Many thanks to SWLing Post contributor, Gary DeBock, for sharing the following guest post:
Supercharging the XHDATA D-808
Installation of High Performance AM and LW Loopsticks
By Gary DeBock, Puyallup, WA, USA, September 2018
Introduction
As a stock receiver the Chinese-made D-808 AM-LW-FM-SW-AIR portable is a very capable performer, with AM reception superior to that of any current Ultralight model, and impressive FM reception as well. The radio was certainly “inspired” (to use a generous term) by the C.Crane Skywave SSB model, which coincidentally was manufactured in the same part of China by C.Crane’s Redsun partner—with the first units going out the door a few months before the D-808 came into existence.
Because foreign intellectual property is routinely copied in China with no punishment from the government, XHDATA essentially had the chance to copy all the good points in the Skywave SSB design and improve upon its weak points as well. The only precaution that XHDATA took after this wholesale design appropriation was to forbid direct shipments of the D-808 from China to North America—presumably to avoid a copyright lawsuit by C.Crane. As such, the first D-808 models were sold to the rest of the world around January of 2018 at a price about half that of the Skywave SSB, while North American DXers were told that since the model couldn’t be shipped to the USA or Canada, they were out of luck.
Of course some D-808 models did make it into North America, where it was found to be a very capable portable with astonishing value for the price. Finally around March, an enterprising Chinese eBay seller came up with a plan to ship the model to North America through Israel, thereby skirting around XHDATA’s direct shipment prohibition. As of late August this eBay seller (harelan ecommerce) has already sold 62 of the D-808 models this way, even though he charges a premium for shipment to North America. Whether this single supply source will continue to serve North American customers is currently unknown, but out of the 7 models that I have purchased from him there hasn’t been a single D-808 model with any issues– despite the apparent lack of any manufacturer’s warranty offered on the radio.
Despite the D-808’s rather dubious design pedigree there is no doubt that the Chinese engineers (or reverse engineers?) did a superb job in creating an awesome radio for the money. Besides directly copying the Skywave’s SSB design and controls, XHDATA also made significant improvements, including a longer loopstick (providing clearly superior AM sensitivity), a much more powerful audio amplifier (correcting a serious shortcoming in the Skywave SSB) and a much lower price (about half that of the $169.99 Skywave SSB, for models shipped outside North America). Another great advantage for someone wishing to perform this loopstick upgrade are the perfectly located, highly accessible Litz wire connections on the RF circuit board—apparently used by the Chinese engineers to conveniently test out various loopsticks, and retained in the final product. The radio’s high quality construction and survivability in adverse conditions were proven repeatedly over the summer here, with the model surviving accidental exposure to a 104 degree (43 degrees C) car trunk temperature, exposure to moderate rain, repeated travel bumps, and use as the main receiver during a 9-day DXpedition to a plunging ocean side cliff in Oregon state. The 3.7v lithium-ion rechargeable battery provides superior run time for extended DXing sessions, and is included in the D-808 shipping package, along with a USB cord to charge the battery, a plug-in wire antenna (for FM,SW and AIR), a vinyl carrying case, and a pretty basic English instruction manual.
One thing you will NOT find supplied with the D-808 is a warranty card– either in the shipping box, or online. This is pretty standard practice in China, incidentally, where concepts like refunds and warranties aren’t generally part of customers’ expectations. This doesn’t necessarily mean that XHDATA won’t repair obvious problems in a new D-808, but it does mean that they aren’t assuming the obligation to do so. I have heard from one North American purchaser who received a new D-808 with a defective speaker, and he is still waiting for the model to be repaired (after paying the shipping charge to send it back to China). Each individual purchaser must decide whether or not this lack of any warranty is a deal breaker. But if you are looking for a final reason to perform this loopstick transplant, why not consider the fact that you will not be violating any manufacturer’s warranty by doing so??
Realistic Expectations
Although this 7.5” loopstick upgrade will certainly make your D-808 far more sensitive than the stock model on Medium Wave or Longwave, it is not designed to compete with large (2’ sided or larger) inductively coupled box loops, or any of the new FSL antennas. The sensitivity upgrade will boost the D-808’s MW band weak-signal performance up to the level of classic portables like the ICF-2010 and RF-2200; however, and since the D-808’s DSP-enhanced selectivity will generally exceed that offered by these classic portables, the overall DXing capability in the AM mode could be considered slightly greater. The D-808 does have SSB capability, although it lacks the SSB tuning convenience offered by the ICF-2010 and RF-2200. It also lacks the ICF-2010’s superb Synch detector, a big advantage in weak signal DXing. But in portability, versatility and DXing value for the price, the “Supercharged” D-808 is a real winner.
Project Overview
This construction article will provide the builder with step-by-step instructions to upgrade the XHDATA D-808’s loopstick to a much more sensitive, externally-mounted 7.5” Medium Wave or Longwave loopstick replacement. Both the Medium Wave and Longwave 7.5” loopstick designs have been thoroughly tested and proven effective in actual DXing by hobbyists other than the author, and as long as the instructions are followed carefully, this relatively inexpensive modification will provide a major improvement in the D-808’s weak-signal reception capability.
This modification project involves close-order soldering on the D-808’s circuit board, and should only be attempted by builders with reasonably good eyesight, good hand coordination and soldering experience. The project also calls for the use of a precut plastic loopstick frame to attach the antenna to the top of the D-808’s top back cabinet surface, and the construction of this precut plastic frame requires either the use of a 12” (or larger) power miter saw, or some rather lengthy cutting with a hacksaw. Use of a power miter saw SHOULD NOT be attempted by those without serious power tool experience! The author assumes that only qualified power tool operators will attempt to use a 12” miter saw to cut these frames quickly, and that other builders who wish to construct them will use a hacksaw. As such, only basic cutting instructions are provided for the 12” power miter saw users, while detailed instructions are provided for the hacksaw users. To assist builders who are not qualified to use power tools, the author has prepared a LIMITED number of these precut plastic loopstick frames on a power miter saw, which will be offered at cost to these builders on a first come, first served basis.
A final warning is in order concerning the step of gluing the precut plastic loopstick frame to the D-808’s top back cabinet surface. Although this step is not dangerous, it is pretty tricky. Since the superglue “grips” very rapidly, you will only get one chance to ensure that the frame is straight, and centered on the D-808’s top cabinet surface. Do yourself a favor, and make multiple “dry runs” to practice this important step before applying the glue! Failure to take this step seriously will probably result in a crooked loopstick frame—which will hold the antenna just fine for DXing purposes, but which will be an eternal reminder to the DXer (and everyone else) of the hazards of haste.
Construction Parts Required
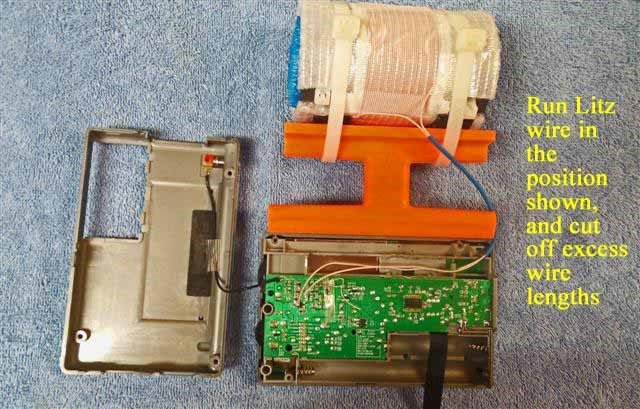
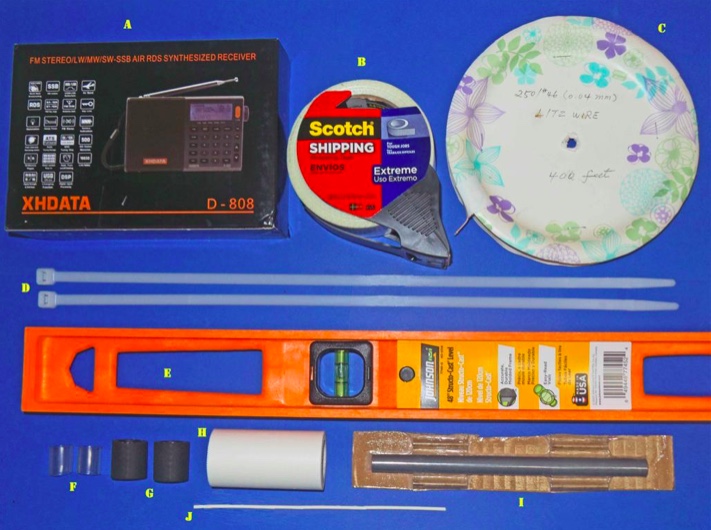
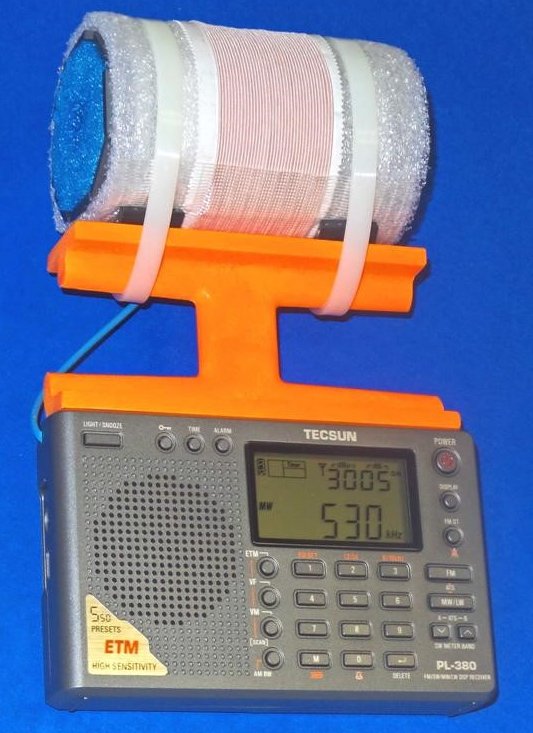
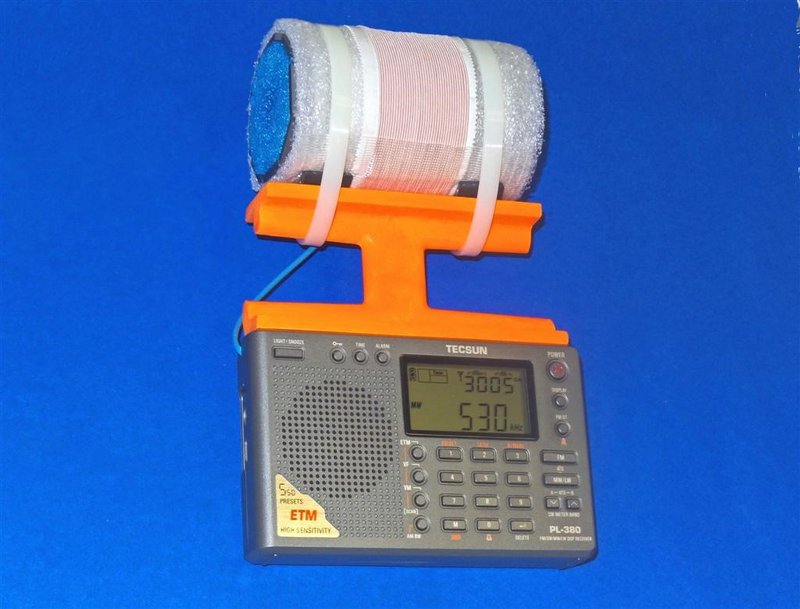
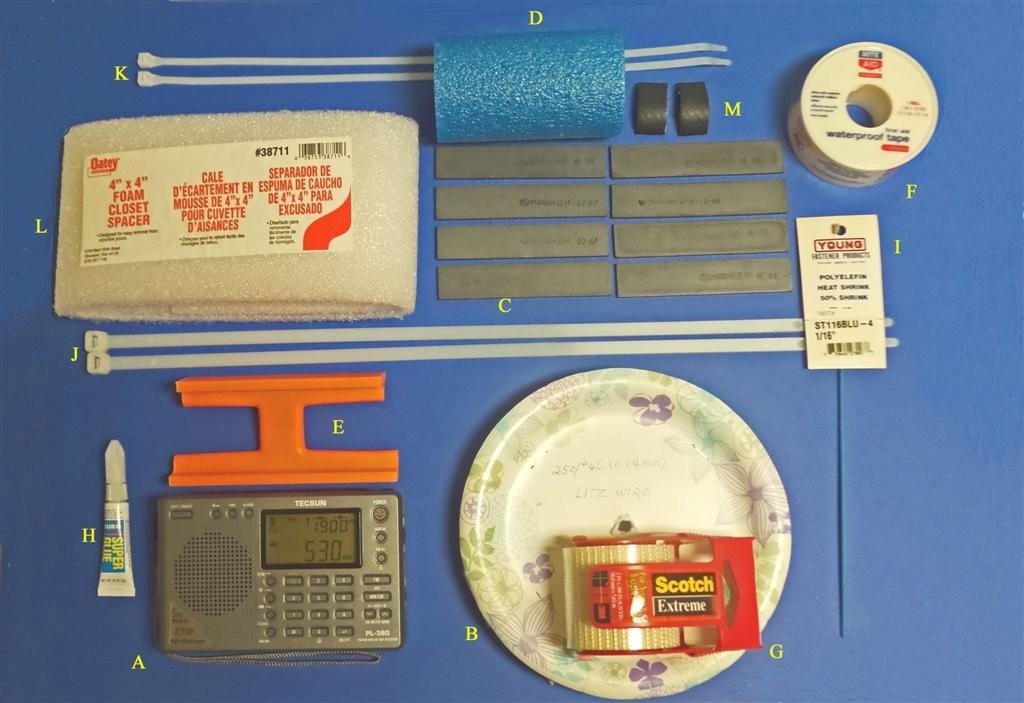
This 7.5” loopstick D-808 construction article will guide you through the assembly of either a 7.5” Medium Wave loopstick D-808 or a 7.5” Longwave loopstick D-808, so make sure that you order the parts necessary for construction of your chosen model. The picture above shows the parts that will be necessary for construction of either model, but the Litz wire and 7.5” ferrite rod components differ according to whether you are building the Medium Wave or Longwave model.
A) XHDATA D-808 Receiver, currently available to North American purchasers (for $112.87 + $10. Click here to search eBay.
B) Scotch brand “Extreme” strapping tape (any size roll)
C) 15 feet (4.6 meters) of 250/46 Litz wire (Medium Wave model). Click here to view on eBay.
OR 25 feet (7.7 meters) of 100/44 Litz wire (Longwave model). Click here to view on eBay.
D) Two 120 lb. test plastic tie wraps (any length over 6”)
E) Johnson Level & Tool Mfg. Co., Inc. 48” orange plastic carpenter’s level, part # 7748-O (provides enough plastic for two loopstick frames)
F) Two 3/4” lengths of 1/2” I.D. clear vinyl hose
G) Two 1” lengths of 5/8” I.D. rubber hose
H) Roll of 2” Johnson & Johnson waterproof (medical) tape OR roll of 1” Rite-Aid waterproof tape
I) Amidon 7.5” x .5” ferrite rod, part no. R61-050-750 (MW model) OR part no. R33-050-750 (LW Model), available at http://www.amidoncorp.com/rods-and-tiles/
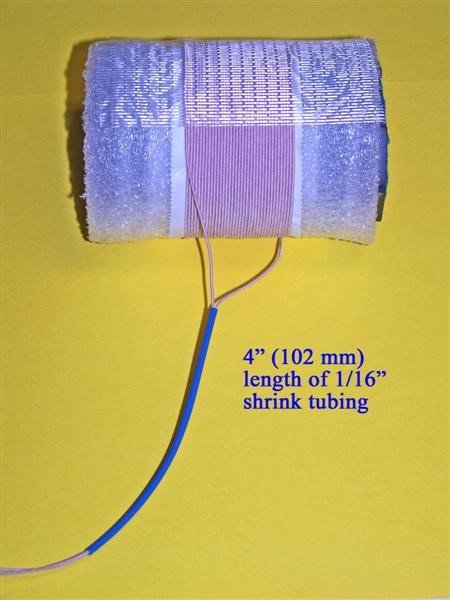
J) 6” of 1/16” shrink tubing
Miscellaneous: One packet of Duro Super Glue (.07 ounce size), solder, 25w (low heat) soldering iron, hacksaw (or power miter saw), screwdriver set, sandpaper, needle nose pliers, diagonal cutters
D-808 Radio Preparation
Before starting the modification give the radio a thorough test on all bands, ensuring that all the stock model functions work properly, and that there are no issues with the display, speaker, headphone jack, battery or charging system. It’s also a good idea to run a daytime DX band scan on the AM or Longwave band (for whichever band you plan to construct an upgrade loopstick) and document the results—to use as a benchmark for the upgrade loopstick’s performance.
Step-By-Step Construction
Antenna Frame and 7.5 inch Loopstick Preparation
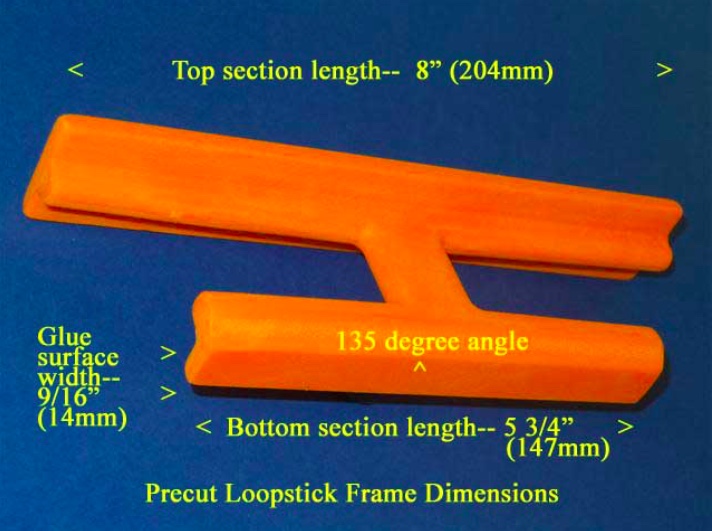
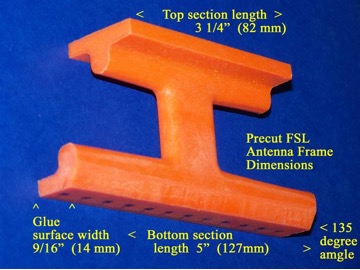
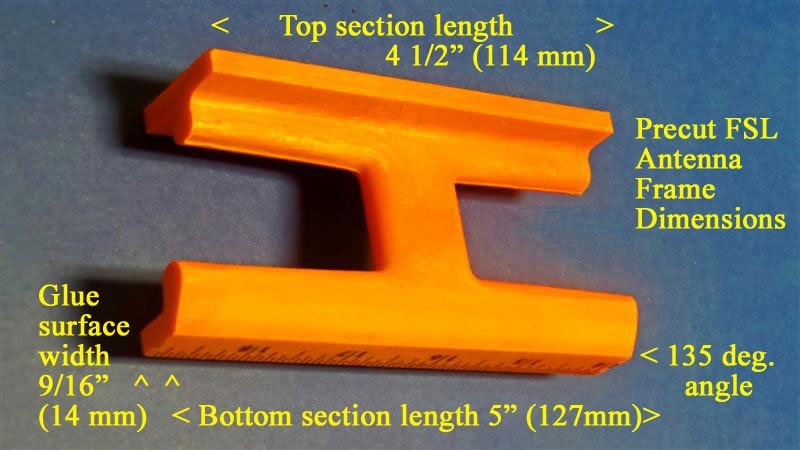
1) Refer to the photo below. Using the “Supercharging the Tecsun PL-380” article (posted at http://www.mediafire.com/file/du3sr5cd9thqvau/7.5inch-LS-PL380.doc/file or available directly from the author) carefully prepare the orange loopstick antenna frame according to construction steps 1-9, EXCEPT note that the lower (glue surface) edge of the antenna frame should be cut to a length of 5 3/4” (147mm), NOT 5” (127mm) as described in the PL-380 transplant article. Pay close attention to the safety precautions concerning power tool usage, and DO NOT attempt to use a power miter saw unless you have SERIOUS power tool experience!
2) If you are constructing an AM (Medium Wave) loopstick, follow construction steps 10-16 in the PL-380 transplant article to construct the antenna. If you are constructing a Longwave loopstick, follow construction steps 10a-16a in the PL-380 transplant article to construct the antenna. If you are constructing both loopsticks, MAKE SURE that the ferrite rod and Litz wire are only used in the antennas for which they were designed. Mixing up these items is very easy, and such a mistake will make both loopsticks perform like clunkers.
3) After construction of either the AM or Longwave loopstick, follow the instructions in steps 29 and 30 of the PL-380 transplant article to install a piece of 3 1/8” (79mm) shrink tubing, EXCEPT note that this length is slightly longer than the 3” (76mm) length called for in the PL-380 article.
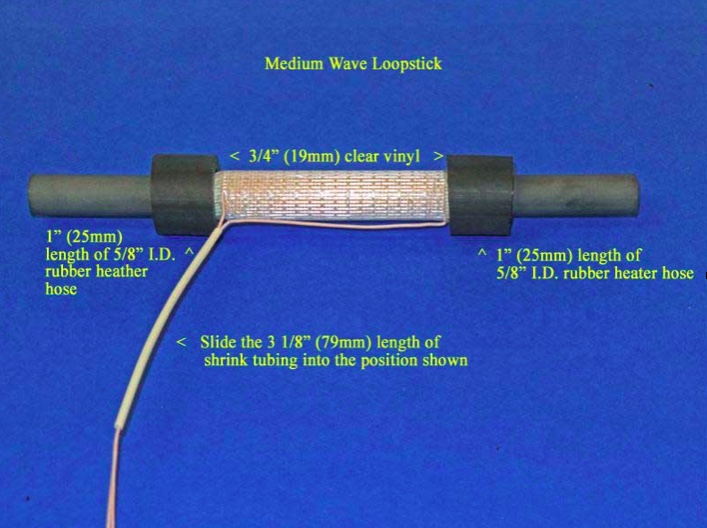
4) Refer to the photo below for the following three steps. [NOTE: Although this photo shows the AM (Medium Wave) loopstick, the procedures in this step are the same for the Longwave loopstick, although the position of the rubber hose lengths and clear vinyl inserts will be closer to the ends of the ferrite rod]. Carefully slide the length of 3 1/8” shrink tubing into the position shown, ensuring that there are no Litz wire kinks or bends inside the shrink tubing.
5) Take the two 3/4” (19mm) clear vinyl inserts and slide them onto the ferrite rod ends, twisting them up against the border of the Scotch “Extreme” tape ends to lock the tape in place under the vinyl inserts. Ensure that the clear vinyl inserts do not touch any Litz wire leads or coil turns.
6) Slide the 1” (25mm) lengths of rubber heater hose over the clear vinyl inserts until the appearance of the loopstick resembles the above photo. Ensure that the rubber hose sections also do not touch either the Litz wire leads or any coil turns. Finally, place the completed loopstick in a safe place until it is called for in Step .
Radio Disassembly
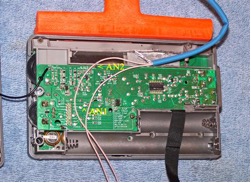
7) Refer to the photo above for this step. Remove the battery from the radio, and using a Jeweler’s Phillips screwdriver of the correct size, remove the six identical screws in the positions shown (NOTE: These screws have a tendency to stick inside their slots, even when the slots are turned upside down. If you cannot remove all six screws it’s not a major problem, but at least ensure that the screws are completely loose in their slots, and that you don’t lose any of them during the remaining steps). Grasp the tuning knob, and pull it out horizontally in a completely straight manner to remove it from the radio. Ensure that the battery, tuning knob and all removed screws are placed in a safe place until the radio is reassembled.
8) Carefully separate the front and back cabinet sections and place them down in the position shown in the photo below. Note that the front and back sections of the radio are connected by a ribbon wire plug-in system– ensure that this plug remains securely inside its slot at all times, and that no great stress is placed on the speaker wires.
9) Refer to the close up photo below, and note the position of the two Litz wire soldering points on the circuit board (in the lower right corner of the photo). Using diagonal cutters, cut the two Litz wire leads at the position shown, UNLESS you wish to salvage this stock loopstick for other projects—in which case you should desolder the entire lengths of the Litz wire leads from the circuit board at the positions shown in the lower right corner (NOTE: The stock loopstick is of a fairly good design, and has an inductance that would be compatible with any DSP-chip Ultralight radio, providing an AM sensitivity boost in the process).
10) Refer to the photo below. Using a flat Jeweler’s screwdriver with a 1/16” blade, carefully probe around all four sides of the stock loopstick to break all of the glue bonds. Work slowly and carefully around the perimeter of the ferrite rod, including the plastic covers on each end. Once most of the glue bonds have been broken the ferrite rod will begin to shift around as you break up the few remaining bonds, but until this point work slowly and patiently to break up the glue.
11) Refer to the photo below. Using the flat Jeweler’s screwdriver, once all of the glue bonds have been broken and the ferrite rod is loose in its slot, lift the ferrite rod out of its slot on one side by prying up under the plastic cover on the end of the ferrite rod. Ensure that the Litz wire leads have either been cut or desoldered from the circuit board, then grasp the ferrite rod with your fingers and pull it completely out of the slot with a slight twisting motion.
12) Remove the wrist strap, and refer to the photo below. Carefully pick up the two sides of the radio and place the back section in a vertical position as shown, with a heavy flat weight (barbell, or other heavy flat item) pressing up against the back cabinet section to keep it in a vertical position. Ensure that there is adequate, even lighting on the top cabinet section for the gluing process in the next step, and that the back cabinet surface will not shift around as you make the gluing “dry runs,” and perform the actual gluing of the loopstick frame to the top of the cabinet.
13) Take the previously prepared orange plastic loopstick frame, and ensure that its bottom glue surface is completely smooth and flat, with no uneven ridges on the edges of the glue surface (remove these with fine sandpaper, but ONLY on the ridges, and not on the rest of the flat glue surface). Using a damp paper towel, wipe the top cabinet glue surface and the loopstick frame glue surface to remove any dust or debris, then wipe them again with a dry, clean paper towel to ensure that they are both completely dry.
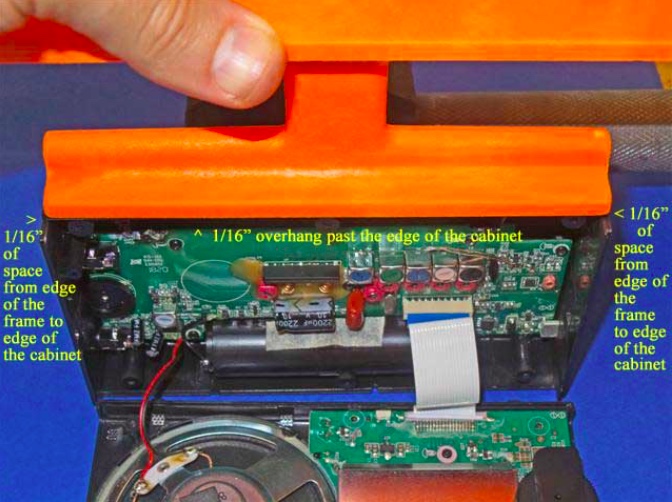
Take the loopstick frame and gently slide the frame over the top cabinet surface to ensure that both surfaces are smooth and flat. Refer to the photo at the top of the next page. Ensure that there is even, bright lighting on the top cabinet surface, and make several “dry runs” to place the loopstick frame in the exact center of the top cabinet surface (with 1/16”, or 1.5mm of space between the frame ends to the cabinet ends), and also 1/16” (1.5mm) of overhang above the front edge of the cabinet’s glue surface (NOTE: if you wish to simplify the process by lining up the front edge of the loopstick frame with the front edge of the cabinet’s glue surface it will still provide an acceptable result, but you will need to do some minor sanding of the whip antenna’s plastic slot post, as shown in the photo below. In either case, make repeated “dry runs” with the loopstick frame to practice placing it in the exact center of the top cabinet’s glue surface, since you will only get one chance to place it in the proper center position once the superglue is applied.
NOTE: The back of the loopstick frame has a beveled surface to permit full operation of the radio’s whip antenna after the frame is glued on the top of the cabinet surface. If the loopstick frame is glued with a 1/16” (1.5mm) overhang in front of the front edge of the cabinet surface then the whip antenna should have enough space for free operation. The alternative is to glue the two front edges lined up with each other to simplify the gluing process, in which case minor sanding may be required on the whip antenna slot post, as shown in the photo below.
14) After making multiple “dry runs” and becoming familiar with accurate placement of the loopstick frame on top of the cabinet, refer to the photo at the top of the next page. After once again ensuring that the back cabinet section will not shift around during the gluing process, take the Duro superglue packet and apply a thin (1/8”, or 3mm) bead of glue along the center of the cabinet’s glue surface, extending it 5 1/4” (133mm)long, with equal spaces on both ends (as shown). While sighting the two sides place the loopstick frame carefully down in the correct center position as practiced previously, with the 1/16” overhang if desired. If satisfied with the position, press down on the frame to lock the two surfaces together securely. Usually the frame may be shifted around slightly within 1 or 2 seconds of placing it on the superglue, so use this brief time to promptly shift the frame to a straight position, if necessary. After a couple of seconds, though, you will need to be satisfied with whatever position the frame has ended up with (regardless, it will still hold the loopstick just fine, for DXing purposes).
15) After the loopstick frame is securely placed and locked on top of the D-808’s cabinet surface, place downward pressure on the loopstick frame along its length in order to ensure a tight glue bond throughout the entire top cabinet surface. Continue this process for about one minute, and sight both ends of the loopstick frame to ensure that they are both completely flat against the D-808 cabinet.
16) Inspect the front and back edges of the loopstick frame’s border with the D-808 cabinet for any glue seepage, and if any is found, remove it promptly with the 1/16” flat Jeweler’s screwdriver blade. Glue should not be allowed to run past the frame edges. This completes the process of gluing the frame to the D-808 cabinet.
7.5” Loopstick Installation
17) [NOTE: The installation procedures of the Medium Wave (AM) and Longwave loopsticks are identical, except that the plastic tie wraps and rubber hose sections are closer to the ends of the ferrite rod in the Longwave version. The following photos are for the Medium Wave (AM) version, but Longwave loopstick builders should follow the same steps, while referring to the Longwave model photo in the “Operation” section as a guide]
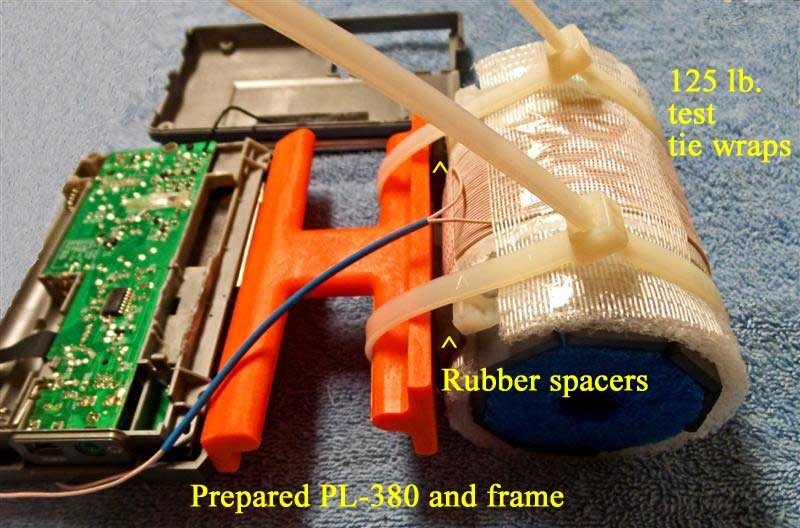
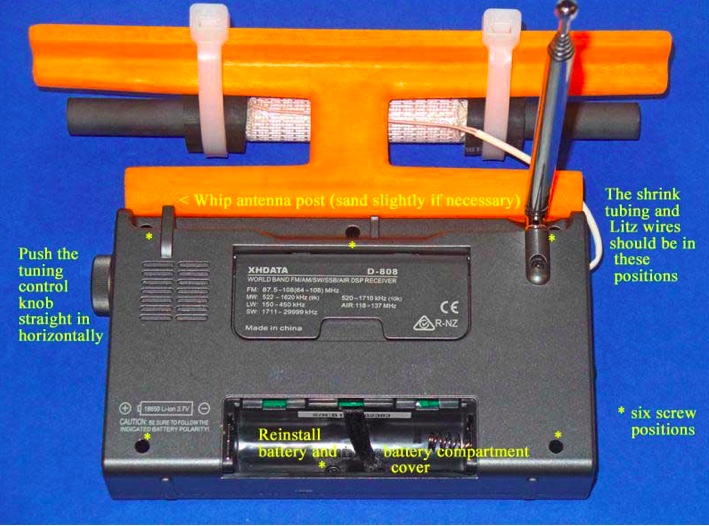
Refer to the photo below. Carefully take the previously prepared 7.5” loopstick and hold it in the position shown—in its slot, centered in the middle of the orange antenna frame, with the shrink tubing and Litz wire leads running down to the left. Take the two plastic tie wraps and install them in the position shown, centered over the rubber hose sections on the loopstick, while ensuring that no Litz wires or shrink tubing is bound under the plastic tie wraps.
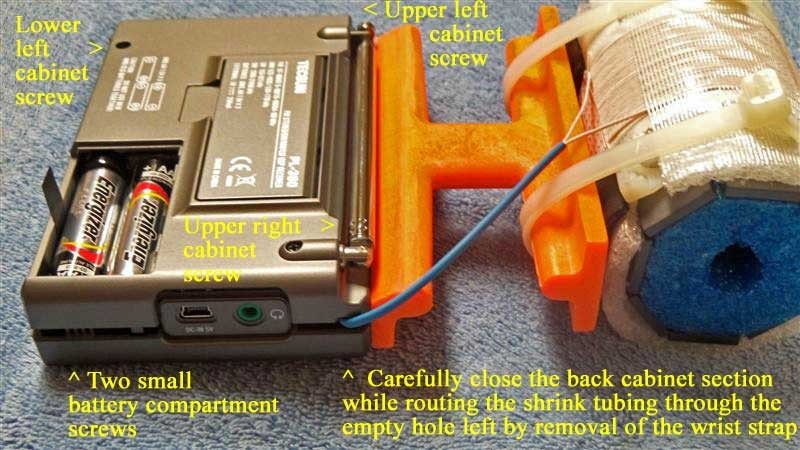
18) Refer to the photo below. Lay the two cabinet sections down flat as shown, ensuring that the Litz wire shrink tubing is in the exact position shown (if it isn’t, carefully slide it along both Litz wires until it is in this exact position). Carefully thread one Litz wire end through the empty wrist strap hole, then thread the other Litz wire end through the hole, as shown. Finally pull on the two Litz wires together from the right while guiding the end of the shrink tubing into the empty wrist strap hole, and pull a short section of the shrink tubing through the hole (as shown) to protect the Litz wire insulation from friction damage.
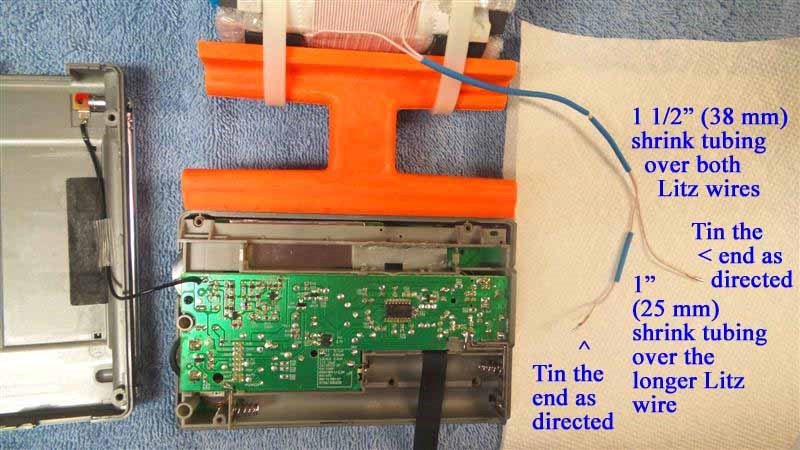
19) Refer to the photo below. Using the previous procedure to install shrink tubing (which is described in the PL-380 transplant article) install a 2.5” (63mm) length of shrink tubing over the two Litz wire ends, and shift the shrink tubing into the position shown in the photo. After this is done cut the two Litz wire leads to the lengths shown in the photo (NOTE: make sure that the ends of both Litz wires are cleanly cut, not frayed and at the minimum diameter before attempting to insert them into the shrink tubing. The process is much easier when the Litz wires pass smoothly through the shrink tubing).
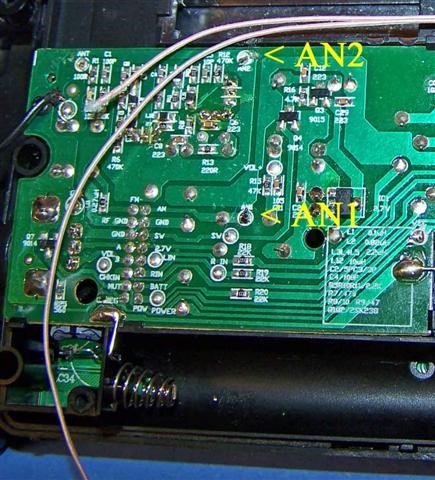
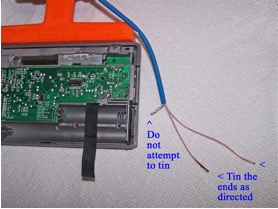
20) Refer to the close up photo below. Using a low heat (25w) pencil-type soldering iron, remove the two stock Litz wire leads at the positions shown, taking care not to use excessive heat, or touch the adjacent components. Ensure that the new Litz wire leads are at the length shown when the leads are in a horizontal position throughout the cabinet, and cut them to this length if they are not.
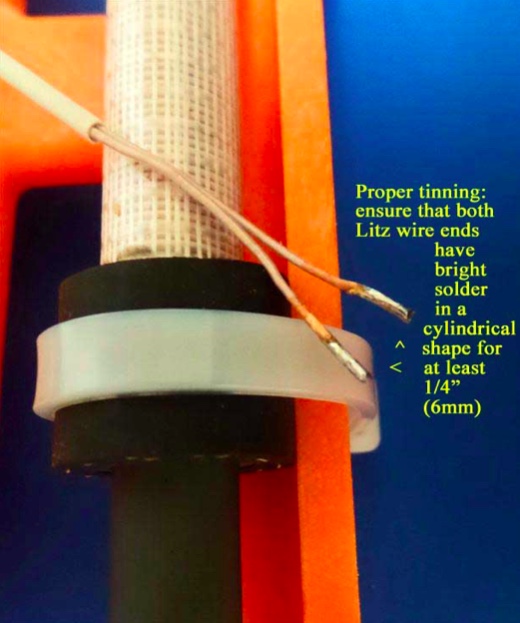
21) NOTE: When tinning the 250/46 Litz wire it is essential that all of the individual Litz wire strands be completely soldered together for a length of at least 1/4” (6mm), with bright, shiny solder around the circumference of the Litz wire ends for this minimum (1/4”) length. The Litz wire must be heated with a clean, hot soldering iron around its circumference in order to melt the solder properly for this step]
Refer to the photo above. Pull the Litz wires up out of the previous position, and place a clean rag underneath them (on top of the circuit board) to completely protect the circuit board from any solder which might accidentally drop down during the tinning process. Using your hot 25w soldering iron melt a generous amount of solder on its tip, and work the soldering iron tip slowly and patiently around the circumference of each Litz wire end until there is a bright, shiny solder length of at least 1/4” (6mm) in a cylindrical pattern at the end of each Litz wire. When doing this, take great care not to allow any solder to drip down onto the circuit board below (i.e., make sure that your rag completely covers the circuit board). The final appearance of your Litz wire lead ends should resemble those in the photo.
22) When your Litz wire lead ends resemble the photo above, cut the soldered portion down to a length of 3/16” (5mm) and observe the appearance of the end of the Litz wire. It should have a bright, solid circular shape, with no gaps or individual Litz wires showing. If not, reheat the end of the Litz wire while adding some solder, and repeat this step.
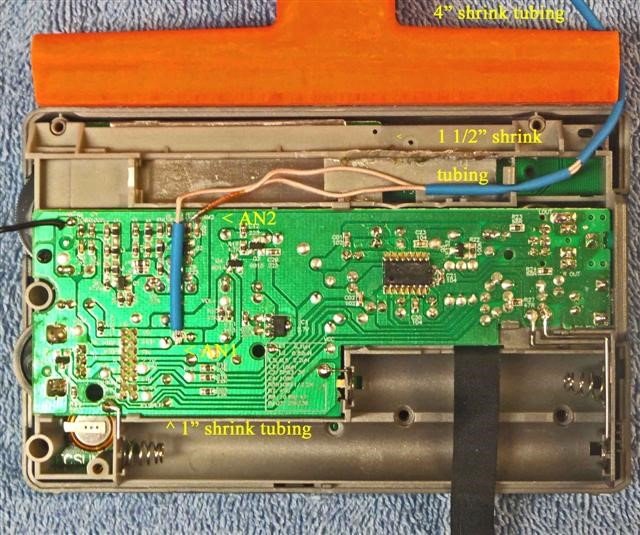
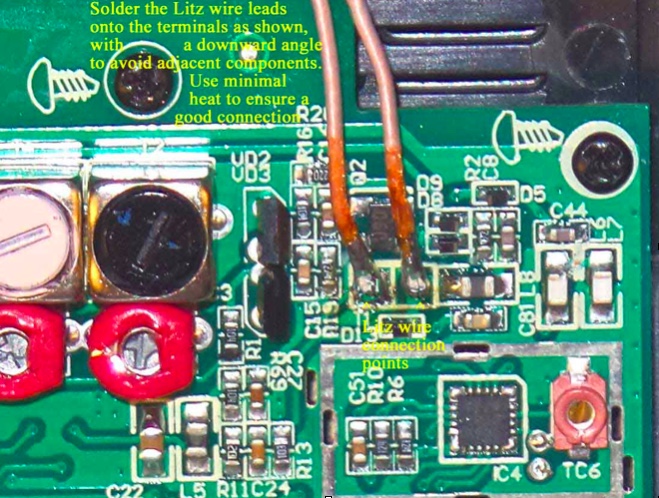
23) NOTE: The Litz wire connection points on the circuit board are surrounded by other important components. It is important to avoid solder drips on these components, or solder bridges to their leads. Solder the Litz wire leads down at an angle to avoid these surrounding components, and use the minimum amount of heat and solder to ensure good electrical connections)
Refer to the close up photo above. Following the precautions described, solder the two Litz wire leads down onto the circuit board at an angle, as shown in the photo. After soldering, make a close visual inspection to ensure that there are no solder bridges across the Litz wire connections, or nearby components. The remaining length of the Litz wire leads should be routed in a horizontal manner to the wrist strap hole.
24) Carefully pick up the front and back cabinet sections, and hold the back cabinet section fairly close to the front section (as the radio would normally be oriented, when assembled). Refer to the photo below, and carefully insert the “Fine Tuning” control thumbwheel from the front cabinet section into its slot on the back cabinet section in a sideway movement. This will allow you to fully close the front and back cabinet sections in the next step.
25) Refer to the photo below. Pick up the two cabinet halves and carefully snap them together (this action should not require any great force). Place the radio face down in the position shown (with a soft surface underneath, for protection), and using the Jewelers Phillips screwdriver of the correct size, carefully screw in the six screws that were loosened previously, starting with the screw near the whip antenna post (you should pick up the radio temporarily and hold the two cabinet sections together tightly at this corner, as you do this).
After all six screws have been retightened take the Tuning control knob and press it back onto its shaft in a straight horizontal motion. Finally, reinstall the battery and battery compartment cover to finish up the reassembly.
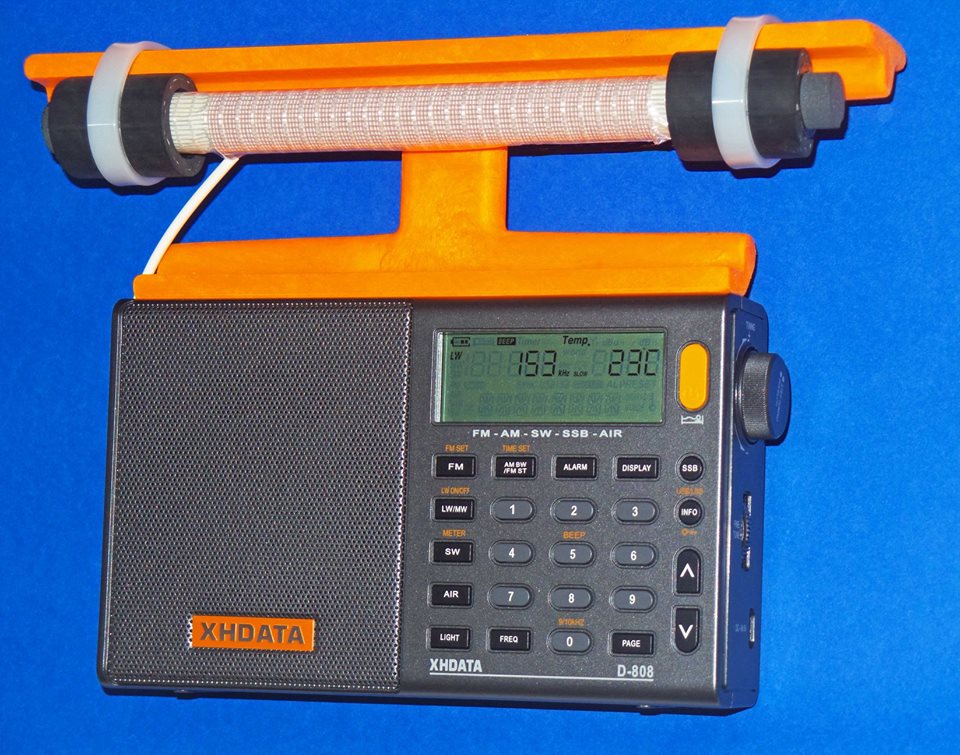
TESTING AND OPERATION– MEDIUM WAVE MODEL
This 7.5” transplant loopstick is designed to provide a major boost in sensitivity from 530-1700 kHz, and if the antenna is working properly both the weak signal reception and the radio’s nulling capability should be greatly enhanced. It is normal for the antenna to receive more background noise on the low band frequencies, although the sensitivity boost should be substantial across the band.
The construction design of the orange antenna frame allows full usage of the whip antenna for checking SW parallels of MW-DX stations, although if you chose to glue the antenna frame flush with the front of the back cabinet surface to simplify the gluing process, you may need to sand the whip antenna slot post slightly to allow free movement of the whip antenna (see step #13).
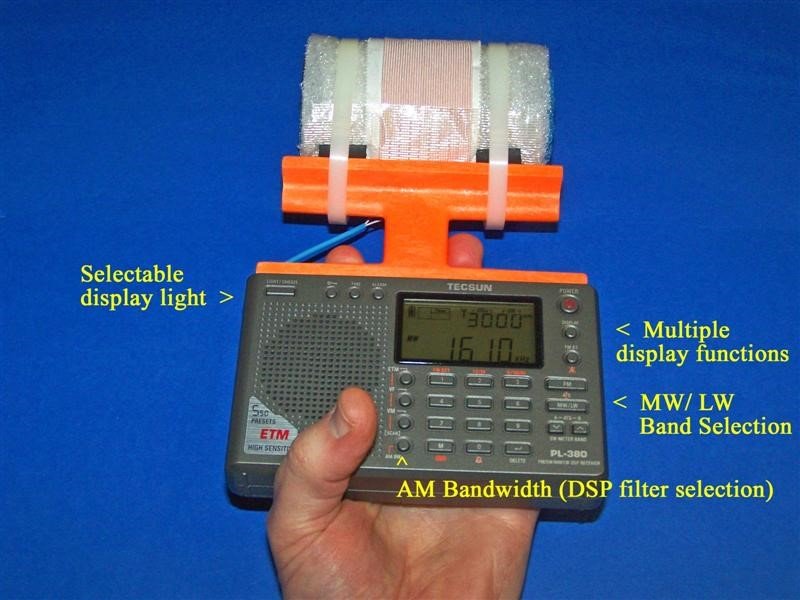
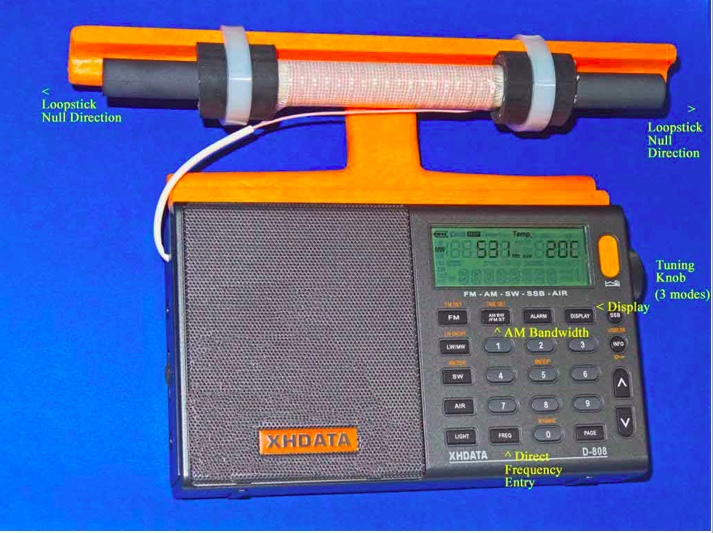
In the photo above, some of the important controls for Medium DXing are highlighted. The AM Bandwidth control allows you to choose multiple DSP filtering selections to enhance selectivity as desired, with the narrowest filtering (1 kHz) providing both the sharpest selectivity and the best weak-signal sensitivity. However this 1 kHz setting also has the poorest audio fidelity, with the higher audio frequencies typically cut off by the DSP filtering. As such, for regular DXing far away from strong local pests, the other AM Bandwidth settings may be more suitable. The Direct Frequency Entry key allows you to manual enter in any MW frequency, to which the radio will shift once the numbers are pressed on the keypad. The Tuning knob has three different modes, which can be toggled by pressing the knob horizontally. The first mode is tuning in either 9 kHz or 10 kHz steps (depending on which of these step you have selected), while the second mode is tuning in 1 kHz steps. The third mode is to lock the frequency in place. Pressing the knob again will return the tuning to 9 or 10 kHz steps.
The XHDATA D-808 has multiple display functions, which can be toggled by the indicated key. The first option is the temperature in either Centigrade or Fahrenheit (depending on your pre-set preference), while the second option is the alarm time. The third option is the current time (which you need to set according whether you prefer UTC or local time), while the fourth option is the received signal strength in both dBu and dB.
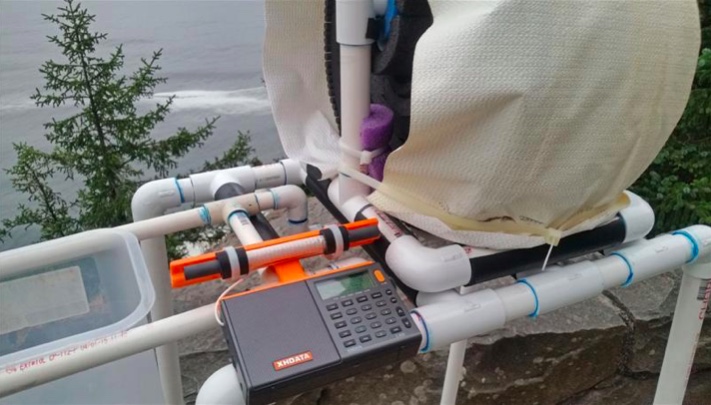
The supplied 3.7v lithium ion battery has superior run time, and may be easily charged using the supplied USB cable to either a computer or AC outlet (with the appropriate adapter). As reported in various posts throughout this year, the D-808 model has rugged construction with an excellent record of survival under tough conditions, including hot summer days, moderate rain exposure and extended usage as the main receiver during a 9-day ocean cliff DXpedition in Oregon—performing flawlessly at all times.
Conclusion
It is the author’s sincere hope that this “Supercharged” D-808 model will bring you a lot of DXing fun during travel, as well as at other times. When conditions are good you should never underestimate this enhanced model’s potential of receiving awesome DX beyond your expectations—as an example, here is the stand-alone performance of a 7.5” loopstick D-808 in receiving 1017-A3Z in Nuku’alofa, Tonga (10 kW at 5,632 miles/ 9,063 km) on the ocean cliff near Manzanita, Oregon at 1301 UTC on August 8th of this year:
Not only Tonga is received, but even the Australian horse racing station 1017-2KY in Sydney (5 kW at 7,630 miles/ 12,280 km) is received as a weak co-channel in the middle of the recording. My hope is that you all will be so lucky with your new Supercharged D-808!
73 and Good DX,
Gary DeBock (in Puyallup, WA, USA)
Absolutely amazing! Thank you for taking the time to put this procedure together and describing the process in such fine detail, Gary! Hats off to you!
Click here to read all of Gary DeBock’s posts on the SWLing Post.
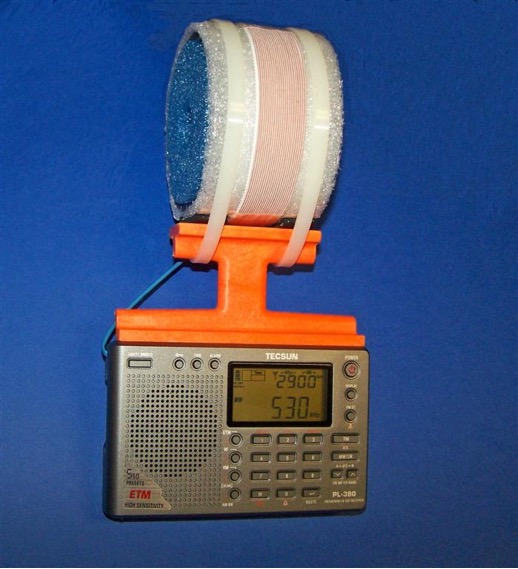























































 4) Refer to the photo above. After ensuring that you are fully prepared for accurate placement of the antenna frame on the PL-380 cabinet, place a 4 1/2” x 3/16” bead of super glue (114 mm x 5 mm) on the PL-380’s front top cabinet surface, as shown in the photo. Refer to the photo on the top of the next page. Ensure that the front side of the antenna frame (as shown) is facing you, then place the antenna frame in a centered position flat against the PL-380 cabinet, with its front edge lining up with the front beveled edge of the cabinet, as shown in the photo. Press the antenna frame down firmly against the cabinet for about one minute, scraping away any excess glue from the front and back edges with a small, flat jeweler’s screwdriver. It is especially important to remove any excess glue from the back edge of the antenna frame in order to allow the PL-380’s back cabinet to close normally. After completion of this step place the PL-380 (with the attached antenna frame) in a secure area until the FSL antenna is constructed.
4) Refer to the photo above. After ensuring that you are fully prepared for accurate placement of the antenna frame on the PL-380 cabinet, place a 4 1/2” x 3/16” bead of super glue (114 mm x 5 mm) on the PL-380’s front top cabinet surface, as shown in the photo. Refer to the photo on the top of the next page. Ensure that the front side of the antenna frame (as shown) is facing you, then place the antenna frame in a centered position flat against the PL-380 cabinet, with its front edge lining up with the front beveled edge of the cabinet, as shown in the photo. Press the antenna frame down firmly against the cabinet for about one minute, scraping away any excess glue from the front and back edges with a small, flat jeweler’s screwdriver. It is especially important to remove any excess glue from the back edge of the antenna frame in order to allow the PL-380’s back cabinet to close normally. After completion of this step place the PL-380 (with the attached antenna frame) in a secure area until the FSL antenna is constructed.





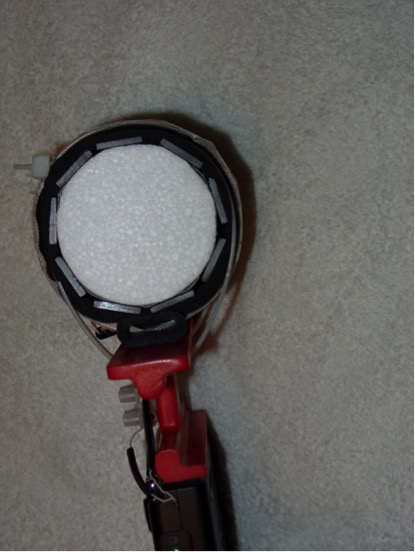
 10) Refer to the photo above. Pull the Oatey foam wrap tightly around the bar assembly, then cut a straight edge to mate evenly with the previously cut straight edge. Before pressing this edge down on the tape cut side notches in the foam where the tie wraps clamps are located, as shown. The press this foam edge tightly down on the tape, mating evenly with the previously cut foam edge. Ensure that there are no gaps or overlaps in the foam edges; if necessary, pull the foam wrap once again all around the bar assembly and cut a new straight edge that will mate evenly, with no gaps or overlaps. Finally, secure this newly cut foam edge with a 2 1/2” (64 mm) strip of waterproof tape, as shown.
10) Refer to the photo above. Pull the Oatey foam wrap tightly around the bar assembly, then cut a straight edge to mate evenly with the previously cut straight edge. Before pressing this edge down on the tape cut side notches in the foam where the tie wraps clamps are located, as shown. The press this foam edge tightly down on the tape, mating evenly with the previously cut foam edge. Ensure that there are no gaps or overlaps in the foam edges; if necessary, pull the foam wrap once again all around the bar assembly and cut a new straight edge that will mate evenly, with no gaps or overlaps. Finally, secure this newly cut foam edge with a 2 1/2” (64 mm) strip of waterproof tape, as shown.