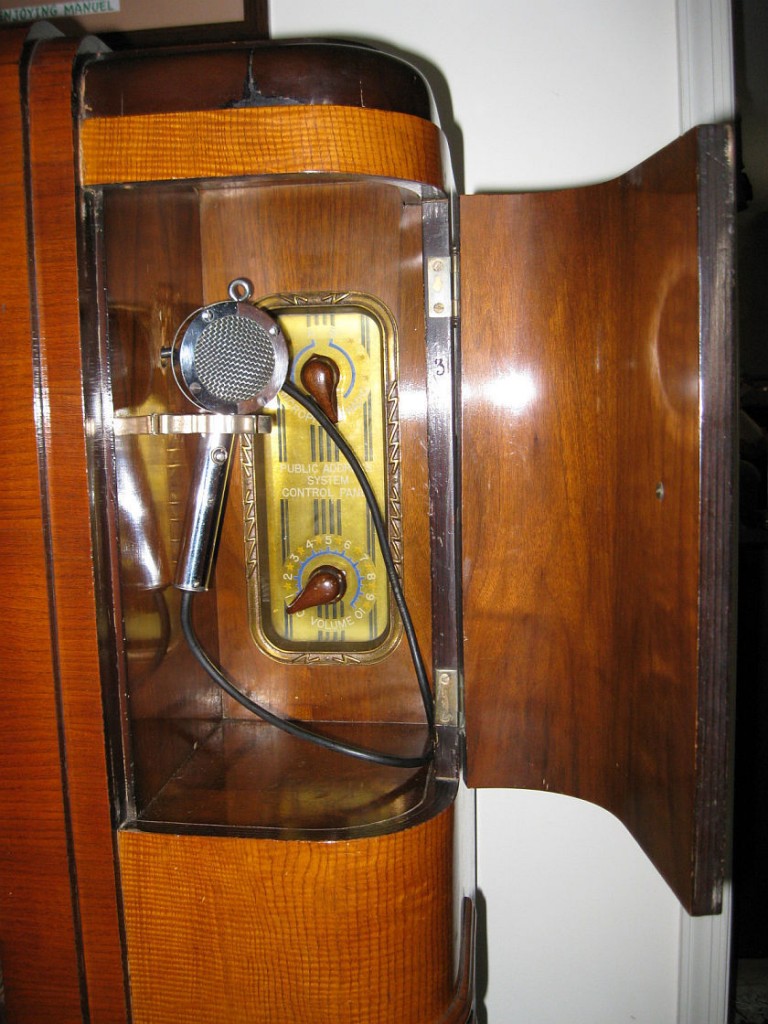
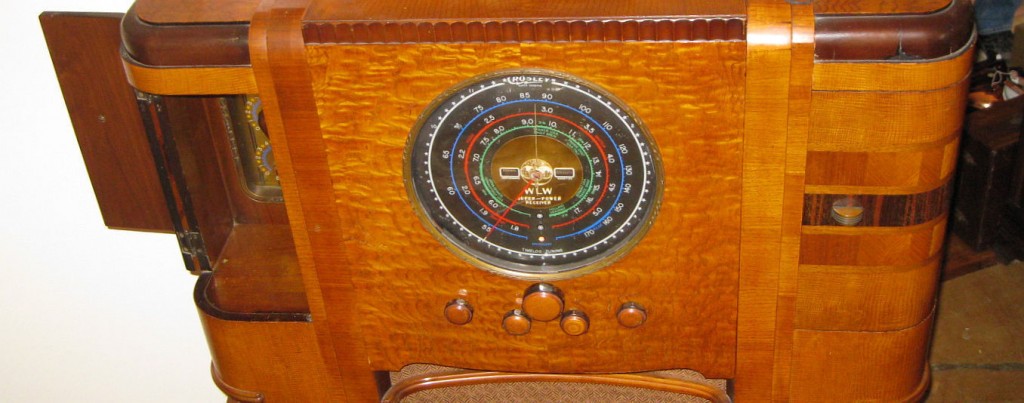
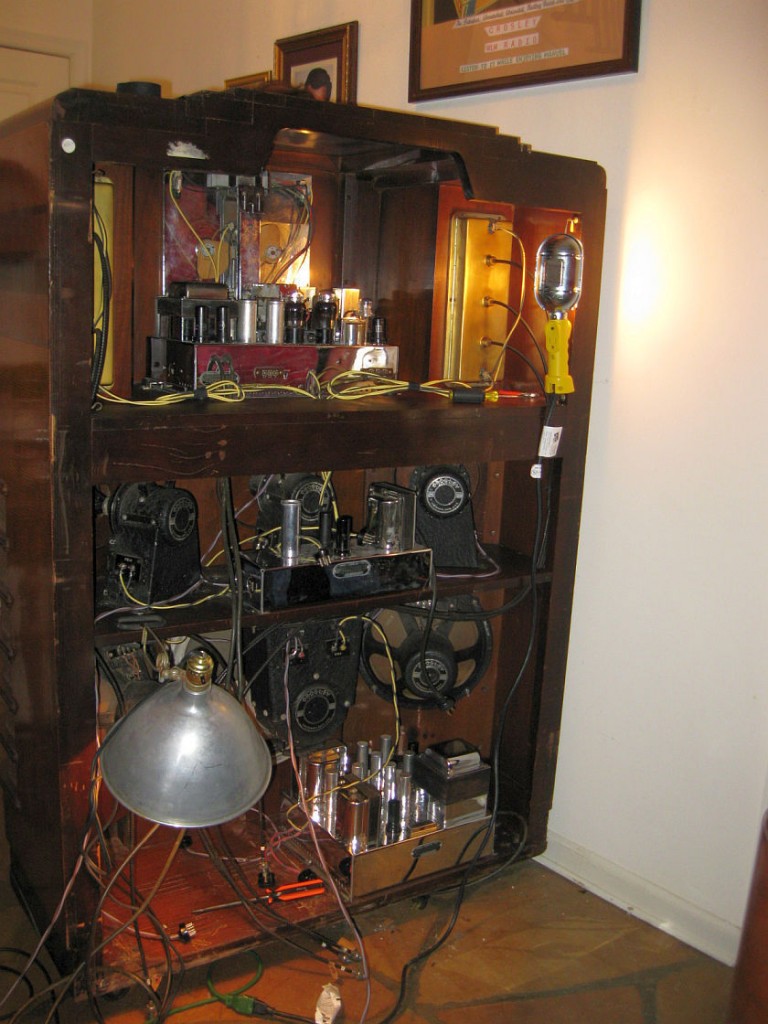





Around the time of the Zenith Stratosphere and the Crosley WLW–the mid to late 30s–radio manufacturers must have either believed there was a market for these high-end, high-fidelity receivers, or they simply enjoyed designing and manufacturing them as a company benchmark or showpiece.
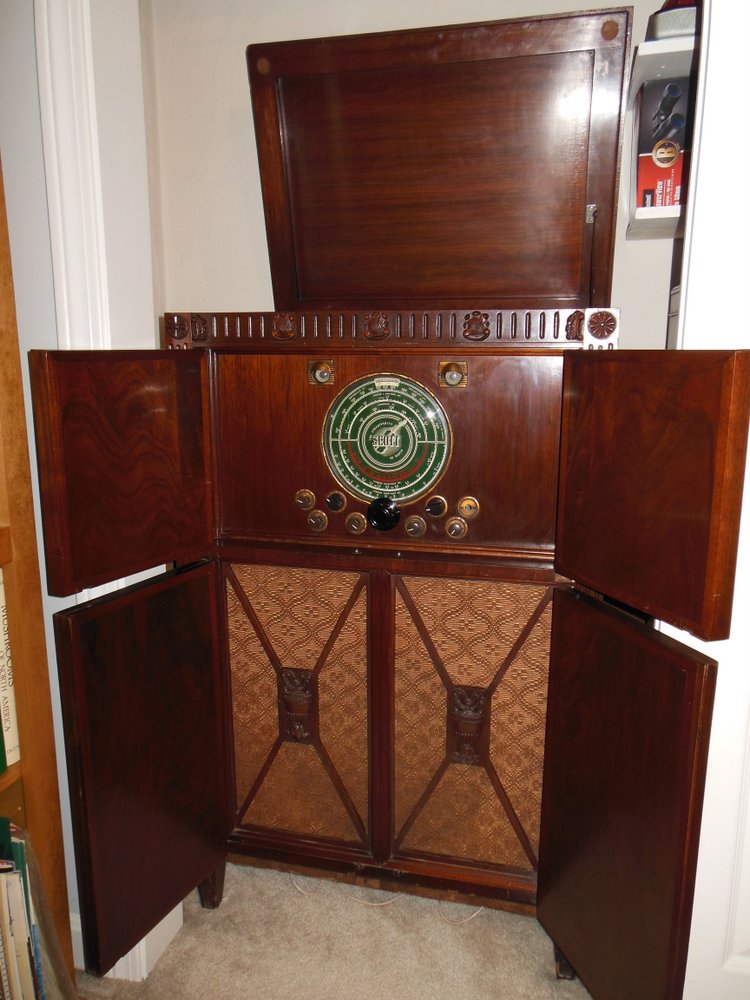
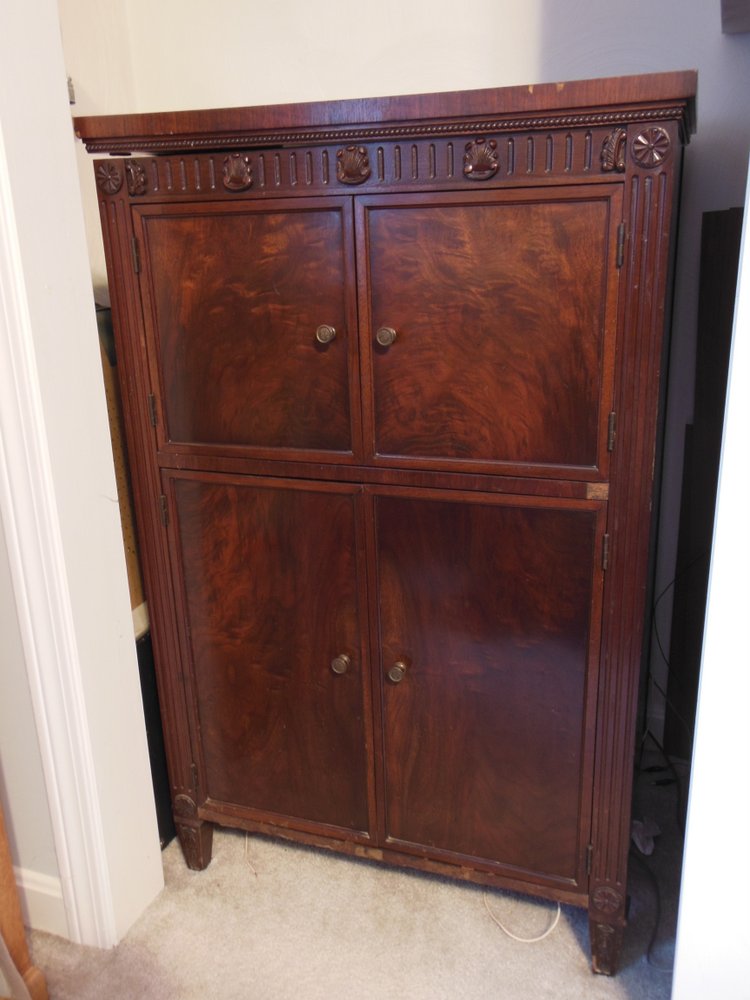
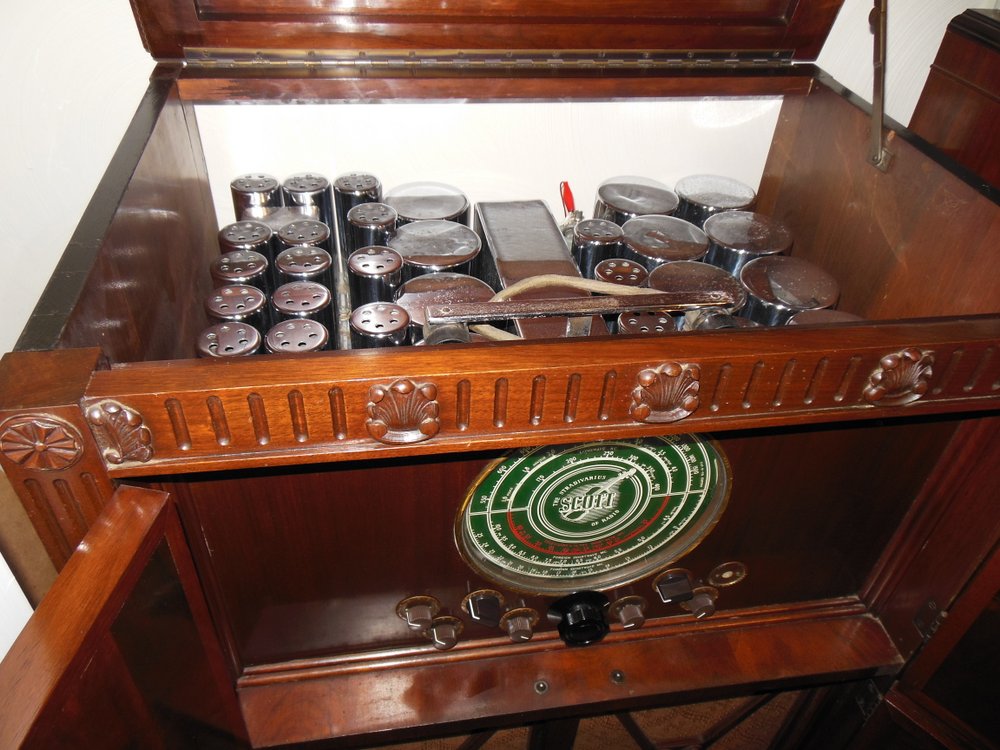
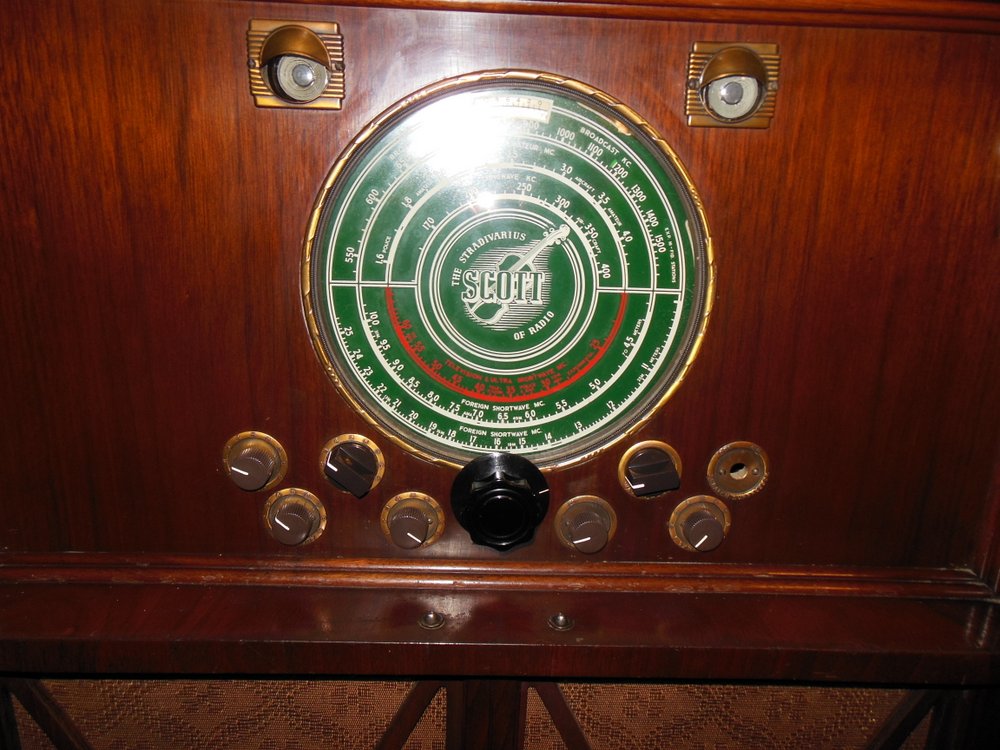
While not as feature-packed as the Crosley WLW receiver, at the National Capital Radio and Television museum last year, I was completely enamored with this gorgeous powerhouse console: the E.H. Scott All-Wave 23 console.
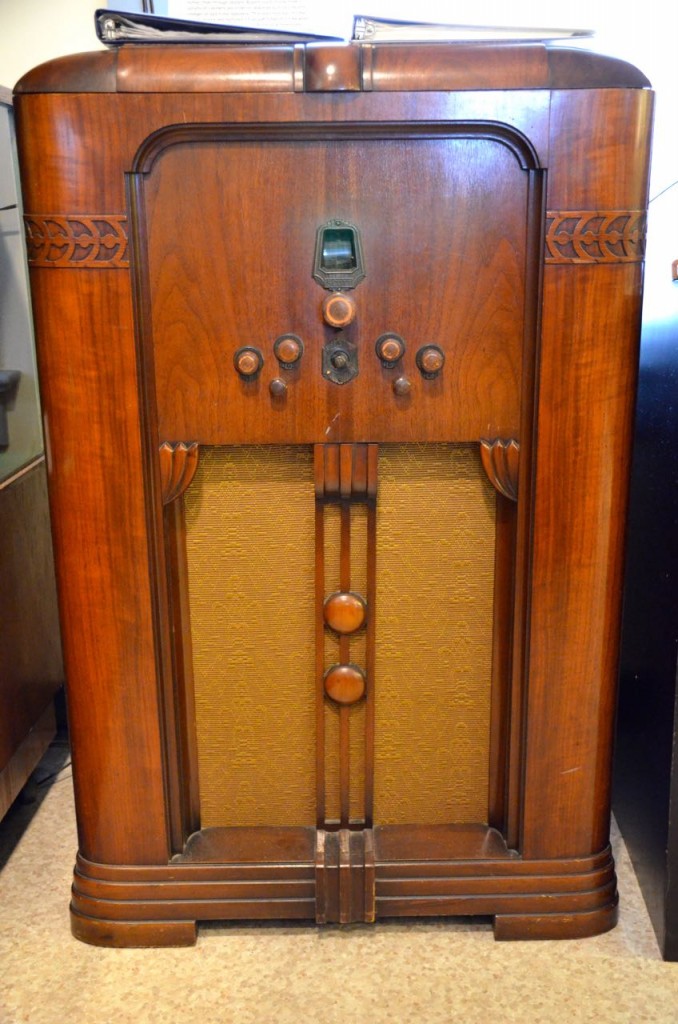

The docent told me that the E.H. Scott All-Wave 23 console could easily fill a banquet hall with hi-fi audio. It sported 23 tubes and a very large speaker. If memory serves, it originally sold for $750–easily three or four times the price of most console radios.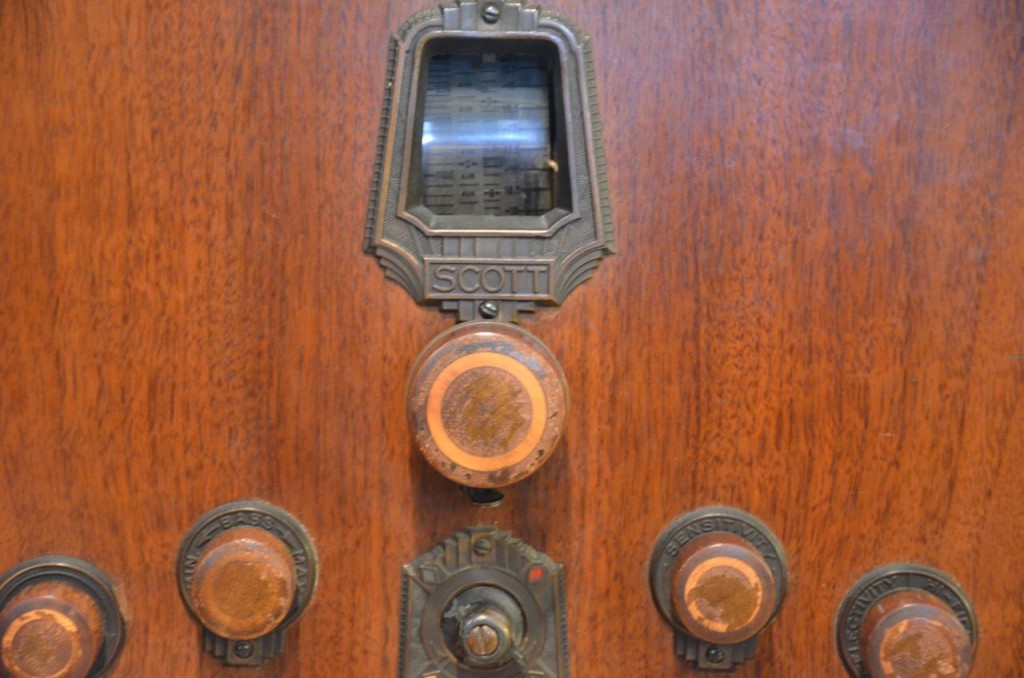
Post readers: Do you know of any other benchmark console radios? Do you own one of these amazing receivers? Please comment!


















