Many thanks to SWLing Post contributor, Bob Colegrove, who shares the following guest post:
Control of Electromagnetic Radiation (CONELRAD)
As recalled by Bob Colegrove
In his comment on my recent posting, Tinkering with History, Mario noted the dial on the featured radio, the General Electric P755A, sported two small triangles, one between 6 and 7, and the other between 11 and 14. He noted that these were civil defense markers intended to show the frequencies of 640 kHz and 1240 kHz, respectively, and that these were characteristic of AM radios produce in the US roughly between 1953 and 1963. Since two full generations have been born and raised to adulthood since that time, and I can’t find any related posting here, I thought it might be useful to bring this subject to light.

In spite of otherwise economic prosperity and general wellbeing, these years were nevertheless filled with anxiety about the prospects of all-out war. Children of the time (myself included) were being shown how to hide under their school desks, and some of their parents were going so far as to construct air-raid shelters in their basements, and stock them with enough provisions to supposedly outlast any catastrophe. So it was that CONELRAD came into being in 1951. The idea was, that in case of a National emergency, all radio and TV stations would go off the air, and only certain medium wave radio stations would stay on either 640 kHz or 1240 kHz. They would remain on for a few minutes and then other stations would take over in a round robin arrangement – this to deter homing by hostile bombers. Needless to say, quickly changing over transmitters and antennas to one of these two frequencies did not bode well for the equipment and there were many failures in subsequent tests. Note that, as originally conceived, the system did not provide for local weather emergencies or other situations.

The banner photo at the top of this posting shows a portion of the Hallicrafters S-38E receiver which conformed to Government law of the time required for marking all AM dials. An S-38E just like it was my first genuine multi-band radio in 1959. Assuming good alignment, the dots next to the CD triangles indicated the 640 kHz and 1240 kHz frequencies. When a test came on, you didn’t have to fish for it, since CONELRAD was the only service transmitting.
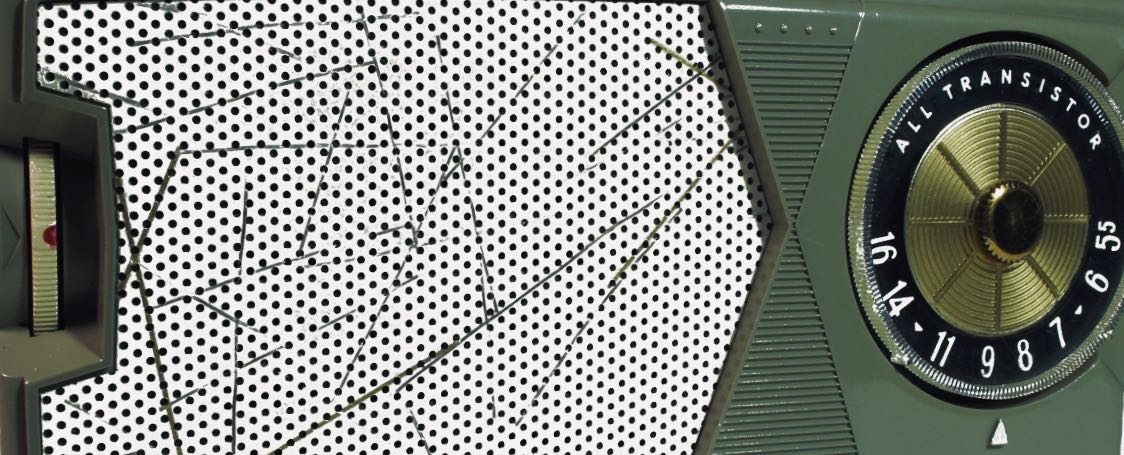
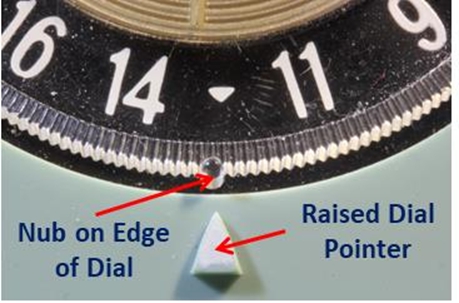
Going back to the radios described in Tinkering with History, GE took this one step further. The figure below shows a portion of the dial on a GE P806A. Note the nub on the outer edge of the dial under the triangle at 1240 kHz. There is another nub on the edge at 640 kHz. Together with the raised triangular dial pointer molded on the cabinet, they provided a braille system, so that someone visually impaired could easily tune to a CONELRAD frequency.
As technology improved, CONELRAD transitioned to the Emergency Broadcast System (EBS) in 1963, and subsequently the Emergency Alert System in 1997. A more thorough description of CONELRAD can be found on Wikipedia https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/CONELRAD. Reprint of an April 1955 Radio & Television News article describing the construction of a transistor CONELRAD receiver is at https://www.rfcafe.com/references/radio-news/conelrad-radio-television-news-april-1955.htm.