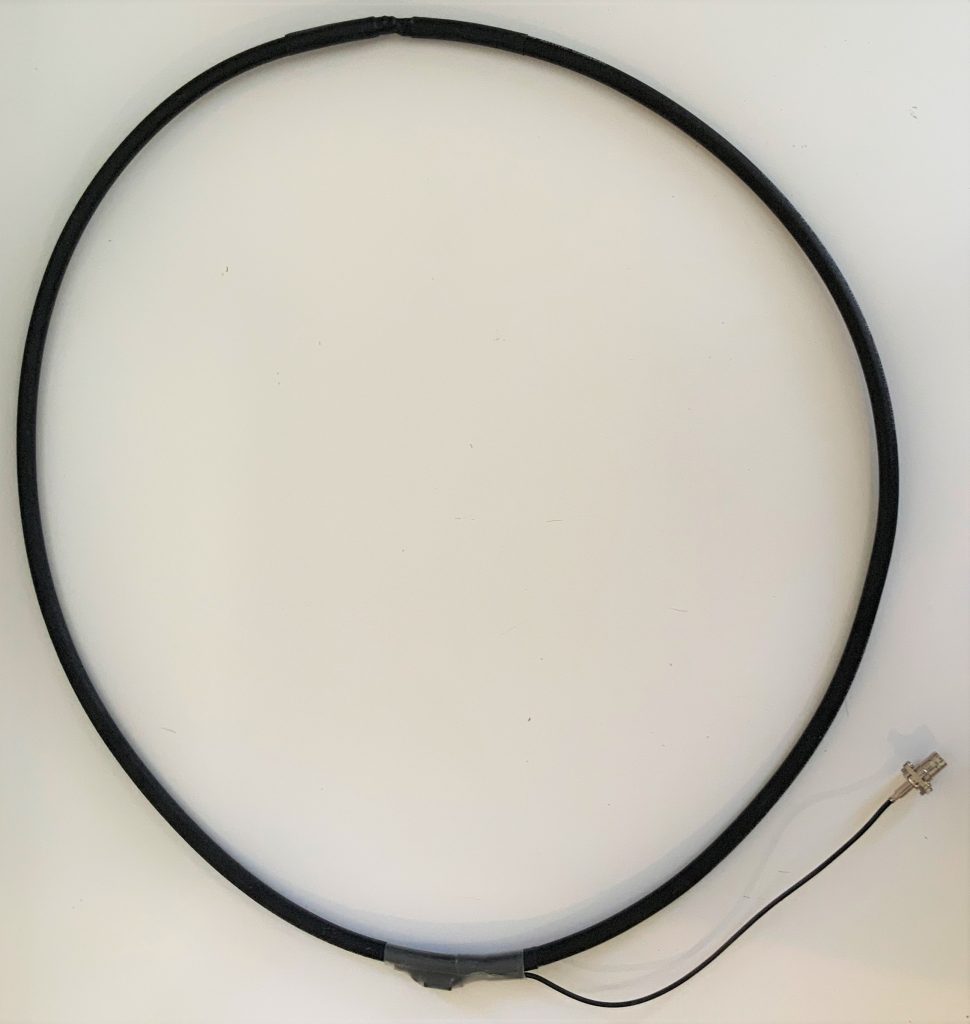
I’ve gotten an number of inquiries from SWLing Post readers asking for a step-by-step guide to building the passive loop antenna I’ve mentioned in a number of previous posts. This antenna is the homebrew version of the commercially-available Airspy Youloop.
I’ve gotten an number of inquiries from SWLing Post readers asking for a step-by-step guide to building the passive loop antenna I’ve mentioned in a number of previous posts. This antenna is the homebrew version of the commercially-available Airspy Youloop.
It works a treat. And, yes, folks…it’s fun to build.
There are a number of loop designs out there, and to distinguish this one, I’m going to henceforth refer to this loop as in the title above: the Noise-Cancelling Passive Loop (NCPL) antenna.
Before we start building, a little antenna theory…
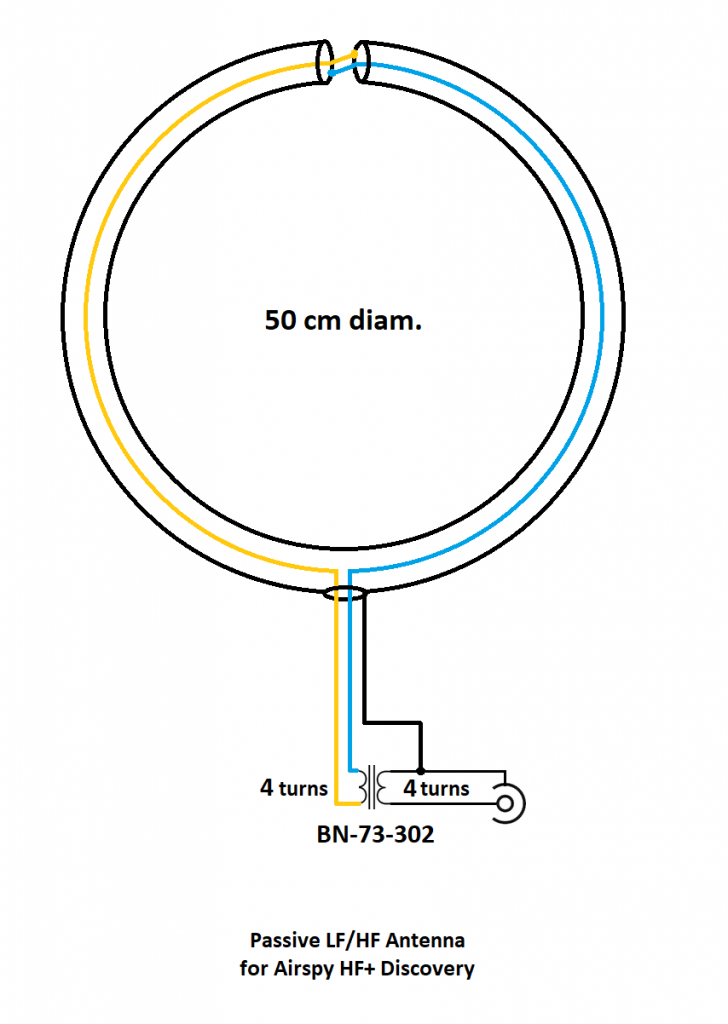
I’m neither an engineer nor am I an antenna expert, so I actually turned to Airspy president and engineer, Youssef Touil, to learn how, exactly, this passive loop works. Youssef was the guy who experimented with several loop designs and ultimately inspired me to build this loop to pair with his HF+ Discovery SDR and the SDRplay RSPdx. “The main characteristic of this loop,” Youssef notes, “is its ability to cancel the electric noise much better than simpler loop designs.” Got that! [See loop diagram below]
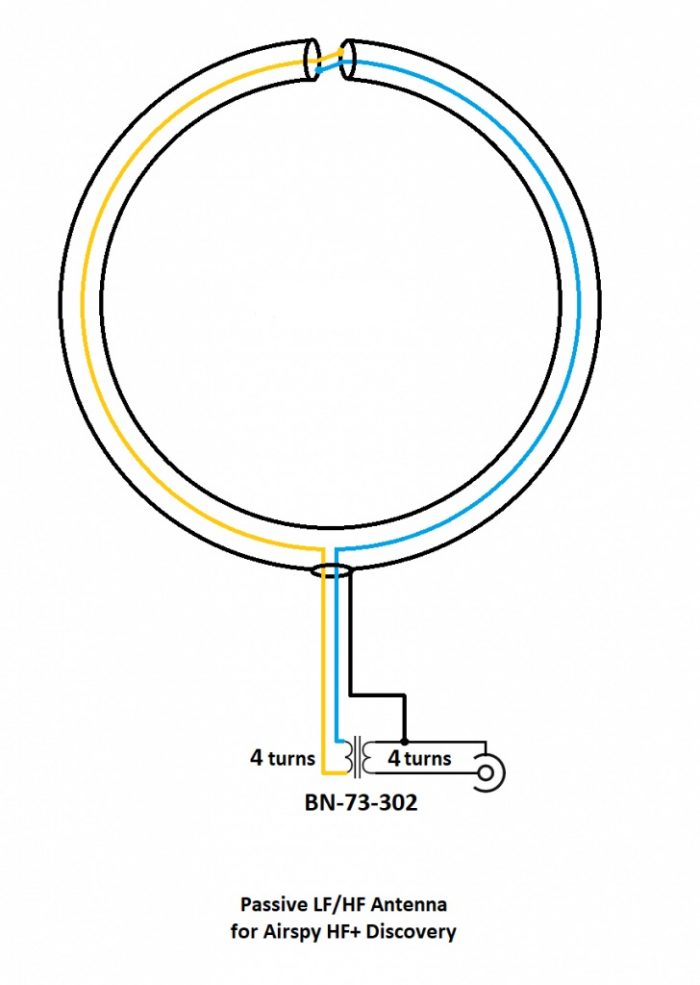
“The second characteristic of this loop antenna is that it is a high impedance loop, which might appear counterintuitive. This means it can work directly with many receivers that have a low noise figure, in order to mitigate the impedance mismatch loss.
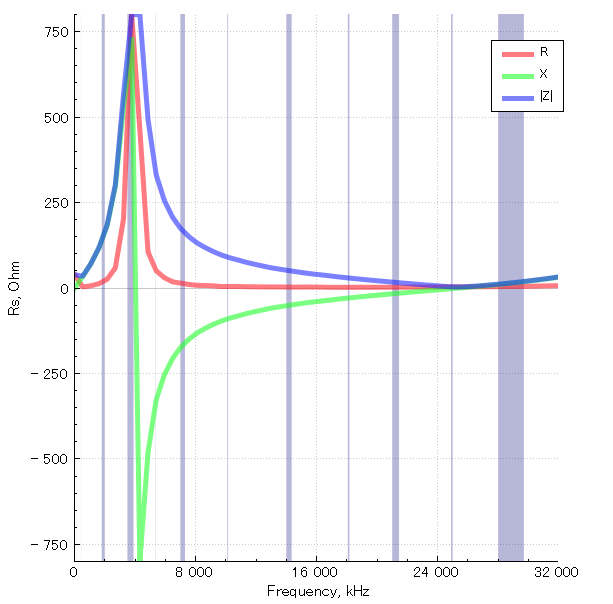
Note the resonance lobe near 4MHz. The resonance frequency is controlled by the diameter of the loop, the parasitic capacitance of the cable, and the loading from the transformer. It happens to be located right where we need it the most.
The transformer is basically a 1:1 BALUN that covers the entire HF band with minimal loss. Our BALUN has typically 0.28 dB loss.
[…]By connecting the center of this outer shield to the ground of the transmission line, you effectively cancel all the electric noise. The BALUN is required for balancing the electric noise, not for adapting the impedance.
[…]If you want to boost the performance in VLF, LW and MW, you can try a different impedance ratio, but this will kill the higher bands.”
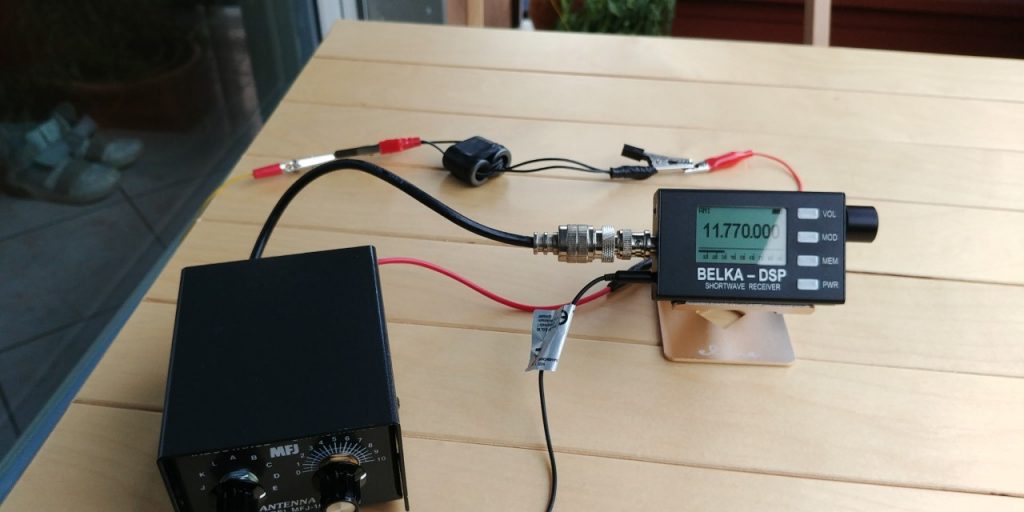
What makes this loop so appealing (to me) is that it can be built with very few and common parts–indeed, many of us have all of the items in our junk boxes already. As the name implies, it is a passive design, so it requires no power source which is incredibly handy when you’re operating portable.
When paired with a high-dynamic range SDR like the Airspy HF+ Discovery or SDRplay RSPdx, you’ll be pleased with the wide bandwidth of this antenna and noise-cancelling properties.
If you don’t care to build this antenna, Airspy sells their own version of this loop for a modest $35 USD.
But building an antenna is fun and you can tweak the design to customize performance, so let’s get started:
Parts list
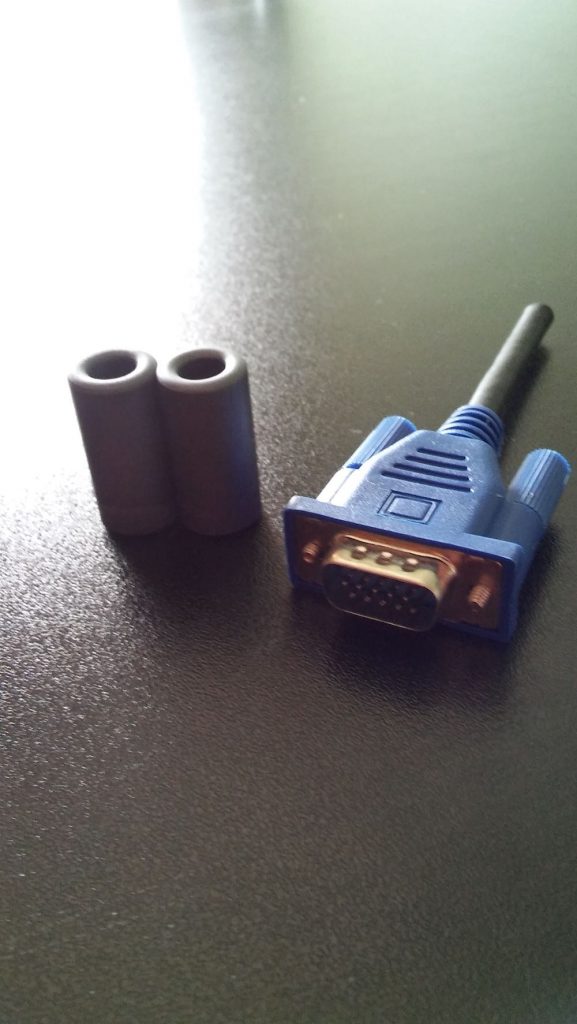
- A length* of coaxial cable for the loop (see notes below regarding length)
- Another length of cable terminated on one end with a connector of your choice as a feed line
- A BN-73-302 Wideband 2-hole Ferrite Core
- Enough coated magnet wire for a total of eight turns on the BN-73-302
- Heat-shrink tubing or some other means to enclose and secure the cable cross-over point and balun. (You may be able to enclose these connection points with PVC or small electrical box enclosures, for example)
- Electrical tape
Tools
- A cable stripper, knife, and/or box-cutter
- Soldering iron and solder
- A heat gun (if using heat shrink)
- Some patience
*A note about loop cable length: Vlado and I made a loop with 1.5 meters of cable. The Airspy Youloop ships with two 1 meter legs that combine to give you an overall loop diameter of about 63.6 cm.
Step-by-step guide
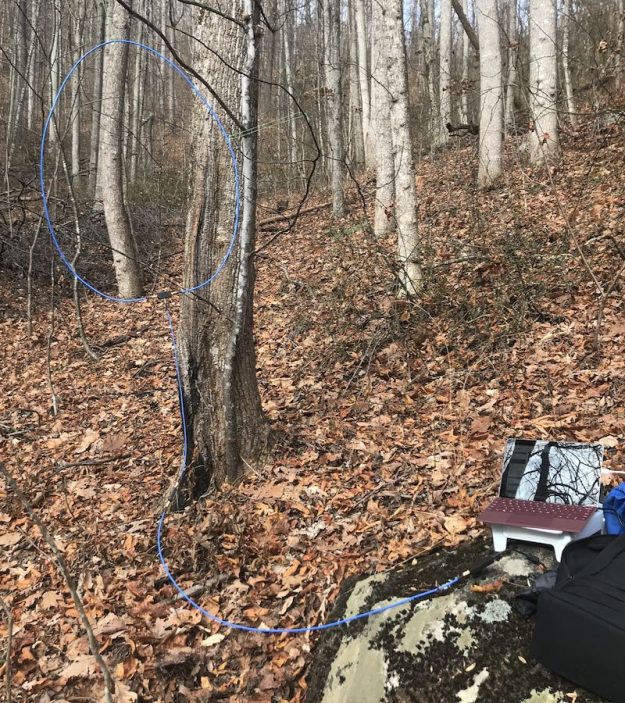
When I first decided to build this loop, it was only a day prior to a trip to the South Carolina coast where I planned to do a little DXing. I didn’t have all of the components, so I popped by to see my buddy Valdo (N3CZ). Vlado, fortunately, had all of the components and was eager to help build this loop. As I’ve mentioned in previous posts, Vlado is an amazing engineer and repair technician, so when I say “we” built it, what I really mean is, Vlado did! But I could’ve done it myself.
This is actually a very simple build––something even a beginner can do, as long as they’re okay with using a soldering iron. It does take patience preparing the loop cable properly. Take your time as you start, and you’ll be on the air in an hour or two.
1. Strip the ends of the loop cable.
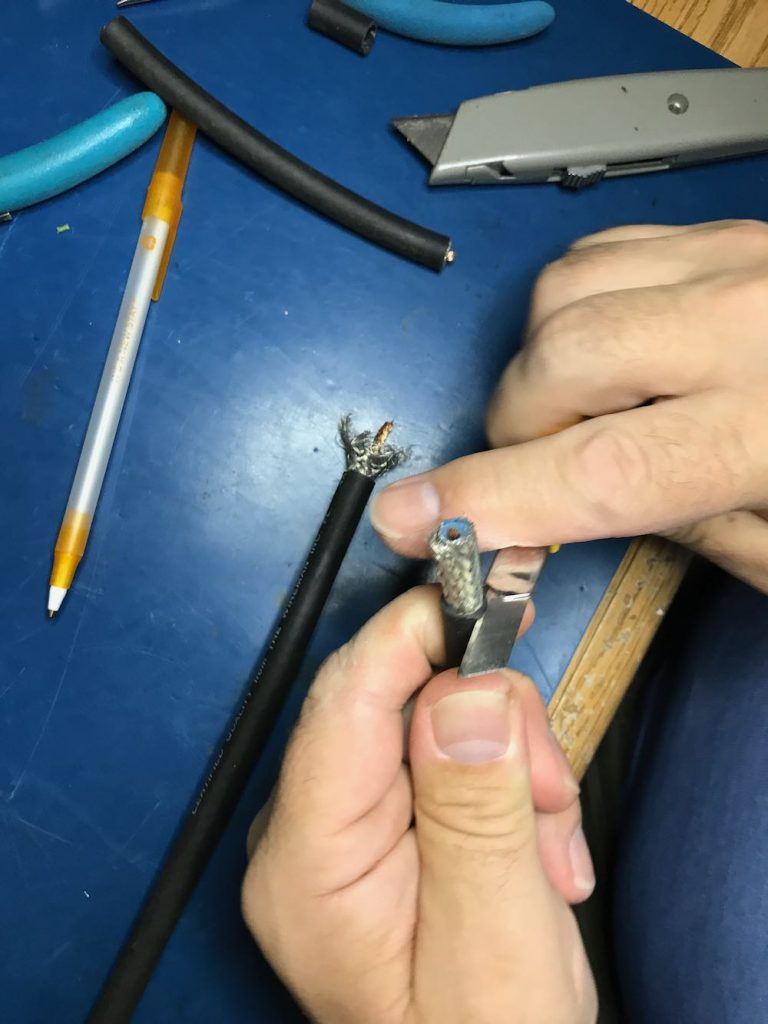

Although your cable type and diameter may vary, strip back the cable ends roughly like this.
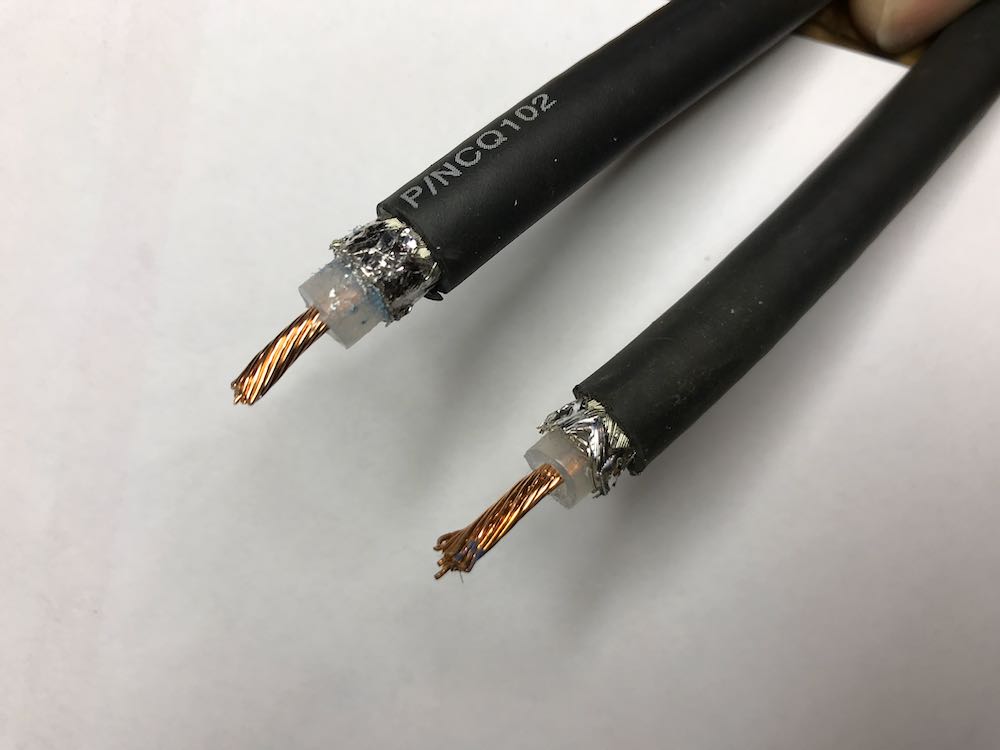 To make finding the middle of the cable easier, we taped off the ends.
To make finding the middle of the cable easier, we taped off the ends.
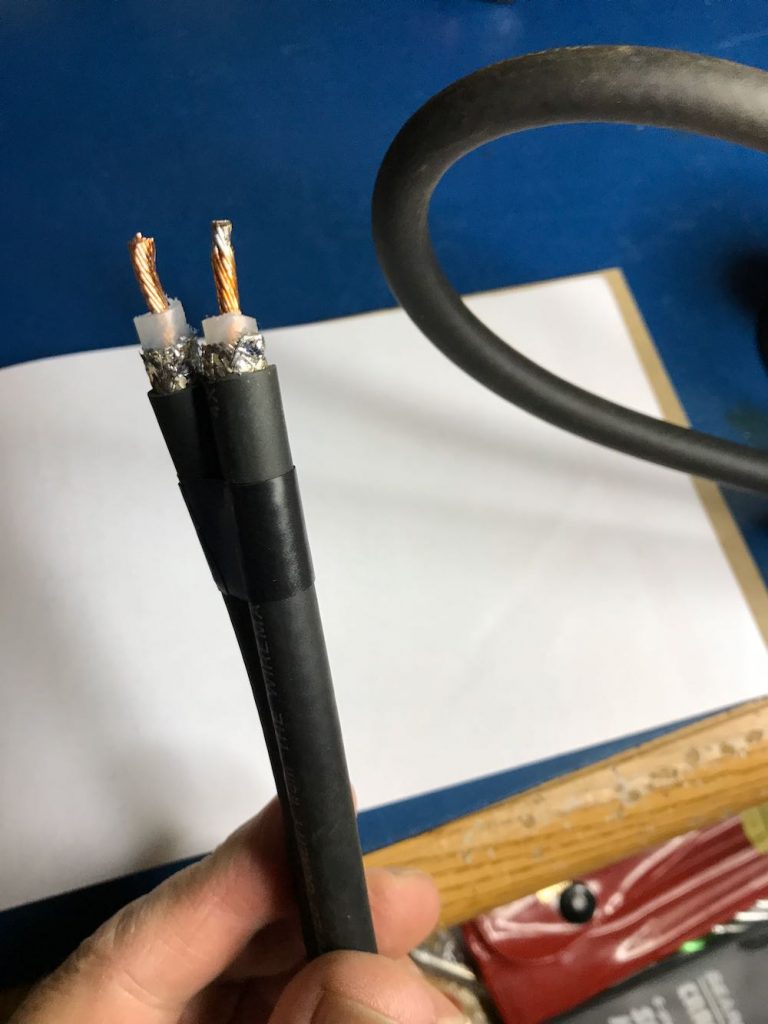

2. Make an opening in the middle of the cable to attach Balun leads to center conductor.
This is the trickiest part of the whole operation. The goal is to create an opening to tap into the center conductor of the cable.
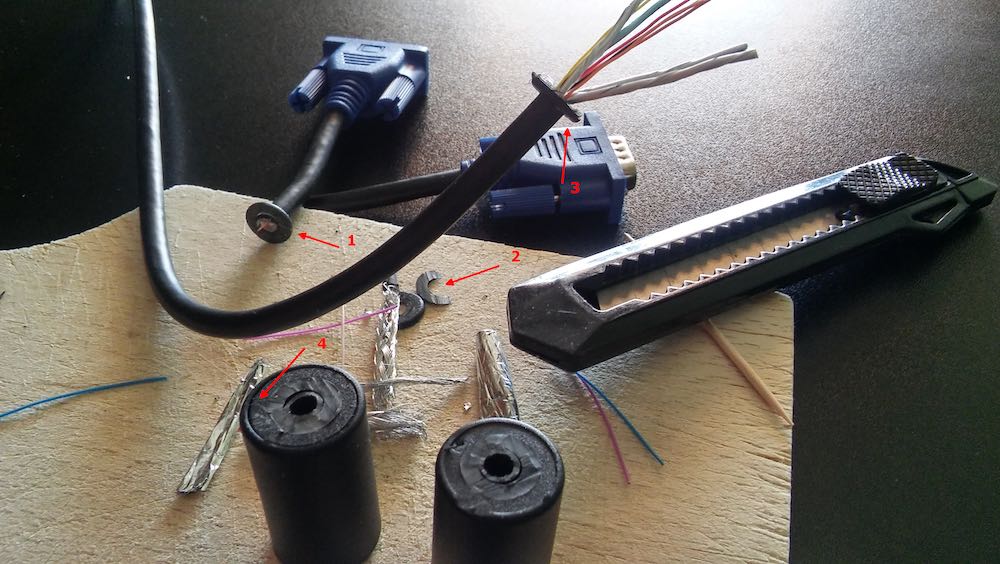
You need to open a hole in the middle of the cable by
1 cutting away a portion of the outer jacket;
2 carefully separating and opening the shielding;
3 digging through the dielectric core, and finally
4 exposing the center conductor of the cable
Try to make an opening just large enough to gain access to the cable’s center conductor, but no bigger. Don’t allow any piece of the shielding to touch the center conductor.
When you reach the center conductor, expose enough of it so that you can clip it in the middle and create an opening to solder your balun leads to both conductor ends.
Once you’ve finished with this step, your cable should look something like this…
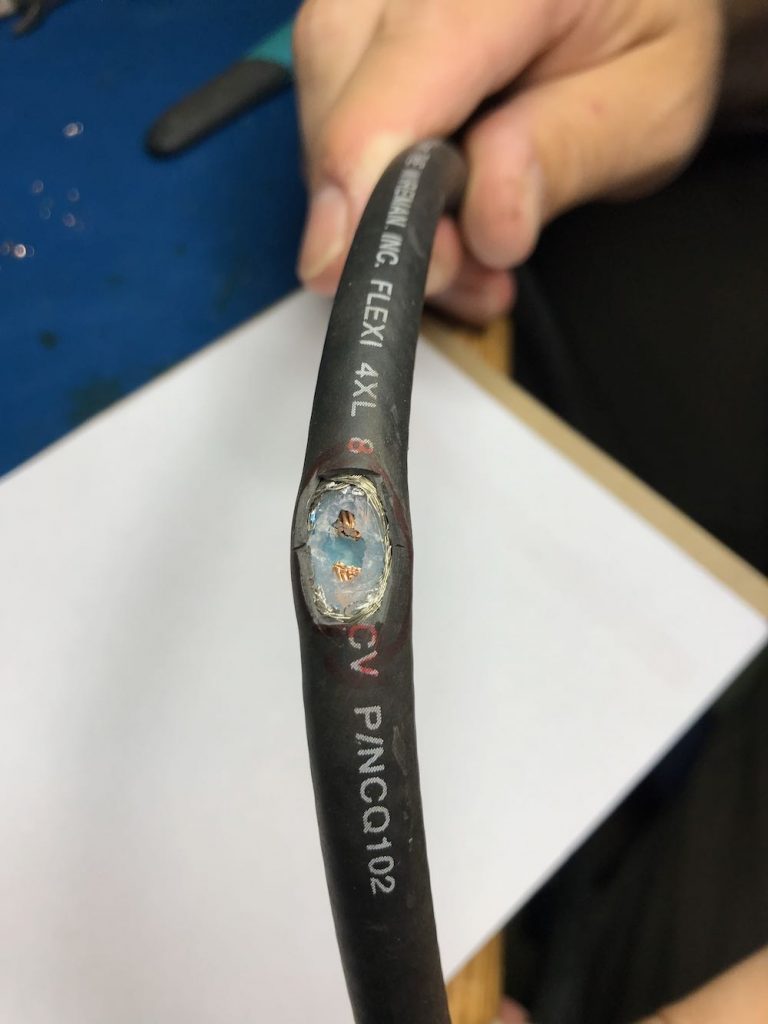

In the photo above, note that the shielding is completely pulled away, the dielectric core has been cut through, and we’ve clipped the center conductor, leaving a gap large enough to solder.
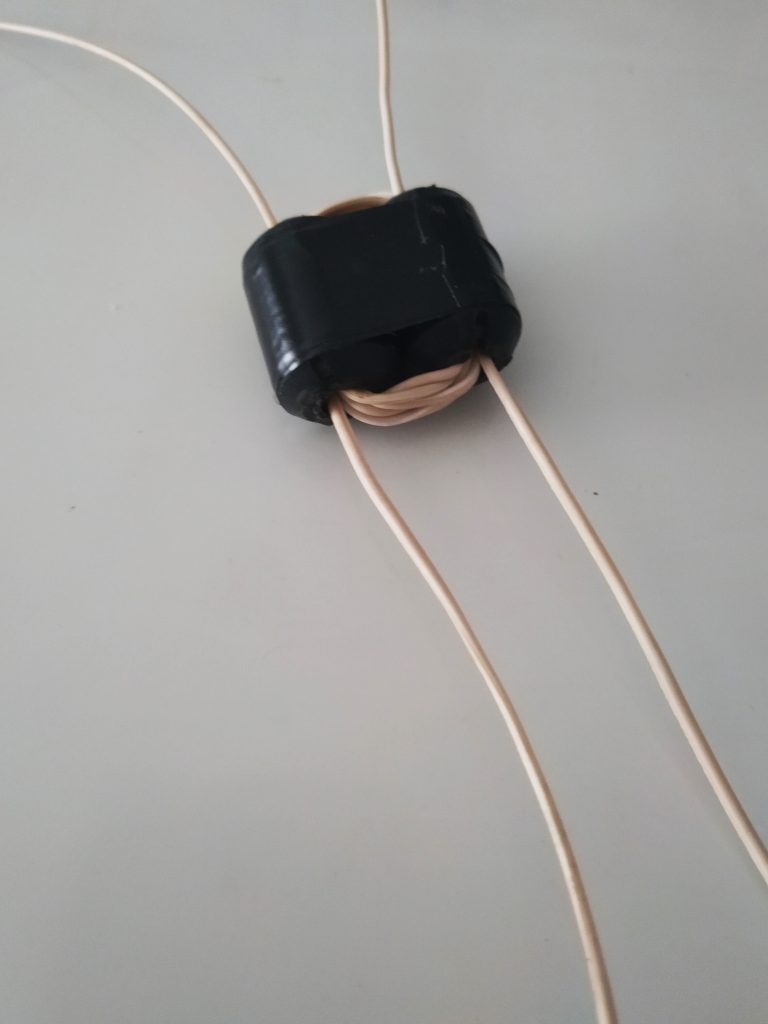
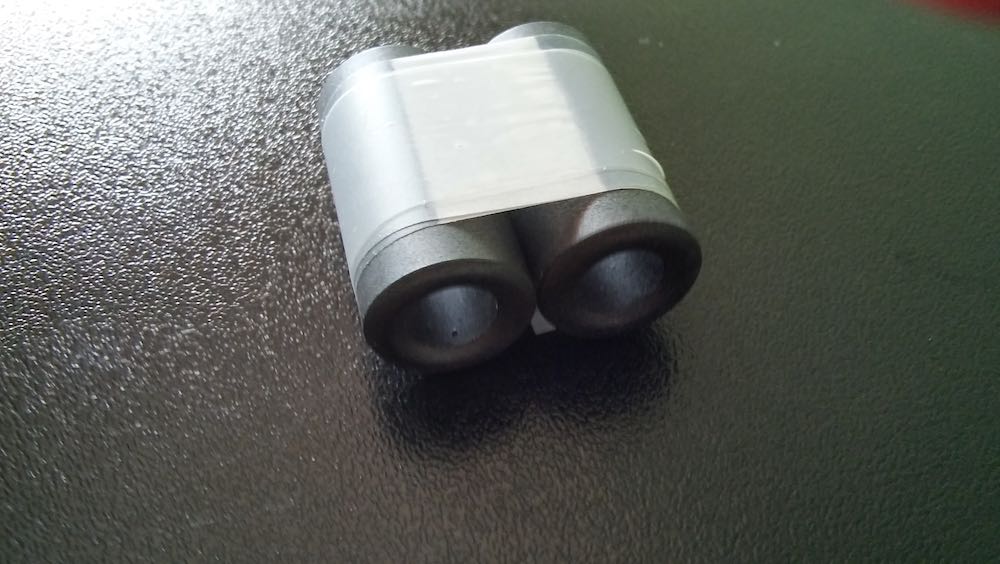
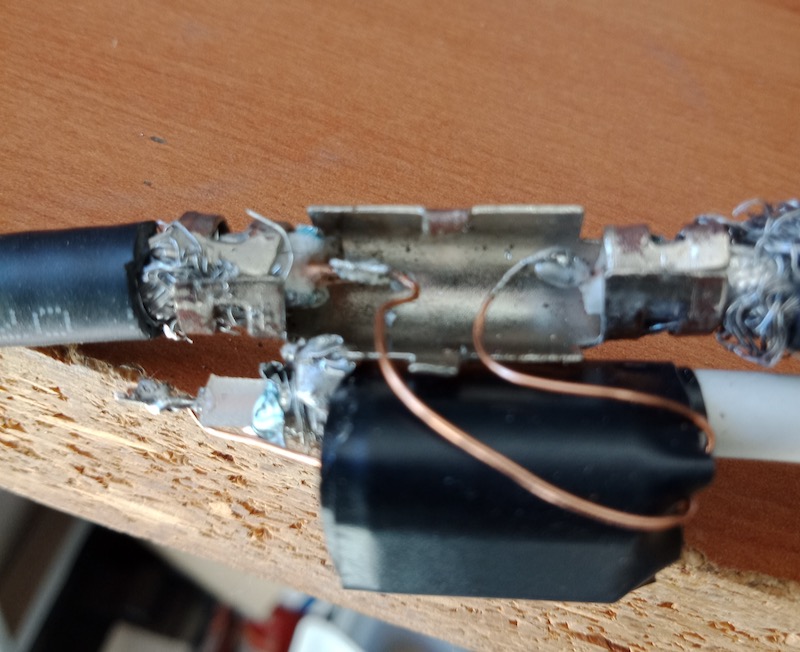
3. Make a 1:1 Balun
Grab your BN-73-302, and with the coated magnet wire, make four windings on one side, and four on the other. It should look like this:
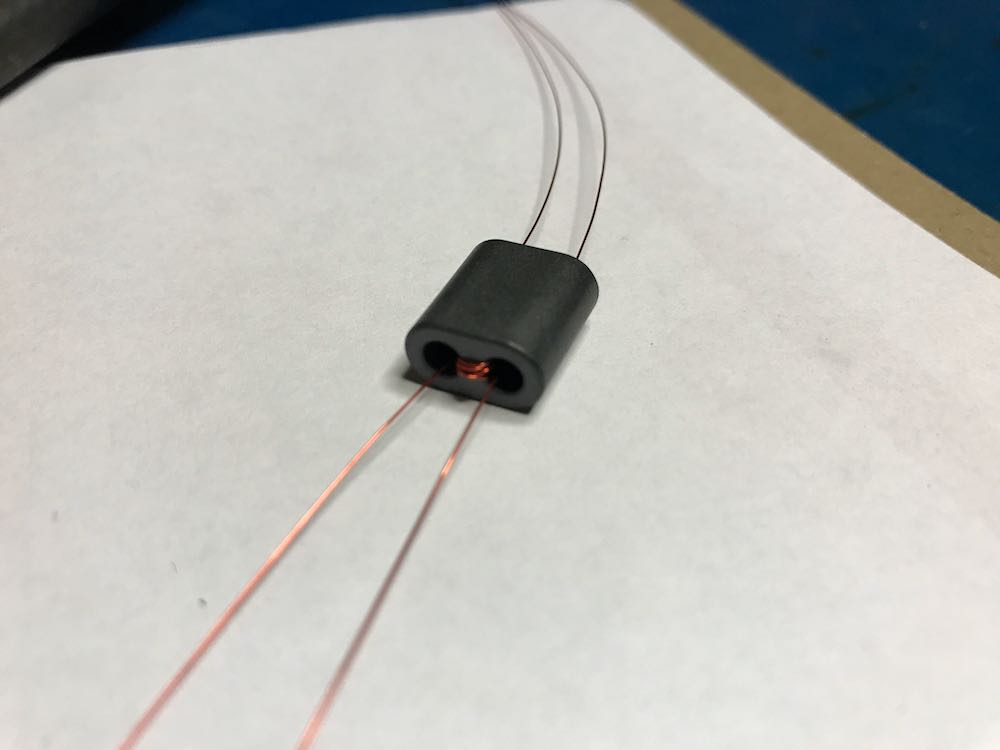
Don’t have a binocular ferrite core like the one above? If you have a broken cable with ferrite cores, you can hack one! Click here to learn more.
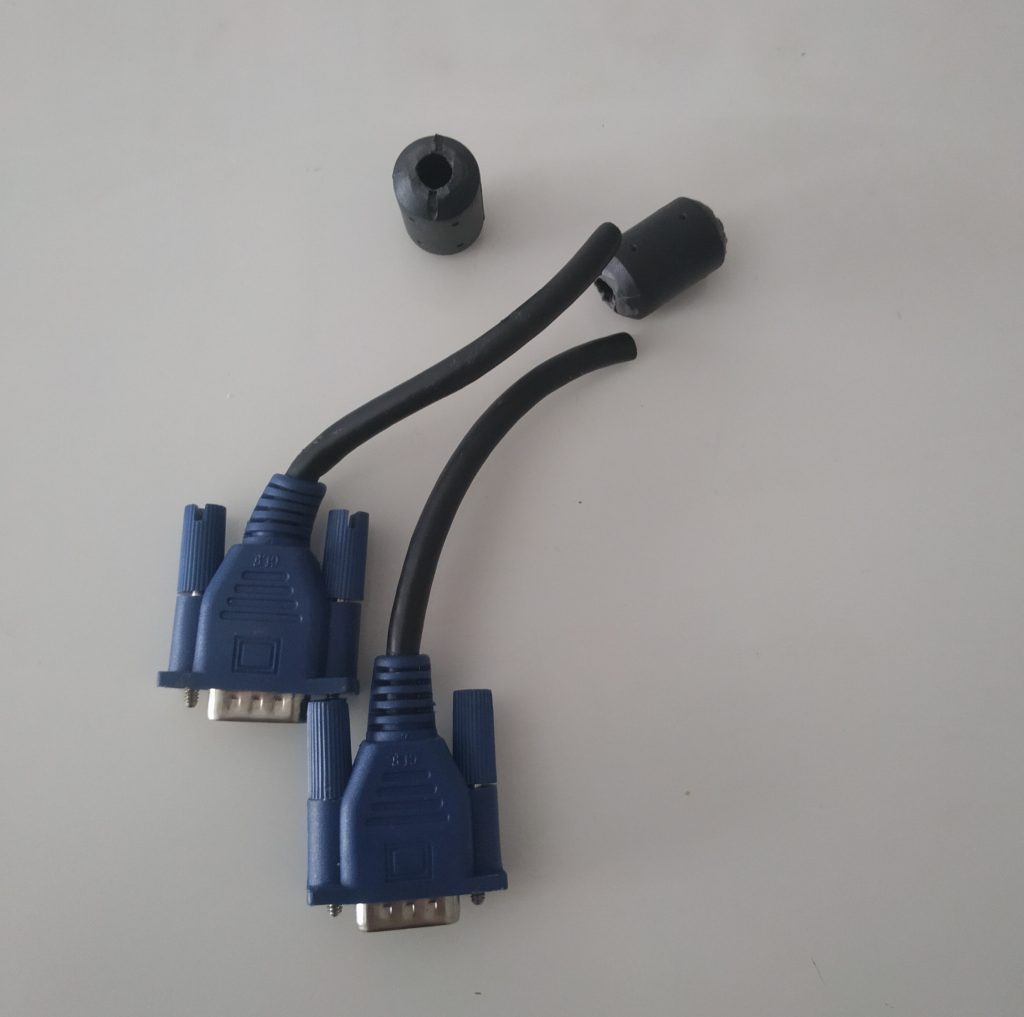
4. Connect the Balun to a feed line.
Vlado just happened to have a BNC pigtail in his shack (he’s that kind of guy), so we cut and stripped one end, then connected the center conductor and shield to one side of the balun. We then enclosed the balun in heat shrink tubing to make it a little easier to attach to the loop later:
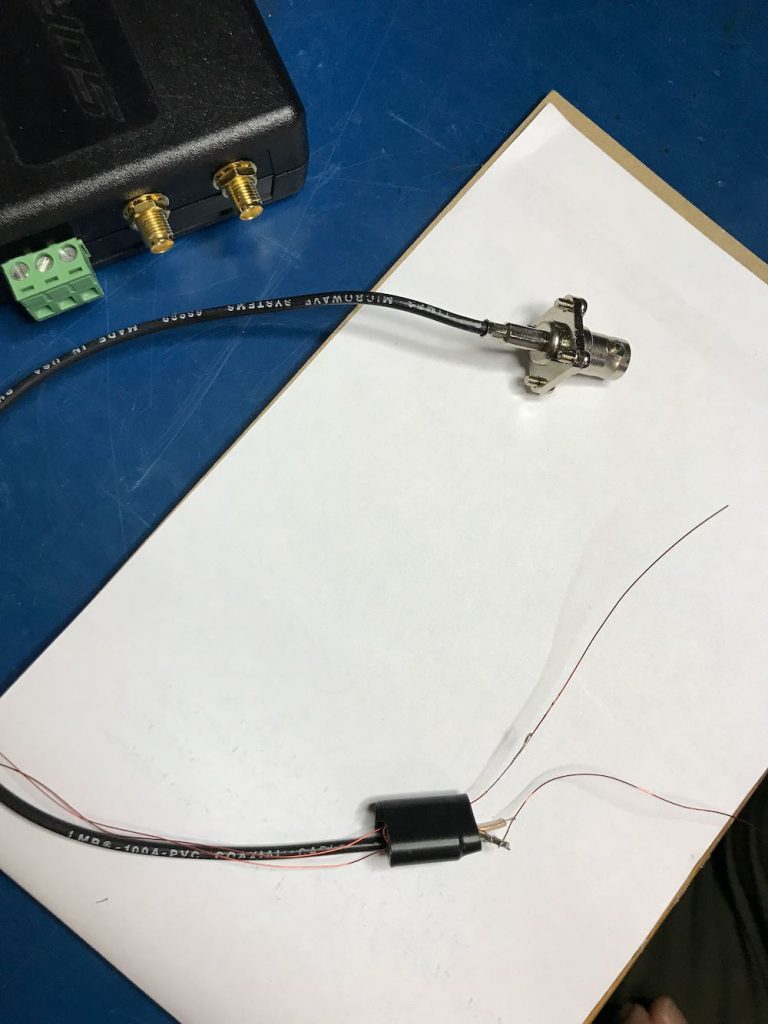

Of course, you could also create this junction in a small enclosure box or short cross-section of PVC. There are a number of ways you could secure this.
Youssef also added the following note about the feedline:
To use the NCPL antenna without a preamp, it is recommended to keep the length of the cable below 10 meters. The supplied Youloop 2 meter cable [for example] is sufficient to keep the antenna away from the magnetic interference of a computer or a tablet, and has very low loss and parasitic capacitance.
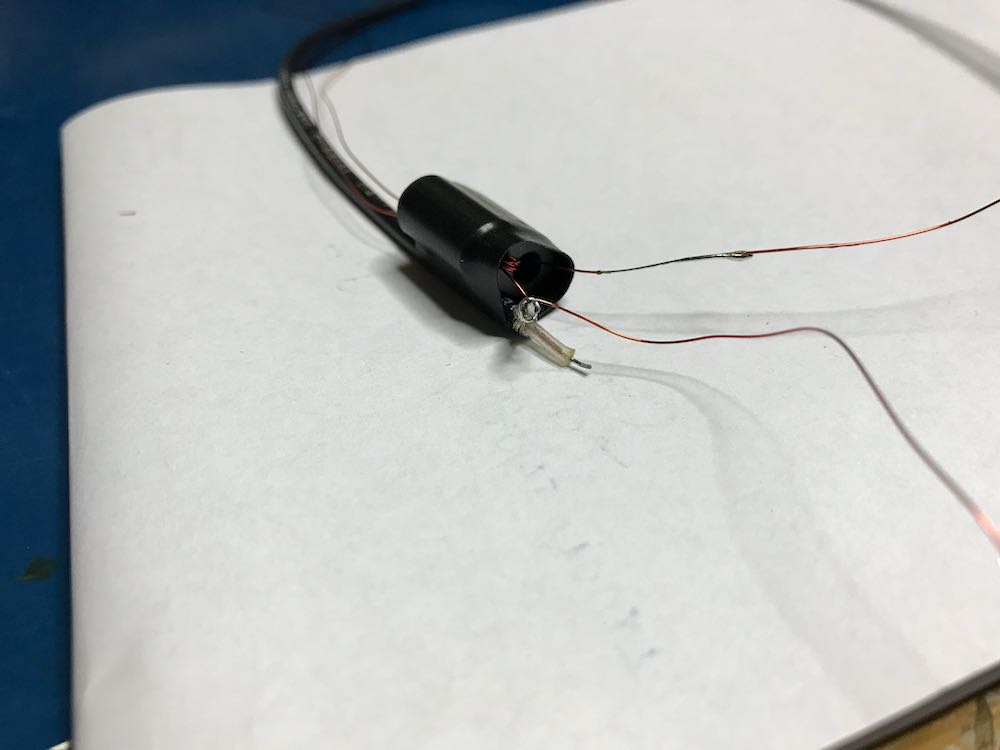
5. Connect Balun to the coaxial loop.
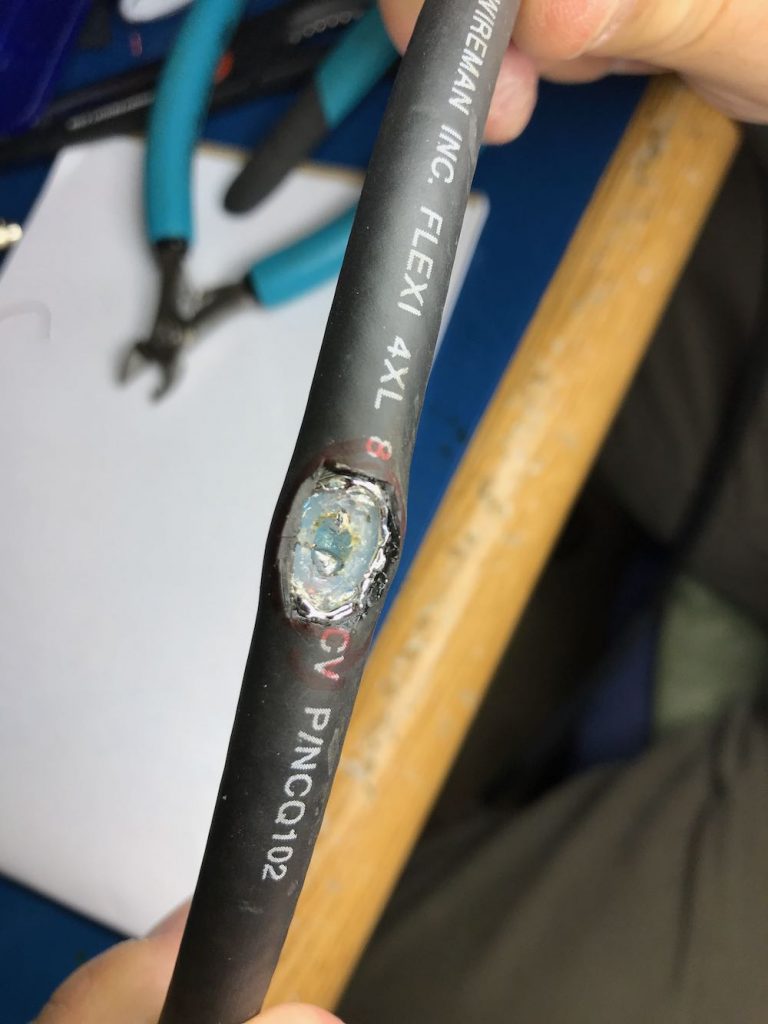

To make a solid connection, tin both sides of the center conductor. Next, attach the other end of the balun leads to each portion of the center conductor, as seen below:
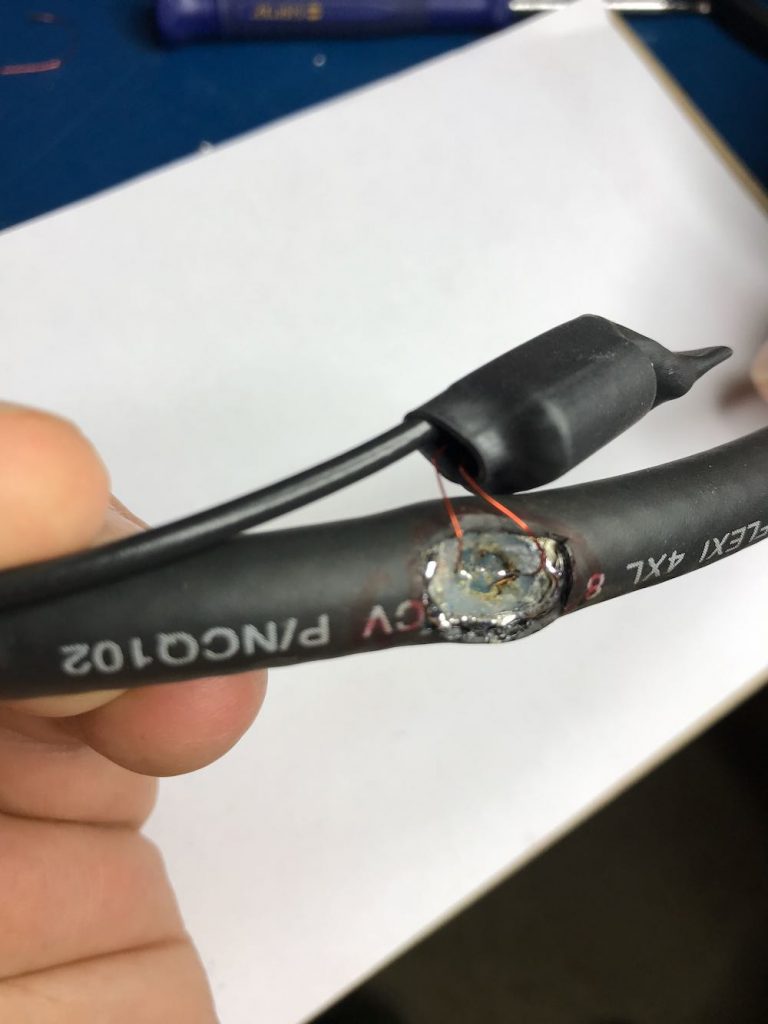

Update: Note in the loop diagram near the top of the page that the ground wire on the output connector connects to the loop coax shielding on the primary side of the balun. I don’t recall that we did this in the build, but I would encourage you to do so. This should result in even lower noise, although admittedly, I’m very impressed with the performance of ours without this connection. Thanks to those of you who pointed out this discrepancy!
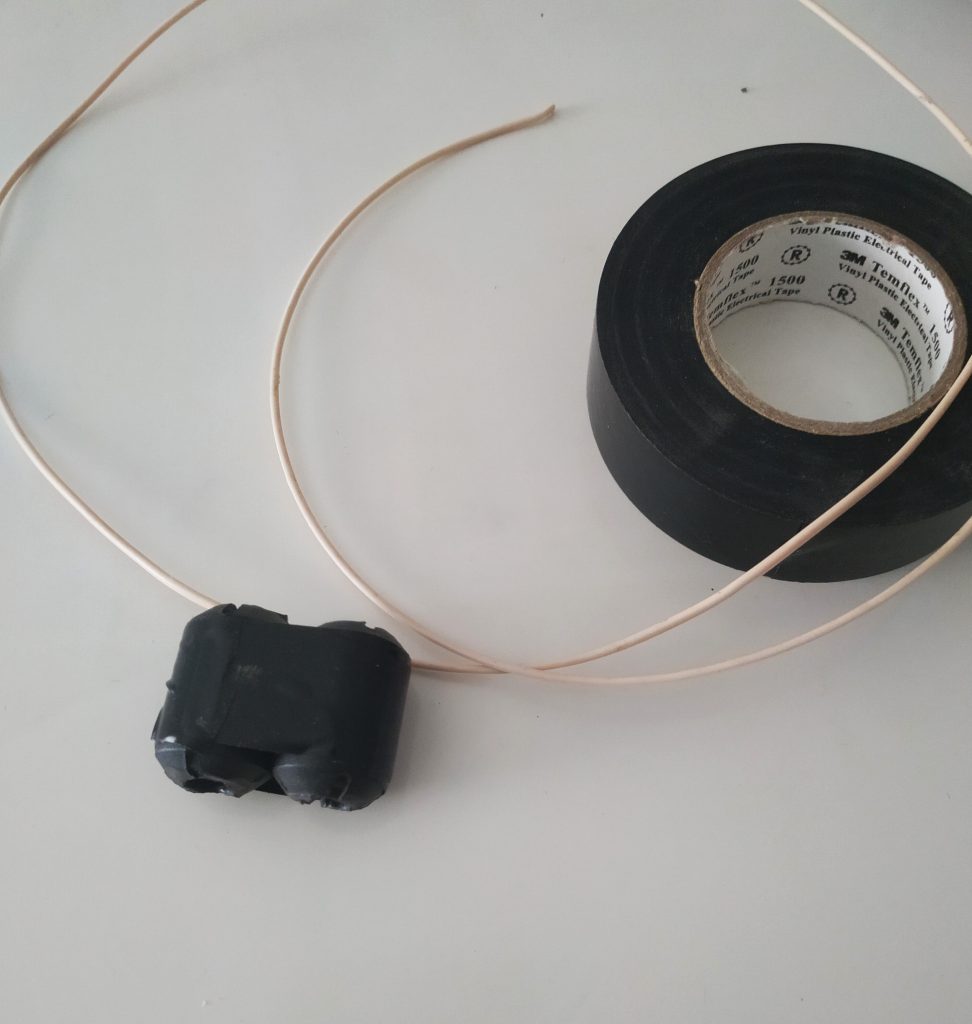
6. Secure the Balun/Coax junction.
Since this loop is intended to be handled quite a lot in the field, make sure the junction point of the balun and coax loop is secure. Again, we used several layers of heat shrink tubing since we had some in the shack.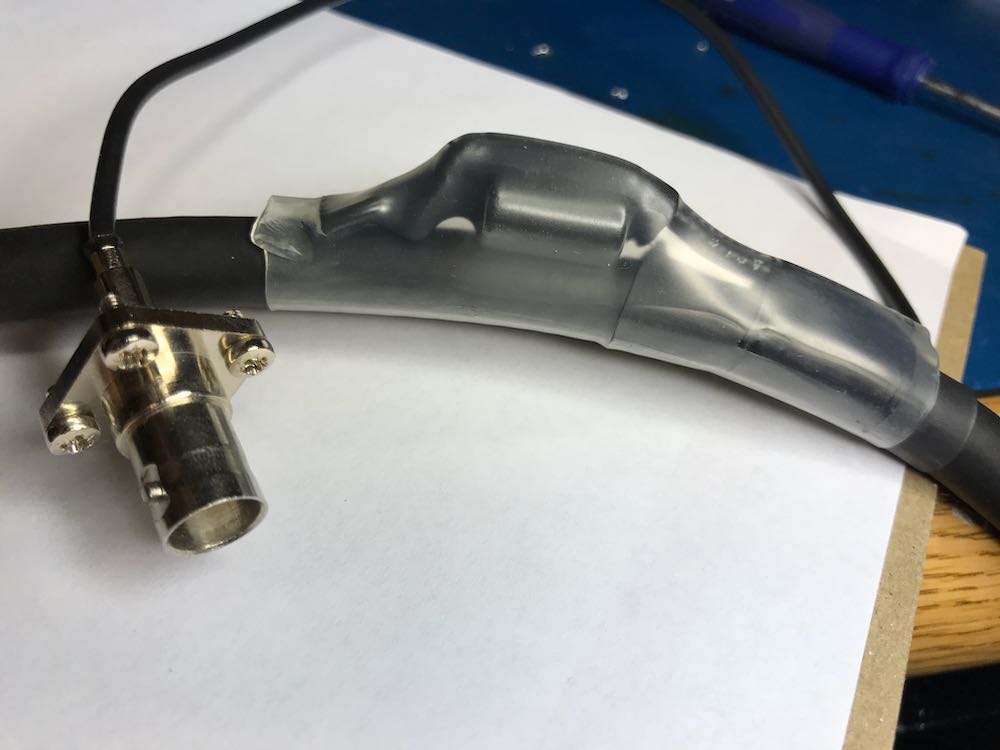 
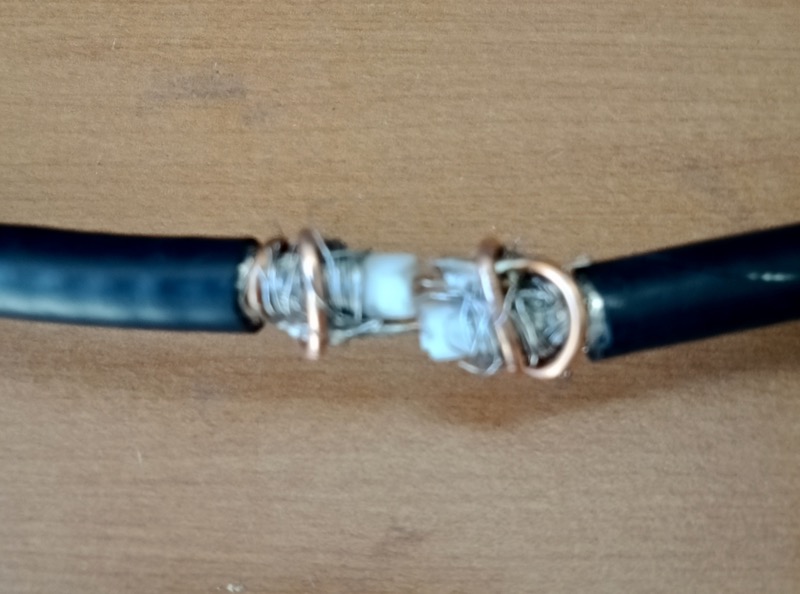
7. Solder and secure the cross-over point.
Next, create the cross-over point of the loop by simply attaching the center conductor of one end of the cable to the shielding on the other end…and vice versa.
Before you grab the soldering iron, however…if, like we did, you’re using heat shrink tubing to secure the cross-over point of the loop in the next step, you’ll first need to slide a length of tubing onto the coax before you solder the ends together. Vlado, of course, thought of this in advance…I’m not so certain I would have!
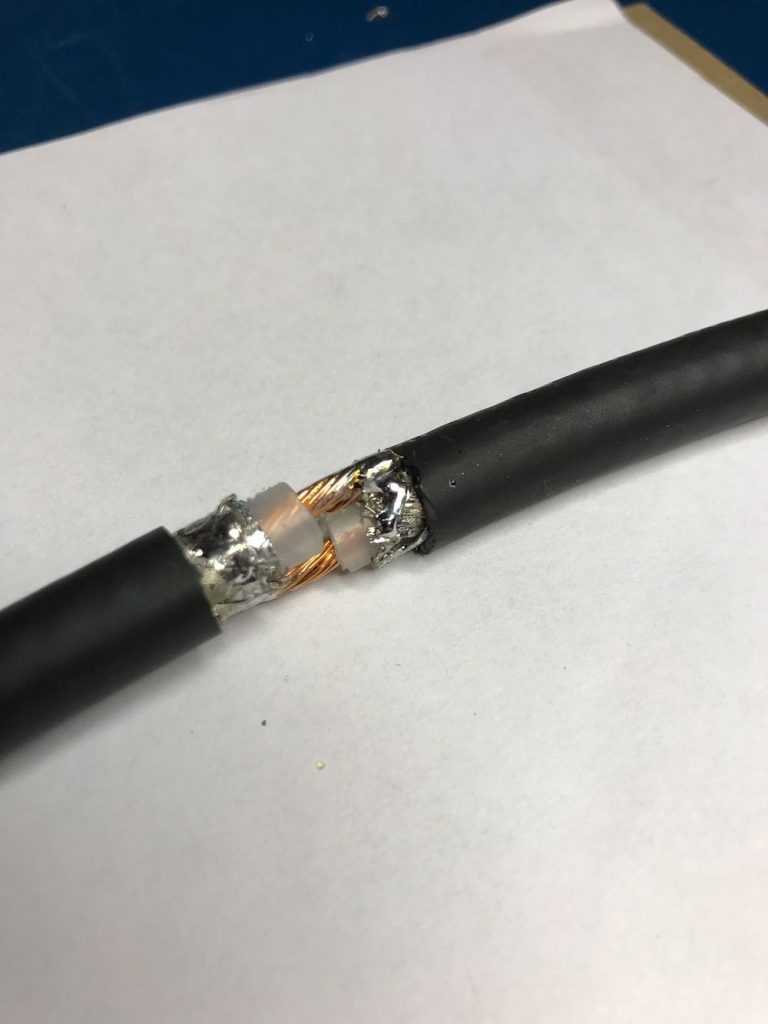 Take your time soldering this connection and making it as solid as you can. If you solder it correctly, and you’re using a high-quality cable as we did, the cross-over point will be surprisingly durable. If you’re using a thinner cable, simply make sure the connection is solid, then use something to make the junction less prone to breaking––for example, consider sealing a length of semi-rigid tubing around this point.
Take your time soldering this connection and making it as solid as you can. If you solder it correctly, and you’re using a high-quality cable as we did, the cross-over point will be surprisingly durable. If you’re using a thinner cable, simply make sure the connection is solid, then use something to make the junction less prone to breaking––for example, consider sealing a length of semi-rigid tubing around this point.
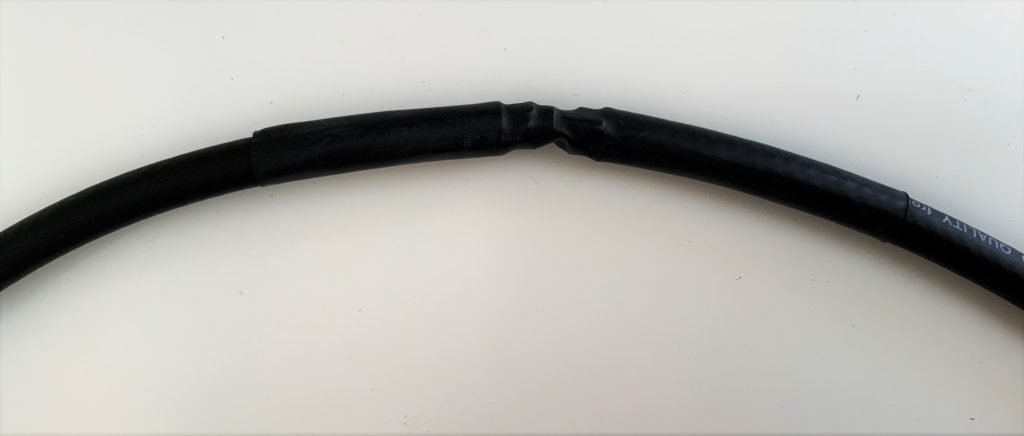

Vlado cleverly added heat shrink tubing around the cross-over point to protect and secure it.
You’re done!
That’s all, folks! Now you’re ready to put your loop on the air.
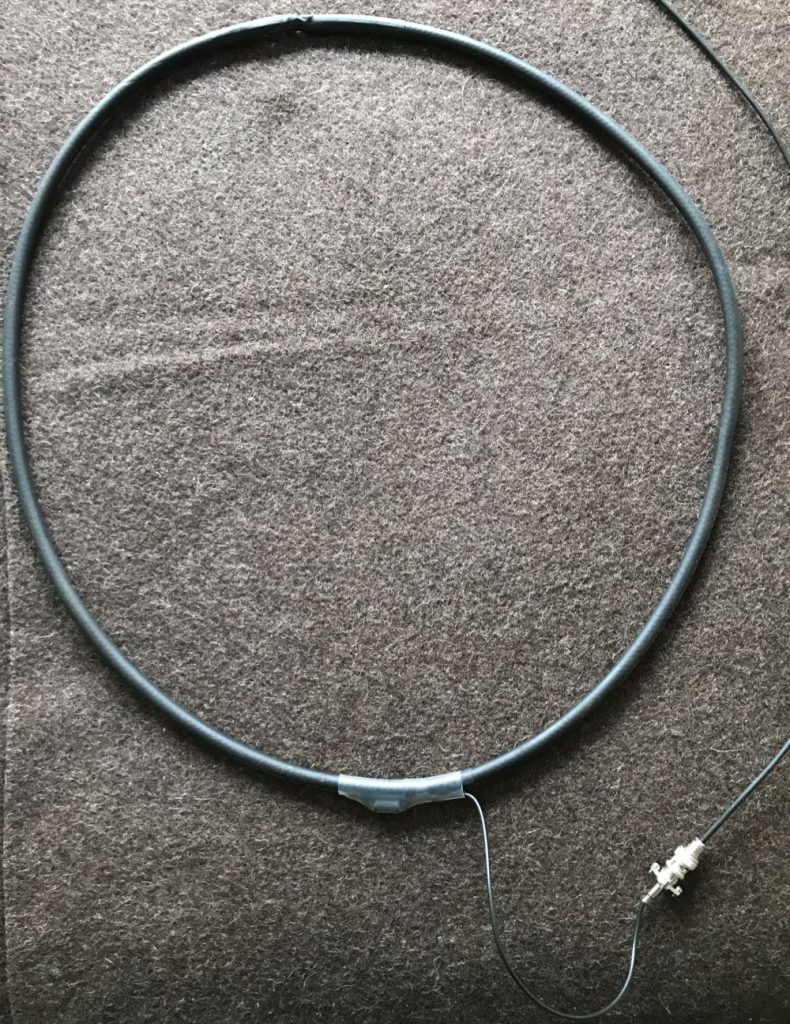

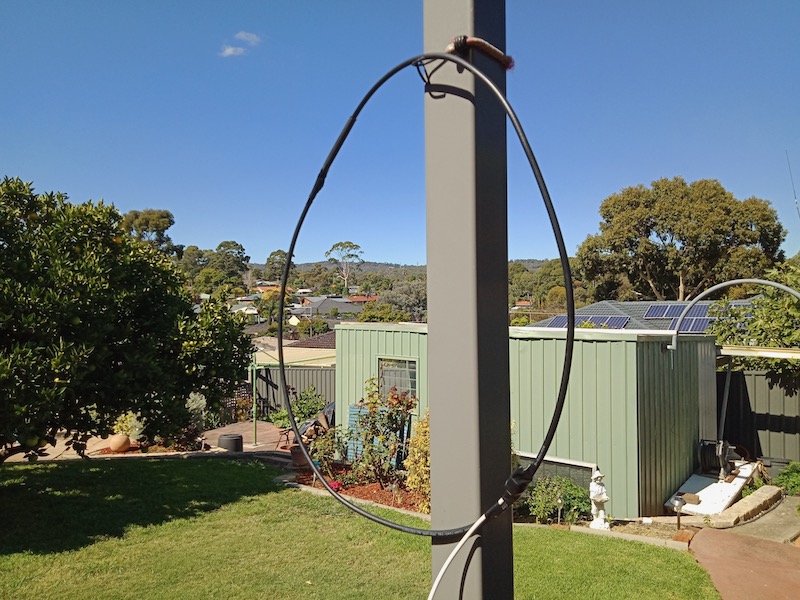
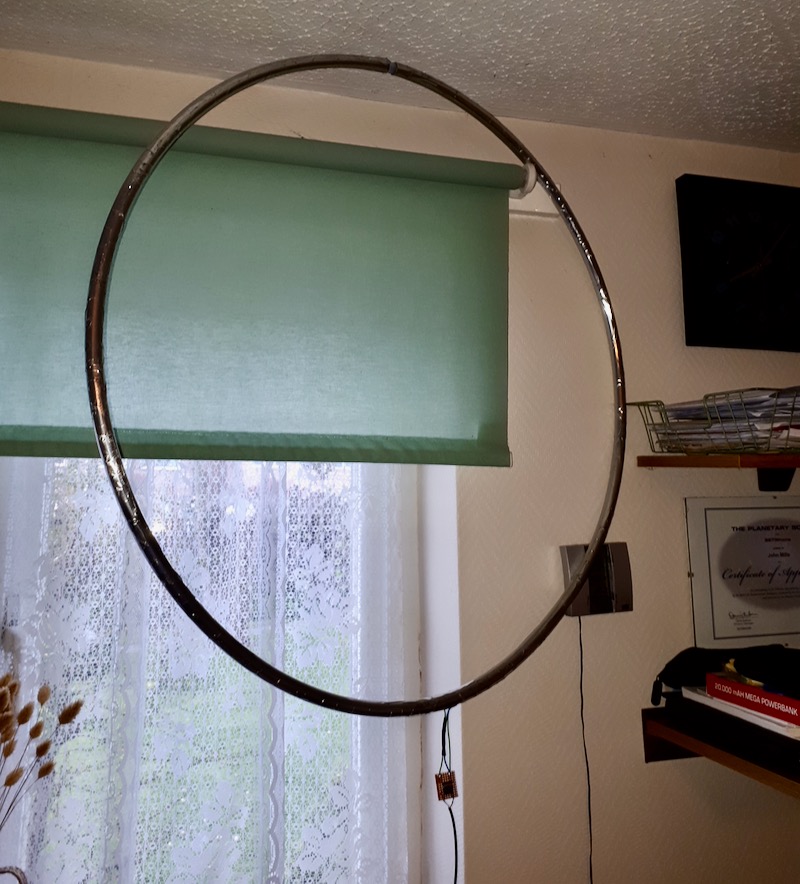
Depending on what type of cable you used for this loop, you might require or prefer some sort of dielectric structure to support the loop so that it maintains the ideal round shape. My loop maintains its integrity pretty well without supports. I’ve supported it a number of times with fishing line/filament from two sides (tying on at 10 and 2 o’clock on the loop). That seems to work rather well.
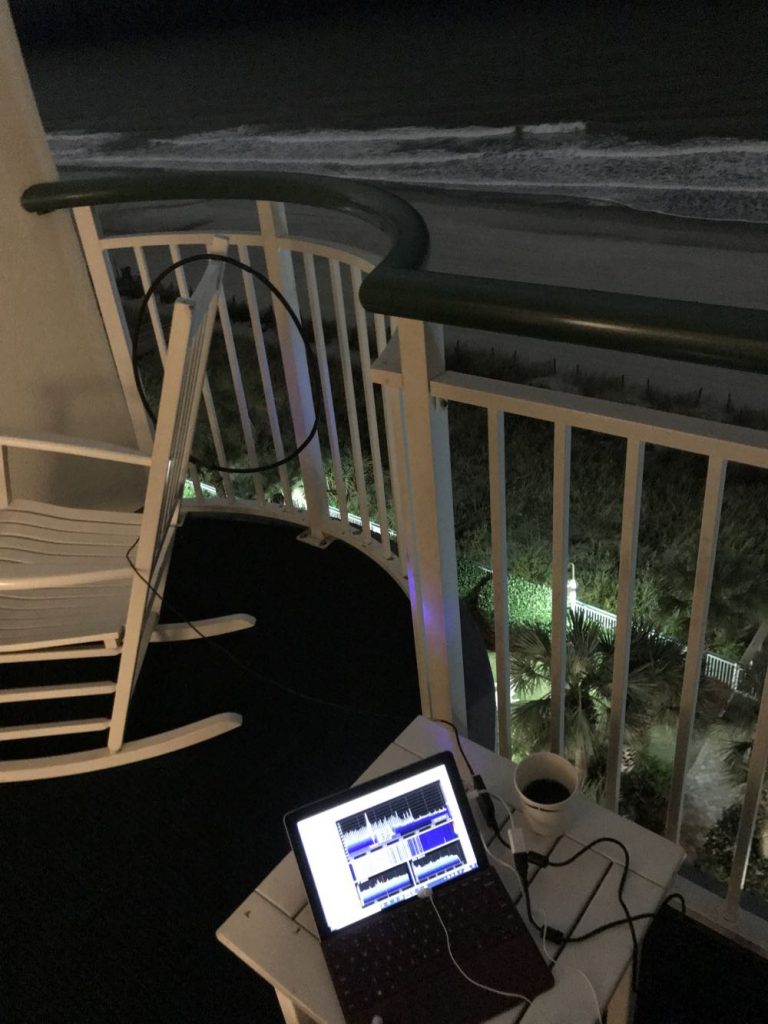

In this setup, I simply used the back of a rocking chair to hold the antenna. As you can see, the loop maintained its shape rather well.
If you’d like to see and hear how this antenna performed on its first outing, check out this post.
Show the Post your loop!
If you build a NCPL antenna, please consider sharing your design here on the SWLing Post! Considering that there are a number of ways this loop can be built, and likely even more optimizations to improve it or make its construction even easier, we’d love to see your designs and/or construction methods. Please comment or, if you prefer, contact me.
And many thanks to my good friend Vlado (N3CZ) for helping me with this project and allowing me to document the process to share it here on the Post. Got a radio in need? Vlado’s the doctor!
Enjoying the SWLing Post?
Please consider supporting us via Patreon or our Coffee Fund!
Your support makes articles like this one possible. Thank you!
 Many thanks to SWLing Post contributor, Patrizio Cardelli, who writes:
Many thanks to SWLing Post contributor, Patrizio Cardelli, who writes: